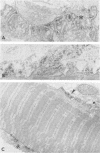
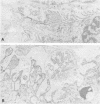
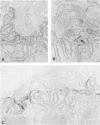
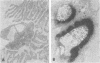
Abstract
Overwhelming evidence now supports Simpson's concept, originally proposed in 1960, that acquired myasthenia gravis (MG) is an autoimmune disease in which antibodies are directed against the nicotine postsynaptic acetylcholine receptor (AChR).1 An autoimmune pathogenesis of acquired MG implies that those myasthenic syndromes which occur in a congenital and familial setting may have a different, non-autoimmune basis. This paper focuses on ultrastructural, immunoelectron microscopic and cytochemical aspects of acquired autoimmune MG and some recently recognised congenital myasthenic syndromes.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. R., Stevens C. F. Voltage clamp analysis of acetylcholine produced end-plate current fluctuations at frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(3):655–691. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Florin T. A statistical analysis of the release of acetylcholine at newly formed synapses in striated muscle. J Physiol. 1974 Apr;238(1):93–107. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biesecker G., Podack E. R., Halverson C. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J. C5b-9 dimer: isolation from complement lysed cells and ultrastructural identification with complement-dependent membrane lesions. J Exp Med. 1979 Feb 1;149(2):448–458. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.2.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. L., Dale H. H., Feldberg W. Reactions of the normal mammalian muscle to acetylcholine and to eserine. J Physiol. 1936 Sep 8;87(4):394–424. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1936.sp003414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
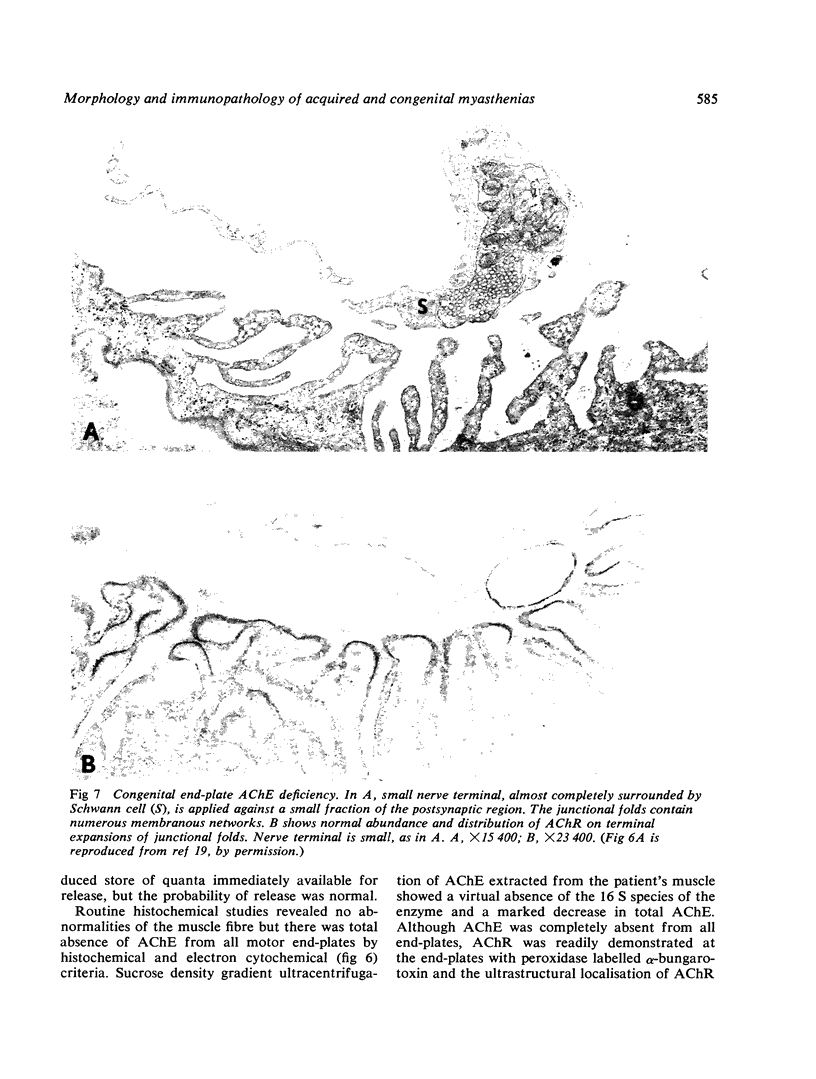
- Engel A. G., Lambert E. H., Gomez M. R. A new myasthenic syndrome with end-plate acetylcholinesterase deficiency, small nerve terminals, and reduced acetylcholine release. Ann Neurol. 1977 Apr;1(4):315–330. doi: 10.1002/ana.410010403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. G., Lambert E. H., Howard F. M. Immune complexes (IgG and C3) at the motor end-plate in myasthenia gravis: ultrastructural and light microscopic localization and electrophysiologic correlations. Mayo Clin Proc. 1977 May;52(5):267–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. G., Lindstrom J. M., Lambert E. H., Lennon V. A. Ultrastructural localization of the acetylcholine receptor in myasthenia gravis and in its experimental autoimmune model. Neurology. 1977 Apr;27(4):307–315. doi: 10.1212/wnl.27.4.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. G. Locating motor end plates for electron microscopy. Mayo Clin Proc. 1970 Jun;45(6):450–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. G., Santa T. Histometric analysis of the ultrastructure of the neuromuscular junction in myasthenia gravis and in the myasthenic syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Sep 15;183:46–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb30741.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fambrough D. M., Drachman D. B., Satyamurti S. Neuromuscular junction in myasthenia gravis: decreased acetylcholine receptors. Science. 1973 Oct 19;182(4109):293–295. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4109.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann S., Merlie J., Lindstrom J. Modulation of acetylcholine receptor in rat diaphragm by anti-receptor sera. Nature. 1978 Jul 6;274(5666):65–68. doi: 10.1038/274065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Miledi R., Vincent A., Newsom-Davis J. Acetylcholine receptors and end-plate electrophysiology in myasthenia gravis. Brain. 1978 Jun;101(2):345–368. doi: 10.1093/brain/101.2.345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The binding of acetylcholine to receptors and its removal from the synaptic cleft. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):549–574. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Cell membrane antigen isolation with the staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 Pt 1):1482–1490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J. M., Lambert E. H. Content of acetylcholine receptor and antibodies bound to receptor in myasthenia gravis, experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis, and Eaton-Lambert syndrome. Neurology. 1978 Feb;28(2):130–138. doi: 10.1212/wnl.28.2.130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J. Complement. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:697–724. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.003405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiness C. G., Weinberg C. B., Hall Z. W. Antibody to acetylcholine receptor increases degradation of junctional and extrajunctional receptors in adult muscle. Nature. 1978 Jul 6;274(5666):68–70. doi: 10.1038/274068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson W. C., Chun R. W., Kornguth S. E. Familial infantile myasthenia. Arch Neurol. 1980 Feb;37(2):117–119. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1980.00500510075018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E. F., Drachman D. B. Effect of myasthenic immunoglobulin on acetylcholine receptors of intact mammalian neuromuscular junctions. Science. 1978 Jun 16;200(4347):1285–1287. doi: 10.1126/science.663610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]