Abstract
Peripheral, cervical and cortical somatosensory evoked potentials after median or ulnar nerve stimulation were recorded in 21 patients with cervical spondylosis with radiculopathy or myelopathy. The test was normal when pain and paraesthesias were the only symptoms, while pathological in radiculopathy with objective neurological signs. The results varied in patients with cervical myelopathy.
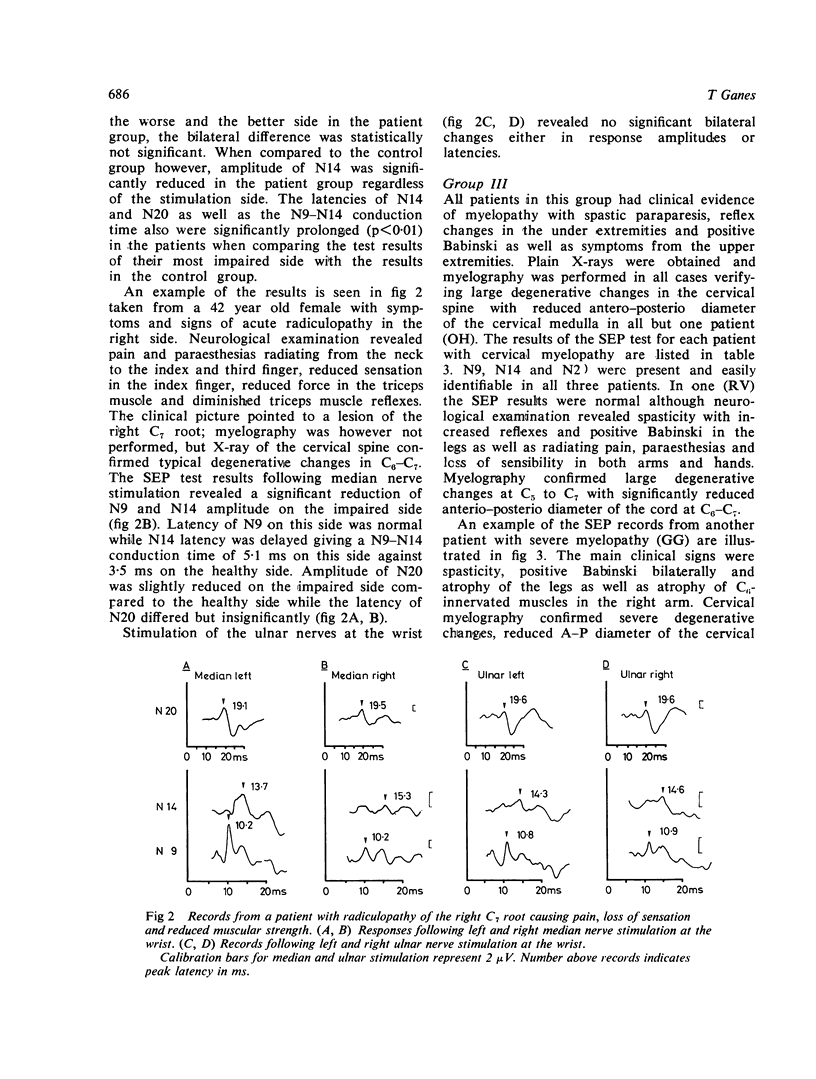
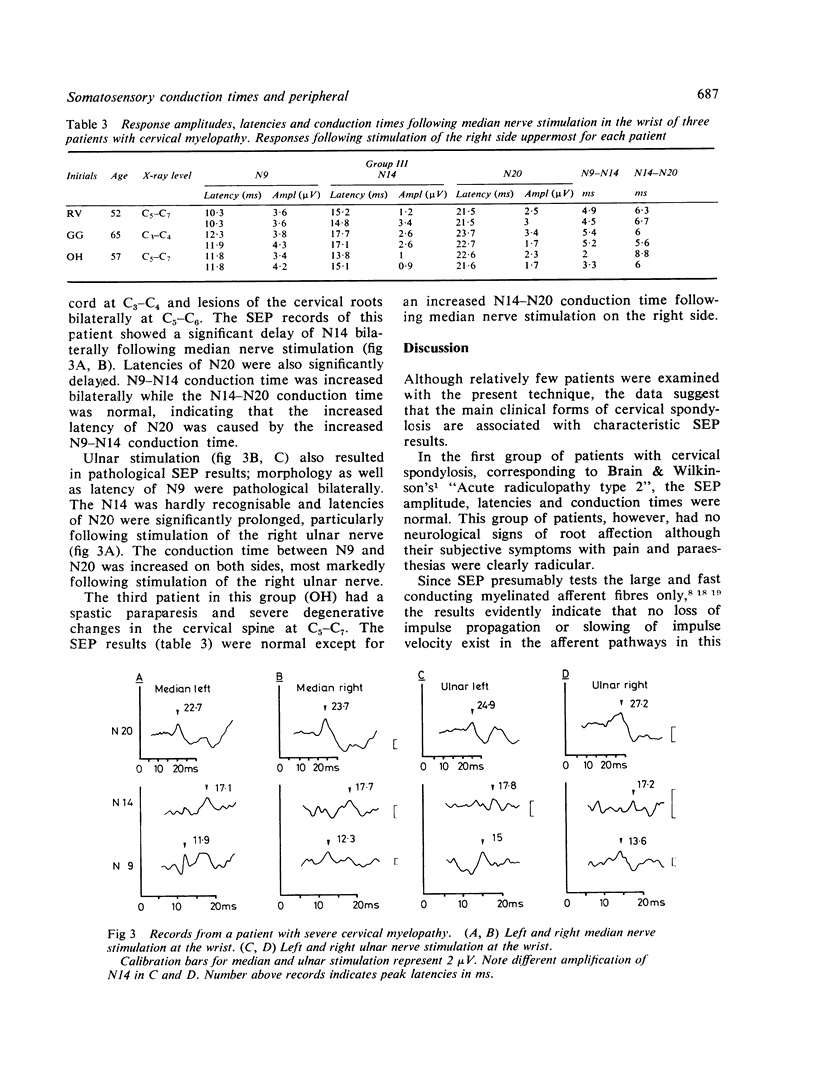
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caccia M. R., Ubiali E., Andreussi L. Spinal evoked responses recorded from the epidural space in normal and diseased humans. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1976 Oct;39(10):962–972. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.39.10.962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell J. W., Crane C. R., Boland G. L. Determinations of intercostal motor conduction time in diagnosis of nerve root compression. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1968 Sep;49(9):515–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cracco R. Q., Bickford R. G. Somatomotor and somatosensory evoked responses. Median nerve stimulation in man. Arch Neurol. 1968 Jan;18(1):52–68. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1968.00470310066006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen A., Schomer D., Melmed C. An electrophysiological method for examining lumbosacral root compression. Can J Neurol Sci. 1977 May;4(2):117–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El Negamy E., Sedgwick E. M. Delayed cervical somatosensory potentials in cervical spondylosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1979 Mar;42(3):238–241. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.42.3.238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ertekin C. Evoked electrospinogram in spinal cord and peripheral nerve disorders. Acta Neurol Scand. 1978 Apr;57(4):329–344. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1978.tb04507.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBLIN D. R. SOMATOSENSORY EVOKED POTENTIALS IN HEALTHY SUBJECTS AND IN PATIENTS WITH LESIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 May 8;112:93–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb26744.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLIDAY A. M., WAKEFIELD G. S. Cerebral evoked potentials in patients with dissociated sensory loss. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1963 Jun;26:211–219. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.26.3.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliday A. M. Changes in the form of cerebral evoked responses in man associated with various lesions of the nervous system. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1967;(Suppl):178+–178+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume A. L., Cant B. R. Conduction time in central somatosensory pathways in man. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1978 Sep;45(3):361–375. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(78)90188-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. J. Investigation of brachial plexus traction lesions by peripheral and spinal somatosensory evoked potentials. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1979 Feb;42(2):107–116. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.42.2.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. J. Short latency potentials recorded from the neck and scalp following median nerve stimulation in man. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1977 Dec;43(6):853–863. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(77)90008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsukado Y., Yoshida M., Goya T., Shimoji K. Classification of cervical spondylosis or disc protrusion by preoperative evoked spinal electrogram. Follow-up study. J Neurosurg. 1976 Apr;44(4):435–441. doi: 10.3171/jns.1976.44.4.0435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews W. B., Beauchamp M., Small D. G. Cervical somato-sensory evoked responses in man. Nature. 1974 Nov 15;252(5480):230–232. doi: 10.1038/252230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perot P. L., Jr Chapter 28. The clinical use of somatosensory evoked potentials in spinal cord injury. Clin Neurosurg. 1973;20:367–381. doi: 10.1093/neurosurgery/20.cn_suppl_1.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


