ABSTRACT
Listeria monocytogenes senses blue light via the flavin mononucleotide-containing sensory protein Lmo0799, leading to activation of the general stress response sigma factor SigB (σB). In this study, we investigated the physiological response of this foodborne pathogen to blue light. We show that blue light (460 to 470 nm) doses of 1.5 to 2 mW cm−2 cause inhibition of growth on agar-based and liquid culture media. The inhibitory effects are dependent on cell density, with reduced effects evident when high cell numbers are present. The addition of 20 mM dimethylthiourea, a scavenger of reactive oxygen species, or catalase to the medium reverses the inhibitory effects of blue light, suggesting that growth inhibition is mediated by the formation of reactive oxygen species. A mutant strain lacking σB (ΔsigB) was found to be less inhibited by blue light than the wild type, likely indicating the energetic cost of deploying the general stress response. When a lethal dose of light (8 mW cm−2) was applied to cells, the ΔsigB mutant displayed a marked increase in sensitivity to light compared to the wild type. To investigate the role of the blue-light sensor Lmo0799, mutants were constructed that either had a deletion of the gene (Δlmo0799) or alteration in a conserved cysteine residue at position 56, which is predicted to play a pivotal role in the photocycle of the protein (lmo0799 C56A). Both mutants displayed phenotypes similar to the ΔsigB mutant in the presence of blue light, providing genetic evidence that residue 56 is critical for light sensing in L. monocytogenes. Taken together, these results demonstrate that L. monocytogenes is inhibited by blue light in a manner that depends on reactive oxygen species, and they demonstrate clear light-dependent phenotypes associated with σB and the blue-light sensor Lmo0799.
IMPORTANCE Listeria monocytogenes is a bacterial foodborne pathogen that can cause life-threatening infections in humans. It is known to be able to sense and respond to visible light. In this study, we examine the effects of blue light on the growth and survival of this pathogen. We show that growth can be inhibited at comparatively low doses of blue light, and that at higher doses, L. monocytogenes cells are killed. We present evidence suggesting that blue light inhibits this organism by causing the production of reactive oxygen species, such as hydrogen peroxide. We help clarify the mechanism of light sensing by constructing a “blind” version of the blue-light sensor protein. Finally, we show that activation of the general stress response by light has a negative effect on growth, probably because cellular resources are diverted into protective mechanisms rather than growth.
INTRODUCTION
Listeria monocytogenes is a Gram-positive bacterium commonly found in the environment. It is a foodborne pathogen capable of causing a severe systemic infection in humans, and it is associated with mortality rates of up to 30% (1–3). Although incidence levels remain far lower than those for outbreaks involving pathogens, such as norovirus and Salmonella, cases of listeriosis rose annually in Europe between 2009 and 2013 and are linked primarily with the consumption of ready-to-eat foods (3). L. monocytogenes displays a number of stress adaptations that aid its survival in a wide range of habitats, including foods, food-processing environments, and the mammalian gastrointestinal tract. In particular, it displays a notable tolerance to osmotic stress, low temperature, and bile (4–7) and has a potent adaptive tolerance response to acid (8).
Many of the stress-resistant properties of L. monocytogenes are under the control of the stress-inducible sigma factor SigB (σB), which drives the transcription of the general stress regulon (9–12). The regulation of σB is not fully understood in L. monocytogenes, but it is believed to involve a signal transduction cascade that ultimately modulates the availability of σB to associate with RNA polymerase. Environmental signals are thought to be sensed and integrated into the regulatory pathway by a high-molecular-weight multisubunit complex called a stressosome (9, 13). Although the structure of this complex has not been determined in L. monocytogenes, it is likely to be similar to the stressosome from Bacillus subtilis, whose structure has been partly solved (14), since all of the genes involved are conserved between these species (15). In B. subtilis, the current model proposes that stress signals are sensed by protrusions on the surface of the stressosome that are formed by the N-terminal domains of RsbRA and its paralogues, RsbRB, RsbRC, and RsbRD (14, 16). These sensory signals are then transduced to the core of the stressosome, resulting in phosphorylation events that lead to the release of RsbT from the stressosome. RsbT then interacts with RsbU to bring about the activation of σB. It is thought that RsbRA and its paralogues (RsbR, Lmo0799, Lmo0161, Lmo1642, and Lmo1842 in L. monocytogenes) can integrate different environmental stress signals, allowing σB activation under a variety of stress conditions, but thus far, only blue light has been shown to be sensed by the stressosome (17–20).
Blue-light sensing in L. monocytogenes requires Lmo0799, a widely conserved protein predicted to be associated with the stressosome that has a light-oxygen-voltage (LOV) domain at its N terminus and a sulfate transporter, the anti-sigma factor (STAS) domain at its C-terminal (17). Mutants lacking lmo0799 have increased motility in the presence of light compared to the wild type, fail to show enhanced invasion into mammalian cells in response to light (17), and are unable to form rings on semisolid agar in response to repeated cycles of light and dark (18). The mechanism of light sensing by Lmo0799 has not yet been fully elucidated, although it is clear that it exhibits photochemical activity similar to the related light sensor from B. subtilis, YtvA, and the formation of a flavin-cysteinyl adduct in response to light was postulated (21). In YtvA, this adduct forms between C-4 of the flavin mononucleotide (FMN) ring and the cysteine residue at position 62 (20), which is conserved in the L. monocytogenes protein but located at position 56. In the present study, we sought to elucidate the mechanism of sensing by mutating Cys56 to determine the impact on light sensing and to clarify the contribution of Lmo0799 to the growth and survival of L. monocytogenes.
Although blue light is known to activate σB in L. monocytogenes, the impact of visible light on growth and survival in this pathogen has not been studied in detail. Visible light has been explored as an antimicrobial treatment in numerous studies, with effectiveness demonstrated against a diverse range of medically important bacteria and fungi (for reviews, see references 22–24). In most cases, high-intensity violet-blue light (405 nm) has been used (25–28). High-intensity light at 405 nm was found to be effective at inactivating L. monocytogenes in liquid suspensions (25) and on surfaces, including acrylic, glass, and agar-based growth medium (26, 29). The presence of photosensitizing compounds, such as sodium chlorophyllin (30) or 5-aminolevulinic acid (31), enhance the killing effect of visible light on surfaces. The mechanism of killing by visible light has not been addressed in L. monocytogenes to date, although studies on other bacteria suggest that excitation of endogenous porphyrins by light under aerobic conditions can lead to the production of damaging reactive oxygen species (32). Indeed, the photosensitizing effect of 5-aminolevulinic acid is thought to be due to its role as a precursor in the biosynthesis of porphyrins (31).
In this study, we investigate the influence of visible light on the physiology of L. monocytogenes. We used blue light with a wavelength of 460 to 470 nm, since this is the wavelength that has been shown to activate the general stress response via the light sensor Lmo0799 and σB. We show that quite low doses of light at this wavelength inhibit the growth of this pathogen in both liquid and solid growth media. We show that the inhibitory mode of action is dependent on the production of reactive oxygen species. The role of σB and Lmo0799 in the response of L. monocytogenes to blue light is further clarified, and the conserved cysteine residue in Lmo0799 is shown to be essential for light sensing.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains, plasmids and culture conditions.
The bacterial strains and plasmids used in this study are listed in Table 1. Listeria monocytogenes strain stocks were stored in brain heart infusion (BHI) (LabM) broth supplemented with 7% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) at −80°C. Strains were grown in BHI agar or broth (LabM). Agar plates were stored at 4°C. Escherichia coli strains used for amplification of vector copy number were grown in Luria-Bertani (LB) broth or agar (Sigma-Aldrich). Before use, unless otherwise stated, broth was inoculated with colonies and incubated overnight with aeration, at 37°C. Where needed, chloramphenicol (Cml), erythromycin (Erm), and ampicillin (Amp) antibiotics were used at concentrations of 10 μg ml−1, 2 μg ml−1, and 100 μg ml−1 for L. monocytogenes and E. coli, respectively.
TABLE 1.
Bacterial strains and plasmids used in this study
| Strain or plasmid | Source or reference | Lab stock no. |
|---|---|---|
| L. monocytogenes strains | ||
| EGD-e (wild type) | C. Gahan | COB261 |
| EGD-e ΔsigB | C. Gahan | COB262 |
| EGD-e Δlmo0799 | Tiensuu et al. (18) | COB644 |
| EGD-e lmo0799 C56A | This study | COB611 |
| EGD-e Δlmo0799 pMK4 lmo0799 | Tiensuu et al. (18) | COB627 |
| EGD-e pMK4 lmo0799 | Tiensuu et al. (18) | COB625 |
| 10403S (wild type) | K. Boor, Cornell University | COB46 |
| 10403S ΔsigB | K. Boor, Cornell University | COB45 |
| 1_02-15 | Swab (floor) (business 1) | COB765 |
| 5_04-15 | Swab (floor) (business 5) | COB766 |
| 2_08-13 | Swab (drain) (business 2) | COB762 |
| 2_10-13 | Swab (drain) (business 2) | COB763 |
| Plasmids | ||
| pMAD | Arnaud et al. (34) | NAa |
| pEX-A | Eurofins MWG Operon | NA |
NA, not applicable.
Light apparatus.
A high-power mounted 470-nm light-emitting diode (LED) (model M470L2; Thorlabs) was the light source (designated light setup 1) used to investigate the effects of blue light across the surface of an agar plate. An aspheric condenser lens (Ø75 mm) was used to create a uniform distribution of light across a circular area of 7 cm in diameter. An irradiance map was created using an optical power sensor (model PM121D; Thorlabs). This setup produced 1.5 to 2.0 mW cm−2, which could be increased to an irradiance of 8.0 mW cm−2 by increasing the current using a T-cube LED driver (LEDD1B; ThorLabs). An irradiance map was created using an optical power sensor (model PM121D; Thorlabs). The lower irradiance setting was used for growth inhibition experiments, while the higher setting was used for survival experiments.
An alternative setup (designated light setup 2) was used to test the effects of light across the area of a 96-well microtiter plate containing liquid medium. This setup was composed of 80 blue (460 nm) 10-mm prewired LEDs (Phenoptix), which were arranged in a 10 by 8 array, measuring 16 by 13.5 cm. A diffuser membrane was placed below the lights to help create a uniform distribution of light across the area of the plate. Again, an irradiance map was generated to confirm that uniform irradiance was delivered across the area of the 96-well microtiter plate (range, 1.5 to 2.0 mW cm−2 across all 96 wells). The lights were fixed in position approximately 16 cm above the 96-well plate.
Construction of lmo0799 C56A ‘“blind” mutant.
The lmo0799 gene was modified to incorporate a Cys-to-Ala missense mutation at codon 56. The sequence of the L. monocytogenes EGD-e genome (33) was sourced at http://genolist.pasteur.fr/ListiList/. At codon 56, the TGT (Cys) codon was changed to GCA (Ala). Silent mutations in three adjacent codons were also modified to facilitate detection by PCR during the strain construction (wild type, TCCAATTGTCAC to AGTAACGCACAT; see Table S1 in the supplemental material). The altered gene, which was 762 bp in length, was synthesized by Eurofins MWG Operon with additional EcoRI and XmaI restriction sites at each end in order to facilitate ligation with the pMAD suicide vector (34). Electrocompetent E. coli cells were transformed with the resulting plasmid (pMAD::lmo0799 C56A), and the plasmid was subsequently introduced into electrocompetent L. monocytogenes EGD-e cells. Integration of the plasmid into the genome was selected by plating strains on BHI agar with erythromycin (2 μg ml−1) at 42°C, as pMAD has a temperature-sensitive replication origin. Strains were then passaged at 30°C to promote excision and loss of the wild-type lmo0799 gene with the pMAD vector. PCR with primers COB736 (specifically designed to bind to the modified sequence around amino acid 56), COB737, COB669, and COB700 (see Table S1) was performed to detect the presence of the lmo0799 C56A missense mutation in the EGD-e genome. The presence of the altered sequence in the mutant was confirmed by Sanger sequencing (Source Bioscience) of a PCR product obtained with primers COB699 and COB700 from the mutant (see Table S1).
Examination of inhibitory effects of light on growth on solid agar.
Strains were grown for 18 to 20 h with aeration at 37°C before use. The cultures were standardized to an optical density at 600 nm (OD600) of 1.0 and then serially diluted 1:10 (unless indicated otherwise) in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Four microliters of each dilution was inoculated on BHI agar and exposed to 470-nm blue light (light setup 1) at 1.5 to 2.0 mW cm−2 or incubated in the dark (plates were wrapped in aluminum foil) at 30°C for 24 h. Agar plates were incubated with the inoculated surface facing downwards and illuminated with the blue-light source from above (see Fig. S1A in the supplemental material). The medium reduced the transmittance of light by approximately 50%. For experiments investigating the involvement of ROS in growth inhibition by light, catalase was added to the medium by spreading 100 μl of 125 U ml−1 catalase (Sigma) on the surface of the agar or including 20 mM dimethylthiourea (Sigma) in the medium during preparation.
Effect of light on Listeria monocytogenes in liquid culture.
Overnight cultures (approximately 16 h) grown in BHI at 37°C with aeration were diluted in fresh medium to an OD600 of 0.05. This suspension was then further serially diluted in BHI to a final dilution of 10−6, with respect to the suspension at an OD600 of 0.05. Two hundred microliters of each dilution was then added to two 96-well microtiter plates. One plate was wrapped in aluminum foil as a dark control, while the other was placed under the light apparatus (light setup 2), which produced blue light at 460 nm with a power density of 1.5 to 2.0 mW cm−2 (see Fig. S2A in the supplemental material). These plates were incubated at 30°C for 14 h, and growth was monitored by recording the OD595 hourly on a Sunrise-Tecan plate reader. The light transmittance through the plates and medium was approximately 68% with this setup. To take these readings, plates were removed from the light apparatus and incubator and were shaken for 10 s immediately prior to each reading. To avoid taking readings throughout the night, a second set of plates was later set up, using an inoculum from the same overnight cultures as were used for the first set of plates. These were incubated as described before in the presence of light or dark for 15 h overnight without taking readings. The OD595 was recorded at the 15-h time point and subsequently every hour until 24 h was reached, allowing a full growth curve to be generated from the two sets of microtiter plate data. Lag phase was defined as the time taken to reach an OD595 of 0.1, and this was derived directly from the growth curves. These growth experiments were carried out with three or six biological replicates per condition. For experiments investigating the involvement of ROS in growth inhibition by light, catalase or dimethylthiourea (both supplied Sigma) was added to the medium throughout the growth experiment at a concentration of 125 U ml−1 or 20 mM, respectively.
Ring phenotype and motility assays.
For the ring phenotype assays, overnight cultures were standardized to an OD600 of 2.0, and a 2-μl aliquot was inoculated onto the center of semisolid BHI agar (0.3% [wt/vol] agar). The plates were exposed to five consecutive 12-h cycles of light (from white fluorescent bulbs producing a power density of approximately 0.1 to 0.2 mW cm−2) and dark (wrapped in aluminum foil) at 30°C. Colonies were then imaged with a charge-coupled device (CCD) camera. For the motility assays, semisolid BHI agar plates were inoculated in the same way and then incubated in the continuous light (from white fluorescent bulbs producing a power density of approximately 0.1 to 0.2 mW cm−2) or dark (wrapped in aluminum foil) at 30°C. Colony diameter (in millimeters) was measured after a 60-h incubation period. Motility data represent average results from four biological replicates, with a maximum of two technical replicates per biological replicate. Significant differences for colony diameters incubated in the light compared to those incubated in the dark were calculated using the unpaired t test.
Light survival assays.
One milliliter of overnight culture was centrifuged, washed with PBS (Oxoid), and then resuspended in PBS. Resuspended cultures were incubated in 96-well round-bottomed plates (Thermo Scientific) at 30°C in the presence of 8 mW cm−2 470-nm blue light or in the dark (wrapped in aluminum foil). Samples were removed from wells for viable counting at 0, 6, and 12 h. The samples were serially diluted in PBS, and 10 μl of each dilution was plated in triplicate on BHI agar plates, which were then incubated at 37°C for 24 h before counting. The average of the results from six biological replicates (with standard deviation) was calculated for each time point.
Statistical analyses.
Unpaired t tests were used to compare endpoint and lag times for strains under the various conditions tested at each dilution. For the motility assays, t tests were again used to determine whether incubation in the light or dark had a significant effect on colony diameter for each strain. In a comparison of mutant strain endpoint and lag time values with those of the wild type in light, Bonferroni's correction was employed to address the issue of multiple comparisons (P < 0.0167).
RESULTS
Blue light inhibits L. monocytogenes growth.
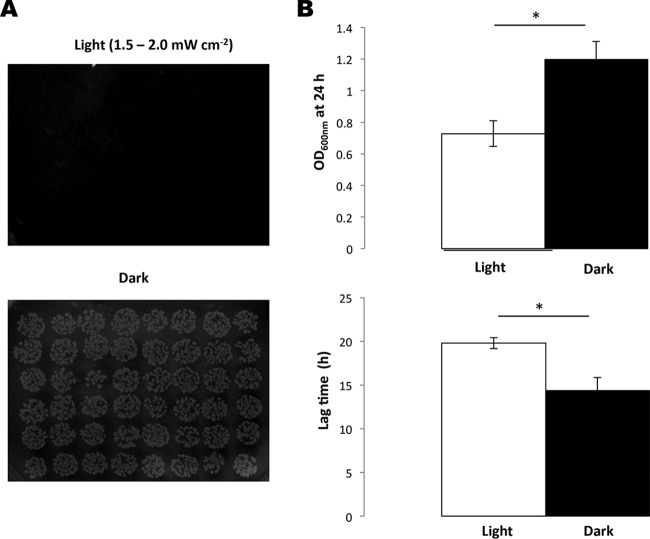
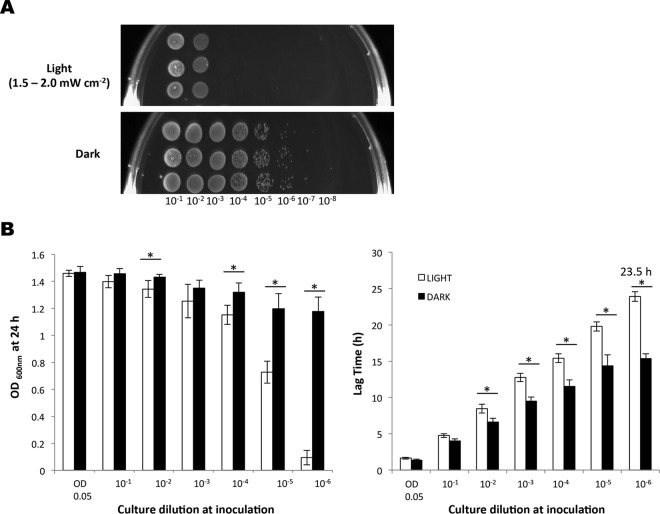
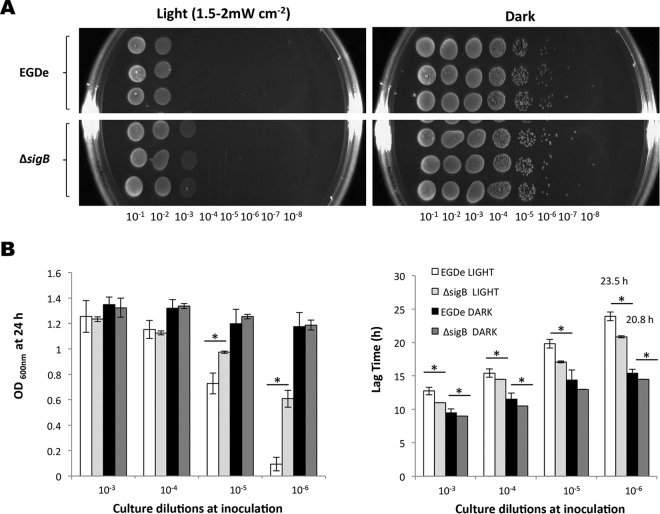
While previous studies have shown that L. monocytogenes responds to blue light, the effects on growth have not been investigated. We devised an apparatus to deliver a uniform dose of light at 460 to 470 nm to agar plates and liquid cultures in 96-well microtiter plates (described in Materials and Methods). When overnight cultures of L. monocytogenes EGD-e were spotted onto BHI agar plates (using a dilution containing approximately 104 cells ml−1) and incubated at 30°C for 24 h under a blue-light irradiance of 2.5 mW cm−2, no growth was detected, while normal growth was observed on the dark control (Fig. 1A). Blue-light inhibitory effects on growth were also recorded for L. monocytogenes 10403S and several food environment isolates (see Fig. S3 and S4 in the supplemental material). The cells were not killed by this exposure to blue light, since a subsequent incubation of the plates inoculated with L. monocytogenes EGD-e in the dark allowed the colonies to form after a further 48 h at 30°C (data not shown). In liquid BHI medium, the same light irradiance significantly inhibited both the culture yield (final optical density at 24 h) and the lag time (time to reach OD600 of 0.1), although growth was not completely inhibited (Fig. 1B). The inhibitory effects of blue light (470 nm) were found to be dependent on the cell density, since only more-dilute cultures (those containing <107 CFU ml−1) were found to be inhibited on agar plates (Fig. 2A). This was also the case in liquid BHI medium, in which the effects of blue light on the 24-h culture OD600 and the lag time were more pronounced as the cell concentration decreased (Fig. 2B). At high cell densities (>107 CFU ml−1), essentially no inhibition of growth was observed at this dose of light (Fig. 2A and B).
FIG 1.
Growth inhibition of EGD-e by blue light. EGD-e was illuminated with blue light (460 to 470 nm, 1.5 to 2.0 mW cm−2) either on BHI agar (A) or in a BHI liquid culture (B). (B) White bars represent growth following continuous illumination, and the black bars represent a dark control. The top graph shows the final OD600 after 24 h, and the bottom graph shows the difference in lag times between the two conditions. Overnight cultures were standardized to an OD600 of 1.0 and diluted to 10−5 (approximately 104 cells ml−1). Cells were incubated at 30°C for 24 h. The values represent the means of the results from three independent replicates. The error bars represent the standard deviations between replicates. Student's t test was carried out to determine the statistical difference (P ≤ 0.05, indicated with an asterisk) between cultures grown in light and dark.
FIG 2.
Cell density influences the extent of growth inhibition of EGD-e by blue light. Dilutions of EGD-e were illuminated with blue light (460 to 470 nm, 1.5 to 2.0 mW cm−2) either on BHI agar (A) or in BHI liquid culture (B). (A) Overnight cultures were standardized to an OD600 of 1.0 and diluted to 10−8. Four microliters of each dilution was spotted in triplicate onto BHI agar and grown at 30°C for 24 h. (B) White bars represent growth in the presence of light, and the black bars represent the dark control. The graphs show final OD600 measurements (left) and lag times (right). The number over the lag time indicates the time taken to reach an OD600 of 0.1. Starting cells were equalized to an OD600 of 0.05 and diluted to 10−6. Cultures were grown in 96-well plates at 30°C for 24 h. The values represent the means of the results from three individual replicates. The error bars represent the standard deviations between replicates. Student's t test was carried out to determine the statistical difference (P ≤ 0.05, indicated with an asterisk) between cultures grown in light and dark.
Inhibitory effects of blue light are dependent on generation of reactive oxygen species.
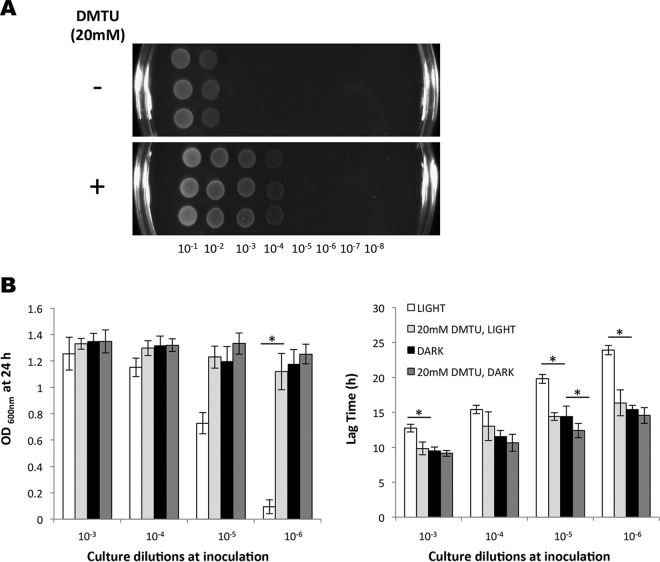
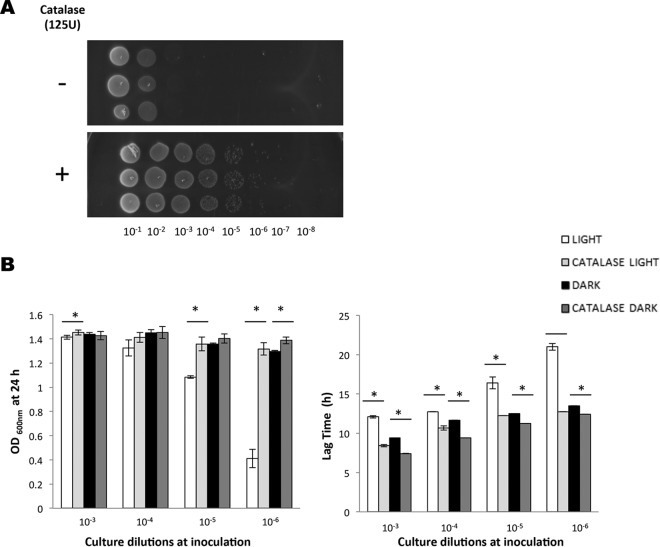
One possible interpretation of these data was that oxygen levels in the medium were influenced by the population cell density, and that this variable might influence the sensitivity to blue light, since other studies have reported that light can lead to the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) (25, 35). To investigate this hypothesis, we measured the inhibitory effect of blue light on cells grown in BHI medium containing the ROS scavenger dimethylthiourea (DMTU). When included at a concentration of 20 mM, DMTU had no significant effect on dark-incubated cultures, but it conferred a significant protective effect against blue light both on solid medium and in liquid medium (Fig. 3A and B). Strikingly, in liquid BHI medium, DMTU completely reversed the potent inhibitory effect of blue light in low-cell-density cultures; both the lag phase and final OD600 at 24 h were restored to the same levels as the dark control when DMTU was present (Fig. 3B). Very similar results were observed when catalase was included in either the agar-based (Fig. 4A) or liquid BHI medium (Fig. 4B); the presence of catalase reversed the growth inhibition and reduced the lag phase caused by blue light. Together, these results suggest that blue light causes the production of ROS in the medium, including hydrogen peroxide, and this is likely to be the principal reason for growth inhibition.
FIG 3.
ROS scavenger DMTU mitigates the inhibitory effect of blue light. EGD-e cells were illuminated with blue light (460 to 470 nm, 1.5 to 2 mW cm−2) either on BHI agar (A) or in liquid culture (B) with or without 20 mM DMTU. (A) Overnight cultures were standardized to an OD600 of 1.0 and diluted to 10−8. Four microliters of each dilution was spotted in triplicate onto BHI agar (−) or BHI agar supplemented with 20 mM DMTU (+) and grown at 30°C for 24 h. (B) Final OD measurements (left) and difference in lag time (right). Starting cells were equalized to an OD600 of 0.05 and diluted to 10−6. Cultures were grown in 96-well plates at 30°C for 24 h in BHI broth with or without 20 mM DMTU. The values represent the means of the results from three individual replicates. The error bars represent the standard deviations between samples. Student's t test was carried out to determine the statistical difference between cultures grown with and without DMTU. (B) Asterisks indicate significant differences (P ≤ 0.05).
FIG 4.
Catalase alleviates growth inhibition of L. monocytogenes by blue light. (A) Wild-type overnight cultures were standardized, diluted serially, and spotted on BHI agar spread with catalase or on agar plates without catalase. The plates were incubated in the presence of light for 24 h. (B) Wild-type overnight cultures were diluted to an OD600 of 0.05 and serially diluted 10-fold to a 10−6 dilution. The dilutions were grown for 24 h in the presence or absence of light, with or without catalase at a concentration of 125 U ml−1. The 24-h endpoint and the time taken to reach an OD600 of 0.1 were calculated for each strain condition at each dilution. The error bars represent standard deviations between samples. Unpaired t tests were used to determine the significance of differences (P ≤ 0.05, indicated by asterisks) between endpoint and lag-phase values between cultures with and without catalase.
A mutant lacking σB has decreased sensitivity to blue light.
As earlier studies have shown that σB is activated in response to blue light, we investigated the effect of a sigB deletion mutation on the sensitivity of L. monocytogenes to blue light. On solid BHI medium, the ΔsigB mutant was found reproducibly to grow better than the parental control when exposed to blue light for 24 h (1.5 to 2 mW cm−2). Growth was detected from the 10−3 dilution for the ΔsigB mutant, while this dilution failed to grow for the wild type under the same conditions (Fig. 5A). The L. monocytogenes 10403S ΔsigB mutant also displayed a growth advantage under these conditions (see Fig. S4 in the supplemental material). In liquid medium, the final OD600 of the EGD-e ΔsigB mutant was significantly higher than that of the wild type, especially for cultures inoculated with low starting cell numbers (10−5 and 10−6 dilutions; Fig. 5B). The ΔsigB mutant also exhibited a shorter lag time than the wild type during illumination with blue light (almost 3 h shorter for the lowest-cell-density inoculum; Fig. 5B). This somewhat surprising result might suggest that at sublethal doses of light, the cost of deploying a σB-controlled stress response is associated with a negative impact on growth rate. As the stress becomes more severe, a survival advantage might be expected. To investigate this, we exposed wild-type and ΔsigB mutant cells to a lethal dose of blue light (8 mW cm−2). Under these conditions, the ΔsigB mutant was found to be significantly more sensitive to light than the wild type, with a 10,000-fold reduction in survivors detected in the mutant populations after 12 h of exposure to light (Fig. 6). This effect was also observed at 16°C, when a lower power density was tested; after 24 h at 6.5 mW cm−2, the sigB mutant had 4-fold-fewer survivors than the wild type (data not shown). These data suggest that σB plays an important role in protecting cells against lethal doses of blue light.
FIG 5.
Cells lacking SigB have decreased sensitivity to blue light. Shown is the influence of blue light (470 nm, 1.5 to 2 mW cm−2) on the growth of L. monocytogenes ΔsigB compared to the wild-type EGD-e on BHI agar (A) and in BHI liquid culture (B). Overnight cultures were standardized to an OD600 of 1.0 and diluted to 10−8. Four microliters of each dilution was spotted in triplicate onto BHI agar and grown at 30°C for 24 h. (B) Final OD measurements (left) and difference in lag time (right). The number over the lag time indicates the time taken to reach 0.1. Starting cells were equalized to an OD600 of 0.05 and diluted to 10−6. Cultures were grown in 96-well plates at 30°C for 24 h. The values represent the means of the results from three individual replicates. The error bars represent the standard deviations between samples. Student's t test was carried out to determine the statistical difference between EGD-e and ΔsigB. The asterisks in panel B indicate a P value of ≤0.05.
FIG 6.
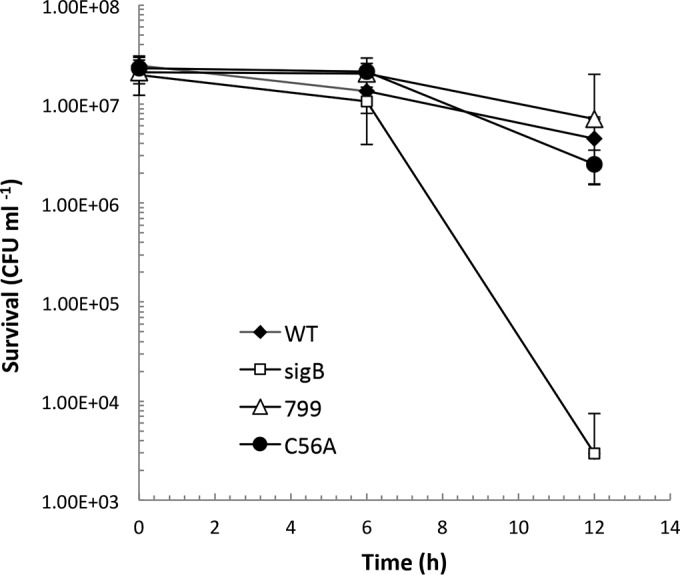
L. monocytogenes ΔsigB mutant displays a survival defect in higher-intensity blue light. Overnight cultures were washed and resuspended in PBS and exposed to 8 mW cm−2 blue light. Viable cell counts were performed at the 0-, 6-, and 12-h time points. WT, wild type. The values represent the means of the results from six individual replicates. The error bars represent the standard deviations between samples.
Role for the blue-light sensor Lmo0799.
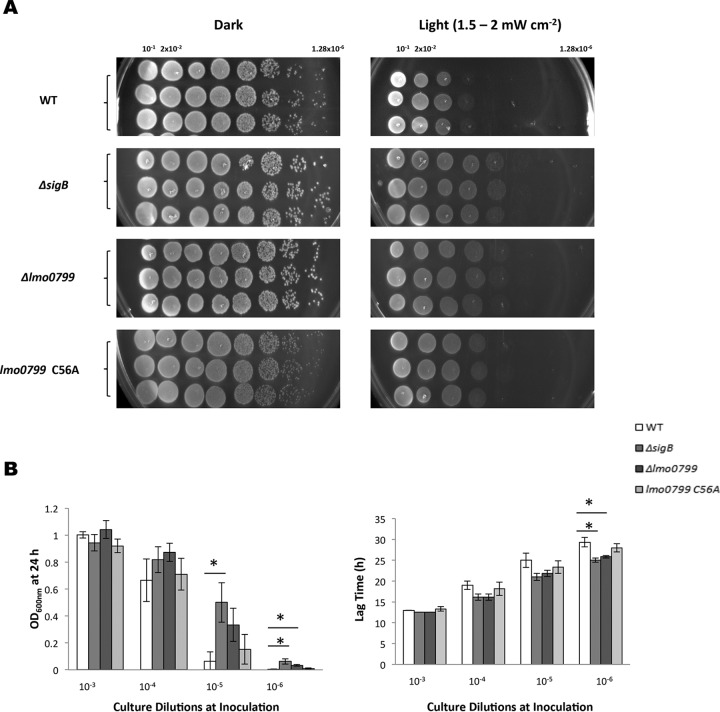
Since σB activation in the presence of blue light occurs via the blue-light sensor protein Lmo0799, we investigated the impact of the loss of this sensor on light sensitivity. A deletion mutant, Δlmo0799, and a missense mutant with an alanine replacing the conserved cysteine at position 56 of the Lmo0799 protein (C56A) were constructed. The lmo0799 C56A mutant was constructed to genetically test the idea that this residue is essential for the light-sensing function of the protein, as proposed by others (20, 21, 35). Two phenotypes known to be associated with the loss of Lmo0799 function were tested: derepressed motility in the presence of light and loss of ring formation in response to light-dark cycles (17, 18). In response to blue light, motility is repressed in the wild type, but this repression is lost in a ΔsigB mutant (Fig. 7). This repressed motility was also found to be lost in the Δlmo0799 and lmo0799 C56A mutants (Fig. 7). Ring formation in response to 12-h cycles of ambient light and dark is observed in the wild type, and this is abolished in a mutant lacking σB (Fig. 8). This phenotype is also lost in the Δlmo0799 and lmo0799 C56A mutants. These data show that light sensing via Lmo0799 is essential for the repression of motility by ambient light and for ring formation. Furthermore, they provide strong genetic evidence that the cysteine residue at position 56 is essential for the light-sensing function of Lmo0799.
FIG 7.
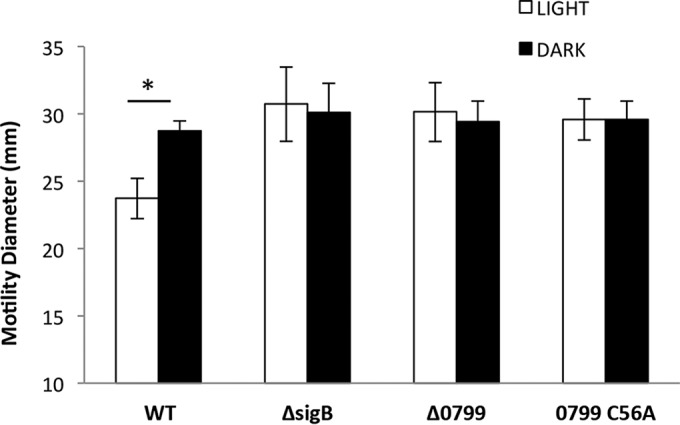
The lmo0799 C56A blind mutant displays derepressed motility in light. Strains were inoculated on 0.3% agar, and colony diameter was measured 60 h after exposure to ambient white light/incubation in dark at 30°C. The values represent the means of the results from four biological replicates. The error bars represent the standard deviations between samples. The asterisk indicates a P value of ≤0.05.
FIG 8.
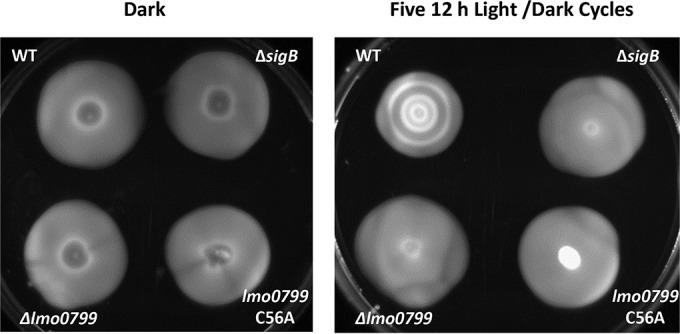
Light-dark ring formation is abolished for the blind lmo0799 C56A mutant. Overnight cultures were standardized and spotted onto 0.3% BHI agar. The plates were incubated in the dark for 60 h or exposed to five consecutive 12-h periods of ambient light and dark.
In the presence of an inhibitory dose of blue light, the Δlmo0799 mutant was found to display a similar decreased-sensitivity phenotype to the ΔsigB mutant. This effect was observed on both BHI agar plates and in liquid medium (Fig. 9A and B). When tested on agar plates, the reintroduction of lmo0799 on plasmid pMK4 removed this growth advantage, and it was observed that the presence of additional Lmo799 (via pMK4 lmo0799) negatively affected growth of the wild-type strain (see Fig. S5 in the supplemental material). The lmo0799 C56A mutant consistently displayed a less-pronounced phenotype, showing only a slight decrease in sensitivity to blue light on agar plates compared to the wild type (Fig. 9A) and no significant difference in liquid medium (Fig. 9B). These data may indicate that the C56A mutant version of Lmo0799 is still able to transmit light-related signals that lead to σB activation (and a corresponding decrease in growth). At lethal doses of light (8 mW cm−2), neither the Δlmo0799 mutant nor the lmo0799 C56A mutant displayed any increase in sensitivity to blue light compared to the wild type (Fig. 6). This result was unexpected but may reflect the fact that at higher doses of light, additional stress signals are generated (e.g., ROS) that still lead to σB activation even in the absence of the capacity to sense blue light itself.
FIG 9.
Removal of SigB or Lmo0799 decreases the inhibitory effect of light on cell growth. (A) Cultures were standardized to an OD600 of 1 and diluted, first 1:10, followed by 1:5 dilutions in PBS. The dilutions were spotted on BHI agar and incubated in the presence or absence of light. (B) Overnight cultures were diluted to an OD600 of 0.05 and serially diluted 10-fold to a 10−6 dilution. The dilutions were grown for 24 h in the presence or absence of light. The 24-h endpoint and the time taken to reach an OD600 of 0.1 were calculated for each strain at each dilution. Student's t tests were used to identify endpoint and lag-phase values that differed significantly from those of the wild-type strain. The values represent the means of the results from three individual replicates. The error bars represent the standard deviations between samples. The asterisks in panel B indicate a P value of ≤0.0167, adjusted for Bonferroni correction.
DISCUSSION
In this study, we have shown that the growth of L. monocytogenes is negatively affected by blue light (460 to 470 nm) at comparatively low irradiance levels (<10 mW cm−2) on both agar-based medium (Fig. 2A) and in liquid culture (Fig. 2B). The data show that blue light extends the lag time of cultures in liquid broth and that this effect can be reversed by the addition of the scavengers of reactive oxygen species (ROS) dimethylthiourea (Fig. 3B) and catalase (Fig. 4B). These results suggest that blue light triggers the formation of ROS and that these species have an inhibitory effect on growth, presumably because they cause oxidative damage of macromolecules in the cell (36). Previous studies have suggested the link between killing of bacteria by high-intensity visible light and ROS production (25, 37). The mechanisms underlying ROS production remain to be elucidated, but endogenous porphyrins have been implicated in light inactivation studies with other bacteria (38–40). As the genes for heme biosynthesis are present in L. monocytogenes (41), it seems likely that photosensitizing porphyrin intermediates, such as the uroporphyrinogen III, could contribute to the light sensitivity observed. Indeed, the addition of the porphyrin precursor 5-aminolevulinic acid to the growth medium increases the sensitivity of L. monocytogenes cells to violet light (31). The explanation for the protective effect of high cell densities on the extent of growth inhibition (Fig. 2A and B) remains unknown, but two possible explanations are suggested: either the total amount of catalase present in the population helps mitigate the effect of ROS or the oxygen level is depleted to a greater extent in dense cultures by respiratory activity, and this limits ROS production. Further studies will be required to differentiate between these possibilities.
The protective response to oxidative stress is known to be partially under σB control (4), and so it was somewhat unexpected to discover that the ΔsigB (and Δlmo0799) mutant displayed an enhanced capacity to withstand the inhibitory effects of light at 1.5 to 2 mW cm−2. However, enhanced growth of sigB mutants has been reported by others both in L. monocytogenes and B. subtilis. Abram et al. (42) observed that a 10403S ΔsigB mutant had a higher growth rate than the wild-type parent in a chemically defined medium with 0.5 M added NaCl. Mutations in rsbT and rsbV that are predicted to negatively affect σB activity also produce a fast-growth phenotype under some conditions (43). A ΔsigB mutant of B. subtilis is known to have a significant growth advantage compared to the wild type when grown in a glucose-limited medium (44). Although these results have not been explained to date, it has been suggested that these effects might arise from sigma factor competition for core RNA polymerase (9). In this model, the increase in growth rate of the mutant lacking sigB arises because the housekeeping sigma factor σA has greater access to the core polymerase and can therefore more efficiently transcribe genes with growth-related functions. A similar model has been proposed to account for the accumulation of rpoS (encoding σS, the general stress response sigma factor) mutations in E. coli when grown under limiting conditions (45, 46). The energetic cost of deploying the general stress response (with associated homeostatic and repair energy requirements) may also contribute to the negative effect on growth rate. As the ΔsigB and Δlmo0799 mutants behaved in a similar manner at inhibitory low doses of blue light (Fig. 9A), it suggests that the activation of the general stress response by σB at this dose of light, which occurs following light sensing and signal transduction by Lmo0799 (17), produces a negative effect on cell growth. Indeed, we recently observed that a nonsense mutation in rsbU, which is predicted to negatively affect SigB activity, also produces reduced light sensitivity to low-intensity light (K. NicAogáin and C. O'Byrne, unpublished data). However, once the dose of blue light reaches a lethal level (8 mW cm−2), it is clear that σB contributes positively to survival (Fig. 6), highlighting the importance of the general stress response for surviving damage caused by visible light. Surprisingly, Lmo0799 did not appear to be required for survival at lethal doses of blue light. It is possible that indirect stress signals (e.g., oxidative damage caused by ROS) are generated at this higher dose of light, and these signals can be sensed independently of Lmo0799, perhaps via RsbR or one of its paralogues (the putative sensory subunits of the stressosome), thereby ensuring an effective stress response independently of light sensing. We are currently pursuing this line of investigation.
The genetic evidence presented here provides strong support for the model proposing that the conserved cysteine residue at position 56 of Lmo0799 plays a crucial role in allowing this protein to sense blue light (Fig. 7 and 8). Previous modeling studies have found the Lmo0799 protein structure to be nearly identical to that of YtvA in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens (17, 47), with both having the conserved cysteine in the FMN-binding pocket. Gaidenko et al. (48) showed that the YtvA conserved residue C62 is critical for light-induced SigB activation of the stress response in B. subtilis. The photocycle of the Lmo0799 protein has been elucidated by Chan et al. (21), and the authors predicted an important role for C56. Replacement of this residue with an alanine produced phenotypes (loss of ring formation during light-dark cycles and increased motility in the presence of ambient light) similar to those observed with the removal of the full Lmo0799 protein and suggests that the predicted light-induced cysteinyl-flavin mononucleotide adduct is crucial for light sensing (17, 18). This single-amino-acid change likely results in the uncoupling of the Lmo0799 LOV domain from its FMN chromophore, resulting in the loss of blue-light-sensing capacity. The enhanced growth phenotype of the lmo0799 C56A mutant was not as pronounced as the Δlmo0799 or ΔsigB mutants on BHI agar plates in the presence of a sublethal blue-light dose (Fig. 9A), suggesting that σB might be partially activated by light in this strain, but this difference was not found to be significant in liquid BHI medium (Fig. 9B). It is worth noting that the impact of Lmo0799 on the overall structure and assembly of the stressosome has not been investigated in L. monocytogenes, and it is possible that the deletion mutation might have indirect effects on the sensing capacity of the stressosome independent of the loss of the Lmo0799 protein itself. This might have contributed to the subtle differences in the behavior of the lmo0799 C56A and Δlmo0799 mutants on BHI agar plates in the presence of light. Alternatively, the Lmo0799 protein might have a secondary sensing function, as has been postulated by Chan et al. (21), which remains unaffected in the lmo0799 C56A mutant.
In this study, we have demonstrated that blue light (460 to 470 nm) exhibits inhibitory effects on the growth and survival of L. monocytogenes and show that these effects are caused by the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). While a number of other studies have also shown the inhibitory effects of visible light on a variety of bacterial species (26, 37, 49–51), most have been conducted with high-intensity violet-blue light (400 to 405 nm) rather than blue light. Thus, we demonstrate that L. monocytogenes growth and survival can be affected by exposure to blue light. Overall, the study raises the interesting possibility that blue-light-emitting diode lights, which are comparatively cheap, energy efficient, and widely available, might be used to control the growth of this pathogen in food-processing environments or even in certain amenable food groups.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful to members of the Bacterial Stress Response Group and colleagues at NUI Galway for helpful discussions.
The research was funded by a Science Foundation Ireland Research Frontiers Programme grant (11/RFP.1/GEN/3267) and by an Irish Department of Agriculture, Food, and the Marine FIRM grant (no. 11F008) to C.O. J.J. was supported by funding from the Swedish Research Council (grant 621-2012-2451) and the European Research Council (grant RNAntibiotics – 260764).
Footnotes
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00685-16.
REFERENCES
- 1.Farber JM, Peterkin PI. 1991. Listeria monocytogenes, a food-borne pathogen. Microbiol Rev 55:476–511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Mead PS, Slutsker L, Dietz V, McCaig LF, Bresee JS, Shapiro C, Griffin PM, Tauxe RV. 1999. Food-related illness and death in the United States. Emerg Infect Dis 5:607–625. doi: 10.3201/eid0505.990502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.European Food Safety Authority. 2015. The European Union summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in 2013. EFSA J 13:4329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ferreira A, O'Byrne CP, Boor KJ. 2001. Role of σB in heat, ethanol, acid, and oxidative stress resistance and during carbon starvation in Listeria monocytogenes. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4454–4457. doi: 10.1128/AEM.67.10.4454-4457.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Moorhead SM, Dykes GA. 2004. Influence of the sigB gene on the cold stress survival and subsequent recovery of two Listeria monocytogenes serotypes. Int J Food Microbiol 91:63–72. doi: 10.1016/S0168-1605(03)00332-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sue D, Fink D, Wiedmann M, Boor KJ. 2004. σB-dependent gene induction and expression in Listeria monocytogenes during osmotic and acid stress conditions simulating the intestinal environment. Microbiology 150:3843–3855. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.27257-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hardy J, Francis KP, DeBoer M, Chu P, Gibbs K, Contag CH. 2004. Extracellular replication of Listeria monocytogenes in the murine gall bladder. Science 303:851–853. doi: 10.1126/science.1092712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Davis MJ, Coote PJ, O'Byrne CP. 1996. Acid tolerance in Listeria monocytogenes: the adaptive acid tolerance response (ATR) and growth-phase-dependent acid resistance. Microbiology 142:2975–2982. doi: 10.1099/13500872-142-10-2975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.O'Byrne CP, Karatzas KAG. 2008. The role of sigma B (σB) in the stress adaptations of Listeria monocytogenes: overlaps between stress adaptation and virulence. Adv Appl Microbiol 65:115–140. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2164(08)00605-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hecker M, Pané-Farré J, Völker U. 2007. SigB-dependent general stress response in Bacillus subtilis and related Gram-positive bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 61:215–236. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.61.080706.093445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kazmierczak MJ, Mithoe SC, Boor KJ, Wiedmann M. 2003. Listeria monocytogenes σB regulates stress response and virulence functions. J Bacteriol 185:5722–5734. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.19.5722-5734.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Toledo-Arana A, Dussurget O, Nikitas G, Sesto N, Guet-Revillet H, Balestrino D, Loh E, Gripenland J, Tiensuu T, Vaitkevicius K, Barthelemy M, Vergassola M, Nahori M-A, Soubigou G, Régnault B, Coppée J-Y, Lecuit M, Johansson J, Cossart P. 2009. The Listeria transcriptional landscape from saprophytism to virulence. Nature 459:950–956. doi: 10.1038/nature08080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Heavin S, O'Byrne CP. 2012. Post-genomic insights into the regulation of transcription in the facultative intracellular pathogen Listeria monocytogenes, p 210–225. In Wong H. (ed), Stress response of food microorganisms. Nova Science Publishers, Hauppauge, NY. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Marles-Wright J, Grant T, Delumeau O, van Duinen G, Firbank SJ, Lewis PJ, Murray JW, Newman JA, Quin MB, Race PR, Rohou A, Tichelaar W, van Heel M, Lewis RJ. 2008. Molecular architecture of the “stressosome,” a signal integration and transduction hub. Science 322:92–96. doi: 10.1126/science.1159572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ferreira A, Gray M, Wiedmann M, Boor KJ. 2004. Comparative genomic analysis of the sigB operon in Listeria monocytogenes and in other Gram-positive bacteria. Curr Microbiol 48:39–46. doi: 10.1007/s00284-003-4020-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Marles-Wright J, Lewis RJ. 2008. The Bacillus subtilis stressosome: a signal integration and transduction hub. Commun Integr Biol 1:182–184. doi: 10.4161/cib.1.2.7225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ondrusch N, Kreft J. 2011. Blue and red light modulates SigB-dependent gene transcription, swimming motility and invasiveness in Listeria monocytogenes. PLoS One 6:e16151. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tiensuu T, Andersson C, Rydén P, Johansson J. 2013. Cycles of light and dark co-ordinate reversible colony differentiation in Listeria monocytogenes. Mol Microbiol 87:909–924. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ávila-Pérez M, Hellingwerf KJ, Kort R. 2006. Blue light activates the σB-dependent stress response of Bacillus subtilis via YtvA. J Bacteriol 188:6411–6414. doi: 10.1128/JB.00716-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Möglich A, Moffat K. 2007. Structural basis for light-dependent signaling in the dimeric LOV domain of the photosensor YtvA. J Mol Biol 373:112–126. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.07.039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Chan RH, Lewis JW, Bogomolni RA. 2012. Photocycle of the LOV-STAS protein from the pathogen Listeria monocytogenes. Photochem Photobiol 89:361–369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Maclean M, McKenzie K, Anderson JG, Gettinby G, MacGregor SJ. 2014. 405 nm light technology for the inactivation of pathogens and its potential role for environmental disinfection and infection control. J Hosp Infect 88:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2014.06.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.St. Denis TG, Dai T, Izikson L, Astrakas C, Anderson RR, Hamblin MR, Tegos GP. 2011. All you need is light; antimicrobial photoinactivation as an evolving and emerging discovery strategy against infectious disease. Virulence 2:509–520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Maisch T, Szeimies R-M, Jori G, Abels C. 2004. Antibacterial photodynamic therapy in dermatology. Photochem Photobiol Sci 3:907–917. doi: 10.1039/b407622b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Endarko E, Maclean M, Timoshkin IV, MacGregor SJ, Anderson JG. 2012. High-intensity 405 nm light inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes. Photochem Photobiol 88:1280–1286. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.2012.01173.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Murdoch LE, Maclean M, Endarko E, MacGregor SJ, Anderson JG. 2012. Bactericidal effects of 405 nm light exposure demonstrated by inactivation of Escherichia, Salmonella, Shigella, Listeria, and Mycobacterium species in liquid suspensions and on exposed surfaces. ScientificWorldJournal 2012:8. doi: 10.1100/2012/137805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Maclean M, Murdoch LE, MacGregor SJ, Anderson JG. 2012. Sporicidal effects of high-intensity 405 nm visible light on endospore-forming bacteria. Photochem Photobiol 89:120–126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Enwemeka CS, Williams D, Hollosi S, Yens D, Enwemeka SK. 2008. Visible 405 nm SLD light photo-destroys methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in vitro. Lasers Surg Med 40:734–737. doi: 10.1002/lsm.20724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.McKenzie K, Maclean M, Timoshkin IV, Endarko E, MacGregor SJ, Anderson JG. 2013. Photoinactivation of bacteria attached to glass and acrylic surfaces by 405 nm light: potential application for biofilm decontamination. Photochem Photobiol 89:927–935. doi: 10.1111/php.12077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Luksiene Z, Buchovec I, Paskeviciute E. 2010. Inactivation of several strains of Listeria monocytogenes attached to the surface of packaging material by Na-chlorophyllin-based photosensitization. J Photochem Photobiol B 101:326–331. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2010.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Buchovec I, Paskeviciute E, Luksiene Z. 2010. Photodynamic inactivation of food pathogen Listeria monocytogenes. Food Technol Biotechnol 48:207–213. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Nitzan Y, Salmon-Divon M, Shporen E, Malik Z. 2004. ALA induced photodynamic effects on Gram positive and negative bacteria. Photochem Photobiol Sci 3:430–435. doi: 10.1039/b315633h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Glaser P, Frangeul L, Buchrieser C, Rusniok C, Amend A, Baquero F, Berche P, Bloecker H, Brandt P, Chakraborty T, Charbit A, Chetouani F, Couvé E, de Daruvar A, Dehoux P, Domann E, Domínguez-Bernal G, Duchaud E, Durant L, Dussurget O, Entian KD, Fsihi H, García-del Portillo F, Garrido P, Gautier L, Goebel W, Gómez-López N, Hain T, Hauf J, Jackson D, Jones LM, Kaerst U, Kreft J, Kuhn M, Kunst F, Kurapkat G, Madueno E, Maitournam A, Vicente JM, Ng E, Nedjari H, Nordsiek G, Novella S, de Pablos B, Pérez-Diaz JC, Purcell R, Remmel B, Rose M, Schlueter T, Simoes N, et al. . 2001. Comparative genomics of Listeria species. Science 294:849–852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Arnaud M, Chastanet A, Débarbouillé M. 2004. New vector for efficient allelic replacement in naturally Gram-positive bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:6887–6891. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.11.6887-6891.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Avila-Pérez M, Vreede J, Tang Y, Bende O, Losi A, Gärtner W, Hellingwerf K. 2009. In vivo mutational analysis of YtvA from Bacillus subtilis: mechanism of light activation of the general stress response. J Biol Chem 284:24958–24964. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.033316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Imlay JA. 2013. The molecular mechanisms and physiological consequences of oxidative stress: lessons from a model bacterium. Nat Rev Microbiol 11:443–454. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Maclean M, Macgregor SJ, Anderson JG, Woolsey GA. 2008. The role of oxygen in the visible-light inactivation of Staphylococcus aureus. J Photochem Photobiol B 92:180–184. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2008.06.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Gábor F, Szocs K, Maillard P, Csík G. 2001. Photobiological activity of exogenous and endogenous porphyrin derivatives in Escherichia coli and Enterococcus hirae cells. Radiat Environ Biophys 40:145–151. doi: 10.1007/s004110100092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hamblin MR, Hasan T. 2004. Photodynamic therapy: a new antimicrobial approach to infectious disease? Photochem Photobiol Sci 3:436–450. doi: 10.1039/b311900a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Nitzan Y, Ashkenazi H. 2001. Photoinactivation of Acinetobacter baumannii and Escherichia coli B by a cationic hydrophilic porphyrin at various light wavelengths. Curr Microbiol 42:408–414. doi: 10.1007/s002840010238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Panek H, O'Brian MR. 2002. A whole genome view of prokaryotic haem biosynthesis. Microbiology 148:2273–2282. doi: 10.1099/00221287-148-8-2273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Abram F, Starr E, Karatzas KAG, Matlawska-Wasowska K, Boyd A, Wiedmann M, Boor KJ, Connally D, O'Byrne CP. 2008. Identification of components of the sigma B regulon in Listeria monocytogenes that contribute to acid and salt tolerance. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:6848–6858. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00442-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Chaturongakul S, Boor KJ. 2004. RsbT and RsbV contribute to σB-dependent survival under environmental, energy, and intracellular stress conditions in Listeria monocytogenes. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:5349–5356. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.9.5349-5356.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Schweder T, Kolyschkow A, Völker U, Hecker M. 1999. Analysis of the expression and function of the σB-dependent general stress regulon of Bacillus subtilis during slow growth. Arch Microbiol 171:439–443. doi: 10.1007/s002030050731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.King T, Seeto S, Ferenci T. 2006. Genotype-by-environment interactions influencing the emergence of rpoS mutations in Escherichia coli populations. Genetics 172:2071–2079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Nyström T. 2004. Growth versus maintenance: a trade-off dictated by RNA polymerase availability and sigma factor competition? Mol Microbiol 54:855–862. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Ogata H, Cao Z, Losi A, Gärtner W. 2009. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of the LOV domain of the blue-light receptor YtvA from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 65:853–855. doi: 10.1107/S1744309109026670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Gaidenko TA, Kim T-J, Weigel AL, Brody MS, Price CW. 2006. The blue-light receptor YtvA acts in the environmental stress signaling pathway of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 188:6387–6395. doi: 10.1128/JB.00691-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Bialka KL, Demirci A. 2008. Efficacy of pulsed UV-light for the decontamination of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella spp. on raspberries and strawberries. J Food Sci 73:201–207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kairyte K, Lapinskas S, Gudelis V, Luksiene Z. 2012. Effective inactivation of food pathogens Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella enterica by combined treatment of hypericin-based photosensitization and high power pulsed light. J Appl Microbiol 112:1144–1151. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2012.05296.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Maclean M, MacGregor SJ, Anderson JG, Woolsey G. 2009. Inactivation of bacterial pathogens following exposure to light from a 405-nanometer light-emitting diode array. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:1932–1937. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01892-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.