Abstract
The cervical somatosensory evoked potential after median nerve stimulation was recorded in 14 patients with cervical spondylosis with radiculopathy and, in 10 cases, myelopathy. Four patients had normal potentials, five showed delayed potentials, and in five others no potential could be seen.
Full text
PDF
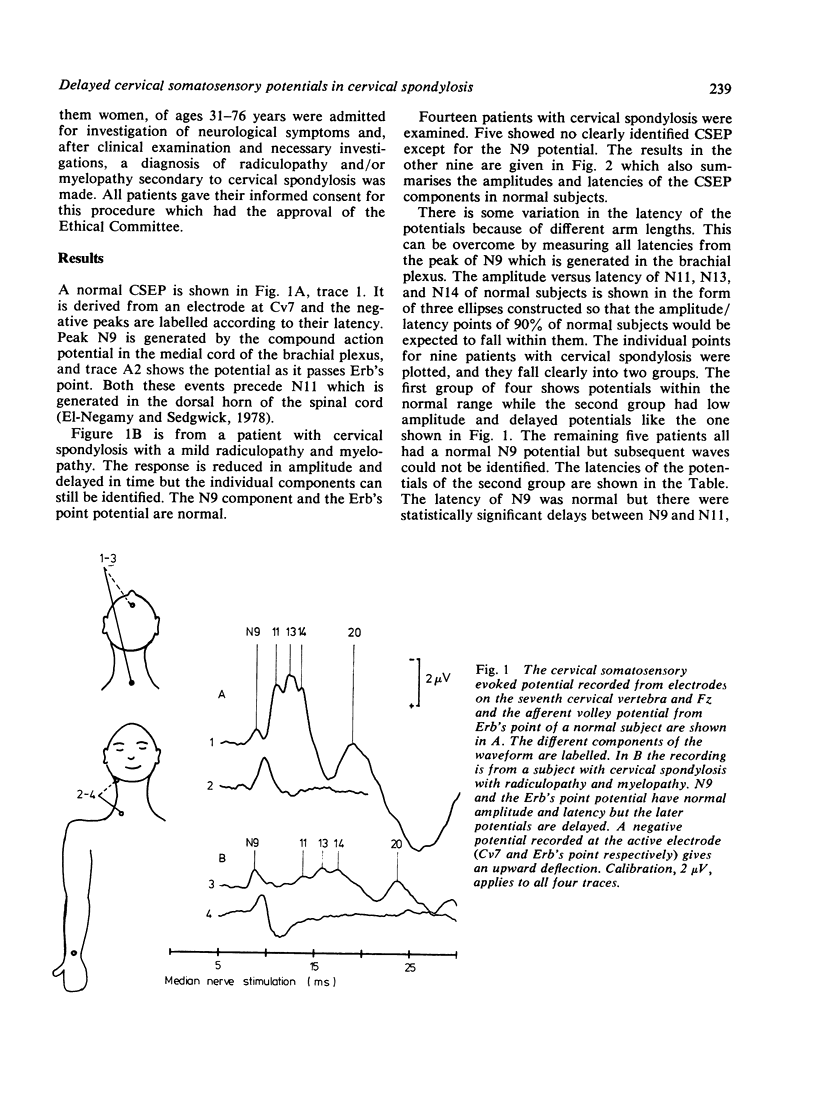
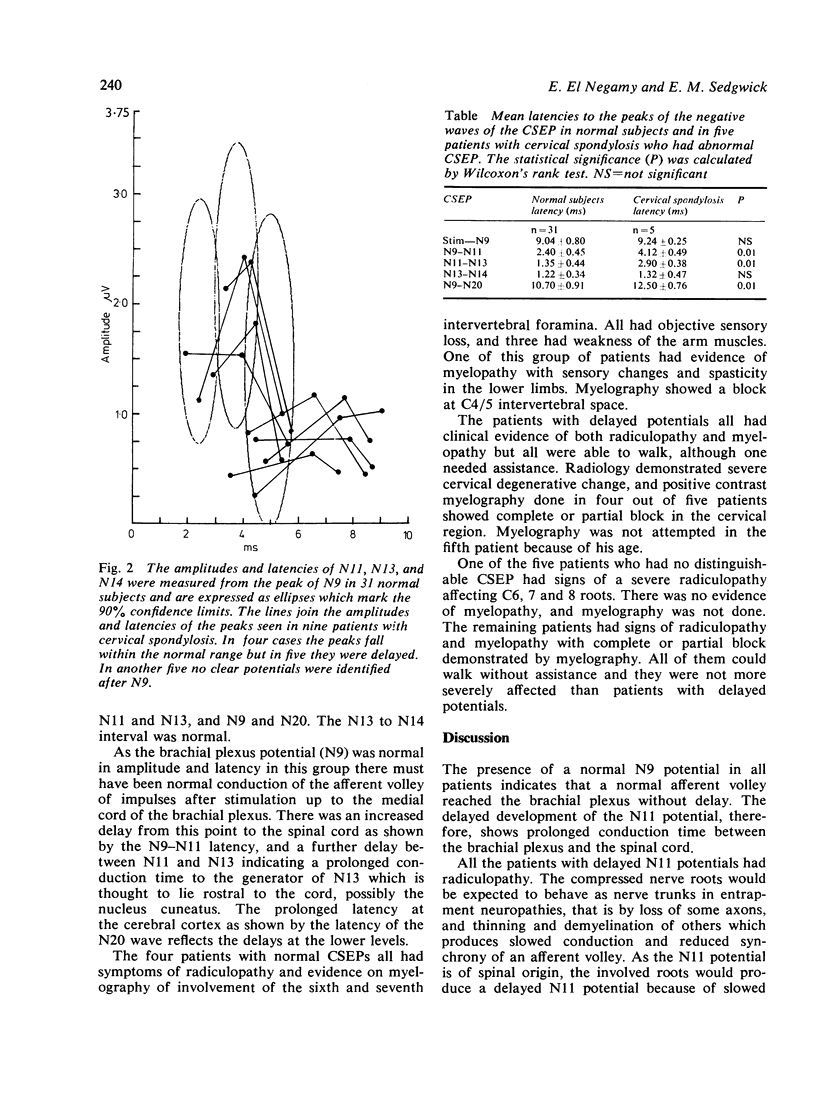

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cracco R. Q., Cracco J. B. Somatosensory evoked potential in man: far field potentials. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1976 Nov;41(5):460–466. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(76)90057-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. J. Short latency potentials recorded from the neck and scalp following median nerve stimulation in man. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1977 Dec;43(6):853–863. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(77)90008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastaglia F. L., Black J. L., Collins D. W. Visual and spinal evoked potentials in diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Br Med J. 1976 Sep 25;2(6038):732–732. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6038.732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews W. B., Beauchamp M., Small D. G. Cervical somato-sensory evoked responses in man. Nature. 1974 Nov 15;252(5480):230–232. doi: 10.1038/252230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D. G., Matthews W. B., Small M. The cervical somatosensory evoked potential (SEP) in the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci. 1978 Feb;35(2-3):211–224. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(78)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON M. The morbid anatomy of cervical spondylosis and myelopathy. Brain. 1960 Dec;83:589–617. doi: 10.1093/brain/83.4.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Negamy E., Sedgwick E. M. Properties of a spinal somatosensory evoked potential recorded in man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1978 Aug;41(8):762–768. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.41.8.762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



