Abstract
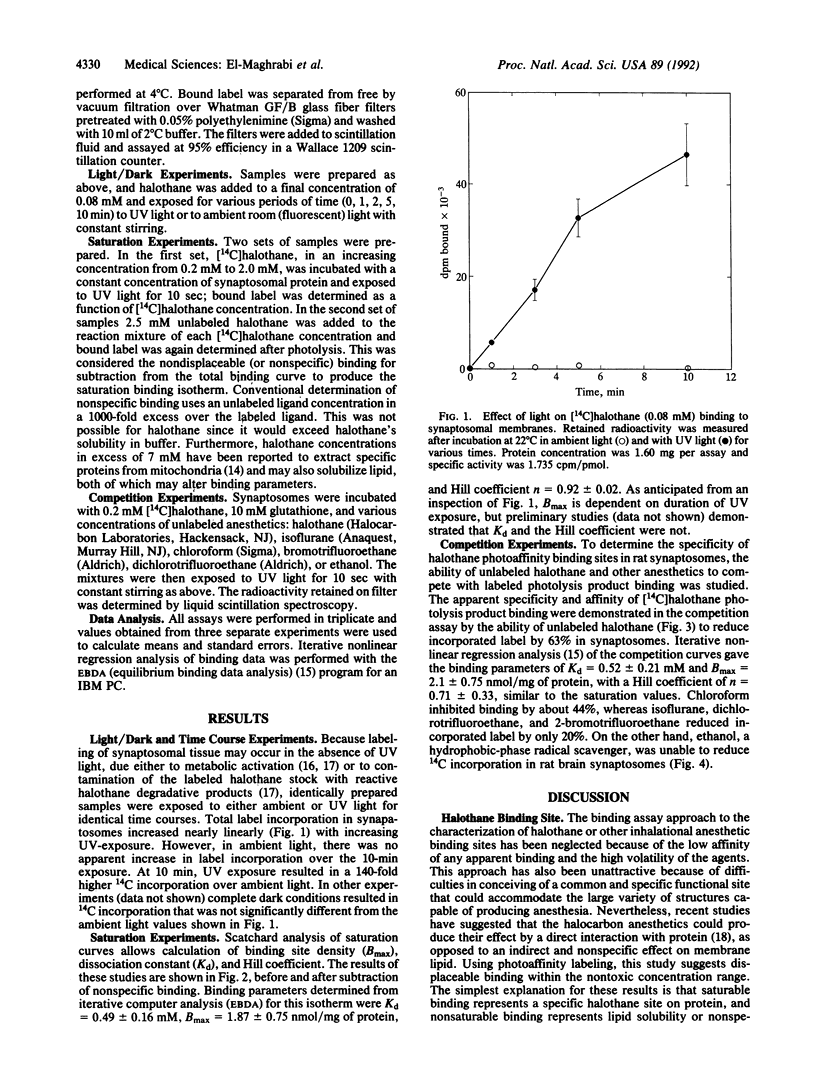
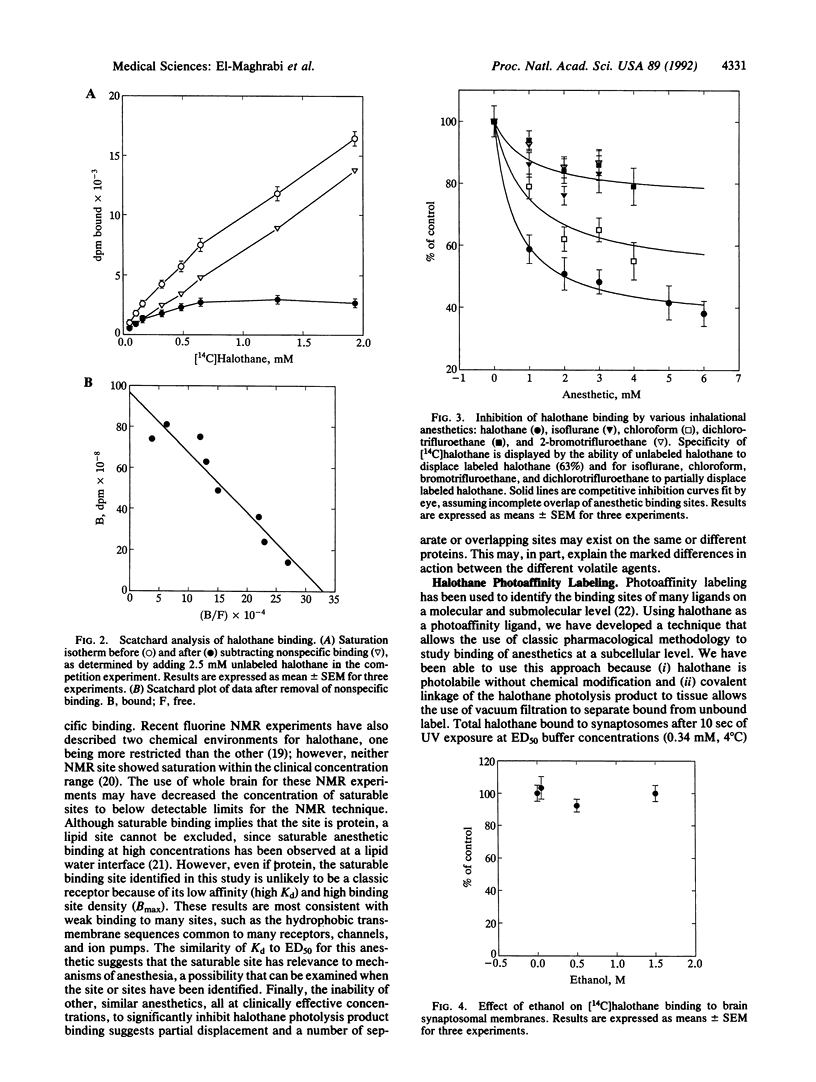
The hypothesis that volatile anesthetics act directly on or bind specifically to membrane proteins remains controversial. In earlier in situ electron probe microanalysis studies in cardiac muscle we showed preferential partitioning of halothane into mitochondria. To determine whether partitioning represents saturable binding or simple solubility, a photoaffinity labeling method was developed for halothane to examine binding in rat brain synaptosomes. Radioligand binding assays were then used to determine binding parameters for this important inhalational anesthetic. UV-light exposure of synaptosomes incubated with clinical concentrations of [14C]halothane resulted in sufficient labeling to allow characterization of binding sites. Analysis of saturation and competition curves showed that greater than 60% of [14C]halothane photolysis product binding to synaptosomes was specific, with low affinity (Kd = 0.49 +/- 0.16 mM) and high binding site concentration (Bmax = 1.87 +/- 0.75 nmol/mg of protein). Halothane photoaffinity labeling was partially inhibited by isoflurane (20%), chloroform (44%), 2-bromotrifluoroethane (20%), and dichlorotrifluoroethane (20%) but not by ethanol. The Kd measured with this photoaffinity approach is similar to the concentration of halothane required to produce anesthesia in rats.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayley H., Knowles J. R. Photoaffinity labeling. Methods Enzymol. 1977;46:69–114. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(77)46012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bösterling B., Trevor A., Trudell J. R. Binding of halothane-free radicals to fatty acids following UV irradiation. Anesthesiology. 1982 May;56(5):380–384. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198205000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN E. N., BREWER H. W., BELLVILLE J. W., SHER R. THE CHEMISTRY AND TOXICOLOGY OF DICHLOROHEXAFLUOROBUTENE. Anesthesiology. 1965 Mar-Apr;26:140–153. doi: 10.1097/00000542-196503000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooperman B. S. Photoaffinity labeling of Escherichia coli ribosomes. Pharmacol Ther. 1987;34(2):271–302. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(87)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doze V. A., Chen B. X., Tinklenberg J. A., Segal I. S., Maze M. Pertussis toxin and 4-aminopyridine differentially affect the hypnotic-anesthetic action of dexmedetomidine and pentobarbital. Anesthesiology. 1990 Aug;73(2):304–307. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199008000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckenhoff R. G., Shuman H. Subcellular distribution of an inhalational anesthetic in situ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):454–457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eger E. I., 2nd, Lundgren C., Miller S. L., Stevens W. C. Anesthetic potencies of sulfur hexafluoride, carbon tetrafluoride, chloroform and Ethrane in dogs: correlation with the hydrate and lipid theories of anesthetic action. Anesthesiology. 1969 Feb;30(2):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evers A. S., Berkowitz B. A., d'Avignon D. A. Correlation between the anaesthetic effect of halothane and saturable binding in brain. Nature. 1989 Oct 26;341(6244):766–766. doi: 10.1038/341766a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks N. P., Lieb W. R. Do general anaesthetics act by competitive binding to specific receptors? Nature. 1984 Aug 16;310(5978):599–601. doi: 10.1038/310599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockhart S. H., Cohen Y., Yasuda N., Kim F., Litt L., Eger E. I., 2nd, Chang L. H., James T. Absence of abundant binding sites for anesthetics in rabbit brain: an in vivo NMR study. Anesthesiology. 1990 Sep;73(3):455–460. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199009000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. W. The nature of the site of general anesthesia. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1985;27:1–61. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60555-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan P. G., Sedensky M., Meneely P. M. Multiple sites of action of volatile anesthetics in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2965–2969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahiro M., Yeh J. Z., Brunner E., Narahashi T. General anesthetics modulate GABA receptor channel complex in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. FASEB J. 1989 May;3(7):1850–1854. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.7.2541038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pradhan D., Williamson P., Schlegel R. A. A photoactivable phospholipid analogue that specifically labels membrane cytoskeletal proteins of intact erythrocytes. Biochemistry. 1989 Aug 22;28(17):6943–6949. doi: 10.1021/bi00443a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter J. J., Sunderland E., Juhl U., Kornguth S. Extraction of mitochondrial proteins by volatile anesthetics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 21;543(1):106–115. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90458-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottenberg H., Waring A., Rubin E. Tolerance and cross-tolerance in chronic alcoholics: reduced membrane binding of ethanol and other drugs. Science. 1981 Jul 31;213(4507):583–585. doi: 10.1126/science.6264608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trudell J. R., Bösterling, Trevor A. 1-Chloro-2,2,2-trifluoroethyl radical: Formation from halothane by human cytochrome P-450 in reconstituted vesicles and binding to phospholipids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Sep 16;102(1):372–377. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91531-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke R. A., Gandolf A. J. Anaerobic release of fluoride from halothane. Relationship to the binding of halothane metabolites to hepatic cellular constituents. Drug Metab Dispos. 1976 Jan-Feb;4(1):40–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida T., Okabayashi H., Kamaya H., Ueda I. Saturable and unsaturable binding of a volatile anesthetic enflurane with model lipid vesicle membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Mar 13;979(3):287–293. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90246-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



