Abstract
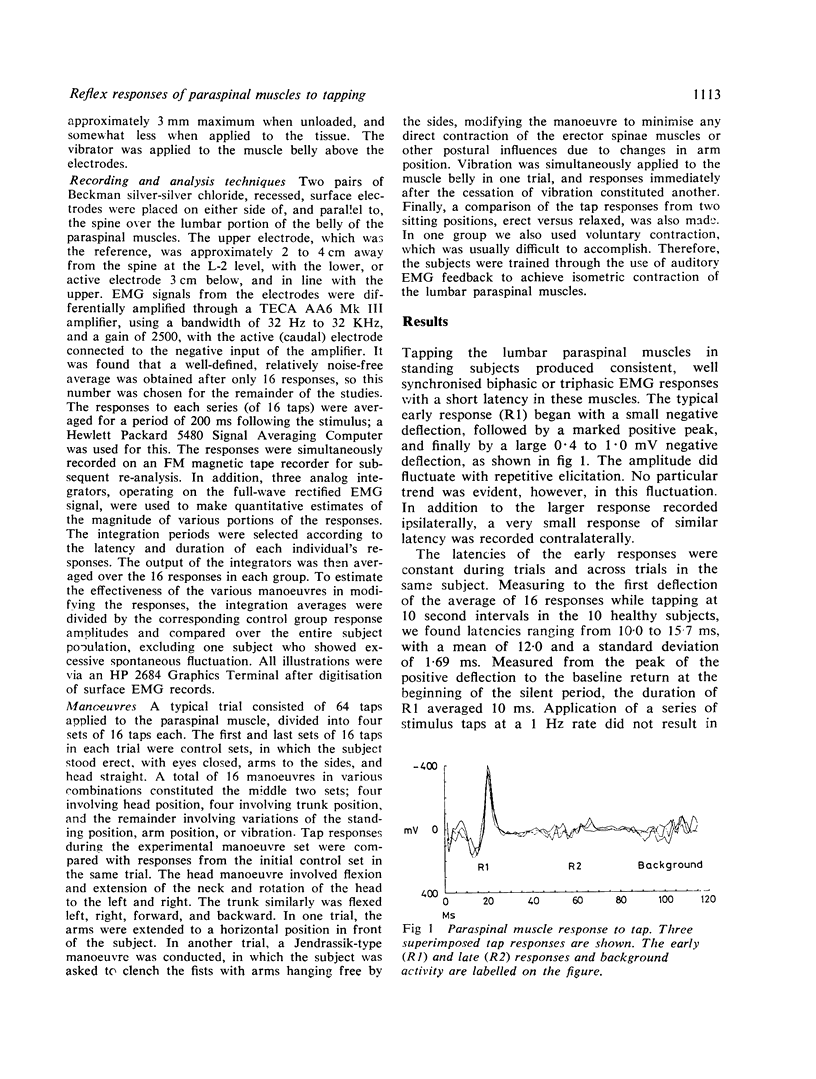
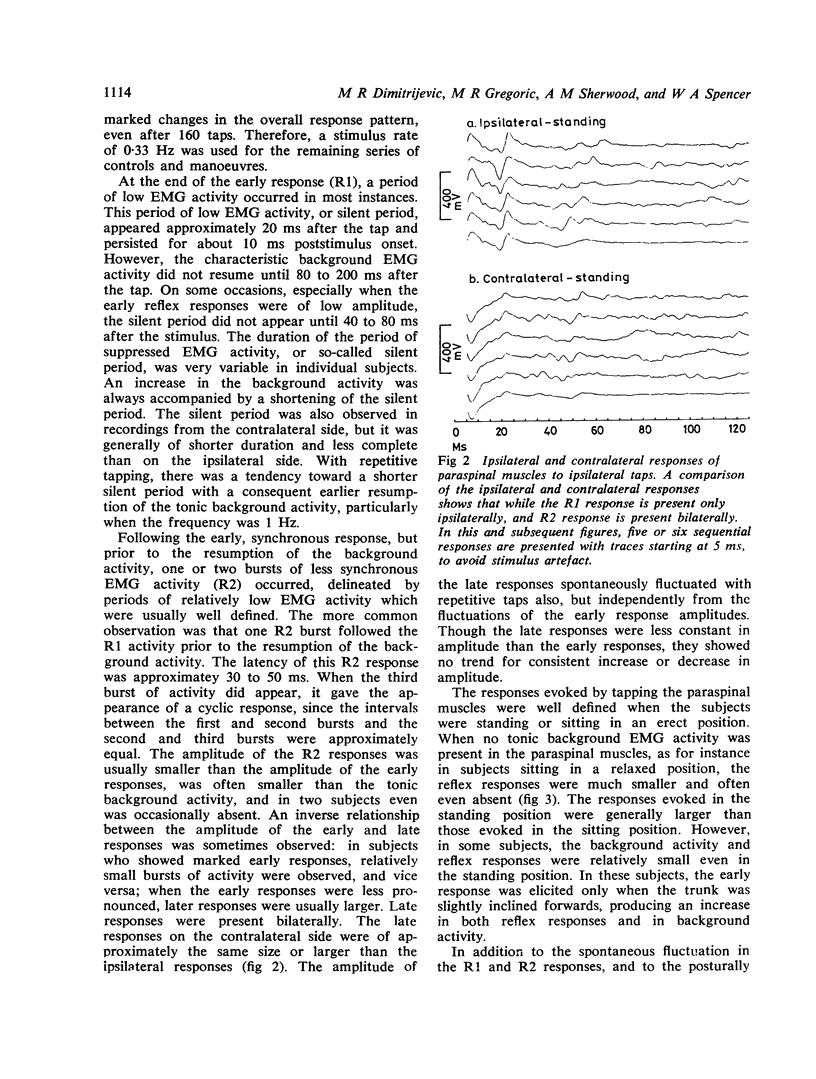
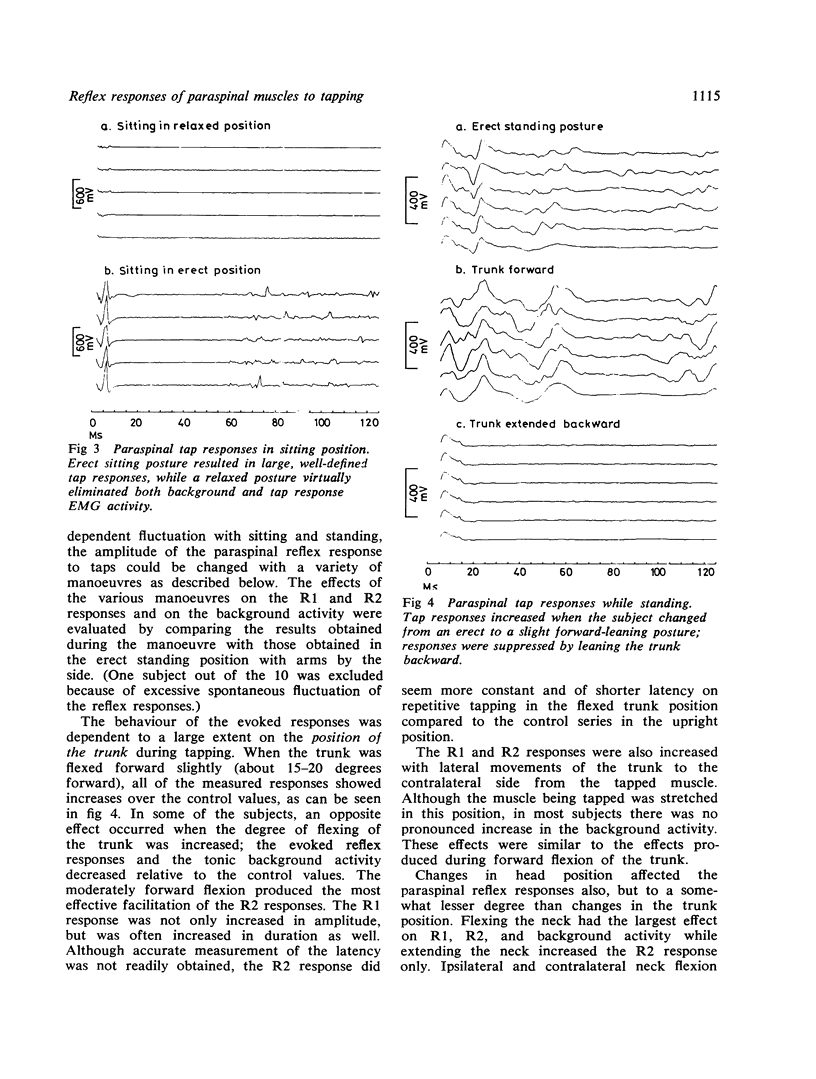
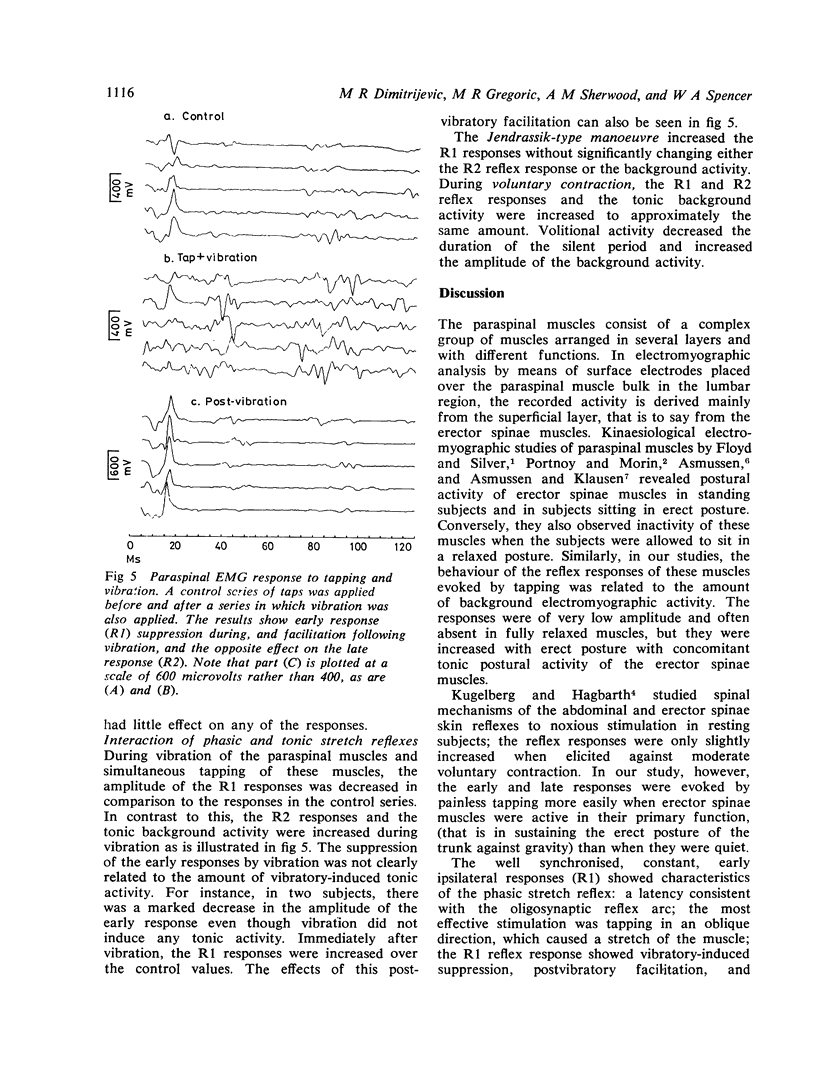
Erector spinae reflex studies in healthy subjects revealed two responses: a 12·0±1·6 ms latency, oligosynaptic response, and a 30 to 50 ms latency response with polysynaptic reflex characteristics. There was a silent period after the first and second responses. The effect of limb position, trunk, neck, postural changes, Jendrassik manoeuvre and vibration on both responses were also evaluated.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASMUSSEN E., KLAUSEN K. Form and function of the erect human spine. Clin Orthop. 1962;25:55–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ASMUSSEN E. The weight-carrying function of the human spine. Acta Orthop Scand. 1960;29:276–290. doi: 10.3109/17453675908988803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delwaide P. J., Figiel C., Richelle C. Effects of postural changes of the upper limb on reflex transmission in the lower limb. Cervicolumbar reflex interactions in man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1977 Jun;40(6):616–621. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.40.6.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmedt J. E., Godaux E. Habituation of exteroceptive suppression and of exteroceptive reflexes in man as influenced by voluntary contraction. Brain Res. 1976 Apr 16;106(1):21–29. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLOYD W. F., SILVER P. H. The function of the erectores spinae muscles in certain movements and postures in man. J Physiol. 1955 Jul 28;129(1):184–203. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRIMBY L. Normal plantar response: integration of flexor and extensor reflex components. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1963 Feb;26:39–50. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.26.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGBARTH K. E., KUGELBERG E. Plasticity of the human abdominal skin reflex. Brain. 1958 Sep;81(3):305–319. doi: 10.1093/brain/81.3.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCE J. W., DEGAIL P. SPREAD OF PHASIC MUSCLE REFLEXES IN NORMAL AND SPASTIC SUBJECTS. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1965 Aug;28:328–334. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.28.4.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORIN F., PORTNOY H. Electromyographic study of postural muscles in various positions and movements. Am J Physiol. 1956 Jul;186(1):122–126. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.186.1.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEDERSEN E. Studies on the central pathway of the flexion reflex in man and animal. Acta Psychiatr Neurol Scand Suppl. 1954;88:1–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trontelj J. V., Pecak F., Dimitrijević M. R. Segmental neurophysiological mechanisms in scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1979 Aug;61-B(3):310–313. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.61B3.479254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



