Abstract
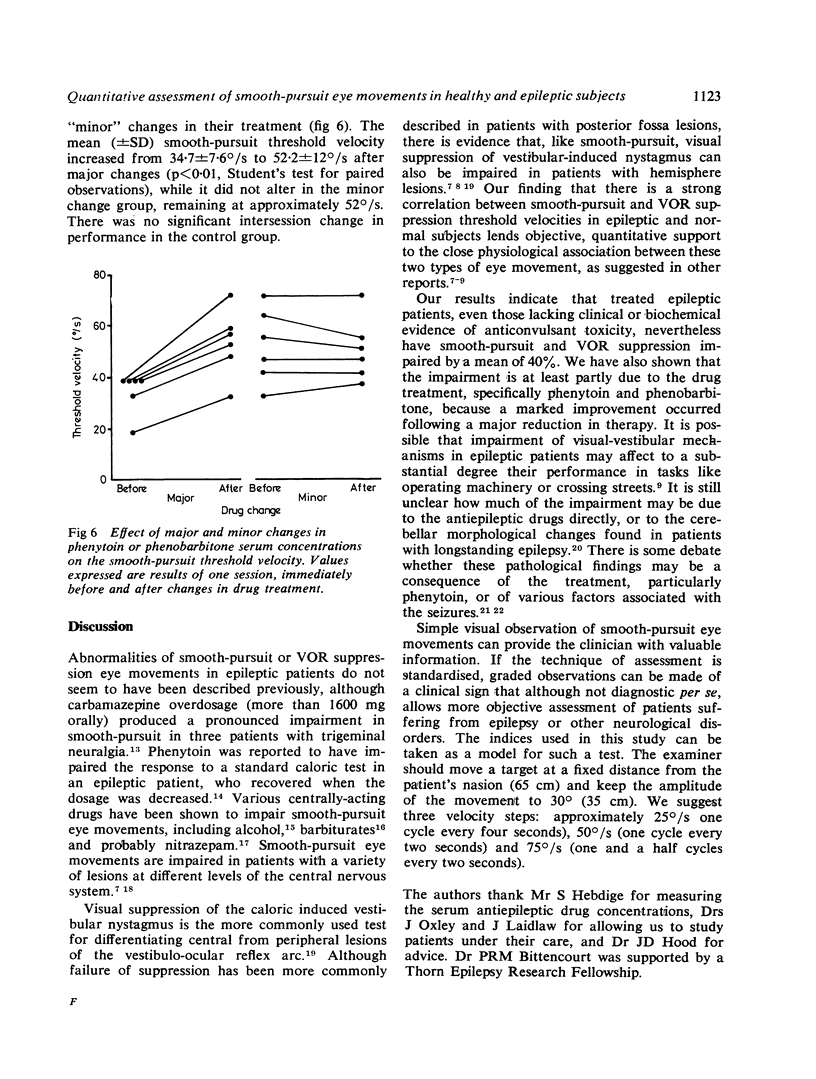
A quantitative electro-oculographic method was used to assess the impairment in smooth-pursuit and vestibulo-ocular reflex suppression eye movements in 12 epileptic patients and eight normal volunteers. Both types of eye movement were impaired by a factor of 40% in the epileptic patients, and the impairment was at least partly due to the treatment with phenytoin and phenobarbitone. There was a strong positive correlation between the performances in vestibulo-ocular reflex suppression and smooth-pursuit.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babin R. W. ENG of the month: Dilantin suppression. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1978 Mar-Apr;87(2 Pt 1):284–285. doi: 10.1177/000348947808700226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baloh R. W., Honrubia V., Sills A. Eye-tracking and optokinetic nystagmus. Results of quantitative testing in patients with well-defined nervous system lesions. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1977 Jan-Feb;86(1 Pt 1):108–114. doi: 10.1177/000348947708600119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baloh R. W., Konrad H. R., Sills A. W., Honrubia V. The saccade velocity test. Neurology. 1975 Nov;25(11):1071–1076. doi: 10.1212/wnl.25.11.1071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baloh R. W., Kumley W. E., Sills A. W., Honrubia V., Konrad H. R. Quantitative measurement of smooth pursuit eye movements. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1976 Jan-Feb;85(1 Pt 1):111–119. doi: 10.1177/000348947608500120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson A. J., Barnes G. R. Vision during angular oscillation: the dynamic interaction of visual and vestibular mechanisms. Aviat Space Environ Med. 1978 Jan;49(1 Pt 2):340–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dichgans J., von Reutern G. M., Römmelt U. Impaired suppression of vestibular nystagmus by fixation in cerebellar and noncerebellar patients. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr (1970) 1978 Dec 14;226(3):183–199. doi: 10.1007/BF00341710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franck M. C., Kuhlo W. Die Wirkung des Alkohols auf die raschen Blickzielbewegungen (Saccaden) beim Menschen. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr (1970) 1970;213(3):238–245. doi: 10.1007/BF00342660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresty M., Leech J. Coordination of the head and eyes in pursuit of predictable and random target motion. Aviat Space Environ Med. 1977 Aug;48(8):741–744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresty M., Trinder E., Leech J. Perception of everyday visual environments during saccadic eye movements. Aviat Space Environ Med. 1976 Sep;47(9):991–992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halmagyi G. M., Gresty M. A. Clinical signs of visual-vestibular interaction. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1979 Oct;42(10):934–939. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.42.10.934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzman P. S., Proctor L. R., Hughes D. W. Eye-tracking patterns in schizophrenia. Science. 1973 Jul 13;181(4095):179–181. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4095.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood J. D., Korres S. Vestibular suppression in peripheral and central vestibular disorders. Brain. 1979 Dec;102(4):785–804. doi: 10.1093/brain/102.4.785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris H. The action of sedatives on brain stem oculomotor systems in man. Neuropharmacology. 1971 Mar;10(21):181–191. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(71)90039-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaa G. L. Acute toxicity of antiepileptic drugs. Epilepsia. 1975 Mar;16(1):183–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1975.tb04734.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RASHBASS C. The relationship between saccadic and smooth tracking eye movements. J Physiol. 1961 Dec;159:326–338. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salcman M., Defendini R., Correll J., Gilman S. Neuropathological changes in cerebellar biopsies of epileptic patients. Ann Neurol. 1978 Jan;3(1):10–19. doi: 10.1002/ana.410030104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shagass C., Roemer R. A., Amadeo M. Eye-tracking performance and engagement of attention. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1976 Jan;33(1):121–125. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1976.01770010077015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimble M. R., Reynolds E. H. Anticonvulsant drugs and mental symptoms: a review. Psychol Med. 1976 May;6(2):169–178. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700013726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umeda Y., Sakata E. Equilibrium disorder in carbamazepine toxicity. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1977 May-Jun;86(3 Pt 1):318–322. doi: 10.1177/000348947708600307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



