Abstract
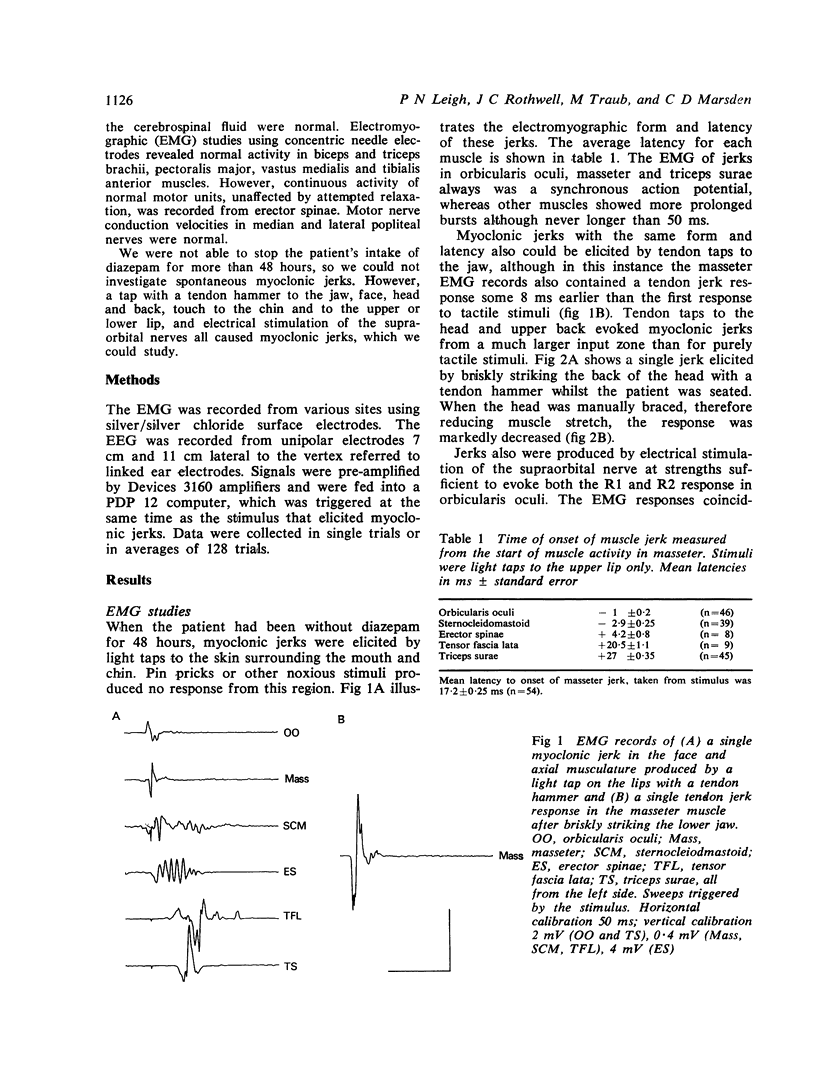
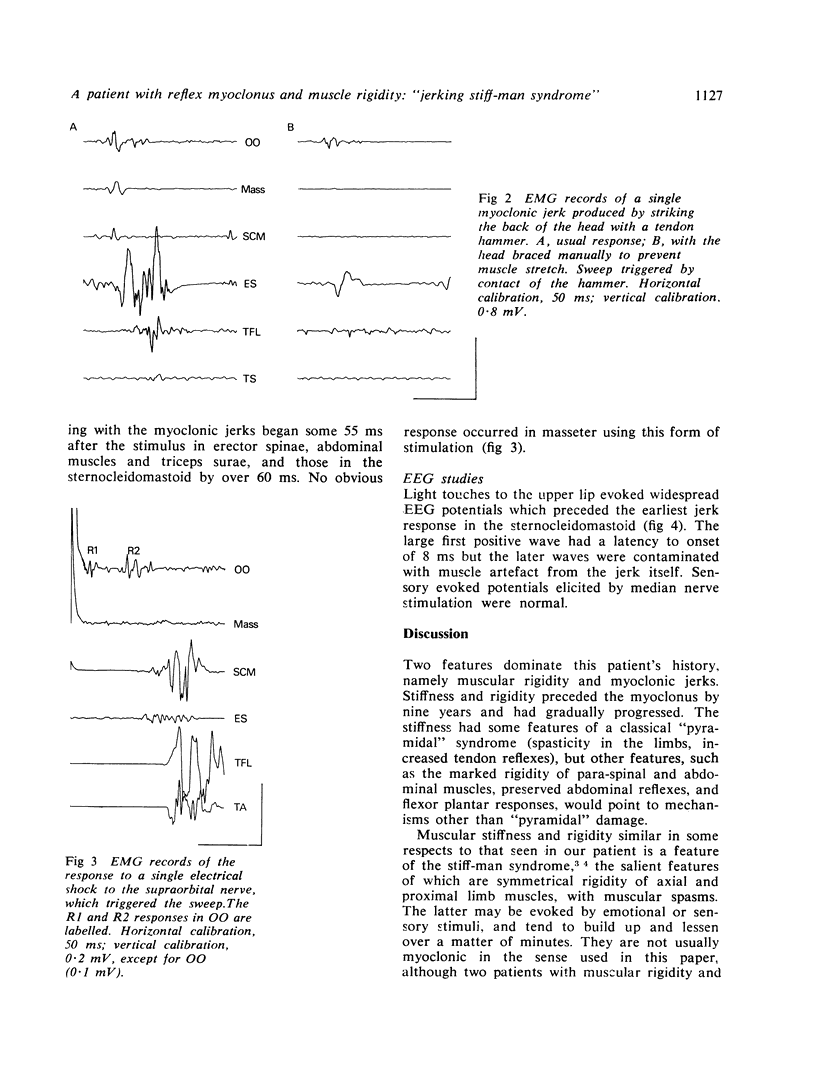
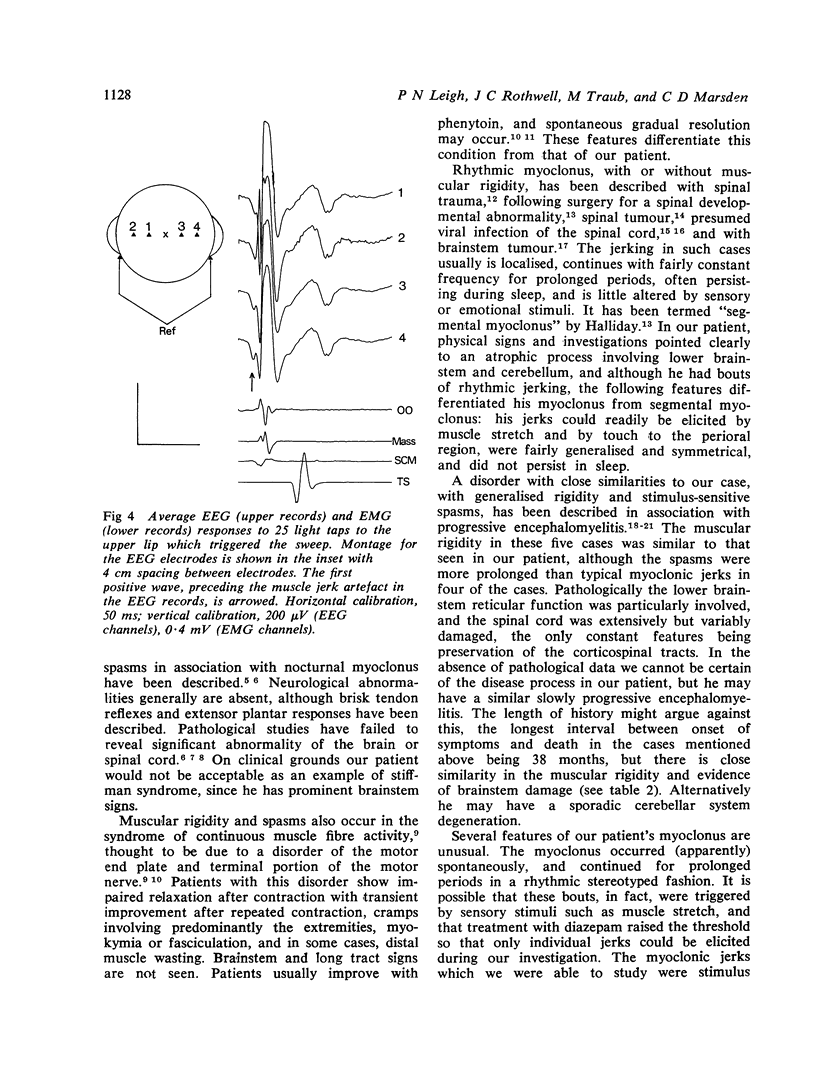
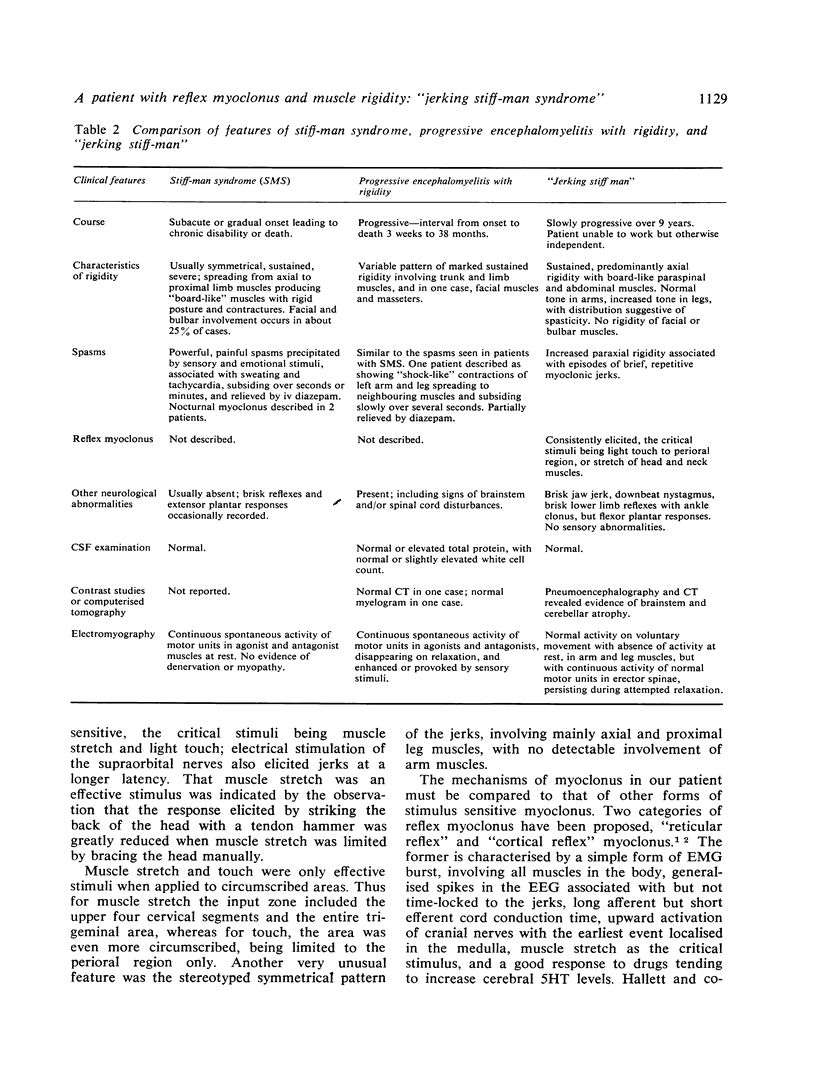
A patient with progressive muscular rigidity associated with reflex myoclonus is described. The muscular rigidity was predominantly axial, and the myoclonic jerks affected axial and leg muscles. Jerks occurred either spontaneously, or in response to touch to the perioral region, or to stretch of head and neck muscles. Physiological investigations suggested that the myoclonus originated in the medulla and was mediated by fast-conducting pathways upwards through the brainstem and down the spinal cord. The relationship of this condition to other types of muscular rigidity with and without myoclonus is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASHER R. A woman with the stiff-man syndrome. Br Med J. 1958 Feb 1;1(5065):265–266. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5065.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avanzini G., Beluffi M., Caraceni T., Leone B. Mioclonie ritmiche scheletriche in corso di neurinoma dell'acustico. Riv Neurobiol. 1968 Oct-Dec;14(4):644–656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL A. M., GARLAND H. Subacute myoclonic spinal neuronitis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1956 Nov;19(4):268–274. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.19.4.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcin R., Rondot P., Guiot G. Rhythmic myoclonus of the right arm as the presenting symptom of a cervical cord tumour. Brain. 1968 Mar;91(1):75–84. doi: 10.1093/brain/91.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon E. E., Januszko D. M., Kaufman L. A critical survey of stiff-man syndrome. Am J Med. 1967 Apr;42(4):582–599. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(67)90057-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilleminault C., Sigwald J., Castaigne P. Sleep studies and therepeutic trial with L-dopa in a case of Stiffman syndrome. Eur Neurol. 1973;10(2):89–96. doi: 10.1159/000114266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallett M., Chadwick D., Adam J., Marsden C. D. Reticular reflex myoclonus: a physiological type of human post-hypoxic myoclonus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1977 Mar;40(3):253–264. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.40.3.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallett M., Chadwick D., Marsden C. D. Cortical reflex myoclonus. Neurology. 1979 Aug;29(8):1107–1125. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.8.1107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell D. A., Lees A. J., Toghill P. J. Spinal internuncial neurones in progressive encephalomyelitis with rigidity. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1979 Sep;42(9):773–785. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.42.9.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs H., Heffron J. J. The syndrome of 'continuous muscle-fibre activity' cured: further studies. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1974 Nov;37(11):1231–1235. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.37.11.1231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasperek S., Zebrowski S. Stiff-man syndrome and encephalomyelitis. Report of a case. Arch Neurol. 1971 Jan;24(1):22–30. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1971.00480310050004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lhermitte F., Chain F., Escourolle R., Chedru F., Guilleminault C., Francoual M. Un nouveau cas de contracture tétaniforme distinct "du stiff man syndrome". Etude pharmacologique et neuropathologique d'un cas d'encéphalomyélite à prédominance médullaire. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1973 Jan;128(1):3–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lütschg J., Jerusalem F., Ludin H. P., Vassella F., Mumenthaler M. The syndrome of 'continuous muscle fiber activity.'. Arch Neurol. 1978 Apr;35(4):198–205. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1978.00500280016003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOERSCH F. P., WOLTMAN H. W. Progressive fluctuating muscular rigidity and spasm ("stiff-man" syndrome); report of a case and some observations in 13 other cases. Proc Staff Meet Mayo Clin. 1956 Jul 25;31(15):421–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinelli P., Pazzaglia P., Montagna P., Coccagna G., Rizzuto N., Simonati S., Lugaresi E. Stiff-man syndrome associated with nocturnal myoclonus and epilepsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1978 May;41(5):458–462. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.41.5.458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedermeyer E., Bauer G., Burnite R., Reichenbach D. Selective stimulus-sensitive myoclonus in acute cerebral anoxia. A case report. Arch Neurol. 1977 Jun;34(6):365–368. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1977.00500180059012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton G. G., Mayer R. F. Focal reflex myoclonus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1974 Feb;37(2):207–217. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.37.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRETHOWAN W. H., ALLSOP J. L., TURNER B. The "stiff-man" syndrome. A report of two further cases. Arch Neurol. 1960 Oct;3:448–456. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1960.00450040098012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteley A. M., Swash M., Urich H. Progressive encephalomyelitis with rigidity. Brain. 1976 Mar;99(1):27–42. doi: 10.1093/brain/99.1.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



