Abstract
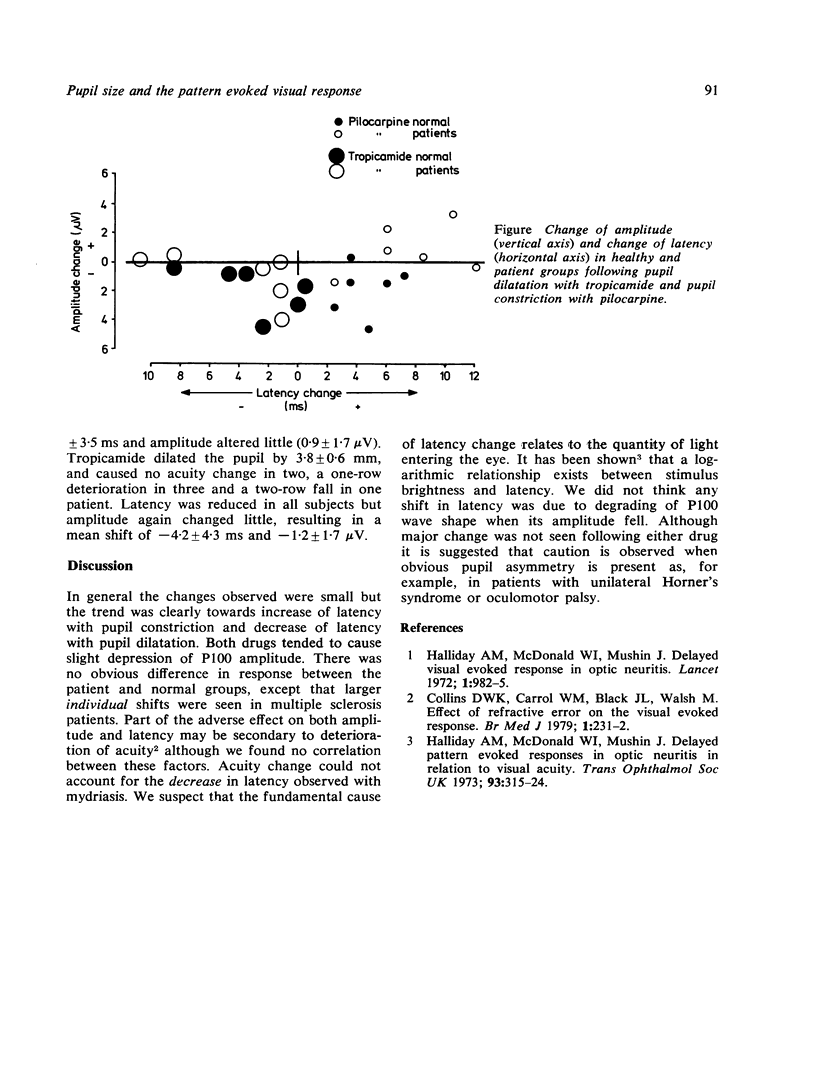
The effect of artificially varying the pupil size upon the pattern evoked visual response was examined in six healthy subjects and six patients with multiple sclerosis who had abnormal visual evoked responses. Slight depression of amplitude was seen whether the pupil was small or large, but the most obvious effect was a reduction of latency with a large pupil and an increase of latency with a small pupil. It is suggested these phenomena relate to the amount of light entering the eye and not any change of acuity.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Collins D. W., Carroll W. M., Black J. L., Walsh M. Effect of refractive error on the visual evoked response. Br Med J. 1979 Jan 27;1(6158):231–232. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6158.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliday A. M., McDonald W. I., Mushin J. Delayed pattern-evoked responses in optic neuritis in relation to visual acuity. Trans Ophthalmol Soc U K. 1973;93(0):315–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliday A. M., McDonald W. I., Mushin J. Delayed visual evoked response in optic neuritis. Lancet. 1972 May 6;1(7758):982–985. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91155-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


