In the title chalcone derivative, molecules are linked into a three-dimensional network by C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and aromatic π–π stacking interactions are also observed. The intermolecular interactions in the crystal structure were quantified and analysed using Hirshfeld surface analysis.
Keywords: crystal structure, chalcone, hydrogen bonding, Hirshfeld surface analysis
Abstract
In the title chalcone derivative, C16H11ClF2O2, the enone group adopts an E conformation. The dihedral angle between the benzene rings is 0.47 (9)° and an intramolecular C—H⋯F hydrogen bond closes an S(6) ring. In the crystal, molecules are linked into a three-dimensional network by C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and aromatic π–π stacking interactions are also observed [centroid–centroid separation = 3.5629 (18) Å]. The intermolecular interactions in the crystal structure were quantified and analysed using Hirshfeld surface analysis.
Chemical context
Chalcone derivatives possess a wide range of biological properties such as antibacterial (Jarag et al., 2011 ▸), anti-inflammatory (Mukherjee et al., 2001 ▸) and anti-oxidant (Arty et al., 2000 ▸) activities. As part of our ongoing studies on chalcone derivatives, we hereby report the synthesis and crystal structure of the title compound, (I).
Structural commentary
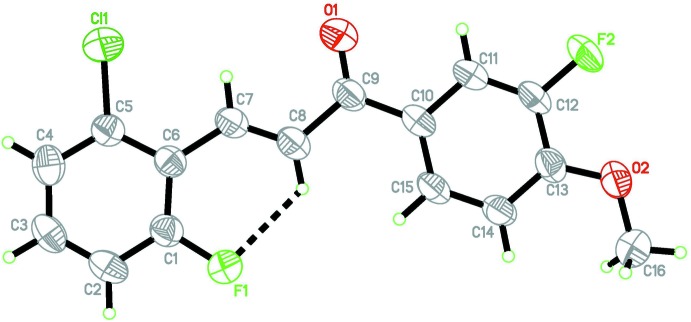
The molecular structure of (I) is shown in Fig. 1 ▸. The enone moiety (O1/C7–C9) adopts an E-conformation with respect to C7=C8 bond. The molecule is slightly twisted at the C9—-C10 bond with a C8—C9—C10—C15 torsion angle of −2.2 (4)° and a maximum deviation of 0.193 (16) Å for atom O1. The dihedral angle between the terminal benzene rings (C1–C6 and C10–C15) is 0.47 (9)°. The least-squares plane through the enone moiety (O1/C7–C9) makes dihedral angles of 2.87 (14) and 3.33 (14)° with the C1–C6 and C10–C15 benzene rings, respectively. An intramolecular C8—H8A⋯F1 hydrogen bond (Table 1 ▸) is observed, generating an S(6) ring motif. The bond lengths and angles are comparable with the equivalent data for previously reported structures; (Razak et al., 2009 ▸; Harrison et al., 2006a ▸).
Figure 1.
The structure of the title compound, showing 50% probability displacement ellipsoids. The intramolecular C—H⋯F hydrogen bond is shown as a dashed line.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2—H2A⋯O1i | 0.93 | 2.50 | 3.391 (4) | 162 |
| C3—H3A⋯O2ii | 0.93 | 2.52 | 3.441 (4) | 171 |
| C8—H8A⋯F1 | 0.93 | 2.21 | 2.842 (4) | 124 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Supramolecular features
In the crystal, molecules are linked into a three-dimensional network via C2—H2A⋯O1 (x −  , −y +
, −y +  , z +
, z +  ) and C3—H3A⋯O2 (x −
) and C3—H3A⋯O2 (x −  , y +
, y +  , z) hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▸), as shown in Fig. 2 ▸. The crystal structure also features π–π interactions [Cg1⋯Cg2 (−1 + x, y, z), centroid-to-centroid distance = 3.5629 (18) Å, where Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the C1–C6 and C10–C15 rings, respectively].
, z) hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▸), as shown in Fig. 2 ▸. The crystal structure also features π–π interactions [Cg1⋯Cg2 (−1 + x, y, z), centroid-to-centroid distance = 3.5629 (18) Å, where Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the C1–C6 and C10–C15 rings, respectively].
Figure 2.
The packing in (I) showing C—H⋯O and π–π interactions as dashed lines.
Analysis of the Hirshfeld Surfaces
Crystal Explorer 3.1(Wolff et al., 2012 ▸) was used to analyse the close contacts in the crystal of (I), which can be summarized with fingerprint plots mapped over d norm, electrostatic potential, shape index and curvedness. The electrostatic potentials were calculated using TONTO (Spackman et al., 2008 ▸; Jayatilaka et al., 2005 ▸) integrated within Crystal Explorer. The electrostatic potentials were mapped on Hirshfeld surfaces using the STO-3G basis set at Hartree–Fock level theory over a range ±0.03 au.
The strong C—H⋯O interactions are visualized as bright-red spots between the respective donor and acceptor atoms on the Hirshfeld surfaces mapped over d norm (Fig. 3 ▸ a) with neighbouring molecules connected by C2—H2A⋯O1 and C3—H3A⋯O2 hydrogen bonds. This finding is corroborated by Hirshfeld surfaces mapped over the electrostatic potential (Fig. 3 ▸ b) showing the negative potential around the oxygen atoms as light-red clouds and the positive potential around hydrogen atoms as light-blue clouds.
Figure 3.
(a) d norm mapped on Hirshfeld surfaces for visualizing the intermolecular interactions of the title chalcone compound. (b) Hirshfeld surfaces mapped over the electrostatic potential. Dotted lines (green) represent hydrogen bonds.
Significant intermolecular interactions are plotted in Fig. 4 ▸: the H⋯H interactions appear as the largest region of the fingerprint plot with a high concentration in the middle region, shown in light blue, at de = di ∼1.4 Å (Fig. 4 ▸ a) with overall Hirshfeld surfaces of 27.5%. The contribution from the O⋯H/H⋯O contacts, corresponding to C—H⋯O interactions, is represented by a pair of sharp spikes characteristic of a strong hydrogen-bond interaction having almost the same de + di ∼2.3 Å (Fig. 4 ▸ b).
Figure 4.

Fingerprint plots for the title chalcone compound, broken down into contributions from specific pairs of atom types. For each plot, the grey shadow is an outline of the complete fingerprint plot. Surfaces to the right highlight the relevant surface patches associated with the specific contacts, with d norm mapped in the same manner as Fig. 3 ▸ a.
The C⋯C contacts, which refer to π–·π stacking interactions, contribute 13.7% of the Hirshfeld surfaces. This appears as a distinct triangle at around de = di ∼1.8 Å (Fig. 4 ▸ c). The presence of the π–π stacking interactions is also indicated by the appearance of red and blue triangles on the shape-indexed surfaces, identified with black arrows in Fig. 5 ▸, and in the flat regions on the Hirshfeld surfaces mapped over curvedness in Fig. 6 ▸.
Figure 5.
Hirshfeld surfaces mapped over the shape index of the title chalcone compound.
Figure 6.
Hirshfeld surfaces mapped over curvedness of the title chalcone compound.
Synthesis and crystallization
A mixture of 3-fluoro-4-methoxyacetophenone (0.1 mol, 0.08 g) and 2-chloro-6-fluorobenzaldehyde (0.1 mol, 0.08 g) was dissolved in methanol (20 ml). A catalytic amount of NaOH (5 ml, 20%) was added to the solution dropwise with vigorous stirring. The reaction mixture was stirred for about 5–6 h at room temperature. After stirring, the contents of the flask were poured into ice-cold water (50 ml) and the resulting crude solid was collected by filtration. Brownish blocks of (I) were grown from an acetone solution by slow evaporation.
Refinement details
Crystal data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. All H atoms were positioned geometrically (C—H = 0.93 Å) and refined using a riding model with U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C). In the final refinement, the most disagreeable reflection (020) was omitted.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C16H11ClF2O2 |
| M r | 308.70 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, C c |
| Temperature (K) | 294 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 9.0832 (13), 11.1072 (13), 13.9564 (17) |
| β (°) | 102.027 (3) |
| V (Å3) | 1377.1 (3) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.30 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.45 × 0.17 × 0.13 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker SMART APEXII CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.791, 0.889 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 14473, 4003, 3111 |
| R int | 0.031 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.705 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.039, 0.116, 1.05 |
| No. of reflections | 4003 |
| No. of parameters | 191 |
| No. of restraints | 2 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.20, −0.27 |
| Absolute structure | Flack x determined using 1298 quotients [(I +)−(I −)]/[(I +)+(I −)] Parsons et al. (2013 ▸) |
| Absolute structure parameter | 0.08 (2) |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016006526/hb7578sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016006526/hb7578Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016006526/hb7578Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1474605
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Malaysian Government and Universiti Sains Malaysia (USM) for the research facilities and Research University Grant No. 1001/PFIZIK/811238 to conduct this work. NCK thanks Malaysian Government for a MyBrain15 (MyPhD) scholarship.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C16H11ClF2O2 | F(000) = 632 |
| Mr = 308.70 | Dx = 1.489 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, Cc | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 9.0832 (13) Å | Cell parameters from 4692 reflections |
| b = 11.1072 (13) Å | θ = 2.9–28.9° |
| c = 13.9564 (17) Å | µ = 0.30 mm−1 |
| β = 102.027 (3)° | T = 294 K |
| V = 1377.1 (3) Å3 | Block, brown |
| Z = 4 | 0.45 × 0.17 × 0.13 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEXII CCD diffractometer | 4003 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3111 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.031 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 30.1°, θmin = 2.9° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009) | h = −12→12 |
| Tmin = 0.791, Tmax = 0.889 | k = −15→15 |
| 14473 measured reflections | l = −19→19 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.039 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0664P)2 + 0.0639P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.116 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.05 | Δρmax = 0.20 e Å−3 |
| 4003 reflections | Δρmin = −0.27 e Å−3 |
| 191 parameters | Absolute structure: Flack x determined using 1298 quotients [(I+)-(I-)]/[(I+)+(I-)] Parsons et al. (2013) |
| 2 restraints | Absolute structure parameter: 0.08 (2) |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.01382 (11) | 0.90043 (10) | 0.28908 (7) | 0.0766 (3) | |
| F1 | 0.2567 (2) | 0.7732 (2) | 0.63725 (14) | 0.0679 (6) | |
| F2 | 1.0123 (2) | 0.5464 (2) | 0.42338 (15) | 0.0676 (5) | |
| O1 | 0.5069 (4) | 0.7363 (3) | 0.3366 (2) | 0.0864 (9) | |
| O2 | 1.0692 (2) | 0.5000 (2) | 0.61111 (18) | 0.0654 (6) | |
| C1 | 0.1380 (3) | 0.8232 (3) | 0.5705 (2) | 0.0473 (6) | |
| C2 | 0.0177 (4) | 0.8618 (3) | 0.6081 (2) | 0.0558 (7) | |
| H2A | 0.0181 | 0.8538 | 0.6745 | 0.067* | |
| C3 | −0.1020 (3) | 0.9121 (3) | 0.5458 (3) | 0.0555 (7) | |
| H3A | −0.1844 | 0.9391 | 0.5698 | 0.067* | |
| C4 | −0.1017 (3) | 0.9231 (3) | 0.4480 (3) | 0.0533 (7) | |
| H4A | −0.1837 | 0.9573 | 0.4057 | 0.064* | |
| C5 | 0.0209 (3) | 0.8832 (2) | 0.4124 (2) | 0.0447 (6) | |
| C6 | 0.1479 (3) | 0.8313 (2) | 0.47289 (19) | 0.0409 (5) | |
| C7 | 0.2772 (3) | 0.7932 (3) | 0.4327 (2) | 0.0480 (6) | |
| H7A | 0.2670 | 0.8034 | 0.3655 | 0.058* | |
| C8 | 0.4052 (4) | 0.7467 (3) | 0.4783 (2) | 0.0527 (6) | |
| H8A | 0.4215 | 0.7321 | 0.5453 | 0.063* | |
| C9 | 0.5248 (3) | 0.7170 (3) | 0.4236 (2) | 0.0501 (6) | |
| C10 | 0.6672 (3) | 0.6632 (2) | 0.4787 (2) | 0.0428 (6) | |
| C11 | 0.7762 (3) | 0.6300 (3) | 0.4255 (2) | 0.0458 (6) | |
| H11A | 0.7598 | 0.6433 | 0.3583 | 0.055* | |
| C12 | 0.9060 (3) | 0.5780 (2) | 0.4739 (2) | 0.0463 (6) | |
| C13 | 0.9367 (3) | 0.5544 (3) | 0.5741 (2) | 0.0478 (6) | |
| C14 | 0.8298 (3) | 0.5889 (3) | 0.6265 (2) | 0.0505 (6) | |
| H14A | 0.8471 | 0.5762 | 0.6938 | 0.061* | |
| C15 | 0.6969 (3) | 0.6426 (3) | 0.5783 (2) | 0.0480 (6) | |
| H15A | 0.6259 | 0.6653 | 0.6142 | 0.058* | |
| C16 | 1.1014 (5) | 0.4726 (5) | 0.7133 (3) | 0.0857 (13) | |
| H16A | 1.1972 | 0.4329 | 0.7304 | 0.129* | |
| H16B | 1.0245 | 0.4206 | 0.7278 | 0.129* | |
| H16C | 1.1041 | 0.5457 | 0.7502 | 0.129* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0769 (5) | 0.1065 (7) | 0.0450 (4) | 0.0182 (5) | 0.0090 (3) | 0.0033 (4) |
| F1 | 0.0590 (11) | 0.0974 (14) | 0.0482 (10) | 0.0220 (9) | 0.0137 (8) | 0.0121 (10) |
| F2 | 0.0564 (9) | 0.0931 (14) | 0.0632 (11) | 0.0103 (9) | 0.0350 (9) | −0.0092 (10) |
| O1 | 0.0880 (18) | 0.125 (2) | 0.0543 (14) | 0.0458 (17) | 0.0320 (13) | 0.0164 (15) |
| O2 | 0.0398 (10) | 0.1009 (18) | 0.0566 (13) | 0.0060 (11) | 0.0124 (9) | −0.0102 (12) |
| C1 | 0.0477 (13) | 0.0491 (14) | 0.0478 (14) | 0.0008 (11) | 0.0161 (11) | 0.0033 (12) |
| C2 | 0.0601 (17) | 0.0623 (17) | 0.0529 (16) | −0.0056 (14) | 0.0297 (14) | −0.0028 (14) |
| C3 | 0.0464 (14) | 0.0587 (16) | 0.0685 (19) | −0.0037 (12) | 0.0281 (13) | −0.0069 (14) |
| C4 | 0.0398 (13) | 0.0518 (15) | 0.068 (2) | −0.0015 (11) | 0.0099 (12) | −0.0036 (14) |
| C5 | 0.0441 (13) | 0.0465 (14) | 0.0436 (13) | −0.0029 (11) | 0.0098 (11) | −0.0027 (10) |
| C6 | 0.0421 (12) | 0.0388 (12) | 0.0435 (13) | −0.0024 (9) | 0.0130 (10) | −0.0011 (10) |
| C7 | 0.0517 (14) | 0.0520 (15) | 0.0441 (14) | 0.0054 (12) | 0.0189 (11) | 0.0010 (11) |
| C8 | 0.0542 (15) | 0.0589 (16) | 0.0501 (15) | 0.0084 (13) | 0.0225 (12) | −0.0005 (13) |
| C9 | 0.0540 (14) | 0.0515 (14) | 0.0510 (15) | 0.0076 (12) | 0.0247 (12) | −0.0003 (12) |
| C10 | 0.0471 (13) | 0.0385 (12) | 0.0490 (14) | −0.0052 (10) | 0.0242 (11) | −0.0053 (10) |
| C11 | 0.0503 (14) | 0.0491 (14) | 0.0437 (13) | −0.0043 (11) | 0.0229 (11) | −0.0057 (11) |
| C12 | 0.0426 (12) | 0.0540 (15) | 0.0491 (14) | −0.0051 (11) | 0.0246 (11) | −0.0112 (12) |
| C13 | 0.0365 (12) | 0.0564 (15) | 0.0527 (15) | −0.0066 (11) | 0.0147 (11) | −0.0110 (12) |
| C14 | 0.0449 (13) | 0.0684 (18) | 0.0418 (14) | −0.0043 (12) | 0.0174 (11) | −0.0068 (13) |
| C15 | 0.0446 (12) | 0.0583 (15) | 0.0473 (14) | −0.0024 (11) | 0.0236 (11) | −0.0070 (12) |
| C16 | 0.0552 (19) | 0.142 (4) | 0.057 (2) | 0.014 (2) | 0.0050 (16) | −0.002 (2) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cl1—C5 | 1.720 (3) | C7—H7A | 0.9300 |
| F1—C1 | 1.386 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.489 (4) |
| F2—C12 | 1.354 (3) | C8—H8A | 0.9300 |
| O1—C9 | 1.209 (4) | C9—C10 | 1.485 (4) |
| O2—C13 | 1.349 (4) | C10—C15 | 1.379 (4) |
| O2—C16 | 1.427 (5) | C10—C11 | 1.405 (3) |
| C1—C2 | 1.376 (4) | C11—C12 | 1.359 (4) |
| C1—C6 | 1.387 (4) | C11—H11A | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.363 (5) | C12—C13 | 1.393 (4) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9300 | C13—C14 | 1.386 (4) |
| C3—C4 | 1.371 (5) | C14—C15 | 1.389 (4) |
| C3—H3A | 0.9300 | C14—H14A | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.383 (4) | C15—H15A | 0.9300 |
| C4—H4A | 0.9300 | C16—H16A | 0.9600 |
| C5—C6 | 1.403 (4) | C16—H16B | 0.9600 |
| C6—C7 | 1.466 (3) | C16—H16C | 0.9600 |
| C7—C8 | 1.309 (4) | ||
| C13—O2—C16 | 117.3 (3) | O1—C9—C8 | 121.0 (3) |
| C2—C1—F1 | 115.9 (3) | C10—C9—C8 | 118.2 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 125.0 (3) | C15—C10—C11 | 118.5 (3) |
| F1—C1—C6 | 119.1 (2) | C15—C10—C9 | 123.7 (2) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 118.4 (3) | C11—C10—C9 | 117.7 (2) |
| C3—C2—H2A | 120.8 | C12—C11—C10 | 118.9 (3) |
| C1—C2—H2A | 120.8 | C12—C11—H11A | 120.6 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.3 (3) | C10—C11—H11A | 120.6 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 119.8 | F2—C12—C11 | 119.4 (3) |
| C4—C3—H3A | 119.8 | F2—C12—C13 | 117.3 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.9 (3) | C11—C12—C13 | 123.3 (2) |
| C3—C4—H4A | 120.1 | O2—C13—C14 | 126.0 (3) |
| C5—C4—H4A | 120.1 | O2—C13—C12 | 116.4 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 122.5 (3) | C14—C13—C12 | 117.6 (3) |
| C4—C5—Cl1 | 117.3 (2) | C13—C14—C15 | 119.8 (3) |
| C6—C5—Cl1 | 120.1 (2) | C13—C14—H14A | 120.1 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 113.8 (2) | C15—C14—H14A | 120.1 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 125.3 (3) | C10—C15—C14 | 121.9 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 120.9 (2) | C10—C15—H15A | 119.1 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 129.1 (3) | C14—C15—H15A | 119.1 |
| C8—C7—H7A | 115.5 | O2—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—H7A | 115.5 | O2—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 120.5 (3) | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—H8A | 119.7 | O2—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8A | 119.7 | H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| O1—C9—C10 | 120.8 (3) | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| F1—C1—C2—C3 | 179.8 (3) | O1—C9—C10—C15 | 177.8 (3) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.1 (5) | C8—C9—C10—C15 | −2.2 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.2 (5) | O1—C9—C10—C11 | −3.2 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.1 (5) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 176.9 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.3 (4) | C15—C10—C11—C12 | 0.5 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—Cl1 | −179.8 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −178.5 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.4 (4) | C10—C11—C12—F2 | −179.6 (2) |
| F1—C1—C6—C5 | 179.9 (2) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.7 (4) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | 178.4 (3) | C16—O2—C13—C14 | 1.7 (5) |
| F1—C1—C6—C7 | −1.3 (4) | C16—O2—C13—C12 | −178.6 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.5 (4) | F2—C12—C13—O2 | −1.1 (4) |
| Cl1—C5—C6—C1 | 180.0 (2) | C11—C12—C13—O2 | 178.6 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −178.3 (3) | F2—C12—C13—C14 | 178.7 (2) |
| Cl1—C5—C6—C7 | 1.2 (3) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −1.7 (4) |
| C1—C6—C7—C8 | −0.7 (5) | O2—C13—C14—C15 | −179.0 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 178.0 (3) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 1.3 (4) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | −178.2 (3) | C11—C10—C15—C14 | −0.9 (4) |
| C7—C8—C9—O1 | 0.8 (5) | C9—C10—C15—C14 | 178.2 (3) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | −179.3 (3) | C13—C14—C15—C10 | −0.1 (4) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C2—H2A···O1i | 0.93 | 2.50 | 3.391 (4) | 162 |
| C3—H3A···O2ii | 0.93 | 2.52 | 3.441 (4) | 171 |
| C8—H8A···F1 | 0.93 | 2.21 | 2.842 (4) | 124 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1/2, −y+3/2, z+1/2; (ii) x−3/2, y+1/2, z.
References
- Arty, I. S., Timmerman, H., Samhoedi, M., Sastrohamidjojo, Sugiyanto & van der Goot, H. (2000). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 35, 449–457. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2009). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Harrison, W. T. A., Yathirajan, H. S., Anilkumar, H. G., Sarojini, B. K. & Narayana, B. (2006a). Acta Cryst. E62, o3251–o3253. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Jarag, K. J., Pinjari, D. V., Pandit, A. B. & Shankarling, G. S. (2011). Ultrason. Sonochem. 18, 617–623. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Jayatilaka, D., Grimwood, D. J., Lee, A., Lemay, A., Russel, A. J., Taylor, C., Wolff, S. K., Cassam-Chenai, P. & Whitton, A. (2005). TONTO. http://hirshfeldsurface.net/
- Mukherjee, S., Kumar, V., Prasad, A. K., Raj, H. G., Bracke, M. E., Olsen, C. E., Jain, S. C. & Parmar, V. S. (2001). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 9, 337–345. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Parsons, S., Flack, H. D. & Wagner, T. (2013). Acta Cryst. B69, 249–259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Razak, I. A., Fun, H.-K., Ngaini, Z., Rahman, N. I. A. & Hussain, H. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o1439–o1440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spackman, M. A., McKinnon, J. J. & Jayatilaka, D. (2008). CrystEngComm, 10, 377–388.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Wolff, S. K., Grimwood, D. J., McKinnon, J. J., Turner, M. J., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2012). Crystal Explorer. University of Western Australia.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016006526/hb7578sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016006526/hb7578Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016006526/hb7578Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1474605
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report