Conditions to obtain two polymorphic forms by crystallization from solution were determined for the analgestic drug hydromorphone. In both polymorphs, the hydromorphone molecules adopt very similar conformations with some small differences observed only in the N-methyl amine part of the molecule. The crystal structures of both polymorphs feature chains of molecules connected by hydrogen bonds
Keywords: crystal structure; polymorphism; hydromorphone,hydrogen bonding
Abstract
Conditions to obtain two polymorphic forms by crystallization from solution were determined for the analgesic drug hydromorphone [C17H19NO3; systematic name: (4R,4aR,7aR,12bS)-9-hydroxy-3-methyl-1,2,4,4a,5,6,7a,13-octahydro-4,12-methanobenzofuro[3,2-e]isoquinolin-7-one]. These two crystalline forms, designated as I and II, belong to the P212121 orthorhombic space group. In both polymorphs, the hydromorphone molecules adopt very similar conformations with some small differences observed only in the N-methyl amine part of the molecule. The crystal structures of both polymorphs feature chains of molecules connected by hydrogen bonds; however, in form I this interaction occurs between the hydroxyl group and the tertiary amine N atom whereas in form II the hydroxyl group acts as a donor of a hydrogen bond to the O atom from the cyclic ether part.
Chemical context
Drug polymorphism has been the subject of hundreds of publications and numerous excellent reviews (Byrn et al., 1999 ▸; Grant, 1999 ▸; Singhal & Curatolo, 2004 ▸; Vippagunta et al., 2001 ▸). It is well established that polymorphs with different stability may have different solubility and dissolution rates, which can affect the bioavailability. The semi-synthetic opiate drug hydromorphone is a potent derivative of morphine and despite poor bioavailability (Parab et al., 1988 ▸) is commonly used to treat moderate to severe pain in the treatment of cancer (Sarhill et al., 2001 ▸). To improve bioavailability of this compound a polymorph screen was performed that resulted in two solvent-free forms, designated as form I and form II.
Structural commentary
The molecular structure of hydromorphone in both polymorphs is nearly identical (Fig. 1 ▸) with some deviations found only for the N-methyl amine part of the piperidine fragment (Fig. 2 ▸). For example the C10—C11—N12—C13 torsion angle is 178.5 (2)° for form I and 169.5 (2)° for form II. The adopted conformation is similar to the conformation observed for morphine (Bye, 1976 ▸; Scheins et al., 2005 ▸).
Figure 1.
Molecular structure and atom-numbering scheme for hydromorphone in the crystals of form I (left) and form II (right). Displacement ellipsoids are shown at the 50% probability level.
Figure 2.
Superposition of the hydromorphone molecules from two polymorphic forms (red form I, blue form II) generated by fitting of the aromatic ring.
Supramolecular features
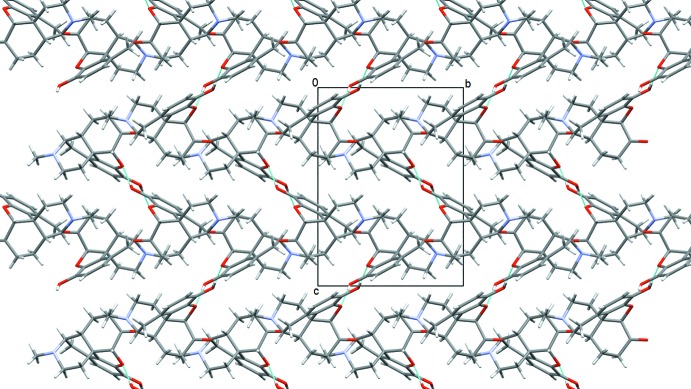
Although both polymorphs crystallize in the same space group P212121 with the same number of molecules in the asymmetric unit, they differ significantly in the packing features (Figs. 3 ▸ and 4 ▸). In form I, the hydrogen-bonded molecules are arranged into chains that run along the a axis with adjacent molecules in the chain related by translation. The hydroxyl group donates a hydrogen atom which is accepted by the free electron pair of the N atom (Fig. 5 ▸, Table 1 ▸). In the crystals of form II, intermolecular hydrogen bonds also generate a chain of molecules that propagates along the a axis; however, adjacent molecules along this chain are related by a 21 symmetry axis. The molecules are connected by O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds with the hydroxyl group as donor and the etheric O atom as acceptor (Table 2 ▸). These chains form a zigzag pattern, as illustrated in Fig. 6 ▸. The packing arrangement of molecules in form II is more dense than in polymorph I, as indicated by the Kitajgorodskij (1973 ▸) packing coefficients of 0.71 and 0.69, respectively.
Figure 3.
Crystal packing diagram of form I, viewed along the a axis. Hydrogen bonds are shown as blue lines.
Figure 4.
Crystal packing diagram of form II, viewed along the a axis. Hydrogen bonds are shown as blue lines.
Figure 5.
The chain of molecules running along the a axis formed by O—H⋯N hydrogen bonds in form I.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (I) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1—H1A⋯N12i | 0.91 (4) | 1.89 (4) | 2.796 (3) | 171 (3) |
Symmetry code: (i) 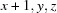 .
.
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (II) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1—H1⋯O4i | 0.84 (3) | 1.96 (3) | 2.791 (2) | 167 (3) |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Figure 6.
The zigzag chain of molecules running along the a axis formed by O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds in form II.
Synthesis and crystallization
10.8 mg of hydromorphone was dissolved in 1.8 mL THF/acetone (1/1, v/v) and left to evaporate slowly under ambient conditions. After several days, colorless prism-like crystals of form I (m.p. 549.8 K) appeared that were used for diffraction studies. Crystals of form II were obtained in the following way: 19.7 mg of hydromorphone was suspended in 0.3 mL of 50/50 mixture of ethanol and toluene. The suspension was heated to 333 K and stirred for about one h until it became clear. Subsequently, the vial was cooled rapidly to 278 K and colorless block-like crystals (m.p. 550.2 K) precipitated that were used for diffraction studies.
Refinement
The H atoms from the methyl group in form II were included from geometry and their isotropic displacement parameters refined. The remaining H atoms were found in a Fourier difference map and freely refined. The absolute configuration of hydromorphone was known from the synthetic route. In the absence of significant anomalous scattering effects, Friedel pairs were merged. Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸.
Table 3. Experimental details.
| (I) | (II) | |
|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | ||
| Chemical formula | C17H19NO3 | C17H19NO3 |
| M r | 285.33 | 285.33 |
| Crystal system, space group | Orthorhombic, P212121 | Orthorhombic, P212121 |
| Temperature (K) | 296 | 296 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 8.9497 (6), 11.0906 (6), 14.2608 (9) | 8.8802 (6), 10.6208 (8), 14.4733 (9) |
| V (Å3) | 1415.49 (15) | 1365.05 (16) |
| Z | 4 | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.09 | 0.10 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.35 × 0.35 × 0.30 | 0.40 × 0.32 × 0.22 |
| Data collection | ||
| Diffractometer | Bruker KappaCCD | Bruker KappaCCD |
| Absorption correction | – | – |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 7054, 3427, 3088 | 15227, 4920, 4693 |
| R int | 0.031 | 0.022 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.671 | 0.758 |
| Refinement | ||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.042, 0.096, 1.05 | 0.033, 0.095, 1.07 |
| No. of reflections | 3427 | 4920 |
| No. of parameters | 266 | 257 |
| H-atom treatment | All H-atom parameters refined | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.19, −0.17 | 0.27, −0.12 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016006563/gk2659sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016006563/gk2659Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016006563/gk2659Isup4.mol
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016006563/gk2659IIsup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016006563/gk2659IIsup5.mol
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
supplementary crystallographic information
(I) (4R,4aR,7aR,12bS)-9-Hydroxy-3-methyl-1,2,4,4a,5,6,7a,13-octahydro-4,12-methanobenzofuro[3,2-e]isoquinolin-7-one] . Crystal data
| C17H19NO3 | Dx = 1.339 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 285.33 | Melting point < 549.8 K |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 8.9497 (6) Å | Cell parameters from 9169 reflections |
| b = 11.0906 (6) Å | θ = 1.0–32.6° |
| c = 14.2608 (9) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| V = 1415.49 (15) Å3 | T = 296 K |
| Z = 4 | Prism, colorless |
| F(000) = 608 | 0.35 × 0.35 × 0.30 mm |
(I) (4R,4aR,7aR,12bS)-9-Hydroxy-3-methyl-1,2,4,4a,5,6,7a,13-octahydro-4,12-methanobenzofuro[3,2-e]isoquinolin-7-one] . Data collection
| Bruker KappaCCD diffractometer | 3088 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.031 |
| Horizonally mounted graphite crystal monochromator | θmax = 28.5°, θmin = 3.4° |
| CCD scans | h = −11→11 |
| 7054 measured reflections | k = −11→14 |
| 3427 independent reflections | l = −17→19 |
(I) (4R,4aR,7aR,12bS)-9-Hydroxy-3-methyl-1,2,4,4a,5,6,7a,13-octahydro-4,12-methanobenzofuro[3,2-e]isoquinolin-7-one] . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.042 | Hydrogen site location: difference Fourier map |
| wR(F2) = 0.096 | All H-atom parameters refined |
| S = 1.05 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0361P)2 + 0.2726P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3427 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.005 |
| 266 parameters | Δρmax = 0.19 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.17 e Å−3 |
(I) (4R,4aR,7aR,12bS)-9-Hydroxy-3-methyl-1,2,4,4a,5,6,7a,13-octahydro-4,12-methanobenzofuro[3,2-e]isoquinolin-7-one] . Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
(I) (4R,4aR,7aR,12bS)-9-Hydroxy-3-methyl-1,2,4,4a,5,6,7a,13-octahydro-4,12-methanobenzofuro[3,2-e]isoquinolin-7-one] . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.91711 (18) | 0.7664 (2) | 0.17051 (12) | 0.0513 (5) | |
| H1A | 0.993 (4) | 0.774 (3) | 0.213 (2) | 0.069 (10)* | |
| C2 | 0.7893 (2) | 0.7337 (2) | 0.21531 (15) | 0.0337 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.6543 (2) | 0.73164 (19) | 0.16755 (13) | 0.0318 (4) | |
| O4 | 0.63079 (17) | 0.74990 (16) | 0.07223 (10) | 0.0409 (4) | |
| C5 | 0.4813 (3) | 0.7006 (2) | 0.05538 (15) | 0.0369 (5) | |
| H5A | 0.439 (3) | 0.745 (2) | 0.0007 (18) | 0.034 (6)* | |
| C6 | 0.4906 (3) | 0.5664 (3) | 0.03355 (16) | 0.0455 (6) | |
| O7 | 0.6063 (3) | 0.5185 (2) | 0.00966 (16) | 0.0692 (6) | |
| C8 | 0.3484 (4) | 0.4980 (3) | 0.0485 (2) | 0.0555 (7) | |
| H8A | 0.362 (4) | 0.413 (3) | 0.031 (2) | 0.073 (10)* | |
| H8B | 0.271 (4) | 0.541 (3) | 0.006 (2) | 0.063 (9)* | |
| C9 | 0.3038 (3) | 0.5078 (2) | 0.1523 (2) | 0.0464 (6) | |
| H9A | 0.387 (4) | 0.480 (3) | 0.193 (2) | 0.057 (8)* | |
| H9B | 0.220 (3) | 0.455 (3) | 0.166 (2) | 0.055 (8)* | |
| C10 | 0.2671 (2) | 0.6384 (2) | 0.17446 (16) | 0.0334 (4) | |
| H10A | 0.175 (3) | 0.660 (2) | 0.1390 (16) | 0.034 (6)* | |
| C11 | 0.2315 (2) | 0.6636 (2) | 0.27875 (16) | 0.0365 (5) | |
| H11A | 0.147 (3) | 0.610 (2) | 0.2993 (18) | 0.043 (7)* | |
| N12 | 0.1698 (2) | 0.78799 (19) | 0.28457 (13) | 0.0381 (4) | |
| C13 | 0.1274 (3) | 0.8219 (3) | 0.3807 (2) | 0.0555 (7) | |
| H13A | 0.072 (4) | 0.750 (3) | 0.410 (2) | 0.068 (9)* | |
| H13B | 0.216 (4) | 0.844 (3) | 0.417 (2) | 0.054 (8)* | |
| H13C | 0.060 (4) | 0.893 (3) | 0.373 (2) | 0.073 (10)* | |
| C14 | 0.2738 (3) | 0.8808 (2) | 0.24843 (19) | 0.0426 (6) | |
| H14A | 0.221 (3) | 0.956 (3) | 0.251 (2) | 0.051 (8)* | |
| H14B | 0.359 (3) | 0.888 (2) | 0.291 (2) | 0.046 (7)* | |
| C15 | 0.3324 (3) | 0.8528 (2) | 0.15154 (17) | 0.0377 (5) | |
| H15A | 0.251 (3) | 0.862 (3) | 0.105 (2) | 0.048 (7)* | |
| H15B | 0.414 (3) | 0.912 (2) | 0.1341 (18) | 0.043 (7)* | |
| C16 | 0.3942 (2) | 0.72389 (19) | 0.14723 (13) | 0.0291 (4) | |
| C17 | 0.5225 (2) | 0.70844 (19) | 0.21381 (14) | 0.0289 (4) | |
| C18 | 0.5145 (2) | 0.6740 (2) | 0.30675 (14) | 0.0315 (4) | |
| C19 | 0.3642 (2) | 0.6356 (3) | 0.34492 (17) | 0.0417 (5) | |
| H19A | 0.364 (3) | 0.548 (3) | 0.356 (2) | 0.058 (9)* | |
| H19B | 0.341 (3) | 0.672 (3) | 0.406 (2) | 0.058 (8)* | |
| C20 | 0.6499 (2) | 0.6686 (2) | 0.35428 (14) | 0.0335 (4) | |
| H20A | 0.655 (3) | 0.640 (2) | 0.4198 (18) | 0.039 (6)* | |
| C21 | 0.7821 (2) | 0.6994 (2) | 0.30952 (15) | 0.0350 (5) | |
| H21A | 0.871 (3) | 0.693 (2) | 0.3430 (17) | 0.038 (6)* |
(I) (4R,4aR,7aR,12bS)-9-Hydroxy-3-methyl-1,2,4,4a,5,6,7a,13-octahydro-4,12-methanobenzofuro[3,2-e]isoquinolin-7-one] . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0239 (8) | 0.0907 (15) | 0.0393 (9) | −0.0080 (8) | 0.0014 (7) | 0.0059 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0235 (9) | 0.0427 (12) | 0.0349 (10) | 0.0002 (9) | 0.0009 (8) | −0.0005 (9) |
| C3 | 0.0293 (10) | 0.0393 (11) | 0.0269 (9) | −0.0021 (8) | 0.0004 (8) | 0.0035 (8) |
| O4 | 0.0315 (8) | 0.0656 (11) | 0.0256 (7) | −0.0051 (7) | 0.0000 (6) | 0.0068 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0321 (10) | 0.0511 (13) | 0.0276 (9) | −0.0006 (10) | −0.0047 (9) | 0.0035 (9) |
| C6 | 0.0490 (14) | 0.0573 (15) | 0.0301 (10) | 0.0061 (12) | −0.0004 (11) | −0.0045 (10) |
| O7 | 0.0662 (14) | 0.0728 (14) | 0.0687 (14) | 0.0171 (11) | 0.0256 (11) | −0.0007 (11) |
| C8 | 0.0547 (16) | 0.0505 (16) | 0.0615 (17) | −0.0015 (14) | −0.0071 (14) | −0.0212 (14) |
| C9 | 0.0390 (13) | 0.0362 (12) | 0.0640 (16) | −0.0067 (10) | −0.0001 (12) | −0.0024 (11) |
| C10 | 0.0262 (9) | 0.0360 (11) | 0.0380 (11) | −0.0030 (8) | −0.0044 (9) | 0.0015 (9) |
| C11 | 0.0257 (10) | 0.0438 (12) | 0.0398 (11) | −0.0059 (9) | 0.0004 (9) | 0.0046 (10) |
| N12 | 0.0266 (8) | 0.0487 (11) | 0.0389 (9) | −0.0015 (8) | 0.0005 (8) | −0.0058 (8) |
| C13 | 0.0374 (13) | 0.084 (2) | 0.0448 (14) | −0.0071 (15) | 0.0034 (12) | −0.0195 (14) |
| C14 | 0.0357 (12) | 0.0383 (13) | 0.0536 (14) | 0.0002 (10) | 0.0000 (11) | −0.0055 (10) |
| C15 | 0.0339 (11) | 0.0353 (11) | 0.0438 (12) | 0.0003 (9) | −0.0037 (10) | 0.0064 (9) |
| C16 | 0.0257 (9) | 0.0340 (10) | 0.0275 (9) | −0.0015 (8) | −0.0034 (8) | 0.0024 (8) |
| C17 | 0.0247 (9) | 0.0340 (10) | 0.0281 (9) | −0.0015 (8) | −0.0033 (8) | 0.0024 (8) |
| C18 | 0.0281 (9) | 0.0391 (11) | 0.0274 (9) | −0.0019 (8) | 0.0000 (8) | 0.0040 (8) |
| C19 | 0.0291 (11) | 0.0599 (15) | 0.0363 (12) | −0.0029 (10) | 0.0027 (10) | 0.0144 (11) |
| C20 | 0.0335 (11) | 0.0414 (11) | 0.0256 (9) | −0.0002 (9) | −0.0037 (8) | 0.0035 (8) |
| C21 | 0.0260 (9) | 0.0441 (12) | 0.0350 (10) | −0.0003 (9) | −0.0074 (9) | −0.0006 (9) |
(I) (4R,4aR,7aR,12bS)-9-Hydroxy-3-methyl-1,2,4,4a,5,6,7a,13-octahydro-4,12-methanobenzofuro[3,2-e]isoquinolin-7-one] . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C2 | 1.360 (3) | C11—C19 | 1.548 (3) |
| O1—H1A | 0.91 (4) | C11—H11A | 1.01 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.387 (3) | N12—C13 | 1.472 (3) |
| C2—C21 | 1.398 (3) | N12—C14 | 1.480 (3) |
| C3—C17 | 1.376 (3) | C13—H13A | 1.03 (4) |
| C3—O4 | 1.390 (2) | C13—H13B | 0.98 (3) |
| O4—C5 | 1.465 (3) | C13—H13C | 1.00 (4) |
| C5—C6 | 1.523 (4) | C14—C15 | 1.510 (3) |
| C5—C16 | 1.546 (3) | C14—H14A | 0.96 (3) |
| C5—H5A | 1.00 (3) | C14—H14B | 0.98 (3) |
| C6—O7 | 1.212 (3) | C15—C16 | 1.534 (3) |
| C6—C8 | 1.498 (4) | C15—H15A | 0.99 (3) |
| C8—C9 | 1.537 (4) | C15—H15B | 1.01 (3) |
| C8—H8A | 0.99 (3) | C16—C17 | 1.500 (3) |
| C8—H8B | 1.03 (3) | C17—C18 | 1.381 (3) |
| C9—C10 | 1.519 (3) | C18—C20 | 1.390 (3) |
| C9—H9A | 1.00 (3) | C18—C19 | 1.512 (3) |
| C9—H9B | 0.97 (3) | C19—H19A | 0.99 (3) |
| C10—C16 | 1.531 (3) | C19—H19B | 0.98 (3) |
| C10—C11 | 1.546 (3) | C20—C21 | 1.387 (3) |
| C10—H10A | 1.00 (2) | C20—H20A | 0.99 (3) |
| C11—N12 | 1.488 (3) | C21—H21A | 0.93 (3) |
| C2—O1—H1A | 110 (2) | C14—N12—C11 | 113.08 (18) |
| O1—C2—C3 | 120.43 (18) | N12—C13—H13A | 108.1 (19) |
| O1—C2—C21 | 124.26 (19) | N12—C13—H13B | 110.6 (17) |
| C3—C2—C21 | 115.31 (18) | H13A—C13—H13B | 111 (3) |
| C17—C3—C2 | 120.96 (17) | N12—C13—H13C | 105 (2) |
| C17—C3—O4 | 111.48 (17) | H13A—C13—H13C | 111 (3) |
| C2—C3—O4 | 127.56 (18) | H13B—C13—H13C | 110 (3) |
| C3—O4—C5 | 104.13 (15) | N12—C14—C15 | 113.2 (2) |
| O4—C5—C6 | 110.4 (2) | N12—C14—H14A | 106.6 (17) |
| O4—C5—C16 | 105.03 (16) | C15—C14—H14A | 112.8 (17) |
| C6—C5—C16 | 111.35 (19) | N12—C14—H14B | 109.2 (16) |
| O4—C5—H5A | 106.7 (14) | C15—C14—H14B | 108.4 (16) |
| C6—C5—H5A | 110.2 (14) | H14A—C14—H14B | 106 (2) |
| C16—C5—H5A | 113.0 (14) | C14—C15—C16 | 110.72 (18) |
| O7—C6—C8 | 122.9 (3) | C14—C15—H15A | 109.5 (16) |
| O7—C6—C5 | 122.2 (3) | C16—C15—H15A | 109.6 (17) |
| C8—C6—C5 | 114.8 (2) | C14—C15—H15B | 110.0 (15) |
| C6—C8—C9 | 108.8 (2) | C16—C15—H15B | 109.6 (15) |
| C6—C8—H8A | 110 (2) | H15A—C15—H15B | 107 (2) |
| C9—C8—H8A | 110 (2) | C17—C16—C10 | 109.73 (16) |
| C6—C8—H8B | 104.6 (18) | C17—C16—C15 | 110.92 (17) |
| C9—C8—H8B | 110.7 (18) | C10—C16—C15 | 107.40 (17) |
| H8A—C8—H8B | 112 (3) | C17—C16—C5 | 97.53 (16) |
| C10—C9—C8 | 108.9 (2) | C10—C16—C5 | 119.10 (18) |
| C10—C9—H9A | 109.6 (18) | C15—C16—C5 | 111.80 (17) |
| C8—C9—H9A | 110.5 (18) | C3—C17—C18 | 123.80 (18) |
| C10—C9—H9B | 111.4 (18) | C3—C17—C16 | 109.37 (17) |
| C8—C9—H9B | 110.3 (18) | C18—C17—C16 | 126.82 (18) |
| H9A—C9—H9B | 106 (2) | C17—C18—C20 | 115.76 (18) |
| C9—C10—C16 | 112.16 (19) | C17—C18—C19 | 118.01 (18) |
| C9—C10—C11 | 114.6 (2) | C20—C18—C19 | 125.99 (18) |
| C16—C10—C11 | 106.56 (17) | C18—C19—C11 | 113.97 (18) |
| C9—C10—H10A | 107.5 (14) | C18—C19—H19A | 109.8 (18) |
| C16—C10—H10A | 109.8 (14) | C11—C19—H19A | 107.0 (18) |
| C11—C10—H10A | 106.0 (14) | C18—C19—H19B | 113.1 (19) |
| N12—C11—C10 | 107.31 (18) | C11—C19—H19B | 107.2 (18) |
| N12—C11—C19 | 115.9 (2) | H19A—C19—H19B | 105 (2) |
| C10—C11—C19 | 113.08 (19) | C21—C20—C18 | 120.57 (18) |
| N12—C11—H11A | 104.9 (15) | C21—C20—H20A | 118.2 (16) |
| C10—C11—H11A | 109.1 (15) | C18—C20—H20A | 121.2 (16) |
| C19—C11—H11A | 106.1 (15) | C20—C21—C2 | 123.27 (19) |
| C13—N12—C14 | 108.0 (2) | C20—C21—H21A | 118.1 (15) |
| C13—N12—C11 | 112.6 (2) | C2—C21—H21A | 118.5 (15) |
| C10—C11—N12—C13 | 178.5 (2) |
(I) (4R,4aR,7aR,12bS)-9-Hydroxy-3-methyl-1,2,4,4a,5,6,7a,13-octahydro-4,12-methanobenzofuro[3,2-e]isoquinolin-7-one] . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1A···N12i | 0.91 (4) | 1.89 (4) | 2.796 (3) | 171 (3) |
Symmetry code: (i) x+1, y, z.
(II) (4R,4aR,7aR,12bS)-9-hydroxy-3-methyl-1,2,4,4a,5,6,7a,13-octahydro-4,12-methanobenzofuro[3,2-e]isoquinoline-7-one. Crystal data
| C17H19NO3 | Dx = 1.388 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 285.33 | Melting point < 550.2 K |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 8.8802 (6) Å | Cell parameters from 7368 reflections |
| b = 10.6208 (8) Å | θ = 0.4–32.6° |
| c = 14.4733 (9) Å | µ = 0.10 mm−1 |
| V = 1365.05 (16) Å3 | T = 296 K |
| Z = 4 | Block, colorless |
| F(000) = 608 | 0.40 × 0.32 × 0.22 mm |
(II) (4R,4aR,7aR,12bS)-9-hydroxy-3-methyl-1,2,4,4a,5,6,7a,13-octahydro-4,12-methanobenzofuro[3,2-e]isoquinoline-7-one. Data collection
| Bruker KappaCCD diffractometer | 4693 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.022 |
| Horizonally mounted graphite crystal monochromator | θmax = 32.6°, θmin = 3.8° |
| CCD scans | h = −13→13 |
| 15227 measured reflections | k = −16→16 |
| 4920 independent reflections | l = −21→16 |
(II) (4R,4aR,7aR,12bS)-9-hydroxy-3-methyl-1,2,4,4a,5,6,7a,13-octahydro-4,12-methanobenzofuro[3,2-e]isoquinoline-7-one. Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.033 | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| wR(F2) = 0.095 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.07 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0623P)2 + 0.0509P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4920 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.011 |
| 257 parameters | Δρmax = 0.27 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.12 e Å−3 |
(II) (4R,4aR,7aR,12bS)-9-hydroxy-3-methyl-1,2,4,4a,5,6,7a,13-octahydro-4,12-methanobenzofuro[3,2-e]isoquinoline-7-one. Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
(II) (4R,4aR,7aR,12bS)-9-hydroxy-3-methyl-1,2,4,4a,5,6,7a,13-octahydro-4,12-methanobenzofuro[3,2-e]isoquinoline-7-one. Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.93240 (13) | 0.77706 (10) | 0.49050 (9) | 0.0470 (3) | |
| H1 | 1.015 (3) | 0.792 (2) | 0.517 (2) | 0.069 (8)* | |
| C2 | 0.94522 (14) | 0.66225 (11) | 0.44868 (8) | 0.0314 (2) | |
| C3 | 0.82077 (12) | 0.60798 (11) | 0.40680 (7) | 0.02819 (19) | |
| O4 | 0.67658 (10) | 0.65856 (9) | 0.39772 (7) | 0.03425 (18) | |
| C5 | 0.60923 (12) | 0.58599 (11) | 0.32226 (8) | 0.0299 (2) | |
| H5 | 0.500 (2) | 0.586 (2) | 0.3283 (14) | 0.039 (4)* | |
| C6 | 0.64963 (14) | 0.64991 (13) | 0.23020 (10) | 0.0362 (2) | |
| O7 | 0.68419 (15) | 0.76008 (11) | 0.22794 (10) | 0.0516 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.6488 (2) | 0.56607 (16) | 0.14696 (10) | 0.0455 (3) | |
| H8A | 0.549 (3) | 0.528 (2) | 0.1420 (15) | 0.048 (5)* | |
| H8B | 0.681 (3) | 0.615 (2) | 0.0937 (18) | 0.058 (6)* | |
| C9 | 0.75507 (16) | 0.45421 (14) | 0.16230 (8) | 0.0366 (3) | |
| H9A | 0.856 (2) | 0.486 (2) | 0.1784 (15) | 0.048 (5)* | |
| H9B | 0.759 (3) | 0.396 (3) | 0.1098 (19) | 0.065 (7)* | |
| C10 | 0.69690 (13) | 0.37489 (11) | 0.24255 (7) | 0.0289 (2) | |
| H10 | 0.601 (2) | 0.3431 (18) | 0.2251 (13) | 0.035 (4)* | |
| C11 | 0.79909 (14) | 0.26306 (11) | 0.26841 (8) | 0.0322 (2) | |
| H11 | 0.810 (2) | 0.2131 (17) | 0.2157 (12) | 0.033 (4)* | |
| N12 | 0.71416 (14) | 0.18458 (10) | 0.33458 (8) | 0.0359 (2) | |
| C13 | 0.7868 (2) | 0.06280 (15) | 0.35203 (14) | 0.0513 (4) | |
| H13A | 0.8072 | 0.0217 | 0.2943 | 0.075 (8)* | |
| H13B | 0.8796 | 0.0760 | 0.3847 | 0.090 (9)* | |
| H13C | 0.7212 | 0.0110 | 0.3885 | 0.081 (8)* | |
| C14 | 0.68139 (17) | 0.24994 (12) | 0.42125 (9) | 0.0367 (2) | |
| H14A | 0.617 (3) | 0.1946 (18) | 0.4586 (14) | 0.044 (5)* | |
| H14B | 0.769 (3) | 0.2710 (19) | 0.4580 (15) | 0.046 (5)* | |
| C15 | 0.59734 (14) | 0.37270 (12) | 0.40416 (8) | 0.0323 (2) | |
| H15A | 0.496 (2) | 0.3593 (17) | 0.3840 (13) | 0.034 (4)* | |
| H15B | 0.592 (2) | 0.4201 (18) | 0.4616 (15) | 0.044 (5)* | |
| C16 | 0.67804 (11) | 0.45335 (10) | 0.33092 (7) | 0.02580 (18) | |
| C17 | 0.83077 (12) | 0.49110 (10) | 0.36541 (7) | 0.02626 (19) | |
| C18 | 0.96269 (12) | 0.42399 (11) | 0.35670 (8) | 0.02859 (19) | |
| C19 | 0.95925 (15) | 0.30434 (12) | 0.30011 (10) | 0.0356 (2) | |
| H19A | 1.020 (3) | 0.318 (2) | 0.2452 (17) | 0.055 (6)* | |
| H19B | 1.006 (3) | 0.233 (3) | 0.3363 (19) | 0.071 (7)* | |
| C20 | 1.09004 (13) | 0.47869 (12) | 0.39737 (8) | 0.0325 (2) | |
| H20 | 1.191 (2) | 0.4392 (19) | 0.3896 (13) | 0.039 (4)* | |
| C21 | 1.07953 (14) | 0.59403 (12) | 0.44358 (8) | 0.0334 (2) | |
| H21 | 1.170 (2) | 0.6333 (17) | 0.4688 (15) | 0.043 (5)* |
(II) (4R,4aR,7aR,12bS)-9-hydroxy-3-methyl-1,2,4,4a,5,6,7a,13-octahydro-4,12-methanobenzofuro[3,2-e]isoquinoline-7-one. Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0399 (5) | 0.0442 (5) | 0.0569 (6) | −0.0038 (4) | −0.0079 (5) | −0.0219 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0304 (5) | 0.0351 (5) | 0.0289 (5) | −0.0049 (4) | −0.0020 (4) | −0.0040 (4) |
| C3 | 0.0249 (4) | 0.0316 (5) | 0.0281 (4) | −0.0005 (4) | 0.0002 (4) | −0.0050 (4) |
| O4 | 0.0277 (4) | 0.0350 (4) | 0.0400 (4) | 0.0037 (3) | −0.0007 (3) | −0.0119 (3) |
| C5 | 0.0232 (4) | 0.0327 (5) | 0.0337 (5) | 0.0021 (3) | −0.0005 (4) | −0.0050 (4) |
| C6 | 0.0263 (5) | 0.0402 (6) | 0.0421 (6) | 0.0046 (4) | −0.0030 (4) | 0.0064 (5) |
| O7 | 0.0452 (6) | 0.0432 (6) | 0.0663 (7) | −0.0039 (5) | −0.0079 (5) | 0.0138 (5) |
| C8 | 0.0511 (8) | 0.0538 (8) | 0.0316 (5) | 0.0087 (7) | −0.0034 (5) | 0.0080 (5) |
| C9 | 0.0400 (6) | 0.0445 (6) | 0.0254 (4) | 0.0030 (5) | 0.0035 (4) | −0.0002 (4) |
| C10 | 0.0285 (5) | 0.0334 (5) | 0.0248 (4) | −0.0008 (4) | 0.0007 (3) | −0.0048 (3) |
| C11 | 0.0352 (5) | 0.0305 (5) | 0.0310 (5) | 0.0001 (4) | 0.0044 (4) | −0.0064 (4) |
| N12 | 0.0415 (6) | 0.0285 (4) | 0.0378 (5) | −0.0021 (4) | 0.0036 (4) | −0.0025 (4) |
| C13 | 0.0601 (10) | 0.0338 (6) | 0.0602 (9) | 0.0061 (6) | 0.0052 (7) | 0.0034 (6) |
| C14 | 0.0438 (6) | 0.0357 (6) | 0.0306 (5) | −0.0041 (5) | 0.0038 (5) | 0.0024 (4) |
| C15 | 0.0314 (5) | 0.0369 (5) | 0.0285 (4) | −0.0044 (4) | 0.0065 (4) | −0.0038 (4) |
| C16 | 0.0228 (4) | 0.0295 (4) | 0.0251 (4) | −0.0013 (3) | 0.0012 (3) | −0.0042 (3) |
| C17 | 0.0237 (4) | 0.0291 (4) | 0.0260 (4) | −0.0012 (3) | −0.0001 (3) | −0.0029 (3) |
| C18 | 0.0248 (4) | 0.0308 (5) | 0.0301 (4) | 0.0018 (4) | 0.0008 (3) | 0.0003 (4) |
| C19 | 0.0296 (5) | 0.0331 (5) | 0.0441 (6) | 0.0039 (4) | 0.0046 (5) | −0.0060 (4) |
| C20 | 0.0240 (4) | 0.0387 (5) | 0.0350 (5) | 0.0014 (4) | −0.0020 (4) | 0.0045 (4) |
| C21 | 0.0272 (5) | 0.0412 (6) | 0.0320 (5) | −0.0054 (4) | −0.0056 (4) | 0.0014 (4) |
(II) (4R,4aR,7aR,12bS)-9-hydroxy-3-methyl-1,2,4,4a,5,6,7a,13-octahydro-4,12-methanobenzofuro[3,2-e]isoquinoline-7-one. Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C2 | 1.3660 (15) | C11—C19 | 1.5574 (18) |
| O1—H1 | 0.84 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.934 (17) |
| C2—C3 | 1.3860 (15) | N12—C14 | 1.4629 (17) |
| C2—C21 | 1.3975 (18) | N12—C13 | 1.467 (2) |
| C3—C17 | 1.3813 (14) | C13—H13A | 0.9600 |
| C3—O4 | 1.3948 (14) | C13—H13B | 0.9600 |
| O4—C5 | 1.4643 (14) | C13—H13C | 0.9600 |
| C5—C6 | 1.5379 (18) | C14—C15 | 1.5225 (19) |
| C5—C16 | 1.5407 (16) | C14—H14A | 0.98 (2) |
| C5—H5 | 0.98 (2) | C14—H14B | 0.97 (2) |
| C6—O7 | 1.2101 (18) | C15—C16 | 1.5398 (15) |
| C6—C8 | 1.498 (2) | C15—H15A | 0.958 (19) |
| C8—C9 | 1.533 (2) | C15—H15B | 0.97 (2) |
| C8—H8A | 0.97 (2) | C16—C17 | 1.4998 (14) |
| C8—H8B | 0.97 (2) | C17—C18 | 1.3770 (15) |
| C9—C10 | 1.5249 (17) | C18—C20 | 1.4010 (16) |
| C9—H9A | 0.98 (2) | C18—C19 | 1.5122 (16) |
| C9—H9B | 0.98 (3) | C19—H19A | 0.97 (2) |
| C10—C16 | 1.5356 (14) | C19—H19B | 1.01 (3) |
| C10—C11 | 1.5409 (17) | C20—C21 | 1.3988 (18) |
| C10—H10 | 0.954 (19) | C20—H20 | 1.00 (2) |
| C11—N12 | 1.4767 (16) | C21—H21 | 0.98 (2) |
| C2—O1—H1 | 107.5 (18) | C13—N12—C11 | 112.62 (12) |
| O1—C2—C3 | 119.90 (11) | N12—C13—H13A | 109.5 |
| O1—C2—C21 | 123.87 (11) | N12—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C21 | 116.22 (10) | H13A—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C17—C3—C2 | 120.81 (11) | N12—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C17—C3—O4 | 111.37 (9) | H13A—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—O4 | 127.81 (10) | H13B—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C3—O4—C5 | 104.03 (8) | N12—C14—C15 | 111.38 (10) |
| O4—C5—C6 | 108.58 (10) | N12—C14—H14A | 107.6 (12) |
| O4—C5—C16 | 104.99 (9) | C15—C14—H14A | 108.4 (12) |
| C6—C5—C16 | 112.43 (9) | N12—C14—H14B | 114.9 (13) |
| O4—C5—H5 | 109.9 (12) | C15—C14—H14B | 106.6 (12) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 108.1 (12) | H14A—C14—H14B | 107.7 (17) |
| C16—C5—H5 | 112.8 (13) | C14—C15—C16 | 111.10 (10) |
| O7—C6—C8 | 123.66 (14) | C14—C15—H15A | 112.6 (11) |
| O7—C6—C5 | 120.62 (14) | C16—C15—H15A | 108.1 (11) |
| C8—C6—C5 | 115.67 (11) | C14—C15—H15B | 109.2 (12) |
| C6—C8—C9 | 109.94 (11) | C16—C15—H15B | 108.9 (12) |
| C6—C8—H8A | 107.9 (13) | H15A—C15—H15B | 106.8 (17) |
| C9—C8—H8A | 104.6 (13) | C17—C16—C10 | 108.88 (9) |
| C6—C8—H8B | 108.7 (15) | C17—C16—C15 | 109.91 (9) |
| C9—C8—H8B | 110.4 (15) | C10—C16—C15 | 108.80 (9) |
| H8A—C8—H8B | 115 (2) | C17—C16—C5 | 98.12 (8) |
| C10—C9—C8 | 109.26 (11) | C10—C16—C5 | 118.14 (9) |
| C10—C9—H9A | 108.6 (13) | C15—C16—C5 | 112.34 (9) |
| C8—C9—H9A | 109.0 (13) | C18—C17—C3 | 124.03 (10) |
| C10—C9—H9B | 104.8 (15) | C18—C17—C16 | 126.91 (10) |
| C8—C9—H9B | 113.6 (16) | C3—C17—C16 | 109.05 (9) |
| H9A—C9—H9B | 111.5 (19) | C17—C18—C20 | 115.70 (10) |
| C9—C10—C16 | 111.81 (10) | C17—C18—C19 | 117.86 (10) |
| C9—C10—C11 | 114.29 (10) | C20—C18—C19 | 126.32 (10) |
| C16—C10—C11 | 106.27 (9) | C18—C19—C11 | 114.49 (9) |
| C9—C10—H10 | 107.3 (11) | C18—C19—H19A | 107.6 (14) |
| C16—C10—H10 | 108.4 (11) | C11—C19—H19A | 108.1 (15) |
| C11—C10—H10 | 108.6 (12) | C18—C19—H19B | 110.0 (16) |
| N12—C11—C10 | 106.97 (10) | C11—C19—H19B | 108.4 (16) |
| N12—C11—C19 | 115.74 (11) | H19A—C19—H19B | 108 (2) |
| C10—C11—C19 | 113.10 (9) | C21—C20—C18 | 120.67 (11) |
| N12—C11—H11 | 105.2 (11) | C21—C20—H20 | 118.9 (12) |
| C10—C11—H11 | 107.5 (11) | C18—C20—H20 | 120.3 (12) |
| C19—C11—H11 | 107.8 (12) | C2—C21—C20 | 122.43 (11) |
| C14—N12—C13 | 110.99 (12) | C2—C21—H21 | 117.6 (11) |
| C14—N12—C11 | 112.94 (9) | C20—C21—H21 | 119.8 (12) |
| C10—C11—N12—C13 | 169.5 (2) |
(II) (4R,4aR,7aR,12bS)-9-hydroxy-3-methyl-1,2,4,4a,5,6,7a,13-octahydro-4,12-methanobenzofuro[3,2-e]isoquinoline-7-one. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1···O4i | 0.84 (3) | 1.96 (3) | 2.791 (2) | 167 (3) |
Symmetry code: (i) x+1/2, −y+3/2, −z+1.
References
- Allen, F. H., Johnson, O., Shields, G. P., Smith, B. R. & Towler, M. (2004). J. Appl. Cryst. 37, 335–338.
- Bye, E. (1976). Acta Chem. Scand. Ser. B, 30, 549–554.
- Byrn, S. R., Pfeiffer, R. R. & Stowell, J. G. (1999). In Solid-State Chemistry of Drugs. West Lafayette, Indiana: Ssci Inc.
- Grant, D. J. (1999). Drugs Pharm. Sci. 95, 1–33.
- Hooft, R. W. W. (1998). COLLECT. Nonius BV, Delft, The Netherlands.
- Kitajgorodskij, A. I. (1973). In Molecular Crystals and Molecules. New York: Academic Press.
- Macrae, C. F., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Shields, G. P., Taylor, R., Towler, M. & van de Streek, J. (2006). J. Appl. Cryst. 39, 453–457.
- Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. (1997). Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 276, Macromolecular Crystallography, Part A, edited by C. W. Carter Jr & R. M. Sweet, pp. 307–326. New York: Academic Press.
- Parab, P. V., Ritschel, W. A., Coyle, D. E., Gregg, R. V. & Denson, D. D. (1988). Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 9, 187–199. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sarhill, N., Walsh, D. & Nelson, K. A. (2001). Support. Care Cancer, 9, 84–96. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Scheins, S., Messerschmidt, M. & Luger, P. (2005). Acta Cryst. B61, 443–448. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Singhal, D. & Curatolo, W. (2004). Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 56, 335–347. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Vippagunta, S. R., Brittain, H. G. & Grant, D. J. (2001). Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 48, 3–26. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016006563/gk2659sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016006563/gk2659Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016006563/gk2659Isup4.mol
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016006563/gk2659IIsup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016006563/gk2659IIsup5.mol
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report