The crystal structure of a binuclear monocarboxylato dirhenium(III) complex with a fulvalene derivative is reported. This compound represents a radical cation salt containing a cluster unit with rhenium–rhenium quadruple bond.
Keywords: crystal structure, radical cation salt, bis(ethylenedithio)tetrathiafulvalene, rhenium, quadruple metal–metal bond
Abstract
The asymmetric unit of the title salt, (C10H8S8)[Re2Br6(CH3COO)]·0.5C2H3Cl3, contains one bis(ethylenedithio)tetrathiafulvalene (ET) radical cation, one μ2-acetato-bis[tribromidorhenate(III)] anion and a 1,1,2-trichloroethane molecule with half-occupancy disordered about a twofold rotation axis. The tetrathiafulvalene fragment adopts an almost planar configuration typical of the ET radical cation. The C atoms of both ethylenedithio fragments in the cation are disordered over two orientations with occupancy factors 0.65:0.35 and 0.77:0.23. In the anion, six Br atoms and a μ2-acetate ligand form a strongly distorted cubic O2Br6 coordination polyhedron around the Re2 dinuclear centre. In the crystal, centrosymmetrically related ET cations and Re2O2Br6 anions are linked into dimers by π–π stacking interactions [centroid-to-centroid distance = 3.826 (8) Å] and by pairs of additional Re⋯Br contacts [3.131 (3) Å], respectively. The dimers are further packed into a three-dimensional network by non-directional interionic electrostatic forces and by C—H⋯Br and C—H⋯S hydrogen bonds. The disordered 1,1,2-trichloroethane molecules occupy solvent-accessible channels along the b axis.
Chemical context
In the past few decades, molecular low-dimensional conducting materials have attracted much interest owing to their physical properties, in particular their electrical, magnetic and spectroscopic properties. The packing of radical cations in the crystal and the properties of radical cation salts depend substantially on the type of anions involved (Mori et al., 1999 ▸; Mori, 1999 ▸). Labile equatorial chloride or bromide groups around the Re2
6+ cluster unit are the reactive centres in interactions with other chemical compounds and biological macromolecules (Shtemenko et al., 2013 ▸, 2015 ▸). Only one radical cation salt containing a rhenium–rhenium quadruple bond has been described so far {(ET)2[Re2Cl8] [ET = bis(ethylenedithio)tetrathiafulvalene]; Reinheimer et al., 2008 ▸}. In this context, we present the synthesis and crystal structure of a new radical cation salt of ET with the dirhenium(III) anion [Re2Br6(CH3COO)]−. Neither acetic acid nor acetate was used in the synthesis of this radical cation salt. Evidently, the acetate ligand arose by hydrolysis of CH3CN (Cotton et al., 1991 ▸). Complex compounds of dirhenium(III) with one equatorial carboxylato ligand are not well studied, the structure of only three such rhenium compounds having been reported to date (Lau et al., 2000 ▸; Vega et al., 2002 ▸; Beck & Zink, 2011 ▸).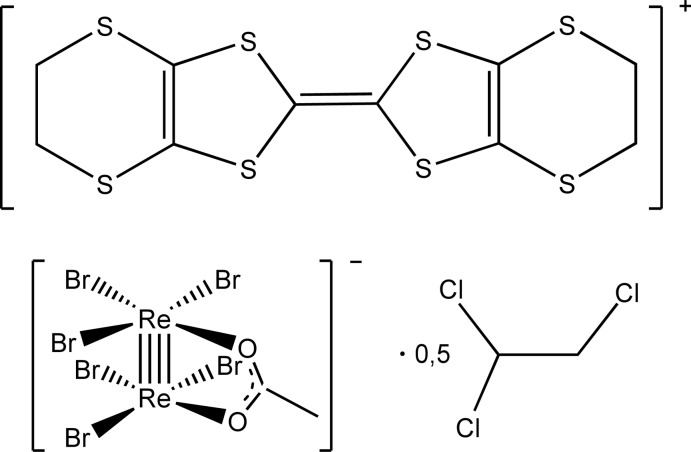
Structural commentary
The title compound (Fig. 1 ▸) consists of bis(ethylenedithio)tetrathiafulvalene (ET) radical cations, μ2-acetato-bis[tribromidorhenate(III)] anions and 1,1,2-trichloroethane molecules in the stoichiometric molar ratio of 1:1:0.5. The solvent molecule is disordered over two orientations of equal occupancy about a twofold rotation axis intersecting the mid-point of the C—C ethane bond. The tetrathiafulvalene fragment adopts an almost planar configuration (r.m.s. deviation = 0.033 Å) that is typical for ET radical cations. The dihedral angle between the five-membered rings is 0.3 (6)°. The carbon atoms of both ethylenedithio fragments (C4/C5 and C9/C10) are disordered over two sets of sites with occupancy ratios of 0.65:0.35 and 0.77:0.23, respectively.
Figure 1.
The asymmetric unit of the title compound, with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level. [Symmetry code: (i) − − x, y, −z.] Only one component of the disordered 1,1,2-trichloroethane molecule and the major component of the ET cation are shown. Colour codes: C, grey; H, white; O, red; S, yellow; Cl, green; Br, brown, Re, violet.
− x, y, −z.] Only one component of the disordered 1,1,2-trichloroethane molecule and the major component of the ET cation are shown. Colour codes: C, grey; H, white; O, red; S, yellow; Cl, green; Br, brown, Re, violet.
In the anion, each ReIII atom is coordinated by three Br atoms forming ReBr3 units which are linked by a Re—Re multiple bond [2.2174 (10) Å] and a bridging μ2-acetate ligand, forming a strongly distorted cubic O2Br6 coordination polyhedron around the Re2 core. The length of the Re—Re bond is very close to the mean value of 2.222 Å for quadruple bonds (Groom et al., 2016 ▸), and the six bromine ligands are arranged into an eclipsed conformation. It is also known that the presence of O,O-bridging ligands in such structures has a negligible effect on the Re—Re bond length [it varies in the range 2.2067 (7)–2.2731 (9) Å for compounds with no bridging ligands and in the range 2.2168 (8)–2.2532 (2) Å for compounds with O,O-bridging ligands (Poineau et al., 2015 ▸)]. Thus, the structure of the Re2Br6CH3COO− anion corresponds to the typical structure of compounds with quadruple Re—Re bonds in an Re2 6+ core (Cotton et al., 2005 ▸). The Re—Br and Re—O bonds vary in the ranges 2.435 (3)–2.451 (3) Å and 2.009 (15)–2.040 (16) Å, respectively. The distortion from an ideal cubic geometry is mainly due to the short distance between the O atoms of the acetate group [2.24 (2) Å], while the Br⋯Br separations between adjacent Br atoms vary in the range 3.411 (3)–3.553 (4) Å.
Supramolecular features
In the crystal (Fig. 2 ▸), pairs of centrosymmetrically related ET cations are linked in a ‘head-to-tail’ manner into dimers by π–π stacking interactions, with centroid-to-centroid separations of 3.836 (8) Å, perpendicular interplanar distances of 3.518 (6) Å and offsets of 1.52 (2) Å. Pairs of Re2O2Br6 anions are also linked into dimers by additional pairwise Re⋯Br contacts [Br6⋯Re2 = 3.131 (3) Å]. Cationic and anionic dimers are packed into a three-dimensional network by non-directional intermolecular electrostatic forces and by C—H⋯Br and C—H⋯S hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▸). Solvent-accessible channels along the b axis are occupied by the disordered 1,1,2-trichloroethane molecules.
Figure 2.
Partial crystal packing of the title compound, with displacement ellipsoids shown at the 50% probability level. Only one component of the disordered 1,1,2-trichloroethane molecule and the major component of the ET molecule are shown. Colour codes: C, grey, H, white, O, red, S, yellow, Cl, green, Br, brown, Re, violet.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C5B—H5BA⋯Br1 | 0.98 | 2.77 | 3.63 (8) | 147 |
| C9A—H9AA⋯Br6i | 0.97 | 2.80 | 3.60 (3) | 140 |
| C9B—H9BA⋯S4ii | 0.97 | 2.75 | 3.46 (10) | 130 |
| C9B—H9BB⋯Br6i | 0.96 | 2.61 | 3.40 (11) | 140 |
| C10A—H10A⋯Br4iii | 0.97 | 2.92 | 3.83 (4) | 156 |
| C10A—H10B⋯S3ii | 0.97 | 2.81 | 3.57 (3) | 136 |
| C10B—H10D⋯Br4iii | 0.98 | 2.67 | 3.61 (11) | 161 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (Version 5.36; last update February 2015; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) for related compounds of bis(ethylenedithio)tetrathiafulvalene with simple Re-containing anions resulted in eight hits, amongst which one closely related structure containing the ET cation and Re2Cl8 anion (Reinheimer et al., 2008 ▸). A search for Re2HalxLy anionic moieties, where Hal is a halogen atom and L is the μ2-carboxylic group, resulted in nine hits. Some closely related patterns were found, e.g. one containing the (μ2-acetato)-hexachloridodirhenate anion exhibiting the same structure of the title compound (Vega et al., 2002 ▸), and one containing the di-μ2-acetato-bis(dibromidorhenate) anion (Koz’min et al., 1981 ▸).
Synthesis and crystallization
The synthesis of the radical cation title salt was performed by galvanostatic anodic oxidation of ET (0.002 mol l−1) in a two-electrode U-shaped glass cell with platinum electrodes. The initial current intensity of 0.1 µA was increased by 0.05 µA per day to a final value of 0.45 µA. A mixture of 1,1,2-trichloroethane/acetonitrile (12:1 v/v) was used as solvent. [(C4H9)4N]2[Re2Br8] (0.008 mol l−1) was used as electrolyte. After a period of 6–7 weeks, black shiny plate-shaped crystals of the title salt suitable for X-ray analysis were formed.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. All hydrogen atoms were placed in idealized positions and refined using a riding-model approximation, with C—H = 0.96–0.97 Å, and with U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C) or 1.5U eq(C) for methyl H atoms. The 1,1,2-trichloroethane molecule is disordered over two sets of sites about a twofold rotation axis with equal occupancy. The C4–C5 and C9–C10 groups of the ET cations are disordered over two orientations with occupancy factors of 0.65/0.35 and 0.77/0.23, respectively. These occupancies were initially obtained as free variables by the full-matrix refinement, and were then fixed in the final refinement cycles. The C—C and C—Cl bond lengths in the solvent molecule were constrained to be 1.52 (1) and 1.80 (1) Å, respectively, and the C—Cl bonds of the solvent molecule were restrained to have the same lengths to within 0.01 Å. The C—S and C—C bonds of the disordered fragments of the ET cation were also restrained to have the same lengths to within 0.005 Å. The atoms of each disordered fragment, including the solvent molecule, were restrained to have approximately the same displacement parameters to within 0.02–0.04 Å2. DELU restraints to within 0.01 Å2 were applied to atoms C4B, C5B, C9B, C10B, C1S and Cl2S. In addition, all non-hydrogen atoms of the solvent molecule were restrained to be approximately isotropic to within 0.03–0.06 Å2. Several outlier reflections (67) that were believed to be affected by the contribution of several unresolved minor twin domains were omitted from the final cycles of refinement, reducing the R factor from 0.061 to 0.052. Attempts to refine the structure using a two-component twin model were unsuccessful. Moreover, the crystals of the title compound are stable but show a strong tendency to splicing. The poor quality of the available crystal may account for the rather low bond precision of the C—C bonds and the presence of several large residual density peaks.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | (C10H8S8)[Re2Br6(C2H3O2)]·0.5C2H3Cl3 |
| M r | 1362.24 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, I2/a |
| Temperature (K) | 298 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 27.1825 (5), 8.53737 (13), 26.0667 (5) |
| β (°) | 100.8440 (17) |
| V (Å3) | 5941.21 (18) |
| Z | 8 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 16.93 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.4 × 0.4 × 0.1 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Agilent Xcalibur Sapphire3 |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2014 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.067, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 36051, 6755, 6304 |
| R int | 0.039 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.650 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.052, 0.137, 1.14 |
| No. of reflections | 6755 |
| No. of parameters | 334 |
| No. of restraints | 99 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 1.77, −1.90 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016006058/rz5188sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016006058/rz5188Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 1473493
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant for Science Research (No. 0111U000111) from the Ministry of Education and Science of Ukraine. We also thank COST Action CM1105 for supporting this study.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| (C10H8S8)[Re2Br6(C2H3O2)]·0.5C2H3Cl3 | F(000) = 4960 |
| Mr = 1362.24 | Dx = 3.046 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, I2/a | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 27.1825 (5) Å | Cell parameters from 18811 reflections |
| b = 8.53737 (13) Å | θ = 2.9–30.7° |
| c = 26.0667 (5) Å | µ = 16.93 mm−1 |
| β = 100.8440 (17)° | T = 298 K |
| V = 5941.21 (18) Å3 | Block, metallic dark violet |
| Z = 8 | 0.4 × 0.4 × 0.1 mm |
Data collection
| Agilent Xcalibur Sapphire3 diffractometer | 6755 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Enhance (Mo) X-ray Source | 6304 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.039 |
| Detector resolution: 16.1827 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 2.9° |
| ω scans | h = −35→35 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2014) | k = −11→9 |
| Tmin = 0.067, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −33→33 |
| 36051 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.052 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.137 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.14 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0534P)2 + 229.8497P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 6755 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 334 parameters | Δρmax = 1.77 e Å−3 |
| 99 restraints | Δρmin = −1.90 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. Absorption correction: CrysAlisPro (Agilent, 2014) Empirical absorption correction using spherical harmonics, implemented in SCALE3 ABSPACK scaling algorithm. |
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| S1 | 0.0279 (2) | −0.3844 (7) | 0.1248 (2) | 0.0486 (13) | |
| S2 | −0.0188 (2) | −0.1562 (6) | 0.0484 (2) | 0.0411 (11) | |
| S3 | −0.0801 (3) | −0.0100 (7) | 0.1157 (3) | 0.0532 (14) | |
| S4 | −0.0284 (3) | −0.2886 (8) | 0.2057 (2) | 0.0602 (17) | |
| S5 | 0.0889 (2) | −0.5248 (8) | 0.0393 (2) | 0.0484 (13) | |
| S6 | 0.0408 (2) | −0.2918 (6) | −0.0354 (2) | 0.0436 (12) | |
| S7 | 0.0915 (3) | −0.3875 (7) | −0.1204 (2) | 0.0586 (17) | |
| S8 | 0.1502 (3) | −0.6653 (9) | −0.0297 (2) | 0.0590 (16) | |
| C1 | 0.0209 (7) | −0.313 (2) | 0.0627 (7) | 0.034 (4) | |
| C2 | −0.0374 (7) | −0.152 (2) | 0.1079 (8) | 0.037 (4) | |
| C3 | −0.0160 (8) | −0.262 (3) | 0.1431 (8) | 0.043 (5) | |
| C4 | −0.065 (3) | −0.122 (6) | 0.220 (3) | 0.064 (11) | 0.35 |
| H4A | −0.1001 | −0.1537 | 0.2165 | 0.077* | 0.35 |
| H4B | −0.0538 | −0.0909 | 0.2563 | 0.077* | 0.35 |
| C4A | −0.0391 (15) | −0.084 (3) | 0.2196 (15) | 0.056 (8) | 0.65 |
| H4AA | −0.0440 | −0.0750 | 0.2554 | 0.067* | 0.65 |
| H4AB | −0.0094 | −0.0242 | 0.2166 | 0.067* | 0.65 |
| C5A | −0.0822 (16) | −0.015 (5) | 0.1850 (9) | 0.060 (9) | 0.65 |
| H5AA | −0.0864 | 0.0909 | 0.1965 | 0.072* | 0.65 |
| H5AB | −0.1118 | −0.0737 | 0.1893 | 0.072* | 0.65 |
| C5B | −0.062 (3) | 0.011 (9) | 0.1862 (9) | 0.061 (12) | 0.35 |
| H5BA | −0.0272 | 0.0463 | 0.1933 | 0.073* | 0.35 |
| H5BB | −0.0817 | 0.0950 | 0.1967 | 0.073* | 0.35 |
| C6 | 0.0472 (7) | −0.372 (2) | 0.0258 (7) | 0.035 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.1061 (8) | −0.523 (2) | −0.0214 (8) | 0.039 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.0834 (9) | −0.415 (2) | −0.0558 (8) | 0.044 (5) | |
| C9A | 0.1534 (9) | −0.479 (4) | −0.1154 (13) | 0.057 (8) | 0.77 |
| H9AA | 0.1634 | −0.4736 | −0.1492 | 0.068* | 0.77 |
| H9AB | 0.1777 | −0.4205 | −0.0908 | 0.068* | 0.77 |
| C9B | 0.134 (4) | −0.548 (10) | −0.130 (4) | 0.05 (2) | 0.23 |
| H9BA | 0.1153 | −0.6449 | −0.1362 | 0.060* | 0.23 |
| H9BB | 0.1493 | −0.5262 | −0.1596 | 0.060* | 0.23 |
| C10A | 0.1547 (13) | −0.643 (4) | −0.0988 (9) | 0.051 (7) | 0.77 |
| H10A | 0.1857 | −0.6902 | −0.1045 | 0.061* | 0.77 |
| H10B | 0.1272 | −0.6987 | −0.1202 | 0.061* | 0.77 |
| C10B | 0.173 (4) | −0.566 (13) | −0.083 (3) | 0.05 (2) | 0.23 |
| H10C | 0.1860 | −0.4639 | −0.0715 | 0.059* | 0.23 |
| H10D | 0.2006 | −0.6266 | −0.0923 | 0.059* | 0.23 |
| Re1 | 0.12639 (3) | 0.02771 (9) | 0.15999 (3) | 0.0325 (2) | |
| Re2 | 0.18894 (3) | 0.19389 (8) | 0.18533 (3) | 0.0285 (2) | |
| Br1 | 0.05027 (9) | 0.1855 (3) | 0.15459 (12) | 0.0621 (7) | |
| Br2 | 0.10600 (9) | −0.1027 (3) | 0.23712 (10) | 0.0541 (6) | |
| Br3 | 0.11180 (11) | 0.0172 (4) | 0.06499 (10) | 0.0623 (7) | |
| Br4 | 0.20677 (9) | 0.2898 (3) | 0.10198 (9) | 0.0529 (6) | |
| Br5 | 0.15056 (10) | 0.4496 (3) | 0.19753 (11) | 0.0560 (6) | |
| Br6 | 0.20369 (9) | 0.1635 (3) | 0.28134 (8) | 0.0476 (5) | |
| O1 | 0.2381 (6) | 0.0139 (18) | 0.1841 (6) | 0.047 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.1742 (6) | −0.1510 (17) | 0.1587 (6) | 0.046 (3) | |
| C11 | 0.2221 (8) | −0.129 (2) | 0.1733 (7) | 0.039 (4) | |
| C12 | 0.2582 (11) | −0.260 (3) | 0.1768 (12) | 0.066 (7) | |
| H12A | 0.2756 | −0.2551 | 0.1480 | 0.100* | |
| H12B | 0.2404 | −0.3578 | 0.1756 | 0.100* | |
| H12C | 0.2819 | −0.2533 | 0.2090 | 0.100* | |
| Cl1S | −0.1993 (6) | 0.0569 (19) | 0.0673 (6) | 0.150 (6) | |
| Cl2S | −0.2811 (11) | 0.288 (3) | 0.0317 (11) | 0.140 (10) | 0.50 |
| C1S | −0.2592 (9) | 0.090 (4) | 0.0257 (5) | 0.15 (2) | |
| H1S | −0.2848 | 0.0099 | 0.0239 | 0.180* | |
| H1SA | −0.2718 | 0.1918 | 0.0336 | 0.180* | 0.50 |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.052 (3) | 0.062 (3) | 0.035 (2) | 0.022 (3) | 0.013 (2) | 0.012 (2) |
| S2 | 0.053 (3) | 0.036 (2) | 0.037 (2) | 0.010 (2) | 0.016 (2) | 0.008 (2) |
| S3 | 0.064 (4) | 0.044 (3) | 0.055 (3) | 0.018 (3) | 0.022 (3) | 0.001 (2) |
| S4 | 0.080 (4) | 0.065 (4) | 0.043 (3) | 0.015 (3) | 0.032 (3) | 0.013 (3) |
| S5 | 0.049 (3) | 0.065 (4) | 0.034 (2) | 0.018 (3) | 0.014 (2) | 0.010 (2) |
| S6 | 0.062 (3) | 0.036 (2) | 0.036 (2) | 0.009 (2) | 0.017 (2) | 0.0036 (19) |
| S7 | 0.102 (5) | 0.041 (3) | 0.040 (3) | 0.018 (3) | 0.032 (3) | 0.006 (2) |
| S8 | 0.064 (4) | 0.075 (4) | 0.042 (3) | 0.028 (3) | 0.020 (3) | 0.008 (3) |
| C1 | 0.033 (9) | 0.043 (10) | 0.028 (8) | 0.000 (8) | 0.008 (7) | 0.002 (7) |
| C2 | 0.040 (10) | 0.038 (10) | 0.036 (9) | −0.002 (8) | 0.015 (8) | 0.000 (8) |
| C3 | 0.049 (11) | 0.050 (12) | 0.033 (9) | 0.010 (9) | 0.015 (8) | 0.007 (9) |
| C4 | 0.071 (17) | 0.065 (16) | 0.061 (15) | 0.002 (14) | 0.025 (14) | −0.003 (12) |
| C4A | 0.070 (18) | 0.053 (15) | 0.057 (15) | 0.000 (14) | 0.040 (14) | −0.015 (13) |
| C5A | 0.074 (19) | 0.059 (17) | 0.058 (15) | 0.008 (16) | 0.043 (14) | −0.007 (14) |
| C5B | 0.066 (18) | 0.061 (16) | 0.060 (16) | 0.000 (14) | 0.023 (13) | −0.004 (12) |
| C6 | 0.039 (10) | 0.039 (10) | 0.030 (8) | −0.002 (8) | 0.011 (7) | 0.002 (7) |
| C7 | 0.042 (10) | 0.045 (11) | 0.031 (9) | 0.004 (8) | 0.012 (8) | −0.004 (8) |
| C8 | 0.067 (14) | 0.036 (10) | 0.030 (9) | −0.010 (10) | 0.014 (9) | −0.007 (8) |
| C9A | 0.07 (2) | 0.061 (19) | 0.050 (17) | −0.023 (17) | 0.030 (16) | −0.004 (15) |
| C9B | 0.05 (2) | 0.05 (3) | 0.05 (2) | 0.000 (17) | 0.013 (15) | 0.001 (17) |
| C10A | 0.058 (18) | 0.050 (17) | 0.050 (16) | 0.014 (15) | 0.025 (14) | 0.003 (14) |
| C10B | 0.05 (2) | 0.05 (3) | 0.05 (2) | 0.000 (17) | 0.013 (15) | −0.001 (17) |
| Re1 | 0.0300 (4) | 0.0326 (4) | 0.0333 (4) | −0.0033 (3) | 0.0025 (3) | 0.0011 (3) |
| Re2 | 0.0294 (4) | 0.0276 (3) | 0.0275 (3) | −0.0007 (2) | 0.0027 (3) | 0.0040 (2) |
| Br1 | 0.0443 (12) | 0.0641 (15) | 0.0752 (17) | 0.0068 (11) | 0.0042 (11) | 0.0085 (13) |
| Br2 | 0.0564 (13) | 0.0555 (13) | 0.0517 (12) | −0.0093 (10) | 0.0140 (10) | 0.0070 (10) |
| Br3 | 0.0602 (15) | 0.0809 (18) | 0.0408 (11) | −0.0144 (13) | −0.0036 (10) | −0.0037 (11) |
| Br4 | 0.0481 (12) | 0.0703 (15) | 0.0389 (11) | −0.0074 (11) | 0.0047 (9) | 0.0135 (10) |
| Br5 | 0.0561 (13) | 0.0389 (11) | 0.0737 (16) | 0.0048 (10) | 0.0142 (12) | 0.0065 (11) |
| Br6 | 0.0513 (12) | 0.0517 (12) | 0.0388 (10) | −0.0108 (10) | 0.0056 (9) | 0.0051 (9) |
| O1 | 0.050 (9) | 0.041 (8) | 0.048 (8) | 0.002 (7) | 0.005 (7) | 0.004 (7) |
| O2 | 0.056 (9) | 0.034 (7) | 0.048 (8) | −0.001 (6) | 0.009 (7) | −0.004 (6) |
| C11 | 0.056 (12) | 0.033 (9) | 0.031 (9) | 0.005 (9) | 0.014 (8) | −0.001 (8) |
| C12 | 0.074 (18) | 0.048 (14) | 0.085 (19) | 0.023 (13) | 0.034 (15) | 0.014 (13) |
| Cl1S | 0.133 (11) | 0.148 (12) | 0.153 (12) | 0.021 (9) | −0.014 (9) | −0.014 (10) |
| Cl2S | 0.15 (2) | 0.115 (17) | 0.14 (2) | 0.048 (16) | −0.024 (17) | 0.005 (15) |
| C1S | 0.15 (4) | 0.12 (2) | 0.19 (4) | 0.02 (3) | 0.05 (3) | −0.01 (3) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—C1 | 1.708 (19) | C7—C8 | 1.35 (3) |
| S1—C3 | 1.72 (2) | C9A—H9AA | 0.9700 |
| S2—C1 | 1.71 (2) | C9A—H9AB | 0.9700 |
| S2—C2 | 1.72 (2) | C9A—C10A | 1.46 (5) |
| S3—C2 | 1.72 (2) | C9B—H9BA | 0.9700 |
| S3—C5A | 1.82 (2) | C9B—H9BB | 0.9700 |
| S3—C5B | 1.82 (2) | C9B—C10B | 1.46 (14) |
| S4—C3 | 1.74 (2) | C10A—H10A | 0.9700 |
| S4—C4 | 1.82 (2) | C10A—H10B | 0.9700 |
| S4—C4A | 1.82 (2) | C10B—H10C | 0.9700 |
| S5—C6 | 1.72 (2) | C10B—H10D | 0.9700 |
| S5—C7 | 1.73 (2) | Re1—Re2 | 2.2174 (10) |
| S6—C6 | 1.716 (19) | Re1—Br1 | 2.451 (3) |
| S6—C8 | 1.72 (2) | Re1—Br2 | 2.451 (2) |
| S7—C8 | 1.75 (2) | Re1—Br3 | 2.435 (3) |
| S7—C9A | 1.84 (2) | Re1—O2 | 2.009 (15) |
| S7—C9B | 1.84 (2) | Re2—Br4 | 2.454 (2) |
| S8—C7 | 1.75 (2) | Re2—Br5 | 2.465 (2) |
| S8—C10A | 1.84 (2) | Re2—Br6 | 2.473 (2) |
| S8—C10B | 1.84 (2) | Re2—O1 | 2.040 (16) |
| C1—C6 | 1.40 (3) | O1—C11 | 1.30 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.36 (3) | O2—C11 | 1.30 (3) |
| C4—H4A | 0.9700 | C11—C12 | 1.48 (3) |
| C4—H4B | 0.9700 | C12—H12A | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5B | 1.46 (4) | C12—H12B | 0.9600 |
| C4A—H4AA | 0.9700 | C12—H12C | 0.9600 |
| C4A—H4AB | 0.9700 | Cl1S—C1S | 1.800 (16) |
| C4A—C5A | 1.46 (4) | Cl2S—C1S | 1.81 (2) |
| C5A—H5AA | 0.9700 | Cl2S—H1SA | 0.8557 |
| C5A—H5AB | 0.9700 | C1S—C1Si | 1.515 (18) |
| C5B—H5BA | 0.9700 | C1S—H1S | 0.9700 |
| C5B—H5BB | 0.9700 | C1S—H1SA | 0.9703 |
| C1—S1—C3 | 94.9 (10) | C10A—C9A—H9AA | 108.9 |
| C1—S2—C2 | 95.6 (9) | C10A—C9A—H9AB | 108.9 |
| C2—S3—C5A | 104.3 (14) | S7—C9B—H9BA | 109.6 |
| C2—S3—C5B | 97 (3) | S7—C9B—H9BB | 109.6 |
| C5A—S3—C5B | 19 (3) | H9BA—C9B—H9BB | 108.1 |
| C3—S4—C4 | 108 (2) | C10B—C9B—S7 | 110 (7) |
| C3—S4—C4A | 97.4 (15) | C10B—C9B—H9BA | 109.6 |
| C4A—S4—C4 | 25 (3) | C10B—C9B—H9BB | 109.6 |
| C6—S5—C7 | 94.9 (9) | S8—C10A—H10A | 109.0 |
| C6—S6—C8 | 94.9 (10) | S8—C10A—H10B | 109.0 |
| C8—S7—C9A | 98.9 (13) | C9A—C10A—S8 | 113 (2) |
| C8—S7—C9B | 103 (3) | C9A—C10A—H10A | 109.0 |
| C9A—S7—C9B | 26 (4) | C9A—C10A—H10B | 109.0 |
| C7—S8—C10A | 102.8 (12) | H10A—C10A—H10B | 107.8 |
| C7—S8—C10B | 96 (4) | S8—C10B—H10C | 109.1 |
| C10B—S8—C10A | 28 (4) | S8—C10B—H10D | 109.1 |
| S1—C1—S2 | 116.1 (11) | C9B—C10B—S8 | 112 (7) |
| C6—C1—S1 | 122.7 (15) | C9B—C10B—H10C | 109.1 |
| C6—C1—S2 | 121.1 (15) | C9B—C10B—H10D | 109.1 |
| S3—C2—S2 | 116.0 (12) | H10C—C10B—H10D | 107.9 |
| C3—C2—S2 | 115.7 (15) | Re2—Re1—Br1 | 104.91 (8) |
| C3—C2—S3 | 128.3 (16) | Re2—Re1—Br2 | 108.99 (7) |
| S1—C3—S4 | 116.6 (12) | Re2—Re1—Br3 | 107.19 (7) |
| C2—C3—S1 | 117.5 (15) | Br1—Re1—Br2 | 88.73 (10) |
| C2—C3—S4 | 125.9 (17) | Br3—Re1—Br1 | 89.29 (11) |
| S4—C4—H4A | 109.2 | Br3—Re1—Br2 | 143.01 (9) |
| S4—C4—H4B | 109.2 | O2—Re1—Re2 | 91.6 (4) |
| H4A—C4—H4B | 107.9 | O2—Re1—Br1 | 163.4 (4) |
| C5B—C4—S4 | 112 (5) | O2—Re1—Br2 | 85.2 (5) |
| C5B—C4—H4A | 109.2 | O2—Re1—Br3 | 86.4 (4) |
| C5B—C4—H4B | 109.2 | Re1—Re2—Br4 | 102.59 (6) |
| S4—C4A—H4AA | 108.8 | Re1—Re2—Br5 | 106.59 (7) |
| S4—C4A—H4AB | 108.8 | Re1—Re2—Br6 | 101.74 (6) |
| H4AA—C4A—H4AB | 107.7 | Br4—Re2—Br5 | 88.72 (9) |
| C5A—C4A—S4 | 114 (3) | Br4—Re2—Br6 | 155.47 (8) |
| C5A—C4A—H4AA | 108.8 | Br5—Re2—Br6 | 87.39 (9) |
| C5A—C4A—H4AB | 108.8 | O1—Re2—Re1 | 88.9 (4) |
| S3—C5A—H5AA | 108.1 | O1—Re2—Br4 | 89.9 (5) |
| S3—C5A—H5AB | 108.1 | O1—Re2—Br5 | 164.3 (4) |
| C4A—C5A—S3 | 117 (2) | O1—Re2—Br6 | 87.4 (5) |
| C4A—C5A—H5AA | 108.1 | C11—O1—Re2 | 120.9 (14) |
| C4A—C5A—H5AB | 108.1 | C11—O2—Re1 | 119.9 (13) |
| H5AA—C5A—H5AB | 107.3 | O1—C11—C12 | 120 (2) |
| S3—C5B—H5BA | 107.3 | O2—C11—O1 | 118.4 (18) |
| S3—C5B—H5BB | 107.3 | O2—C11—C12 | 121 (2) |
| C4—C5B—S3 | 120 (5) | C11—C12—H12A | 109.5 |
| C4—C5B—H5BA | 107.3 | C11—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5B—H5BB | 107.3 | C11—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| H5BA—C5B—H5BB | 106.9 | H12A—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| S6—C6—S5 | 116.3 (11) | H12A—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—S5 | 122.5 (15) | H12B—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—S6 | 121.2 (15) | C1S—Cl2S—H1SA | 8.9 |
| S5—C7—S8 | 114.5 (12) | Cl1S—C1S—Cl2S | 112 (2) |
| C8—C7—S5 | 116.4 (16) | Cl1S—C1S—H1S | 118.6 |
| C8—C7—S8 | 129.0 (16) | Cl1S—C1S—H1SA | 109.2 |
| S6—C8—S7 | 115.3 (13) | Cl2S—C1S—H1S | 114.7 |
| C7—C8—S6 | 117.5 (16) | Cl2S—C1S—H1SA | 7.8 |
| C7—C8—S7 | 127.2 (18) | C1Si—C1S—Cl1S | 97 (2) |
| S7—C9A—H9AA | 108.9 | C1Si—C1S—Cl2S | 104.2 (12) |
| S7—C9A—H9AB | 108.9 | C1Si—C1S—H1S | 108.0 |
| H9AA—C9A—H9AB | 107.7 | C1Si—C1S—H1SA | 112.0 |
| C10A—C9A—S7 | 114 (2) | H1S—C1S—H1SA | 111.3 |
| S1—C1—C6—S5 | 0 (3) | C7—S8—C10A—C9A | 40 (3) |
| S1—C1—C6—S6 | −177.4 (11) | C7—S8—C10B—C9B | −63 (7) |
| S2—C1—C6—S5 | 177.7 (11) | C8—S6—C6—S5 | 0.2 (14) |
| S2—C1—C6—S6 | 0 (2) | C8—S6—C6—C1 | 178.1 (17) |
| S2—C2—C3—S1 | 2 (3) | C8—S7—C9A—C10A | 58 (3) |
| S2—C2—C3—S4 | −178.8 (14) | C8—S7—C9B—C10B | −42 (7) |
| S3—C2—C3—S1 | −177.1 (13) | C9A—S7—C8—S6 | 158.8 (15) |
| S3—C2—C3—S4 | 2 (3) | C9A—S7—C8—C7 | −22 (2) |
| S4—C4—C5B—S3 | 58 (9) | C9A—S7—C9B—C10B | 42 (6) |
| S4—C4A—C5A—S3 | −61 (4) | C9B—S7—C8—S6 | −175 (4) |
| S5—C7—C8—S6 | 1 (2) | C9B—S7—C8—C7 | 4 (4) |
| S5—C7—C8—S7 | −178.2 (13) | C9B—S7—C9A—C10A | −43 (8) |
| S7—C9A—C10A—S8 | −71 (3) | C10A—S8—C7—S5 | 174.5 (16) |
| S7—C9B—C10B—S8 | 77 (9) | C10A—S8—C7—C8 | −4 (3) |
| S8—C7—C8—S6 | 179.3 (13) | C10A—S8—C10B—C9B | 43 (6) |
| S8—C7—C8—S7 | 0 (3) | C10B—S8—C7—S5 | −158 (4) |
| C1—S1—C3—S4 | 176.8 (14) | C10B—S8—C7—C8 | 23 (4) |
| C1—S1—C3—C2 | −4 (2) | C10B—S8—C10A—C9A | −40 (8) |
| C1—S2—C2—S3 | −179.7 (12) | Re1—Re2—O1—C11 | −3.2 (15) |
| C1—S2—C2—C3 | 0.9 (19) | Re1—O2—C11—O1 | −6 (2) |
| C2—S2—C1—S1 | −3.7 (13) | Re1—O2—C11—C12 | 175.2 (17) |
| C2—S2—C1—C6 | 178.7 (17) | Re2—Re1—O2—C11 | 3.0 (15) |
| C2—S3—C5A—C4A | 22 (4) | Re2—O1—C11—O2 | 6 (3) |
| C2—S3—C5B—C4 | −61 (7) | Re2—O1—C11—C12 | −175.0 (17) |
| C3—S1—C1—S2 | 4.6 (14) | Br1—Re1—Re2—Br4 | −90.90 (10) |
| C3—S1—C1—C6 | −177.8 (18) | Br1—Re1—Re2—Br5 | 1.54 (11) |
| C3—S4—C4—C5B | −19 (7) | Br1—Re1—Re2—Br6 | 92.30 (10) |
| C3—S4—C4A—C5A | 63 (3) | Br1—Re1—Re2—O1 | 179.4 (5) |
| C4—S4—C3—S1 | 168 (3) | Br1—Re1—O2—C11 | −174.7 (11) |
| C4—S4—C3—C2 | −11 (4) | Br2—Re1—Re2—Br4 | 175.23 (10) |
| C4—S4—C4A—C5A | −54 (6) | Br2—Re1—Re2—Br5 | −92.32 (10) |
| C4A—S4—C3—S1 | 144.9 (18) | Br2—Re1—Re2—Br6 | −1.56 (10) |
| C4A—S4—C3—C2 | −34 (3) | Br2—Re1—Re2—O1 | 85.6 (5) |
| C4A—S4—C4—C5B | 50 (4) | Br2—Re1—O2—C11 | −105.9 (15) |
| C5A—S3—C2—S2 | −169.7 (19) | Br3—Re1—Re2—Br4 | 3.05 (11) |
| C5A—S3—C2—C3 | 10 (3) | Br3—Re1—Re2—Br5 | 95.49 (11) |
| C5A—S3—C5B—C4 | 53 (6) | Br3—Re1—Re2—Br6 | −173.75 (10) |
| C5B—S3—C2—S2 | −152 (3) | Br3—Re1—Re2—O1 | −86.6 (5) |
| C5B—S3—C2—C3 | 28 (3) | Br3—Re1—O2—C11 | 110.1 (15) |
| C5B—S3—C5A—C4A | −48 (8) | Br4—Re2—O1—C11 | −105.8 (15) |
| C6—S5—C7—S8 | −179.3 (12) | Br5—Re2—O1—C11 | 169.2 (11) |
| C6—S5—C7—C8 | −0.5 (19) | Br6—Re2—O1—C11 | 98.6 (15) |
| C6—S6—C8—S7 | 178.5 (13) | O2—Re1—Re2—Br4 | 89.8 (5) |
| C6—S6—C8—C7 | −0.6 (19) | O2—Re1—Re2—Br5 | −177.8 (5) |
| C7—S5—C6—S6 | 0.1 (14) | O2—Re1—Re2—Br6 | −87.0 (5) |
| C7—S5—C6—C1 | −177.7 (18) | O2—Re1—Re2—O1 | 0.1 (6) |
Symmetry code: (i) −x−1/2, y, −z.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C5B—H5BA···Br1 | 0.98 | 2.77 | 3.63 (8) | 147 |
| C9A—H9AA···Br6ii | 0.97 | 2.80 | 3.60 (3) | 140 |
| C9B—H9BA···S4iii | 0.97 | 2.75 | 3.46 (10) | 130 |
| C9B—H9BB···Br6ii | 0.96 | 2.61 | 3.40 (11) | 140 |
| C10A—H10A···Br4iv | 0.97 | 2.92 | 3.83 (4) | 156 |
| C10A—H10B···S3iii | 0.97 | 2.81 | 3.57 (3) | 136 |
| C10B—H10D···Br4iv | 0.98 | 2.67 | 3.61 (11) | 161 |
Symmetry codes: (ii) x, −y−1/2, z−1/2; (iii) −x, −y−1, −z; (iv) −x+1/2, y−1, −z.
References
- Agilent (2014). CrysAlis PRO. Agilent Technologies, Yarnton, England.
- Beck, J. & Zink, G. (2011). J. Chem. Crystallogr. 41, 1185–1189.
- Cotton, F. A., DeCanio, E. C., Kibala, P. A. & Vidyasagar, K. (1991). Inorg. Chim. Acta, 184, 221–228.
- Cotton, F. A., Murillo, C. A. & Walton, R. A. (2005). Multiple Bonds between Metal Atoms, 3rd ed., pp. 271–376. New York: Springer Science and Business Media Inc.
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Koz’min, P. A., Surazhskaya, M. D. & Larina, T. B. (1981). Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 26, 57–60.
- Lau, S. S., Fanwick, P. E. & Walton, R. A. (2000). Inorg. Chim. Acta, 308, 8–16.
- Mori, T. (1999). Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn, 72, 2011–2027.
- Mori, T., Mori, H. & Tanaka, Sh. (1999). Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn, 72, 179–197.
- Poineau, F., Sattelberger, A. P., Lu, E. & Liddle, S. T. (2015). Molecular Metal–Metal Bonds: Compounds, Synthesis, Properties, edited by S. T. Liddle, pp. 205–216. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH.
- Reinheimer, E. W., Galán-Mascarós, J. R., Gómez-García, C. J., Zhao, H., Fourmigué, M. & Dunbar, K. R. (2008). J. Mol. Struct. 890, 81–89.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Shtemenko, N. I., Chifotides, H. T., Domasevitch, K. V., Golichenko, A. A., Babiy, S. A., Li, Z., Paramonova, K. V., Shtemenko, A. V. & Dunbar, K. R. (2013). J. Inorg. Biochem. 129, 127–134. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Shtemenko, A. V., Chifotides, H. T., Yegorova, D. E., Shtemenko, N. I. & Dunbar, K. R. (2015). J. Inorg. Biochem. 153, 114–120. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Vega, A., Calvo, V., Manzur, J., Spodine, E. & Saillard, J.-Y. (2002). Inorg. Chem. 41, 5382–5387. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016006058/rz5188sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016006058/rz5188Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 1473493
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




