A new ferrocene complex, 16-ferrocenylmethyl-3β-hydroxyestra-1,3,5(10)-trien-17-one, has been synthesized and structurally characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction techniques. The ferrocenylmethyl group is positioned at the β face of the estrone moiety; as a result, a new stereogenic center is formed leading to an R stereochemical configuration. No head-to-tail hydrogen bonding is observed in the crystal packing, as is the case in estrone and other derivatives.
Keywords: crystal structure, anticancer compound, ferrocene, medicinal chemistry
Abstract
A new ferrocene complex, 16-ferrocenylmethyl-3β-hydroxyestra-1,3,5(10)-trien-17-one dimethyl sulfoxide monosolvate, [Fe(C5H5)(C24H27O2)]·C2H6OS, has been synthesized and structurally characterized by single-crystal X-ray diffraction techniques. The molecule crystallizes in the space group P21 with one molecule of dimethyl sulfoxide. A hydrogen bond links the phenol group and the dimethyl sulfoxide O atom, with an O⋯O distance of 2.655 (5) Å. The ferrocene group is positioned in the β face of the estrone moiety, with an O—C—C—C torsion angle of 44.1 (5)°, and the carbonyl bond length of the hormone moiety is 1.216 (5) Å, typical of a C=O double bond. The average Fe—C bond length of the substituted Cp ring [Fe—C(Cp*)] is similar to that of the unsubstituted one [Fe—C(Cp)], i.e. 2.048 (3) versus 2.040 (12) Å. The structure of the complex is compared with those of estrone and ethoxymethylestrone.
Chemical context
The discovery of cisplatin antineoplastic activity was a notable event in medicinal chemistry history, opening new alternatives and routes on the use of metal-based drugs and their structure–activity relationships in cancer chemotherapy. However, its remarkable success (Galanski et al., 2005 ▸; Sandler et al., 2011 ▸) came at the high cost of undesired detrimental side effects (neurotoxicity, nephrotoxicity, etc; Pabla & Dong, 2008 ▸). In this context, our research group has been working on other transition metals (e.g., titanium, iron, vanadium and tungsten, among others) with promising results for chemotherapeutic applications (Domínguez-García et al., 2013 ▸; Ramos et al., 2014 ▸; Vera et al., 2014 ▸). Recently, particular attention has been focused on the antineoplastic activity of ferrocene complexes (Richard et al., 2015 ▸) due to their desired physical and chemical properties such as aqueous stability and high synthetic homology to benzene chemistry, with the advantage that they exhibit fewer toxic side effects than cisplatin. Our group has been working on the synthesis and application of ferrocene complexes coupled to hormones in order to develop new metal-based therapeutic drugs with high selective index for hormone-dependent-breast-cancer treatment (Vera et al., 2011 ▸, 2014 ▸). In connection with the relationship between structure and the activity against hormone-dependent breast cancer, we intend to explore the functionalization of estrogens at C16 position with ferrocene using estrone (1) as starting material, due to the versatility which, for synthetic transformations, provides the carbonyl group over other estrogens not containing a carbonyl group. In this context, we present herein the synthesis and crystal structure of 16-ferrocenylmethyl-3β-hydroxyestra-1,3,5(10)-trien-17-one dimethyl sulfoxide monosolvate (2) and compare it with the structure of estrogen (1) and 16β-ethoxymethylestrone (3) (Allan et al., 2006 ▸).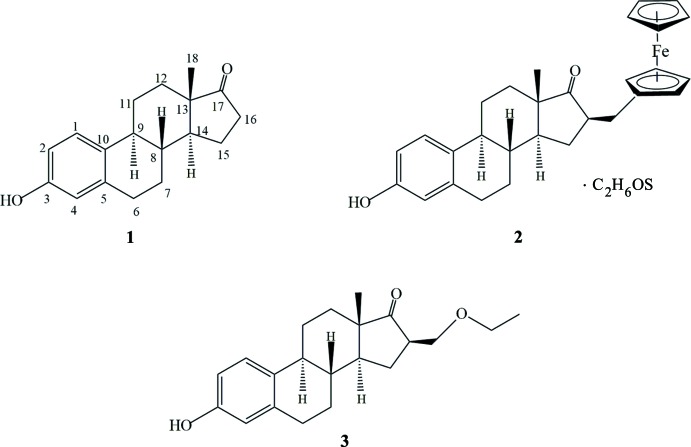
Structural commentary
The ferrocenylmethyl group of 2 is positioned at the beta face of the estrone moiety (Fig. 1 ▸). As a result, a new stereogenic center was formed after substitution at position 16 (C16) of estrone with a ferrocenylmethyl group. This C16 atom has an R stereochemical configuration. Table 1 ▸ contains the most relevant bond lengths and angles. The carbonyl bond (C17=O2) of the hormone moiety of 2 is 1.216 (5) Å, which is very similar to in estrogen and 16β-ethoxymethylestrone [1.215 (2) and 1.219 (2) Å, respectively], corresponding to a carbon–oxygen double (C=O) bond. However, the substitution at C16 of the steroid in 2 and 3, ferrocenylmethyl and ethoxymethyl groups, respectively, makes torsion angles and bond angles at the 16-position slightly different. Both substituents are located on the beta face but, the torsion angle (between C19 and carbonyl group) defined as C19–C16—C17—O2 in 2 is smaller than in 3 (between the carbonyl and the methoxy groups), 44.1 (5) and 49.7 (2)°, respectively. The ferrocene moiety is positioned at 112.6 (3)° from C16 (∠C20—C19—C16) while the ethoxymethyl group is at 108.4 (1)° (∠C16—C1—O3). The average Fe—C bond length of the substituted Cp ring [Fe—C(Cp*] is similar to the unsubstituted one, 2.048 (3) vs 2.040 (12) Å (McAdam et al., 2015 ▸). We might expect that the substitution on the Cp ring with a electron-donating methyl group could enhance the Fe—C(Cp*) bonding, but such an effect is not observed. It is not clear if this is a steric rather than an electronic effect. It is worth mentioning the steroselectivity of this reaction showed the beta steroisomer but it is also the position of the ethoxymethyl group on ethoxymethylestrone. We might expect the beta face of the estrone moiety to be more hindered due to the methyl group on C13 which is located in this face but, according to the mechanism of hydrogen addition to a double bond, the addition is favored on the less hindered alpha face and, as a consequence, the ferrocenyl group is positioned on the beta face.
Figure 1.
The asymmetric unit of 2. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Table 1. Selected geometrical parameters (Å, °) for compounds 1, 2 and 3 .
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bond lengths | |||
| Fe—C(Cp)avg | 2.040 (12) | ||
| Fe—C(Cp*)subt | 2.048 (3) | ||
| C(Cp)subt—CH2 | 1.505 (5) | ||
| C17—O2 | 1.219 (2) | 1.216 (5) | 1.215 (2) |
| C3—O1 | 1.374 (2) | 1.368 (5) | 1.371 (2) |
| Hydrogen-bond parameters | |||
| D—H | 0.86 | 0.84 | 0.84 |
| H⋯A | 1.97 (O2⋯H1) | 1.82 [O3(DMSO)⋯H1] | 1.93 (O2⋯H1) |
| D⋯A | 2.819 (2) (O1⋯O2) | 2.655 (5) (O1⋯O3) | 2.760 (2) (O1⋯O2) |
| D—H⋯A | 174 | 174 | 170 |
| Bond angles | |||
| C20—C19—C16 | 112.6 (3) | ||
| O3—C1—C16 | 108.4 (1) | ||
| Torsion angles | |||
| O2—C17—C16—C19 | 44.1 (5) | 49.7 (2) [O(2)—C(17)—C(16)—C(1)] |
Supramolecular features
In the crystal structure of 2 there is a hydrogen bond involving the hydroxyl group at C3 and the DMSO oxygen (Table 2 ▸, Fig. 2 ▸). No head-to-tail hydrogen bonding is observed, as is the case in 1 and 3 (Shikii et al., 2004 ▸; Allan et al., 2006 ▸). In the latter structures, the hydrogen bonds at the two ends are the driving force for packing. It seems that the ferrocenylmethyl substitution on C16 inhibits the hydrogen bonding at the carbonyl oxygen atom, thus eliminating the head-to-tail hydrogen-bonding network existing in 1 and 3.
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1—H1⋯O3i | 0.84 | 1.82 | 2.655 (5) | 174 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Figure 2.
Packing diagram for 2, projected along the b axis. The ferrocene moieties are shown in polyhedral representation for clarity. The O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds are highlighted (in cyan dashed lines).
Synthesis and crystallization
In a 500 mL Parr bottle, 16-ferrocenylidene-3β-hydroxyestra-1,3,5(10)-trien-17-one complex was dissolved in a mixture of tetrahydrofuran (THF) and ethanol (1:1) and Pd/C (10wt%, catalytic). The system was purged three times with H2 at 40 psi. The reaction mixture was stirred overnight at room temperature under 40 psi of H2. The mixture was then filtered through Celite, and the filtrate was evaporated in vacuo, resulting in a yellow solid that was purified by column chromatography using CHCl3: ethyl acetate (9:1) as mobile phase, affording 67% of 2 as a yellow solid. Yellow rod-shaped crystals were obtained after dissolving the solid 16-ferrocenylmethyl-3β-hydroxyestra-1,3,5(10)-trien-17-one in a solution of CH2Cl2 with a few drops of dimethyl sulfoxide, to assure a concentrate solution, layered in hexane.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. H atoms were positioned in idealized locations: d(C—H) = 0.95 Å, U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C); d(C—H2) = 0.99 Å,U iso(H) = 1.2 Ueq (C); d(C—H3) = 0.98 Å, U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(C).
Table 3. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | [Fe(C5H5)(C24H27O2)]·C2H6OS |
| M r | 546.52 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21 |
| Temperature (K) | 100 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 7.4178 (12), 11.2436 (15), 16.1160 (18) |
| β (°) | 93.148 (4) |
| V (Å3) | 1342.1 (3) |
| Z | 2 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.67 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.30 × 0.25 × 0.03 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker APEXII Ultra |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2013 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.064, 0.093 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 9583, 5327, 4816 |
| R int | 0.048 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.625 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.043, 0.097, 1.02 |
| No. of reflections | 5327 |
| No. of parameters | 329 |
| No. of restraints | 1 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.32, −0.44 |
| Absolute structure | Flack x determined using 1990 quotients [(I +)−(I −)]/[(I +)+(I −)] (Parsons et al., 2013 ▸) |
| Absolute structure parameter | 0.004 (14) |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016008446/bg2586sup1.cif
CCDC reference: 1479699
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
We thank the NIH, the Alfred P. Sloan Program and its representative Dr Rodolfo Romañach for financial support. We also extend special thanks to Dr Robert Ríos for allowing JACN to perform the synthesis in his research laboratory. EM acknowledges the financial support of NSF–CREST II 000743–00002.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| [Fe(C5H5)(C24H27O2)]·C2H6OS | F(000) = 580 |
| Mr = 546.52 | Dx = 1.352 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 7.4178 (12) Å | Cell parameters from 4213 reflections |
| b = 11.2436 (15) Å | θ = 3.0–26.2° |
| c = 16.1160 (18) Å | µ = 0.67 mm−1 |
| β = 93.148 (4)° | T = 100 K |
| V = 1342.1 (3) Å3 | Block, yellow |
| Z = 2 | 0.3 × 0.25 × 0.03 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII Ultra diffractometer | 5327 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Micro Focus Rotating Anode, Bruker TXS | 4816 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Double Bounce Multilayer Mirrors monochromator | Rint = 0.048 |
| Detector resolution: 7.9 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 26.4°, θmin = 2.2° |
| ω and φ scans | h = −9→9 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2013) | k = −13→14 |
| Tmin = 0.064, Tmax = 0.093 | l = −20→19 |
| 9583 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.043 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0266P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.097 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| S = 1.02 | Δρmax = 0.32 e Å−3 |
| 5327 reflections | Δρmin = −0.44 e Å−3 |
| 329 parameters | Absolute structure: Flack x determined using 1990 quotients [(I+)-(I-)]/[(I+)+(I-)] (Parsons et al., 2013) |
| 1 restraint | Absolute structure parameter: 0.004 (14) |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Fe1 | −0.29444 (8) | 0.50023 (5) | 1.06433 (3) | 0.01977 (16) | |
| S1 | 0.26603 (16) | 0.46255 (9) | 0.35262 (6) | 0.0224 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.1244 (5) | 0.4378 (3) | 0.41388 (17) | 0.0285 (8) | |
| O2 | −0.2299 (4) | 0.2860 (3) | 0.79220 (17) | 0.0247 (7) | |
| O1 | 0.9351 (4) | 0.6126 (3) | 0.47762 (17) | 0.0232 (7) | |
| H1 | 0.9886 | 0.5548 | 0.4569 | 0.035* | |
| C17 | −0.1502 (6) | 0.3780 (4) | 0.7790 (2) | 0.0176 (9) | |
| C13 | 0.0422 (6) | 0.3895 (4) | 0.7523 (2) | 0.0181 (9) | |
| C8 | 0.2258 (6) | 0.5542 (4) | 0.6908 (2) | 0.0163 (9) | |
| H8 | 0.3108 | 0.5484 | 0.7410 | 0.020* | |
| C15 | −0.0744 (6) | 0.5880 (4) | 0.7724 (2) | 0.0188 (9) | |
| H15A | −0.1175 | 0.6629 | 0.7458 | 0.023* | |
| H15B | −0.0055 | 0.6068 | 0.8251 | 0.023* | |
| C14 | 0.0394 (5) | 0.5159 (4) | 0.7143 (2) | 0.0170 (8) | |
| H14 | −0.0347 | 0.5095 | 0.6608 | 0.020* | |
| C22 | −0.0406 (7) | 0.4352 (4) | 1.0540 (3) | 0.0219 (10) | |
| H22 | 0.0203 | 0.3809 | 1.0910 | 0.026* | |
| C5 | 0.5284 (6) | 0.6214 (4) | 0.5951 (2) | 0.0166 (9) | |
| C10 | 0.4657 (5) | 0.5020 (4) | 0.58935 (19) | 0.0168 (8) | |
| C21 | −0.1534 (6) | 0.4044 (4) | 0.9831 (3) | 0.0202 (10) | |
| H21 | −0.1811 | 0.3259 | 0.9646 | 0.024* | |
| C24 | −0.1427 (7) | 0.6073 (4) | 0.9925 (3) | 0.0212 (10) | |
| H24 | −0.1619 | 0.6894 | 0.9811 | 0.025* | |
| C12 | 0.1022 (6) | 0.3007 (4) | 0.6877 (2) | 0.0225 (10) | |
| H12A | 0.0111 | 0.2978 | 0.6405 | 0.027* | |
| H12B | 0.1112 | 0.2204 | 0.7127 | 0.027* | |
| C2 | 0.7268 (6) | 0.4550 (4) | 0.5087 (2) | 0.0198 (9) | |
| H2 | 0.7945 | 0.3980 | 0.4800 | 0.024* | |
| C7 | 0.2328 (7) | 0.6806 (4) | 0.6564 (3) | 0.0195 (10) | |
| H7A | 0.1600 | 0.6854 | 0.6031 | 0.023* | |
| H7B | 0.1813 | 0.7368 | 0.6960 | 0.023* | |
| C19 | −0.3372 (5) | 0.5193 (4) | 0.8660 (2) | 0.0208 (9) | |
| H19A | −0.3982 | 0.5976 | 0.8641 | 0.025* | |
| H19B | −0.4316 | 0.4571 | 0.8671 | 0.025* | |
| C30 | 0.1457 (6) | 0.4879 (5) | 0.2554 (2) | 0.0270 (10) | |
| H30A | 0.0824 | 0.4150 | 0.2375 | 0.041* | |
| H30B | 0.2308 | 0.5106 | 0.2137 | 0.041* | |
| H30C | 0.0578 | 0.5519 | 0.2615 | 0.041* | |
| C1 | 0.5698 (6) | 0.4215 (4) | 0.5459 (2) | 0.0200 (9) | |
| H1A | 0.5317 | 0.3410 | 0.5417 | 0.024* | |
| C11 | 0.2860 (6) | 0.3367 (4) | 0.6560 (3) | 0.0218 (10) | |
| H11A | 0.3801 | 0.3274 | 0.7015 | 0.026* | |
| H11B | 0.3164 | 0.2827 | 0.6103 | 0.026* | |
| C20 | −0.2179 (5) | 0.5112 (5) | 0.9444 (2) | 0.0184 (9) | |
| C3 | 0.7837 (6) | 0.5728 (4) | 0.5137 (2) | 0.0192 (10) | |
| C16 | −0.2314 (5) | 0.5037 (4) | 0.7870 (2) | 0.0200 (8) | |
| H16 | −0.3205 | 0.5140 | 0.7386 | 0.024* | |
| C6 | 0.4272 (6) | 0.7143 (4) | 0.6427 (2) | 0.0193 (9) | |
| H6A | 0.4283 | 0.7904 | 0.6119 | 0.023* | |
| H6B | 0.4916 | 0.7272 | 0.6974 | 0.023* | |
| C4 | 0.6851 (6) | 0.6544 (4) | 0.5575 (2) | 0.0182 (9) | |
| H4 | 0.7257 | 0.7344 | 0.5619 | 0.022* | |
| C29 | −0.3916 (9) | 0.5424 (7) | 1.1756 (3) | 0.059 (2) | |
| H29 | −0.3244 | 0.5803 | 1.2200 | 0.071* | |
| C31 | 0.3441 (7) | 0.6100 (4) | 0.3730 (3) | 0.0266 (11) | |
| H31A | 0.2407 | 0.6624 | 0.3804 | 0.040* | |
| H31B | 0.4111 | 0.6383 | 0.3261 | 0.040* | |
| H31C | 0.4235 | 0.6106 | 0.4236 | 0.040* | |
| C18 | 0.1621 (6) | 0.3784 (4) | 0.8337 (2) | 0.0225 (10) | |
| H18A | 0.1284 | 0.4401 | 0.8728 | 0.034* | |
| H18B | 0.2891 | 0.3881 | 0.8214 | 0.034* | |
| H18C | 0.1445 | 0.2998 | 0.8584 | 0.034* | |
| C23 | −0.0348 (6) | 0.5606 (4) | 1.0600 (2) | 0.0224 (10) | |
| H23 | 0.0299 | 0.6055 | 1.1018 | 0.027* | |
| C28 | −0.4933 (9) | 0.5984 (6) | 1.1132 (4) | 0.0490 (17) | |
| H28 | −0.5090 | 0.6819 | 1.1079 | 0.059* | |
| C9 | 0.2869 (6) | 0.4657 (4) | 0.6246 (2) | 0.0177 (9) | |
| H9 | 0.1941 | 0.4698 | 0.5773 | 0.021* | |
| C26 | −0.5157 (9) | 0.4035 (6) | 1.0890 (4) | 0.0523 (18) | |
| H26 | −0.5483 | 0.3294 | 1.0642 | 0.063* | |
| C27 | −0.5681 (6) | 0.5152 (7) | 1.0601 (3) | 0.0412 (14) | |
| H27 | −0.6432 | 0.5311 | 1.0117 | 0.049* | |
| C25 | −0.4046 (9) | 0.4208 (7) | 1.1623 (4) | 0.059 (2) | |
| H25 | −0.3493 | 0.3603 | 1.1960 | 0.071* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Fe1 | 0.0179 (3) | 0.0243 (3) | 0.0174 (3) | −0.0018 (3) | 0.0034 (2) | −0.0014 (3) |
| S1 | 0.0250 (6) | 0.0214 (6) | 0.0210 (5) | 0.0067 (5) | 0.0035 (4) | 0.0027 (4) |
| O3 | 0.039 (2) | 0.0249 (18) | 0.0233 (15) | 0.0017 (15) | 0.0130 (14) | 0.0014 (13) |
| O2 | 0.0264 (19) | 0.0243 (17) | 0.0239 (16) | −0.0099 (15) | 0.0072 (14) | −0.0039 (13) |
| O1 | 0.0227 (18) | 0.0230 (17) | 0.0243 (16) | −0.0023 (14) | 0.0042 (13) | 0.0020 (13) |
| C17 | 0.019 (2) | 0.023 (2) | 0.0106 (18) | −0.0015 (19) | −0.0024 (16) | −0.0033 (17) |
| C13 | 0.020 (2) | 0.018 (2) | 0.016 (2) | −0.0036 (19) | 0.0002 (17) | −0.0001 (17) |
| C8 | 0.019 (2) | 0.016 (2) | 0.0147 (18) | 0.0000 (18) | −0.0002 (16) | −0.0002 (16) |
| C15 | 0.020 (2) | 0.018 (2) | 0.018 (2) | 0.0025 (19) | 0.0000 (17) | −0.0006 (17) |
| C14 | 0.019 (2) | 0.018 (2) | 0.0145 (17) | −0.0011 (19) | 0.0001 (14) | −0.0002 (17) |
| C22 | 0.021 (3) | 0.025 (3) | 0.020 (2) | 0.006 (2) | 0.0048 (19) | 0.0007 (19) |
| C5 | 0.019 (2) | 0.019 (2) | 0.0121 (19) | 0.0009 (18) | −0.0024 (16) | 0.0005 (16) |
| C10 | 0.020 (2) | 0.0190 (19) | 0.0116 (16) | −0.001 (2) | −0.0015 (14) | 0.002 (2) |
| C21 | 0.022 (3) | 0.023 (2) | 0.016 (2) | −0.003 (2) | 0.0014 (18) | −0.0052 (18) |
| C24 | 0.019 (2) | 0.020 (2) | 0.024 (2) | −0.003 (2) | 0.0042 (19) | −0.0035 (19) |
| C12 | 0.026 (3) | 0.018 (2) | 0.024 (2) | −0.007 (2) | 0.0057 (19) | −0.0033 (18) |
| C2 | 0.024 (2) | 0.019 (2) | 0.0165 (19) | 0.0005 (19) | 0.0031 (17) | −0.0040 (17) |
| C7 | 0.024 (3) | 0.017 (2) | 0.018 (2) | 0.0002 (19) | 0.0030 (18) | −0.0009 (17) |
| C19 | 0.014 (2) | 0.027 (3) | 0.0211 (18) | 0.001 (2) | 0.0012 (15) | −0.0017 (19) |
| C30 | 0.029 (2) | 0.029 (3) | 0.0219 (19) | −0.002 (2) | −0.0025 (17) | 0.000 (2) |
| C1 | 0.025 (2) | 0.019 (2) | 0.0168 (19) | −0.0036 (19) | 0.0014 (17) | 0.0016 (17) |
| C11 | 0.028 (3) | 0.016 (2) | 0.022 (2) | −0.005 (2) | 0.0076 (19) | −0.0018 (18) |
| C20 | 0.0141 (19) | 0.025 (2) | 0.0164 (17) | −0.001 (2) | 0.0029 (14) | −0.0025 (19) |
| C3 | 0.018 (2) | 0.025 (2) | 0.0145 (19) | −0.0017 (19) | −0.0002 (17) | 0.0051 (18) |
| C16 | 0.017 (2) | 0.025 (2) | 0.0171 (17) | 0.000 (2) | −0.0013 (15) | 0.000 (2) |
| C6 | 0.026 (2) | 0.014 (2) | 0.018 (2) | −0.0020 (18) | 0.0011 (17) | −0.0023 (17) |
| C4 | 0.022 (2) | 0.017 (2) | 0.0158 (19) | −0.0018 (18) | −0.0022 (17) | 0.0018 (16) |
| C29 | 0.030 (3) | 0.121 (7) | 0.029 (3) | −0.024 (4) | 0.018 (2) | −0.026 (3) |
| C31 | 0.027 (3) | 0.028 (3) | 0.024 (2) | −0.007 (2) | −0.0020 (19) | 0.001 (2) |
| C18 | 0.022 (2) | 0.024 (2) | 0.021 (2) | −0.006 (2) | 0.0005 (18) | 0.0057 (18) |
| C23 | 0.017 (3) | 0.033 (3) | 0.017 (2) | −0.003 (2) | −0.0016 (18) | −0.003 (2) |
| C28 | 0.033 (4) | 0.043 (4) | 0.074 (4) | 0.003 (3) | 0.033 (3) | −0.009 (3) |
| C9 | 0.024 (2) | 0.016 (2) | 0.0133 (17) | −0.0004 (18) | 0.0009 (16) | −0.0023 (16) |
| C26 | 0.040 (4) | 0.053 (4) | 0.067 (4) | −0.028 (3) | 0.030 (3) | −0.022 (3) |
| C27 | 0.018 (2) | 0.076 (5) | 0.030 (2) | 0.004 (3) | 0.0067 (19) | 0.006 (3) |
| C25 | 0.039 (4) | 0.092 (6) | 0.049 (4) | 0.016 (4) | 0.020 (3) | 0.048 (4) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Fe1—C22 | 2.035 (5) | C12—H12A | 0.9900 |
| Fe1—C21 | 2.030 (4) | C12—H12B | 0.9900 |
| Fe1—C24 | 2.049 (5) | C12—C11 | 1.536 (6) |
| Fe1—C20 | 2.047 (3) | C2—H2 | 0.9500 |
| Fe1—C29 | 2.026 (5) | C2—C1 | 1.391 (6) |
| Fe1—C23 | 2.047 (5) | C2—C3 | 1.392 (6) |
| Fe1—C28 | 2.035 (6) | C7—H7A | 0.9900 |
| Fe1—C26 | 2.026 (6) | C7—H7B | 0.9900 |
| Fe1—C27 | 2.035 (5) | C7—C6 | 1.518 (6) |
| Fe1—C25 | 2.025 (6) | C19—H19A | 0.9900 |
| S1—O3 | 1.506 (3) | C19—H19B | 0.9900 |
| S1—C30 | 1.783 (4) | C19—C20 | 1.505 (5) |
| S1—C31 | 1.781 (4) | C19—C16 | 1.543 (5) |
| O2—C17 | 1.216 (5) | C30—H30A | 0.9800 |
| O1—H1 | 0.8400 | C30—H30B | 0.9800 |
| O1—C3 | 1.368 (5) | C30—H30C | 0.9800 |
| C17—C13 | 1.518 (6) | C1—H1A | 0.9500 |
| C17—C16 | 1.545 (6) | C11—H11A | 0.9900 |
| C13—C14 | 1.548 (6) | C11—H11B | 0.9900 |
| C13—C12 | 1.527 (5) | C11—C9 | 1.536 (6) |
| C13—C18 | 1.548 (5) | C3—C4 | 1.389 (6) |
| C8—H8 | 1.0000 | C16—H16 | 1.0000 |
| C8—C14 | 1.516 (5) | C6—H6A | 0.9900 |
| C8—C7 | 1.527 (6) | C6—H6B | 0.9900 |
| C8—C9 | 1.545 (5) | C4—H4 | 0.9500 |
| C15—H15A | 0.9900 | C29—H29 | 0.9500 |
| C15—H15B | 0.9900 | C29—C28 | 1.376 (9) |
| C15—C14 | 1.527 (5) | C29—C25 | 1.387 (10) |
| C15—C16 | 1.529 (6) | C31—H31A | 0.9800 |
| C14—H14 | 1.0000 | C31—H31B | 0.9800 |
| C22—H22 | 0.9500 | C31—H31C | 0.9800 |
| C22—C21 | 1.422 (6) | C18—H18A | 0.9800 |
| C22—C23 | 1.414 (6) | C18—H18B | 0.9800 |
| C5—C10 | 1.422 (6) | C18—H18C | 0.9800 |
| C5—C6 | 1.519 (6) | C23—H23 | 0.9500 |
| C5—C4 | 1.390 (6) | C28—H28 | 0.9500 |
| C10—C1 | 1.402 (6) | C28—C27 | 1.365 (9) |
| C10—C9 | 1.527 (5) | C9—H9 | 1.0000 |
| C21—H21 | 0.9500 | C26—H26 | 0.9500 |
| C21—C20 | 1.423 (7) | C26—C27 | 1.387 (10) |
| C24—H24 | 0.9500 | C26—C25 | 1.416 (9) |
| C24—C20 | 1.425 (6) | C27—H27 | 0.9500 |
| C24—C23 | 1.415 (6) | C25—H25 | 0.9500 |
| C22—Fe1—C24 | 68.00 (19) | C1—C2—C3 | 119.4 (4) |
| C22—Fe1—C20 | 68.81 (16) | C3—C2—H2 | 120.3 |
| C22—Fe1—C23 | 40.53 (16) | C8—C7—H7A | 109.7 |
| C22—Fe1—C28 | 156.9 (2) | C8—C7—H7B | 109.7 |
| C21—Fe1—C22 | 40.95 (17) | H7A—C7—H7B | 108.2 |
| C21—Fe1—C24 | 68.24 (16) | C6—C7—C8 | 109.7 (4) |
| C21—Fe1—C20 | 40.86 (19) | C6—C7—H7A | 109.7 |
| C21—Fe1—C23 | 68.60 (19) | C6—C7—H7B | 109.7 |
| C21—Fe1—C28 | 161.4 (2) | H19A—C19—H19B | 107.8 |
| C21—Fe1—C27 | 124.8 (2) | C20—C19—H19A | 109.1 |
| C20—Fe1—C24 | 40.73 (18) | C20—C19—H19B | 109.1 |
| C29—Fe1—C22 | 122.2 (2) | C20—C19—C16 | 112.6 (3) |
| C29—Fe1—C21 | 156.4 (3) | C16—C19—H19A | 109.1 |
| C29—Fe1—C24 | 126.6 (2) | C16—C19—H19B | 109.1 |
| C29—Fe1—C20 | 162.2 (3) | S1—C30—H30A | 109.5 |
| C29—Fe1—C23 | 109.5 (2) | S1—C30—H30B | 109.5 |
| C29—Fe1—C28 | 39.6 (3) | S1—C30—H30C | 109.5 |
| C29—Fe1—C26 | 67.7 (3) | H30A—C30—H30B | 109.5 |
| C29—Fe1—C27 | 66.9 (2) | H30A—C30—H30C | 109.5 |
| C29—Fe1—C25 | 40.0 (3) | H30B—C30—H30C | 109.5 |
| C23—Fe1—C24 | 40.42 (18) | C10—C1—H1A | 118.7 |
| C23—Fe1—C20 | 68.75 (16) | C2—C1—C10 | 122.5 (4) |
| C28—Fe1—C24 | 109.4 (2) | C2—C1—H1A | 118.7 |
| C28—Fe1—C20 | 125.3 (2) | C12—C11—H11A | 109.2 |
| C28—Fe1—C23 | 122.5 (2) | C12—C11—H11B | 109.2 |
| C26—Fe1—C22 | 125.9 (3) | H11A—C11—H11B | 107.9 |
| C26—Fe1—C21 | 107.1 (2) | C9—C11—C12 | 112.2 (4) |
| C26—Fe1—C24 | 154.4 (2) | C9—C11—H11A | 109.2 |
| C26—Fe1—C20 | 119.2 (2) | C9—C11—H11B | 109.2 |
| C26—Fe1—C23 | 163.4 (3) | C21—C20—Fe1 | 68.9 (2) |
| C26—Fe1—C28 | 66.6 (2) | C21—C20—C24 | 106.9 (3) |
| C26—Fe1—C27 | 39.9 (3) | C21—C20—C19 | 125.9 (4) |
| C27—Fe1—C22 | 162.4 (2) | C24—C20—Fe1 | 69.7 (2) |
| C27—Fe1—C24 | 120.7 (2) | C24—C20—C19 | 127.3 (5) |
| C27—Fe1—C20 | 106.95 (17) | C19—C20—Fe1 | 128.0 (3) |
| C27—Fe1—C23 | 155.6 (2) | O1—C3—C2 | 122.7 (4) |
| C27—Fe1—C28 | 39.2 (3) | O1—C3—C4 | 117.9 (4) |
| C25—Fe1—C22 | 108.7 (2) | C4—C3—C2 | 119.4 (4) |
| C25—Fe1—C21 | 120.9 (3) | C17—C16—H16 | 106.6 |
| C25—Fe1—C24 | 163.2 (3) | C15—C16—C17 | 104.5 (3) |
| C25—Fe1—C20 | 155.1 (3) | C15—C16—C19 | 118.9 (3) |
| C25—Fe1—C23 | 126.4 (2) | C15—C16—H16 | 106.6 |
| C25—Fe1—C28 | 66.7 (3) | C19—C16—C17 | 113.0 (4) |
| C25—Fe1—C26 | 40.9 (3) | C19—C16—H16 | 106.6 |
| C25—Fe1—C27 | 67.5 (2) | C5—C6—C7 | 113.7 (3) |
| O3—S1—C30 | 105.8 (2) | C5—C6—H6A | 108.8 |
| O3—S1—C31 | 106.4 (2) | C5—C6—H6B | 108.8 |
| C31—S1—C30 | 98.9 (2) | C7—C6—H6A | 108.8 |
| C3—O1—H1 | 109.5 | C7—C6—H6B | 108.8 |
| O2—C17—C13 | 126.6 (4) | H6A—C6—H6B | 107.7 |
| O2—C17—C16 | 124.6 (4) | C5—C4—H4 | 119.3 |
| C13—C17—C16 | 108.8 (4) | C3—C4—C5 | 121.4 (4) |
| C17—C13—C14 | 101.4 (3) | C3—C4—H4 | 119.3 |
| C17—C13—C12 | 116.8 (3) | Fe1—C29—H29 | 125.0 |
| C17—C13—C18 | 105.0 (3) | C28—C29—Fe1 | 70.6 (3) |
| C14—C13—C18 | 113.8 (3) | C28—C29—H29 | 126.1 |
| C12—C13—C14 | 109.2 (3) | C28—C29—C25 | 107.9 (6) |
| C12—C13—C18 | 110.5 (4) | C25—C29—Fe1 | 69.9 (4) |
| C14—C8—H8 | 108.7 | C25—C29—H29 | 126.1 |
| C14—C8—C7 | 113.9 (4) | S1—C31—H31A | 109.5 |
| C14—C8—C9 | 107.3 (3) | S1—C31—H31B | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 108.7 | S1—C31—H31C | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 109.4 (3) | H31A—C31—H31B | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 108.7 | H31A—C31—H31C | 109.5 |
| H15A—C15—H15B | 109.2 | H31B—C31—H31C | 109.5 |
| C14—C15—H15A | 111.3 | C13—C18—H18A | 109.5 |
| C14—C15—H15B | 111.3 | C13—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C14—C15—C16 | 102.5 (3) | C13—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C16—C15—H15A | 111.3 | H18A—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C16—C15—H15B | 111.3 | H18A—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C13—C14—H14 | 105.7 | H18B—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C8—C14—C13 | 111.5 (3) | Fe1—C23—H23 | 126.3 |
| C8—C14—C15 | 123.1 (4) | C22—C23—Fe1 | 69.3 (3) |
| C8—C14—H14 | 105.7 | C22—C23—C24 | 107.6 (4) |
| C15—C14—C13 | 103.9 (3) | C22—C23—H23 | 126.2 |
| C15—C14—H14 | 105.7 | C24—C23—Fe1 | 69.9 (3) |
| Fe1—C22—H22 | 126.2 | C24—C23—H23 | 126.2 |
| C21—C22—Fe1 | 69.3 (3) | Fe1—C28—H28 | 126.1 |
| C21—C22—H22 | 125.9 | C29—C28—Fe1 | 69.8 (4) |
| C23—C22—Fe1 | 70.2 (3) | C29—C28—H28 | 125.3 |
| C23—C22—H22 | 125.9 | C27—C28—Fe1 | 70.4 (3) |
| C23—C22—C21 | 108.2 (4) | C27—C28—C29 | 109.4 (6) |
| C10—C5—C6 | 120.9 (4) | C27—C28—H28 | 125.3 |
| C4—C5—C10 | 120.1 (4) | C8—C9—H9 | 106.3 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 119.0 (4) | C10—C9—C8 | 112.2 (3) |
| C5—C10—C9 | 121.1 (4) | C10—C9—C11 | 113.3 (4) |
| C1—C10—C5 | 117.1 (4) | C10—C9—H9 | 106.3 |
| C1—C10—C9 | 121.7 (4) | C11—C9—C8 | 111.9 (3) |
| Fe1—C21—H21 | 125.8 | C11—C9—H9 | 106.3 |
| C22—C21—Fe1 | 69.7 (3) | Fe1—C26—H26 | 125.4 |
| C22—C21—H21 | 125.8 | C27—C26—Fe1 | 70.3 (3) |
| C22—C21—C20 | 108.3 (4) | C27—C26—H26 | 126.4 |
| C20—C21—Fe1 | 70.2 (2) | C27—C26—C25 | 107.2 (6) |
| C20—C21—H21 | 125.8 | C25—C26—Fe1 | 69.5 (4) |
| Fe1—C24—H24 | 126.8 | C25—C26—H26 | 126.4 |
| C20—C24—Fe1 | 69.6 (2) | Fe1—C27—H27 | 125.6 |
| C20—C24—H24 | 125.5 | C28—C27—Fe1 | 70.4 (3) |
| C23—C24—Fe1 | 69.7 (3) | C28—C27—C26 | 108.2 (5) |
| C23—C24—H24 | 125.5 | C28—C27—H27 | 125.9 |
| C23—C24—C20 | 108.9 (4) | C26—C27—Fe1 | 69.7 (3) |
| C13—C12—H12A | 109.5 | C26—C27—H27 | 125.9 |
| C13—C12—H12B | 109.5 | Fe1—C25—H25 | 125.6 |
| C13—C12—C11 | 110.6 (3) | C29—C25—Fe1 | 70.0 (4) |
| H12A—C12—H12B | 108.1 | C29—C25—C26 | 107.3 (6) |
| C11—C12—H12A | 109.5 | C29—C25—H25 | 126.4 |
| C11—C12—H12B | 109.5 | C26—C25—Fe1 | 69.6 (3) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.3 | C26—C25—H25 | 126.4 |
| Fe1—C22—C21—C20 | 59.8 (3) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 50.4 (4) |
| Fe1—C22—C23—C24 | −59.6 (3) | C7—C8—C9—C11 | 179.0 (4) |
| Fe1—C21—C20—C24 | 59.6 (3) | C1—C10—C9—C8 | 162.9 (3) |
| Fe1—C21—C20—C19 | −122.3 (4) | C1—C10—C9—C11 | 35.0 (5) |
| Fe1—C24—C20—C21 | −59.1 (3) | C1—C2—C3—O1 | −179.0 (4) |
| Fe1—C24—C20—C19 | 122.9 (4) | C1—C2—C3—C4 | 1.5 (6) |
| Fe1—C24—C23—C22 | 59.2 (4) | C20—C24—C23—Fe1 | −58.6 (3) |
| Fe1—C29—C28—C27 | 59.4 (4) | C20—C24—C23—C22 | 0.5 (6) |
| Fe1—C29—C25—C26 | −59.9 (4) | C20—C19—C16—C17 | 65.7 (5) |
| Fe1—C28—C27—C26 | 59.7 (4) | C20—C19—C16—C15 | −57.3 (6) |
| Fe1—C26—C27—C28 | −60.1 (4) | C3—C2—C1—C10 | −0.4 (6) |
| Fe1—C26—C25—C29 | 60.2 (5) | C16—C17—C13—C14 | −20.6 (4) |
| O2—C17—C13—C14 | 159.3 (4) | C16—C17—C13—C12 | −139.1 (3) |
| O2—C17—C13—C12 | 40.7 (6) | C16—C17—C13—C18 | 98.1 (4) |
| O2—C17—C13—C18 | −82.0 (5) | C16—C15—C14—C13 | −43.4 (4) |
| O2—C17—C16—C15 | 174.7 (4) | C16—C15—C14—C8 | −171.2 (3) |
| O2—C17—C16—C19 | 44.1 (5) | C16—C19—C20—Fe1 | −169.8 (4) |
| O1—C3—C4—C5 | 179.2 (4) | C16—C19—C20—C21 | −79.7 (5) |
| C17—C13—C14—C8 | 173.9 (3) | C16—C19—C20—C24 | 97.9 (5) |
| C17—C13—C14—C15 | 39.3 (4) | C6—C5—C10—C1 | −178.5 (3) |
| C17—C13—C12—C11 | 170.1 (4) | C6—C5—C10—C9 | 5.1 (5) |
| C13—C17—C16—C15 | −5.4 (4) | C6—C5—C4—C3 | 179.5 (3) |
| C13—C17—C16—C19 | −136.0 (3) | C4—C5—C10—C1 | 1.0 (5) |
| C13—C12—C11—C9 | −53.2 (5) | C4—C5—C10—C9 | −175.5 (3) |
| C8—C7—C6—C5 | 49.2 (4) | C4—C5—C6—C7 | 161.2 (4) |
| C14—C13—C12—C11 | 55.8 (5) | C29—C28—C27—Fe1 | −59.1 (4) |
| C14—C8—C7—C6 | 174.5 (3) | C29—C28—C27—C26 | 0.6 (6) |
| C14—C8—C9—C10 | 174.3 (3) | C18—C13—C14—C8 | 61.8 (4) |
| C14—C8—C9—C11 | −57.1 (4) | C18—C13—C14—C15 | −72.8 (4) |
| C14—C15—C16—C17 | 29.6 (4) | C18—C13—C12—C11 | −70.0 (4) |
| C14—C15—C16—C19 | 156.7 (3) | C23—C22—C21—Fe1 | −59.6 (4) |
| C22—C21—C20—Fe1 | −59.5 (3) | C23—C22—C21—C20 | 0.2 (6) |
| C22—C21—C20—C24 | 0.1 (4) | C23—C24—C20—Fe1 | 58.7 (3) |
| C22—C21—C20—C19 | 178.1 (4) | C23—C24—C20—C21 | −0.4 (5) |
| C5—C10—C1—C2 | −0.8 (6) | C23—C24—C20—C19 | −178.4 (4) |
| C5—C10—C9—C8 | −20.9 (5) | C28—C29—C25—Fe1 | 60.7 (4) |
| C5—C10—C9—C11 | −148.8 (3) | C28—C29—C25—C26 | 0.8 (8) |
| C10—C5—C6—C7 | −19.3 (5) | C9—C8—C14—C13 | 61.4 (4) |
| C10—C5—C4—C3 | 0.0 (6) | C9—C8—C14—C15 | −174.1 (3) |
| C21—C22—C23—Fe1 | 59.1 (3) | C9—C8—C7—C6 | −65.6 (4) |
| C21—C22—C23—C24 | −0.4 (6) | C9—C10—C1—C2 | 175.6 (4) |
| C12—C13—C14—C8 | −62.1 (4) | C27—C26—C25—Fe1 | −60.5 (4) |
| C12—C13—C14—C15 | 163.2 (3) | C27—C26—C25—C29 | −0.4 (7) |
| C12—C11—C9—C8 | 54.3 (5) | C25—C29—C28—Fe1 | −60.3 (5) |
| C12—C11—C9—C10 | −177.6 (3) | C25—C29—C28—C27 | −0.9 (7) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −1.3 (6) | C25—C26—C27—Fe1 | 60.0 (4) |
| C7—C8—C14—C13 | −177.5 (3) | C25—C26—C27—C28 | −0.2 (6) |
| C7—C8—C14—C15 | −53.0 (5) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1···O3i | 0.84 | 1.82 | 2.655 (5) | 174 |
Symmetry code: (i) x+1, y, z.
References
- Allan, G. M., Lawrence, H. R., Cornet, J., Bubert, C., Fischer, D. S., Vicker, N., Smith, A., Tutill, H. J., Purohit, A., Day, J. M., Mahon, M. F., Reed, M. J. & Potter, B. V. L. (2006). J. Med. Chem. 49, 1325–1345. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2013). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Domínguez-García, M., Ortega-Zúñiga, C. & Meléndez, E. (2013). J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 18, 195–209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Galanski, M., Jakupec, M. A. & Keppler, B. K. (2005). Curr. Med. Chem. 12, 2075–2094. [DOI] [PubMed]
- McAdam, C. J., Moratti, S. C. & Simpson, J. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 1100–1105. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Pabla, N. & Dong, Z. (2008). Kidney Int. 73, 994–1007. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Parsons, S., Flack, H. D. & Wagner, T. (2013). Acta Cryst. B69, 249–259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Ramos, G., Loperena, Y., Ortiz, G., Reyes, F., Szeto, A., Vera, J., Velez, J., Morales, J., Morrero, D., Castillo, L., Dharmawardhane, S., Melendez, E. & Washington, A. V. (2014). Anticancer Res. 34, 1609–1615. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Richard, M.-A., Hamels, D., Pigeon, P., Top, S., Dansette, P. M., Lee, H. Z. S., Vessières, A., Mansuy, D. & Jaouen, G. (2015). ChemMedChem, 10, 981–990. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sandler, A., Graham, C., Baggstrom, M., Herbst, R., Zergebel, C., Saito, K. & Jones, D. (2011). J. Thorac. Oncol. 6, 1400–1406. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Shikii, K., Sakamoto, S., Seki, H., Utsumi, H. & Yamaguchi, K. (2004). Tetrahedron, 60, 3487–3492.
- Vera, J., Gao, L. M., Santana, A., Matta, J. & Meléndez, E. (2011). Dalton Trans. 40, 9557–9565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Vera, J. L., Rullán, J., Santos, N., Jiménez, J., Rivera, J., Santana, A., Briggs, J., Rheingold, A. L., Matta, J. & Meléndez, E. (2014). J. Organomet. Chem. 749, 204–214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016008446/bg2586sup1.cif
CCDC reference: 1479699
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




