The supramolecular architecture in a co-crystal of N(7)—H tautomeric form of N 6-benzoyladenine-adipic acid (1/0.5) is reported. The typical C=O⋯π and C—H⋯π interactions are also present in this structure.
Keywords: crystal structure, N6-benzoyladenine, adipic acid, hydrogen bond, supramolecular sheet, π–π stacking, co-crystal
Abstract
The asymmetric unit of the title co-crystal, C12H9N5O·0.5C6H10O4, consists of one molecule of N 6-benzoyladenine (BA) and one half-molecule of adipic acid (AA), the other half being generated by inversion symmetry. The dihedral angle between the adenine and phenyl ring planes is 26.71 (7)°. The N 6-benzoyladenine molecule crystallizes in the N(7)—H tautomeric form with three non-protonated N atoms. This tautomeric form is stabilized by intramolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl (C=O) group and the N(7)—H hydrogen atom on the Hoogsteen face of the purine ring, forming an S(7) ring motif. The two carboxyl groups of adipic acid interact with the Watson–Crick face of the BA molecules through O—H⋯N and N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, generating an R 2 2(8) ring motif. The latter units are linked by N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds, forming layers parallel to (10-5). A weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bond is also present, linking adipic acid molecules in neighbouring layers, enclosing R 2 2(10) ring motifs and forming a three-dimensional structure. C=O⋯π and C—H⋯π interactions are also present in the structure.
Chemical context
Adipic acid has been widely used in controlled-release formulations of many drugs and food additives (Roew et al., 2009 ▸). N
6-benzoyladenine is a synthetic analogue of a group of naturally occurring N
6-substituted adenines having plant-growth-stimulating activity (cytokinins) (McHugh & Erxleben, 2011 ▸). A number of co-crystals involving adipic acid have been reported in the literature (Lemmerer et al., 2012 ▸; Lin et al., 2012 ▸; Matulková et al., 2014 ▸; Thanigaimani et al., 2012 ▸). This paper deals with a co-crystal formed between N
6-benzoyladenine and adipic acid (I).
Structural commentary
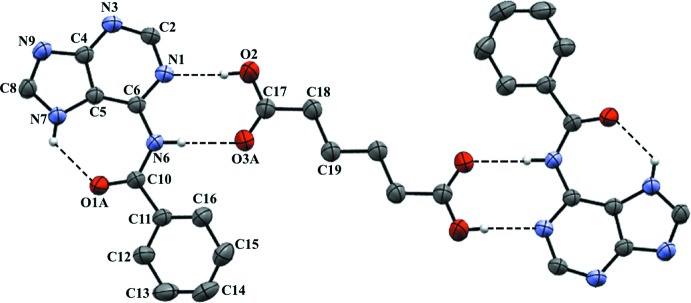
The asymmetric unit of (I) contains one N 6-benzoyladenine (BA) molecule and a half-molecule of adipic acid (AA). As evident from the angles at N7 [C8—N7—C5 = 106.82 (11)°] and N9 [C8—N9—C4 = 103.90 (11)°], the N 6-benzoyladenine moiety exists in the N(7)—H tautomeric form with non-protonated N1, N3 and N9 atoms. In addition, the C8—N7 bond [1.3415 (17) Å)] is longer than C8—N9 [1.3175 (19) Å]. These values are similar to those in neutral N 6-benzoyladenine (Raghunathan & Pattabhi, 1981 ▸). An intramolecular hydrogen bond in the Hoogsteen face between N7—H7 and the benzoyl oxygen atom O1 forms a S(7) ring motif. The dihedral angle between the adenine and phenyl ring plane is 26.71 (7)° and the C6—N6—C10—C11 torsion angle is 173.08 (14)°. The bond lengths and bond angles of AA are in the range of values reported (Srinivasa Gopalan et al., 1999 ▸; 2000 ▸). The values for the torsion angles C18—C19—C19a—C18a [180.00 (13)°] and C17—C18—C19—C19a [–176.09 (14)°] indicate that the carbon chain of AA is fully extended.
In the crystal structures of N 6-benzyladenine (Raghunathan & Pattabhi, 1981 ▸), N 6-furfuryladenine (Soriano-Garcia & Parthasarathy, 1977 ▸), N 6-benzyladenine hydrobromide (Umadevi et al., 2001 ▸), N 6-furfuryladenine hydrochloride (Stanley et al., 2003 ▸), N 6-benzyladeninium p-toluenesulfonate (Tamilselvi & Muthiah, 2011 ▸), N 6-benzyladeninium nitrate, N 6-benzyladeninium 3-hydroxy picolinate (Nirmalram et al., 2011 ▸) and the hydrate adduct of N 6-benzyladenine-5-sulfosalicylic acid (Xia et al., 2010 ▸), the N 6-substituent is distal to the N7 position, whereas in the crystal structures of N 6-benzoyladenine (Raghunathan et al., 1983 ▸), N 6-benzoyladenine-3-hydroxypyridinium-2-carboxylate (1:1), N 6-benzoyladenine-dl-tartaric acid (1:1) (Karthikeyan et al., 2015 ▸), N 6-benzoyladeninium nitrate (Karthikeyan et al., 2015 ▸) and the title compound, the N 6-substituent is distal to N1 and syn to adenine nitrogen atom N7. In the present structure, this may be attributed to the presence of the N7—H7⋯O1A intramolecular hydrogen bond (Table 1 ▸).
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg is the centroid of the C11–C16 phenyl ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2—H2A⋯N1i | 0.82 | 1.92 | 2.7327 (19) | 175 |
| N6—H6⋯O3A ii | 0.86 | 2.09 | 2.904 (11) | 157 |
| N7—H7⋯O1A | 0.86 | 2.04 | 2.616 (16) | 124 |
| N7—H7⋯N9iii | 0.86 | 2.17 | 2.9271 (17) | 146 |
| C19—H19B⋯O3A iv | 0.97 | 2.54 | 3.481 (11) | 164 |
| C2—H2⋯Cg3v | 0.93 | 2.94 | 3.4611 (16) | 117 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  ; (v)
; (v)  .
.
Supramolecular features
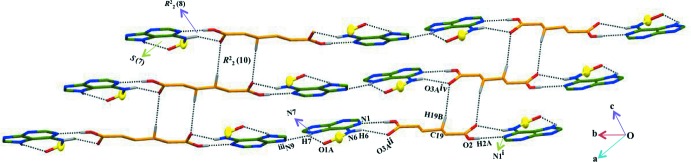
Each of the two carboxyl groups of adipic acid interacts with the Watson–Crick face (atoms N1 and N6) of the corresponding BA through O—H⋯N and N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, generating an  (8) ring motif (Fig. 1 ▸). Thus each adipic acid molecule bridges two BA molecules. The latter units are linked by N7—H7⋯N9iii hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▸) forming layers parallel to plane (10
(8) ring motif (Fig. 1 ▸). Thus each adipic acid molecule bridges two BA molecules. The latter units are linked by N7—H7⋯N9iii hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▸) forming layers parallel to plane (10 ). A weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bond (C19—H19B⋯O3A
iv) is also present (Table 1 ▸ and Fig. 2 ▸), linking adipic acid molecules in neighbouring layers, enclosing
). A weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bond (C19—H19B⋯O3A
iv) is also present (Table 1 ▸ and Fig. 2 ▸), linking adipic acid molecules in neighbouring layers, enclosing  (10) ring motifs and forming a three-dimensional structure. Thus atom O3A functions as a bifurcated hydrogen-bond acceptor whereas N7—H is a bifurcated hydrogen-bond donor.
(10) ring motifs and forming a three-dimensional structure. Thus atom O3A functions as a bifurcated hydrogen-bond acceptor whereas N7—H is a bifurcated hydrogen-bond donor.
Figure 1.
A Mercury (Macrae et al., 2008 ▸) view of the title compound (I), showing the atom-numbering scheme. Disordered oxygen atoms are omitted for clarity. H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonding have been omitted for clarity. Unlabelled atoms are related by the symmetry operation 1 − x, 1 − y, −z.
Figure 2.
A view of the sheet-like supramolecular architecture generated via C19—H19B⋯O3A hydrogen bonds (black dotted lines). Phenyl rings are indicated as yellow balls. H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonding have been omitted for clarity. Symmetry codes are as given in Table 1 ▸.
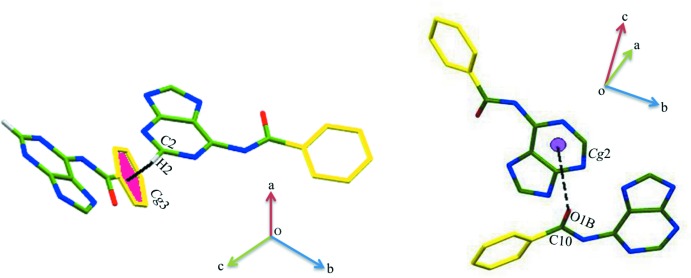
The crystal structure also features C2—H2⋯π interactions between purine and phenyl rings (Fig. 3 ▸
a) and C10=O1B⋯π interactions between the carbonyl oxygen O1B and the centroid of the (N1/C2/N3/C4/C5/C6) pyrimidine ring [O⋯centroid = 3.407 (10) Å; symmetry code: 1 − x,  + y,
+ y,  − z; Fig. 3 ▸
b] (Safaei-Ghomi et al., 2009 ▸).
− z; Fig. 3 ▸
b] (Safaei-Ghomi et al., 2009 ▸).
Figure 3.
(a) A view of the C—H⋯π interaction in compound (I). Cg3 is the centroid of the phenyl ring of the BA molecule (symmetry code: x, −1 + y, z). (b) A view of the C=O⋯π interaction. Cg2 is the centroid of the pyrimidine ring of the BA molecule (symmetry code: 1 − x,  + y,
+ y,  − z).
− z).
Database survey
The neutral molecule N 6-benzoyladenine was reported by Raghunathan & Pattabhi (1981 ▸). Co-crystals have also been reported: N 6-benzoyladenine-3-hydroxypyridinium-2-carboxylate (1:1), N 6-benzoyladenine-dl-tartaric acid (1:1) (Karthikeyan et al., 2015 ▸) and N 6-benzoyladeninium nitrate (Karthikeyan et al., 2016 ▸). Similarly, co-crystals of adipic acid with pyrimidine derivatives [adenine (Byres et al., 2009 ▸), caffeine (Bučar et al., 2007 ▸), cytosine (Das & Baruah, 2011 ▸), bis-pyrimidine-amine-linked xylene spacer (Goswami et al., 2010 ▸)] have also been reported.
Synthesis and crystallization
The title co-crystal was synthesized by mixing a DMF solution of N 6-benzoyladenine (30 mg) and adipic acid (19 mg) (total volume = 10 mL). The mixture was warmed in a water bath for 20 min. After cooling to room temperature, colourless plate-like crystals were collected from the mother liquor after a few days (m.p. 438 K).
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. Atoms O1 and O3 are disordered over two positions with refined occupancy ratios of 0.57 (3):0.43 (3) and 0.63 (3):0.37 (3), respectively. Hydrogen atoms were readily located in difference Fourier maps and were subsequently treated as riding atoms in geometrically idealized positions, with C—H = 0.93 (aromatic) or 0.97 (methylene), N—H = 0.86, and O—H = 0.82 Å, and with U iso(H) = kU eq(C,N,O), where k = 1.5 for hydroxy and 1.2 for all other H atoms.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C12H9N5O·0.5C6H10O4 |
| M r | 312.31 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 293 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 6.1776 (4), 9.2296 (4), 25.7480 (15) |
| β (°) | 97.117 (6) |
| V (Å3) | 1456.76 (14) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.10 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.60 × 0.60 × 0.40 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Agilent SuperNova Dual Source diffractometer with an Atlas detector |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2013 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.756, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 9480, 3325, 2755 |
| R int | 0.020 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.649 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.045, 0.122, 1.05 |
| No. of reflections | 3325 |
| No. of parameters | 230 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.25, −0.22 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016007581/hg5474sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016007581/hg5474Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016007581/hg5474Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1478504
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
RSD thanks the UGC–BSR India for the award of an RFSMS. PTM is thankful to the UGC, New Delhi, for a UGC–BSR one-time grant to Faculty. FP thanks the Slovenian Research Agency for financial support (P1–0230-0175), as well as the EN–FIST Centre of Excellence, Ljubljana, Slovenia, for the use of the SuperNova diffractometer.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C12H9N5O·0.5C6H10O4 | F(000) = 652 |
| Mr = 312.31 | Dx = 1.424 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 6.1776 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 4139 reflections |
| b = 9.2296 (4) Å | θ = 3.3–30.1° |
| c = 25.7480 (15) Å | µ = 0.10 mm−1 |
| β = 97.117 (6)° | T = 293 K |
| V = 1456.76 (14) Å3 | Prism, colorless |
| Z = 4 | 0.60 × 0.60 × 0.40 mm |
Data collection
| Agilent SuperNova Dual Source diffractometer with an Atlas detector | 3325 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: SuperNova (Mo) X-ray Source | 2755 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Mirror monochromator | Rint = 0.020 |
| Detector resolution: 10.4933 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 3.2° |
| ω scans | h = −8→7 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Agilent, 2013) | k = −11→11 |
| Tmin = 0.756, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −33→31 |
| 9480 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.045 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0541P)2 + 0.3295P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.122 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.05 | Δρmax = 0.25 e Å−3 |
| 3325 reflections | Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3 |
| 230 parameters | Extinction correction: SHELXL2014 (Sheldrick, 2015), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction coefficient: 0.0130 (18) |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| O1A | 0.7104 (15) | 0.6427 (14) | 0.1669 (8) | 0.094 (4) | 0.57 (3) |
| O1B | 0.6582 (19) | 0.6621 (6) | 0.1877 (4) | 0.054 (2) | 0.43 (3) |
| N1 | 0.3308 (2) | 0.27081 (12) | 0.16588 (5) | 0.0415 (3) | |
| N3 | 0.5648 (2) | 0.09828 (13) | 0.21438 (5) | 0.0477 (3) | |
| N6 | 0.39990 (19) | 0.51100 (12) | 0.15270 (5) | 0.0391 (3) | |
| H6 | 0.2702 | 0.5109 | 0.1361 | 0.047* | |
| N7 | 0.85319 (19) | 0.42515 (12) | 0.22672 (5) | 0.0402 (3) | |
| H7 | 0.8790 | 0.5157 | 0.2226 | 0.048* | |
| N9 | 0.9054 (2) | 0.19667 (13) | 0.25397 (5) | 0.0470 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.3848 (3) | 0.13827 (15) | 0.18545 (6) | 0.0468 (4) | |
| H2 | 0.2811 | 0.0660 | 0.1774 | 0.056* | |
| C4 | 0.7054 (2) | 0.20808 (14) | 0.22480 (5) | 0.0389 (3) | |
| C5 | 0.6683 (2) | 0.35149 (13) | 0.20707 (5) | 0.0352 (3) | |
| C6 | 0.4717 (2) | 0.38085 (13) | 0.17619 (5) | 0.0347 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.9855 (3) | 0.32896 (15) | 0.25376 (6) | 0.0451 (4) | |
| H8 | 1.1219 | 0.3535 | 0.2709 | 0.054* | |
| C10 | 0.5100 (3) | 0.63803 (16) | 0.15283 (7) | 0.0493 (4) | |
| C11 | 0.4104 (2) | 0.75951 (14) | 0.11985 (6) | 0.0412 (3) | |
| C12 | 0.5550 (3) | 0.86137 (17) | 0.10534 (7) | 0.0544 (4) | |
| H12 | 0.7028 | 0.8527 | 0.1173 | 0.065* | |
| C13 | 0.4831 (3) | 0.97575 (19) | 0.07333 (8) | 0.0627 (5) | |
| H13 | 0.5825 | 1.0423 | 0.0630 | 0.075* | |
| C14 | 0.2660 (3) | 0.99109 (19) | 0.05686 (7) | 0.0628 (5) | |
| H14 | 0.2168 | 1.0681 | 0.0353 | 0.075* | |
| C15 | 0.1208 (3) | 0.8931 (2) | 0.07213 (8) | 0.0655 (5) | |
| H15 | −0.0274 | 0.9047 | 0.0611 | 0.079* | |
| C16 | 0.1909 (3) | 0.77622 (18) | 0.10389 (7) | 0.0538 (4) | |
| H16 | 0.0908 | 0.7102 | 0.1142 | 0.065* | |
| O2 | 0.9399 (2) | 0.25032 (13) | 0.10377 (6) | 0.0694 (4) | |
| H2A | 1.0565 | 0.2620 | 0.1223 | 0.104* | |
| O3A | 1.0228 (15) | 0.4644 (11) | 0.0753 (5) | 0.072 (2) | 0.63 (3) |
| O3B | 0.951 (3) | 0.4828 (6) | 0.0985 (9) | 0.070 (5) | 0.37 (3) |
| C17 | 0.8870 (3) | 0.36824 (17) | 0.07825 (6) | 0.0494 (4) | |
| C18 | 0.6762 (3) | 0.36172 (16) | 0.04285 (6) | 0.0491 (4) | |
| H18A | 0.5619 | 0.3312 | 0.0631 | 0.059* | |
| H18B | 0.6882 | 0.2888 | 0.0162 | 0.059* | |
| C19 | 0.6100 (3) | 0.50345 (16) | 0.01626 (6) | 0.0494 (4) | |
| H19A | 0.6069 | 0.5781 | 0.0427 | 0.059* | |
| H19B | 0.7188 | 0.5308 | −0.0060 | 0.059* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1A | 0.047 (3) | 0.085 (4) | 0.138 (8) | −0.023 (2) | −0.033 (4) | 0.071 (4) |
| O1B | 0.052 (3) | 0.028 (2) | 0.073 (4) | −0.0097 (15) | −0.024 (2) | 0.011 (2) |
| N1 | 0.0423 (6) | 0.0333 (6) | 0.0467 (7) | −0.0045 (5) | −0.0037 (5) | 0.0046 (5) |
| N3 | 0.0559 (8) | 0.0299 (6) | 0.0536 (7) | −0.0047 (5) | −0.0074 (6) | 0.0067 (5) |
| N6 | 0.0365 (6) | 0.0308 (6) | 0.0470 (6) | 0.0002 (4) | −0.0071 (5) | 0.0062 (5) |
| N7 | 0.0399 (6) | 0.0269 (5) | 0.0503 (7) | 0.0015 (5) | −0.0079 (5) | 0.0000 (5) |
| N9 | 0.0495 (7) | 0.0310 (6) | 0.0561 (7) | 0.0051 (5) | −0.0108 (6) | 0.0036 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0519 (9) | 0.0325 (7) | 0.0528 (8) | −0.0091 (6) | −0.0060 (7) | 0.0062 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0444 (8) | 0.0292 (6) | 0.0412 (7) | 0.0023 (5) | −0.0023 (6) | 0.0017 (5) |
| C5 | 0.0381 (7) | 0.0280 (6) | 0.0383 (7) | 0.0015 (5) | −0.0002 (6) | −0.0008 (5) |
| C6 | 0.0380 (7) | 0.0290 (6) | 0.0362 (6) | 0.0006 (5) | 0.0007 (6) | 0.0015 (5) |
| C8 | 0.0423 (8) | 0.0341 (7) | 0.0550 (8) | 0.0045 (6) | −0.0101 (7) | −0.0007 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0461 (8) | 0.0357 (7) | 0.0611 (9) | −0.0047 (6) | −0.0131 (7) | 0.0124 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0472 (8) | 0.0303 (6) | 0.0441 (7) | 0.0017 (6) | −0.0019 (6) | 0.0044 (5) |
| C12 | 0.0510 (9) | 0.0398 (8) | 0.0710 (11) | −0.0011 (7) | 0.0017 (8) | 0.0131 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0716 (12) | 0.0437 (9) | 0.0746 (12) | 0.0012 (8) | 0.0155 (10) | 0.0202 (8) |
| C14 | 0.0809 (13) | 0.0479 (9) | 0.0590 (10) | 0.0163 (9) | 0.0061 (9) | 0.0205 (8) |
| C15 | 0.0542 (10) | 0.0617 (11) | 0.0771 (12) | 0.0142 (9) | −0.0059 (9) | 0.0204 (9) |
| C16 | 0.0464 (9) | 0.0455 (8) | 0.0672 (10) | 0.0021 (7) | −0.0019 (8) | 0.0146 (7) |
| O2 | 0.0568 (7) | 0.0461 (6) | 0.0963 (10) | −0.0026 (5) | −0.0264 (7) | 0.0128 (6) |
| O3A | 0.061 (3) | 0.072 (2) | 0.076 (4) | −0.026 (2) | −0.024 (3) | 0.027 (2) |
| O3B | 0.069 (5) | 0.037 (2) | 0.092 (8) | −0.006 (2) | −0.035 (5) | 0.002 (2) |
| C17 | 0.0477 (9) | 0.0428 (8) | 0.0544 (9) | −0.0017 (7) | −0.0073 (7) | 0.0029 (7) |
| C18 | 0.0472 (8) | 0.0408 (8) | 0.0558 (9) | −0.0017 (6) | −0.0071 (7) | −0.0016 (7) |
| C19 | 0.0481 (9) | 0.0411 (8) | 0.0554 (9) | −0.0023 (6) | −0.0070 (7) | 0.0023 (7) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1A—C10 | 1.247 (6) | C12—C13 | 1.378 (2) |
| O1B—C10 | 1.221 (6) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C6 | 1.3424 (17) | C13—C14 | 1.363 (3) |
| N1—C2 | 1.3489 (17) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| N3—C2 | 1.3125 (19) | C14—C15 | 1.365 (3) |
| N3—C4 | 1.3401 (18) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| N6—C10 | 1.3551 (18) | C15—C16 | 1.390 (2) |
| N6—C6 | 1.3926 (16) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| N6—H6 | 0.8600 | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| N7—C8 | 1.3415 (17) | O2—C17 | 1.2923 (18) |
| N7—C5 | 1.3712 (17) | O2—H2A | 0.8200 |
| N7—H7 | 0.8601 | O3A—C17 | 1.230 (4) |
| N9—C8 | 1.3175 (19) | O3B—C17 | 1.223 (6) |
| N9—C4 | 1.3684 (18) | C17—C18 | 1.495 (2) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C18—C19 | 1.509 (2) |
| C4—C5 | 1.4096 (17) | C18—H18A | 0.9700 |
| C5—C6 | 1.3931 (18) | C18—H18B | 0.9700 |
| C8—H8 | 0.9300 | C19—C19i | 1.506 (3) |
| C10—C11 | 1.4924 (18) | C19—H19A | 0.9700 |
| C11—C16 | 1.376 (2) | C19—H19B | 0.9700 |
| C11—C12 | 1.380 (2) | ||
| C6—N1—C2 | 119.23 (11) | C13—C12—H12 | 119.6 |
| C2—N3—C4 | 112.56 (12) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.6 |
| C10—N6—C6 | 127.77 (11) | C14—C13—C12 | 119.81 (17) |
| C10—N6—H6 | 116.0 | C14—C13—H13 | 120.1 |
| C6—N6—H6 | 116.2 | C12—C13—H13 | 120.1 |
| C8—N7—C5 | 106.82 (11) | C13—C14—C15 | 119.86 (15) |
| C8—N7—H7 | 126.7 | C13—C14—H14 | 120.1 |
| C5—N7—H7 | 126.5 | C15—C14—H14 | 120.1 |
| C8—N9—C4 | 103.90 (11) | C14—C15—C16 | 121.01 (16) |
| N3—C2—N1 | 128.29 (13) | C14—C15—H15 | 119.5 |
| N3—C2—H2 | 115.9 | C16—C15—H15 | 119.5 |
| N1—C2—H2 | 115.9 | C11—C16—C15 | 119.12 (16) |
| N3—C4—N9 | 124.79 (12) | C11—C16—H16 | 120.4 |
| N3—C4—C5 | 124.74 (12) | C15—C16—H16 | 120.4 |
| N9—C4—C5 | 110.47 (12) | C17—O2—H2A | 109.5 |
| N7—C5—C6 | 137.86 (12) | O3B—C17—O2 | 117.6 (6) |
| N7—C5—C4 | 104.56 (11) | O3A—C17—O2 | 120.5 (3) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 117.57 (12) | O3B—C17—C18 | 120.5 (3) |
| N1—C6—N6 | 113.77 (11) | O3A—C17—C18 | 122.7 (2) |
| N1—C6—C5 | 117.61 (11) | O2—C17—C18 | 114.98 (13) |
| N6—C6—C5 | 128.60 (12) | C17—C18—C19 | 114.09 (13) |
| N9—C8—N7 | 114.25 (12) | C17—C18—H18A | 108.7 |
| N9—C8—H8 | 122.9 | C19—C18—H18A | 108.7 |
| N7—C8—H8 | 122.9 | C17—C18—H18B | 108.7 |
| O1B—C10—N6 | 119.4 (5) | C19—C18—H18B | 108.7 |
| O1A—C10—N6 | 120.7 (5) | H18A—C18—H18B | 107.6 |
| O1B—C10—C11 | 120.0 (3) | C19i—C19—C18 | 112.99 (16) |
| O1A—C10—C11 | 117.6 (3) | C19i—C19—H19A | 109.0 |
| N6—C10—C11 | 118.50 (12) | C18—C19—H19A | 109.0 |
| C16—C11—C12 | 119.33 (13) | C19i—C19—H19B | 109.0 |
| C16—C11—C10 | 125.15 (14) | C18—C19—H19B | 109.0 |
| C12—C11—C10 | 115.52 (13) | H19A—C19—H19B | 107.8 |
| C13—C12—C11 | 120.82 (16) | ||
| C4—N3—C2—N1 | 0.6 (3) | C6—N6—C10—O1B | −23.5 (8) |
| C6—N1—C2—N3 | −0.5 (3) | C6—N6—C10—O1A | 13.7 (14) |
| C2—N3—C4—N9 | −179.85 (15) | C6—N6—C10—C11 | 173.08 (14) |
| C2—N3—C4—C5 | −0.1 (2) | O1B—C10—C11—C16 | −138.8 (8) |
| C8—N9—C4—N3 | 179.82 (16) | O1A—C10—C11—C16 | −175.5 (14) |
| C8—N9—C4—C5 | 0.06 (18) | N6—C10—C11—C16 | 24.5 (3) |
| C8—N7—C5—C6 | −179.15 (18) | O1B—C10—C11—C12 | 40.7 (9) |
| C8—N7—C5—C4 | −0.01 (16) | O1A—C10—C11—C12 | 4.0 (14) |
| N3—C4—C5—N7 | −179.79 (15) | N6—C10—C11—C12 | −156.02 (16) |
| N9—C4—C5—N7 | −0.03 (17) | C16—C11—C12—C13 | −2.8 (3) |
| N3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.4 (2) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 177.68 (17) |
| N9—C4—C5—C6 | 179.31 (13) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 1.8 (3) |
| C2—N1—C6—N6 | 178.40 (13) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 0.0 (3) |
| C2—N1—C6—C5 | −0.2 (2) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −0.7 (3) |
| C10—N6—C6—N1 | −175.34 (15) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | 2.0 (3) |
| C10—N6—C6—C5 | 3.0 (3) | C10—C11—C16—C15 | −178.52 (16) |
| N7—C5—C6—N1 | 179.62 (16) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | −0.3 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—N1 | 0.6 (2) | O3B—C17—C18—C19 | 26.0 (16) |
| N7—C5—C6—N6 | 1.3 (3) | O3A—C17—C18—C19 | −19.2 (10) |
| C4—C5—C6—N6 | −177.74 (14) | O2—C17—C18—C19 | 176.05 (16) |
| C4—N9—C8—N7 | −0.08 (19) | C17—C18—C19—C19i | −176.11 (18) |
| C5—N7—C8—N9 | 0.06 (19) |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg is the centroid of the C11–C16 phenyl ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O2—H2A···N1ii | 0.82 | 1.92 | 2.7327 (19) | 175 |
| N6—H6···O3Aiii | 0.86 | 2.09 | 2.904 (11) | 157 |
| N7—H7···O1A | 0.86 | 2.04 | 2.616 (16) | 124 |
| N7—H7···N9iv | 0.86 | 2.17 | 2.9271 (17) | 146 |
| C19—H19B···O3Av | 0.97 | 2.54 | 3.481 (11) | 164 |
| C2—H2···Cg3vi | 0.93 | 2.94 | 3.4611 (16) | 117 |
Symmetry codes: (ii) x+1, y, z; (iii) x−1, y, z; (iv) −x+2, y+1/2, −z+1/2; (v) −x+2, −y+1, −z; (vi) x, y−1, z.
References
- Agilent (2013). CrysAlis PRO. Agilent Technologies UK Ltd, Yarnton, England.
- Bučar, D. K., Henry, R. F., Lou, X., Borchardt, T. & Zhang, G. G. Z. (2007). Chem. Commun. pp. 525–527. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Byres, M., Cox, P. J., Kay, G. & Nixon, E. (2009). CrystEngComm, 11, 135–142.
- Das, B. & Baruah, J. B. (2011). J. Mol. Struct. 1001, 134–138.
- Goswami, S., Hazra, A. & Fun, H.-K. (2010). J. Incl Phenom. Macrocycl Chem. 68, 461–466.
- Karthikeyan, A., Jeeva Jasmine, N., Thomas Muthiah, P. & Perdih, F. (2016). Acta Cryst. E72, 140–143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Karthikeyan, A., Swinton Darious, R., Thomas Muthiah, P. & Perdih, F. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 985–990. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Lemmerer, A., Bernstein, J. & Kahlenberg, V. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Lin, S., Jia, R., Gao, F. & Zhou, X. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o3457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Matulková, I., Císařová, I., Němec, I. & Fábry, J. (2014). Acta Cryst. C70, 927–933. [DOI] [PubMed]
- McHugh, C. & Erxleben, A. (2011). Cryst. Growth Des. 11, 5096–5104.
- Nirmalram, J. S., Tamilselvi, D. & Muthiah, P. T. (2011). J. Chem. Crystallogr. 41, 864–867.
- Palatinus, L. & Chapuis, G. (2007). J. Appl. Cryst. 40, 786–790.
- Raghunathan, S. & Pattabhi, V. (1981). Acta Cryst. B37, 1670–1673.
- Raghunathan, S., Sinha, B. K., Pattabhi, V. & Gabe, E. J. (1983). Acta Cryst. C39, 1545–1547.
- Roew, R., Sheskey, P. & Quinn, M. (2009). Adipic Acid, Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients, pp. 11–12.
- Safaei-Ghomi, J., Aghabozorg, H., Motyeian, E. & Ghadermazi, M. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, m2–m3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Soriano-Garcia, M. & Parthasarathy, R. (1977). Acta Cryst. B33, 2674–2677.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Srinivasa Gopalan, R., Kumaradhas, P. & Kulkarni, G. U. (1999). J. Solid State Chem. 148, 129–134.
- Srinivasa Gopalan, R., Kumaradhas, P., Kulkarni, G. U. & Rao, C. N. R. (2000). J. Mol. Struct. 521, 97–106.
- Stanley, N., Muthiah, P. T. & Geib, S. J. (2003). Acta Cryst. C59, o27–o29. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Tamilselvi, D. & Muthiah, P. T. (2011). Acta Cryst. C67, o192–o194. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Thanigaimani, K., Razak, I. A., Arshad, S., Jagatheesan, R. & Santhanaraj, K. J. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o2938–o2939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Umadevi, B., Stanley, N., Muthiah, P. T., Bocelli, G. & Cantoni, A. (2001). Acta Cryst. E57, o881–o883.
- Xia, M., Ma, K. & Zhu, Y. (2010). J. Chem. Crystallogr. 40, 634–638.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016007581/hg5474sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016007581/hg5474Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016007581/hg5474Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1478504
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report