The crystal structures of three N-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]benzamides are reported. The 3-fluorobenzamide crystallized with two independent molecules in the asymmetric unit; the dihedral angles between the two benzene rings are 43.94 (8) and 55.66 (7)°. In the 3-bromobenzamide and the 3-iodobenzamide, this dihedral angle is much smaller, viz. 10.40 (12) and 12.5 (2)°, respectively.
Keywords: crystal structure, amide, benzamide, 2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl, N—H⋯O hydrogen bonding, halogen–halogen contacts
Abstract
In the title compounds, C14H9F4NO, (I), C14H9BrF3NO, (II), and C14H9F3INO, (III), the two benzene rings are inclined to one another by 43.94 (8)° in molecule A and 55.66 (7)° in molecule B of compound (I), which crystallizes with two independent molecules in the asymmetric unit, but by only 10.40 (12)° in compound (II) and 12.5 (2)° in compound (III). In the crystals of all three compounds, N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link the molecules to form chains propagating along the a-axis direction for (I), and along the b-axis direction for (II) and (III). In the crystal of (I), –A–B–A–B– chains are linked by C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming layers parallel to (010). Within the layers there are weak offset π–π interactions present [intercentroid distances = 3.868 (1) and 3.855 (1) Å]. In the crystals of (II) and (III), the chains are linked via short halogen–halogen contacts [Br⋯Br = 3.6141 (4) Å in (II) and I⋯I = 3.7797 (5) Å in (III)], resulting in the formation of ribbons propagating along the b-axis direction.
Chemical context
Amides are very common in nature, and are easily synthesized and provide structural rigidity to various molecules (Gowda et al., 2003 ▸). Furthermore, N-arylamides show a broad spectrum of pharmacological properties, including antibacterial (Manojkumar et al., 2013a
▸), antitumor (Abdou et al., 2004 ▸), antioxidant, analgesic and antiviral activity (Manojkumar et al., 2013b
▸). In view of their importance, the title N-(2-trifluoromethylphenyl)benzamides (I)–(III) were synthesized and we report herein on their crystal structures.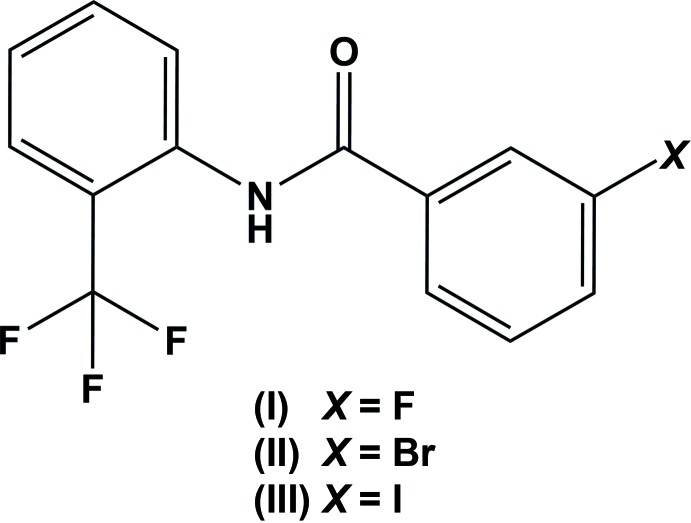
Structural commentary
The molecular structure of compound (I) is illustrated in Fig. 1 ▸. It crystallizes with two independent molecules (A and B) in the asymmetric unit, which slightly differ in their molecular conformations, as shown in the AutoMolFit diagram (Fig. 2 ▸; Spek, 2009 ▸). In both molecules, the 3-fluoro substituent on the benzoic acid ring and the 2-CF3 substituent on the aniline ring are anti to one another, and the 3-fluoro substituent is anti to the N—H bond in the central –Car—C(=O)—N—Car– (ar = aromatic) segment of the molecules. The dihedral angle between the two benzene rings is 43.94 (8)° in molecule A, while in molecule B it is larger, being 55.66 (7)°. The torsion angle of the central –Car—C(=O)—N—Car– segment is 176.74 (12)° in molecule A and −179.58 (12)° in molecule B.
Figure 1.
A view of the molecular structure of compound (I), showing the atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Figure 2.
A view of the molecular fit of molecules A (black) and B (red) of compound (I).
The molecular structures of compounds (II) and (III) are illustrated in Figs. 3 ▸ and 4 ▸, respectively. Here, the 3-bromo and 3-iodo substituents on the benzoic acid ring and the 2-CF3 substitution on the aniline ring are anti to one another, and the 3-bromo and 3-iodo substituents are anti to the N—H bond in the central –Car—C(=O)—N—Car– segment of the molecules, similar to situation observed in (I). The dihedral angle between the two benzene rings is 10.40 (12)° in (II) and 12.5 (2)° in (III), which is much less than observed for molecules A and B of compound (I). The torsion angle of the central –Car—C(=O)—N—Car– segment is −175.5 (2)° in (II) and 174.8 (3)° in (III), again similar to that in molecules A and B of compound (I).
Figure 3.
A view of the molecular structure of compound (II), showing the atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Figure 4.
A view of the molecular structure of compound (III), showing the atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Supramolecular features
In the crystal of (I), strong N1—H1⋯O2 and N2—H2⋯O1 hydrogen bonds link the molecules to form –A–B–A–B– C(4) chains running along the a-axis direction (Table 1 ▸ and Fig. 5 ▸). Neighbouring chains are linked via C5—H5⋯O2 and C12—H12⋯O1 hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▸), forming layers lying parallel to the ac plane (Fig. 6 ▸). Within the layers there are weak offset π–π interactions present involving the aniline and benzoic acid rings [Cg1⋯Cg4 = 3.8682 (9) Å and Cg2⋯Cg3i = 3.8553 (9) Å; Cg1 and Cg3 are the centroids of the aniline rings C1–C6 and C15–C20, respectively; Cg2 and Cg4 are the centroids of the benzoic acid rings C8–C13 and C22–C27, respectively; symmetry code (i) x − 1, y, z]. The crystal structure does not feature any C—H⋯F or F⋯F interactions (Fig. 6 ▸).
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (I) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯O2 | 0.87 (2) | 2.01 (2) | 2.8239 (16) | 157 (1) |
| N2—H2⋯O1i | 0.89 (2) | 1.99 (2) | 2.8303 (16) | 158 (1) |
| C5—H5⋯O2ii | 0.95 | 2.35 | 3.2861 (18) | 167 |
| C12—H12⋯O1iii | 0.95 | 2.45 | 3.3172 (17) | 152 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
Figure 5.
A view along the c axis of the crystal packing of compound (I). The N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines (see Table 1 ▸).
Figure 6.
A view along the b axis of the crystal packing of compound (I). The C—H⋯O (see Table 1 ▸) and π–π interactions are shown as dashed lines.
The crystal structure of (II), features strong N1—H1⋯O1 hydrogen bonds (Fig. 7 ▸ and Table 2 ▸) similar to those observed in (I), linking the molecules into C(4) chains running parallel to the b axis (Fig. 7 ▸). Adjacent chains are connected via short Br⋯Br contacts [3.6141 (4) Å], forming ribbons along [010]; see Fig. 7 ▸.
Figure 7.
A view along the b axis of the crystal packing of compound (II). The N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (see Table 2 ▸) and the Br⋯Br contacts are shown as dashed lines.
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (II) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯O1i | 0.89 (2) | 2.00 (2) | 2.835 (2) | 156 (3) |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
The crystal structure of (III), features similar characteristics to that of (II). Strong N1—H1⋯O1 hydrogen bonds link the molecules into C(4) chains running parallel to the b axis (Table 3 ▸ and Fig. 8 ▸). Adjacent chains are linked via short I⋯I contacts [3.7797 (5) Å], forming ribbons along [010]; see Fig. 8 ▸.
Table 3. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (III) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯O1i | 0.89 (3) | 1.99 (4) | 2.826 (5) | 156 (5) |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Figure 8.
A view along the b axis of the crystal packing of compound (III). The N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (see Table 3 ▸) and the I⋯I contacts are shown as dashed lines.
From the above observations, it can be concluded that the bromo and iodo substitutions on the meta position of the benzoic acid ring have a similar effect on the molecular conformations and the supramolecular architectures exhibited by this class of compounds, whereas the fluoro substitution has a very different influence. For instance, there are two molecules in the asymmetric unit of (I) compared to one molecules in those of (II) and (III). Also, the dihedral angle between the two benzene rings is much larger in the two molecules (A and B) of (I), compared to the values observed in (II) and (III). Furthermore, the crystal structures of both (II) and (III) feature short halogen⋯halogen contacts, in addition to the N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, resulting in one-dimensional structures, whereas in (I), in the absence of F⋯F contacts, C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and π–π interactions are observed, in addition to the strong N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, resulting in a two-dimensional architecture.
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD; Version 5.37, update February 2016; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) for similar compounds viz. N-(2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)arylamides, gave four hits. They include N-(2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)benzamide, for which there are three reports: JOZFUB and JOZFUB01 in space group P43 (Hathwar et al., 2014 ▸) and LASHOE in space group P41 (Panini & Chopra, 2012 ▸), and 2-(trifluoromethyl)-N-(2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)benzamide (LASKAT; Panini & Chopra, 2012 ▸). In compounds LASHOE and LASKAT, the 2-CF3 group in the aniline ring is nearly syn to the N—H bond in the central amide segment of the molecule, as observed in the title compounds. In LASHOE (Panini & Chopra, 2012 ▸), the dihedral angle between the two benzene rings is 41.3 (1)°, and the torsion angle of the central –Car—N—C(=O)—Car– segment is 175.1 (5)°, which is very close to the values observed for the two independent molecules in compound (I). This shows that introducing a fluorine atom into the meta position of the benzoyl ring, as in compound (I), has little effect on the molecular conformation of this class of compounds.
Synthesis and crystallization
The different substituted benzoic acids (3 mmol) were dissolved in phosphorous oxychloride taken in a 250 ml round-bottomed flask. The mixtures were refluxed for an hour and later cooled to 273 K. An equimolar amount of 2-(trifluoromethyl)aniline was added dropwise to these mixtures with continuous stirring. After completion of the addition, the reaction mixtures were brought to room temperature and stirring was continued for 1 h. The reaction mixtures were poured into ice-cold water. The solids that separated were washed thoroughly with water, followed by washing with dilute hydrochloric acid, water, aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution and again with water. The compounds were filtered under suction, dried and recrystallized from aqueous ethanol to constant melting points. Prismatic colourless single crystals of all three compounds were obtained by slow evaporation of solutions in methanol, with a few drops of water.
Refinement details
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 4 ▸. In all three compounds the NH H atoms were located in difference Fourier maps and refined with a distance restraint: N—H = 0.90 (4) Å. The C-bound H atoms were positioned with idealized geometry and refined using a riding model: C—H = 0.95 Å, with U
iso = 1.2U
eq(C). In the final cycles of refinement of compound (III), a bad reflection ( 2 2) was omitted, which lead to an improvement in the values of R1, wR2, and GOF.
2 2) was omitted, which lead to an improvement in the values of R1, wR2, and GOF.
Table 4. Experimental details.
| (I) | (II) | (III) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | |||
| Chemical formula | C14H9F4NO | C14H9BrF3NO | C14H9F3INO |
| M r | 283.22 | 344.13 | 391.12 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c | Monoclinic, P21/n | Monoclinic, P21/n |
| Temperature (K) | 173 | 173 | 173 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 8.0258 (2), 39.7598 (12), 7.8932 (2) | 12.9456 (6), 4.7377 (2), 21.9025 (10) | 13.3358 (6), 4.7471 (2), 22.3558 (10) |
| β (°) | 103.937 (1) | 104.770 (2) | 105.848 (2) |
| V (Å3) | 2444.60 (11) | 1298.94 (10) | 1361.47 (10) |
| Z | 8 | 4 | 4 |
| Radiation type | Cu Kα | Cu Kα | Cu Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 1.22 | 4.63 | 18.78 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.29 × 0.22 × 0.19 | 0.28 × 0.24 × 0.20 | 0.27 × 0.22 × 0.18 |
| Data collection | |||
| Diffractometer | Bruker APEXII CCD | Bruker APEXII CCD | Bruker APEXII CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009 ▸) | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009 ▸) | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.760, 0.793 | 0.315, 0.396 | 0.081, 0.133 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 13874, 3997, 3816 | 8466, 2114, 1986 | 7120, 2223, 2124 |
| R int | 0.034 | 0.039 | 0.053 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.584 | 0.585 | 0.584 |
| Refinement | |||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.033, 0.091, 1.06 | 0.034, 0.090, 1.05 | 0.043, 0.109, 1.09 |
| No. of reflections | 3997 | 2114 | 2223 |
| No. of parameters | 369 | 185 | 185 |
| No. of restraints | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.19, −0.17 | 0.62, −0.34 | 1.84, −1.41 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, II, III, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016007866/su5298sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016007866/su5298Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016007866/su5298IIsup3.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) III. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016007866/su5298IIIsup4.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016007866/su5298Isup5.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016007866/su5298IIsup6.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016007866/su5298IIIsup7.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Institution of Excellence, Vijnana Bhavana, University of Mysore, Mysore, for providing the single-crystal X-ray diffraction data.
supplementary crystallographic information
(I) 3-Fluoro-N-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]benzamide . Crystal data
| C14H9F4NO | Prism |
| Mr = 283.22 | Dx = 1.539 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Melting point: 377 K |
| a = 8.0258 (2) Å | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å |
| b = 39.7598 (12) Å | Cell parameters from 143 reflections |
| c = 7.8932 (2) Å | θ = 2.2–64.2° |
| β = 103.937 (1)° | µ = 1.22 mm−1 |
| V = 2444.60 (11) Å3 | T = 173 K |
| Z = 8 | Prism, colourless |
| F(000) = 1152 | 0.29 × 0.22 × 0.19 mm |
(I) 3-Fluoro-N-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]benzamide . Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 3997 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3816 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.034 |
| phi and φ scans | θmax = 64.2°, θmin = 2.2° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009) | h = −9→7 |
| Tmin = 0.760, Tmax = 0.793 | k = −44→45 |
| 13874 measured reflections | l = −6→9 |
(I) 3-Fluoro-N-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]benzamide . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.033 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.091 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.06 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0464P)2 + 0.8967P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3997 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 369 parameters | Δρmax = 0.19 e Å−3 |
| 2 restraints | Δρmin = −0.17 e Å−3 |
(I) 3-Fluoro-N-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]benzamide . Special details
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
(I) 3-Fluoro-N-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]benzamide . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| H2 | 0.667 (2) | 0.1103 (4) | 0.558 (2) | 0.034 (5)* | |
| H1 | 0.140 (2) | 0.1376 (4) | 0.456 (2) | 0.029 (4)* | |
| F5 | 0.33100 (11) | 0.07085 (2) | 0.60352 (10) | 0.0292 (2) | |
| F6 | 0.35108 (12) | 0.01935 (2) | 0.52831 (11) | 0.0329 (2) | |
| F7 | 0.57809 (11) | 0.04694 (2) | 0.65368 (10) | 0.0292 (2) | |
| O2 | 0.35341 (12) | 0.15177 (2) | 0.38529 (12) | 0.0247 (2) | |
| N2 | 0.56532 (16) | 0.11452 (3) | 0.48712 (15) | 0.0222 (3) | |
| F8 | 0.45852 (14) | 0.24815 (2) | 0.79593 (13) | 0.0436 (3) | |
| C21 | 0.48174 (17) | 0.14343 (3) | 0.49780 (17) | 0.0198 (3) | |
| C22 | 0.54636 (17) | 0.16483 (3) | 0.65650 (17) | 0.0210 (3) | |
| C28 | 0.42663 (18) | 0.04946 (3) | 0.53435 (18) | 0.0234 (3) | |
| C15 | 0.51404 (17) | 0.09248 (3) | 0.34014 (17) | 0.0209 (3) | |
| C20 | 0.53464 (19) | 0.10260 (4) | 0.17839 (19) | 0.0254 (3) | |
| H20 | 0.5775 | 0.1244 | 0.1644 | 0.030* | |
| C23 | 0.47773 (19) | 0.19705 (4) | 0.65248 (18) | 0.0252 (3) | |
| H23 | 0.3996 | 0.2052 | 0.5506 | 0.030* | |
| C27 | 0.66387 (18) | 0.15357 (4) | 0.80616 (18) | 0.0238 (3) | |
| H27 | 0.7132 | 0.1318 | 0.8083 | 0.029* | |
| C24 | 0.5257 (2) | 0.21680 (4) | 0.7997 (2) | 0.0291 (3) | |
| C26 | 0.70845 (19) | 0.17425 (4) | 0.95187 (19) | 0.0280 (3) | |
| H26 | 0.7879 | 0.1664 | 1.0537 | 0.034* | |
| C25 | 0.6385 (2) | 0.20607 (4) | 0.95048 (19) | 0.0291 (3) | |
| H25 | 0.6675 | 0.2201 | 1.0506 | 0.035* | |
| C19 | 0.49280 (19) | 0.08093 (4) | 0.03697 (18) | 0.0280 (3) | |
| H19 | 0.5084 | 0.0878 | −0.0734 | 0.034* | |
| C18 | 0.4285 (2) | 0.04928 (4) | 0.05599 (19) | 0.0283 (3) | |
| H18 | 0.3997 | 0.0345 | −0.0413 | 0.034* | |
| C17 | 0.40585 (19) | 0.03907 (4) | 0.21705 (18) | 0.0254 (3) | |
| H17 | 0.3613 | 0.0173 | 0.2300 | 0.030* | |
| C16 | 0.44841 (17) | 0.06066 (4) | 0.35957 (18) | 0.0212 (3) | |
| F1 | 0.01785 (11) | 0.19821 (2) | 0.34114 (10) | 0.0316 (2) | |
| F3 | −0.21044 (11) | 0.17739 (2) | 0.39516 (11) | 0.0316 (2) | |
| F2 | −0.14591 (13) | 0.22917 (2) | 0.45373 (12) | 0.0392 (2) | |
| O1 | −0.08868 (12) | 0.09581 (2) | 0.62751 (12) | 0.0247 (2) | |
| F4 | −0.13792 (16) | −0.00092 (3) | 0.21276 (14) | 0.0509 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.07498 (16) | 0.13350 (3) | 0.52692 (15) | 0.0227 (3) | |
| C7 | −0.01510 (17) | 0.10475 (3) | 0.51462 (17) | 0.0211 (3) | |
| C13 | −0.00037 (19) | 0.09805 (4) | 0.19810 (19) | 0.0263 (3) | |
| H13 | 0.0340 | 0.1209 | 0.1952 | 0.032* | |
| C8 | −0.02734 (17) | 0.08437 (4) | 0.35245 (18) | 0.0223 (3) | |
| C14 | −0.07845 (19) | 0.19824 (4) | 0.45914 (18) | 0.0243 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.09082 (18) | 0.15641 (4) | 0.66916 (18) | 0.0221 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.02149 (18) | 0.18867 (4) | 0.63846 (18) | 0.0223 (3) | |
| C6 | 0.17972 (19) | 0.14752 (4) | 0.83585 (19) | 0.0291 (3) | |
| H6 | 0.2254 | 0.1255 | 0.8577 | 0.035* | |
| C9 | −0.07529 (19) | 0.05080 (4) | 0.3572 (2) | 0.0275 (3) | |
| H9 | −0.0945 | 0.0411 | 0.4610 | 0.033* | |
| C12 | −0.0237 (2) | 0.07837 (4) | 0.04937 (19) | 0.0310 (3) | |
| H12 | −0.0068 | 0.0879 | −0.0557 | 0.037* | |
| C3 | 0.0453 (2) | 0.21184 (4) | 0.7738 (2) | 0.0300 (3) | |
| H3 | −0.0009 | 0.2339 | 0.7528 | 0.036* | |
| C10 | −0.0941 (2) | 0.03200 (4) | 0.2076 (2) | 0.0325 (4) | |
| C11 | −0.0716 (2) | 0.04501 (4) | 0.0527 (2) | 0.0334 (4) | |
| H11 | −0.0886 | 0.0314 | −0.0490 | 0.040* | |
| C5 | 0.2025 (2) | 0.17060 (5) | 0.9713 (2) | 0.0357 (4) | |
| H5 | 0.2633 | 0.1643 | 1.0856 | 0.043* | |
| C4 | 0.1367 (2) | 0.20270 (4) | 0.9394 (2) | 0.0364 (4) | |
| H4 | 0.1543 | 0.2186 | 1.0318 | 0.044* |
(I) 3-Fluoro-N-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]benzamide . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| F5 | 0.0319 (5) | 0.0342 (5) | 0.0230 (4) | 0.0058 (4) | 0.0097 (3) | −0.0001 (3) |
| F6 | 0.0415 (5) | 0.0273 (5) | 0.0320 (5) | −0.0069 (4) | 0.0132 (4) | 0.0028 (4) |
| F7 | 0.0296 (5) | 0.0343 (5) | 0.0208 (4) | 0.0041 (4) | 0.0002 (3) | 0.0055 (3) |
| O2 | 0.0234 (5) | 0.0309 (6) | 0.0180 (5) | 0.0025 (4) | 0.0015 (4) | 0.0013 (4) |
| N2 | 0.0225 (6) | 0.0228 (6) | 0.0182 (6) | −0.0006 (5) | −0.0009 (5) | −0.0026 (5) |
| F8 | 0.0592 (7) | 0.0246 (5) | 0.0447 (6) | 0.0047 (4) | 0.0078 (5) | −0.0076 (4) |
| C21 | 0.0200 (7) | 0.0234 (7) | 0.0170 (6) | −0.0028 (5) | 0.0061 (5) | 0.0024 (5) |
| C22 | 0.0216 (7) | 0.0234 (7) | 0.0190 (7) | −0.0043 (5) | 0.0070 (5) | 0.0002 (5) |
| C28 | 0.0243 (7) | 0.0229 (7) | 0.0223 (7) | 0.0008 (6) | 0.0042 (6) | 0.0006 (5) |
| C15 | 0.0197 (7) | 0.0230 (7) | 0.0182 (7) | 0.0010 (5) | 0.0011 (5) | −0.0014 (5) |
| C20 | 0.0272 (8) | 0.0250 (7) | 0.0236 (7) | −0.0005 (6) | 0.0055 (6) | 0.0022 (6) |
| C23 | 0.0275 (7) | 0.0247 (7) | 0.0230 (7) | −0.0017 (6) | 0.0057 (6) | 0.0013 (6) |
| C27 | 0.0246 (7) | 0.0258 (7) | 0.0204 (7) | −0.0018 (6) | 0.0041 (6) | 0.0001 (6) |
| C24 | 0.0357 (8) | 0.0209 (7) | 0.0328 (8) | −0.0026 (6) | 0.0124 (7) | −0.0031 (6) |
| C26 | 0.0298 (8) | 0.0331 (8) | 0.0196 (7) | −0.0053 (6) | 0.0032 (6) | −0.0007 (6) |
| C25 | 0.0345 (8) | 0.0308 (8) | 0.0227 (7) | −0.0105 (6) | 0.0081 (6) | −0.0072 (6) |
| C19 | 0.0309 (8) | 0.0346 (8) | 0.0180 (7) | 0.0021 (6) | 0.0053 (6) | 0.0020 (6) |
| C18 | 0.0327 (8) | 0.0294 (8) | 0.0210 (7) | 0.0032 (6) | 0.0029 (6) | −0.0055 (6) |
| C17 | 0.0267 (8) | 0.0238 (7) | 0.0241 (7) | 0.0002 (6) | 0.0030 (6) | −0.0027 (6) |
| C16 | 0.0199 (7) | 0.0235 (7) | 0.0193 (7) | 0.0023 (5) | 0.0028 (5) | 0.0008 (6) |
| F1 | 0.0357 (5) | 0.0376 (5) | 0.0238 (4) | 0.0038 (4) | 0.0115 (4) | 0.0090 (4) |
| F3 | 0.0284 (5) | 0.0391 (5) | 0.0241 (4) | −0.0029 (4) | 0.0002 (3) | 0.0043 (4) |
| F2 | 0.0486 (6) | 0.0281 (5) | 0.0412 (5) | 0.0161 (4) | 0.0112 (4) | 0.0085 (4) |
| O1 | 0.0253 (5) | 0.0299 (5) | 0.0187 (5) | −0.0009 (4) | 0.0051 (4) | 0.0028 (4) |
| F4 | 0.0739 (8) | 0.0355 (6) | 0.0510 (6) | −0.0214 (5) | 0.0300 (6) | −0.0176 (5) |
| N1 | 0.0272 (6) | 0.0217 (6) | 0.0213 (6) | 0.0022 (5) | 0.0096 (5) | 0.0012 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0187 (7) | 0.0241 (7) | 0.0194 (7) | 0.0062 (5) | 0.0025 (5) | 0.0046 (5) |
| C13 | 0.0262 (7) | 0.0295 (8) | 0.0230 (7) | 0.0023 (6) | 0.0054 (6) | 0.0037 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0186 (7) | 0.0265 (7) | 0.0213 (7) | 0.0027 (5) | 0.0038 (5) | 0.0014 (6) |
| C14 | 0.0271 (7) | 0.0221 (7) | 0.0246 (7) | 0.0033 (6) | 0.0081 (6) | 0.0025 (6) |
| C1 | 0.0219 (7) | 0.0251 (7) | 0.0197 (7) | −0.0002 (6) | 0.0061 (5) | 0.0009 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0234 (7) | 0.0232 (7) | 0.0214 (7) | −0.0005 (6) | 0.0072 (5) | 0.0005 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0267 (8) | 0.0348 (8) | 0.0247 (8) | 0.0019 (6) | 0.0040 (6) | 0.0072 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0284 (8) | 0.0295 (8) | 0.0258 (7) | −0.0019 (6) | 0.0088 (6) | −0.0003 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0288 (8) | 0.0437 (9) | 0.0203 (7) | 0.0016 (7) | 0.0057 (6) | 0.0014 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0359 (9) | 0.0274 (8) | 0.0287 (8) | −0.0034 (6) | 0.0115 (7) | −0.0060 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0325 (8) | 0.0307 (8) | 0.0357 (9) | −0.0069 (7) | 0.0112 (7) | −0.0077 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0298 (8) | 0.0444 (10) | 0.0264 (8) | −0.0021 (7) | 0.0074 (6) | −0.0112 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0318 (8) | 0.0542 (11) | 0.0191 (7) | −0.0077 (8) | 0.0022 (6) | 0.0032 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0410 (9) | 0.0450 (10) | 0.0244 (8) | −0.0117 (8) | 0.0100 (7) | −0.0115 (7) |
(I) 3-Fluoro-N-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]benzamide . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| F5—C28 | 1.3462 (16) | F1—C14 | 1.3459 (17) |
| F6—C28 | 1.3377 (16) | F3—C14 | 1.3440 (17) |
| F7—C28 | 1.3503 (17) | F2—C14 | 1.3403 (17) |
| O2—C21 | 1.2324 (17) | O1—C7 | 1.2338 (17) |
| N2—H2 | 0.889 (18) | F4—C10 | 1.3583 (19) |
| N2—C21 | 1.3438 (18) | N1—H1 | 0.868 (18) |
| N2—C15 | 1.4327 (18) | N1—C7 | 1.3437 (19) |
| F8—C24 | 1.3557 (18) | N1—C1 | 1.4273 (18) |
| C21—C22 | 1.4998 (19) | C7—C8 | 1.498 (2) |
| C22—C23 | 1.392 (2) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| C22—C27 | 1.396 (2) | C13—C8 | 1.398 (2) |
| C28—C16 | 1.4993 (19) | C13—C12 | 1.385 (2) |
| C15—C20 | 1.386 (2) | C8—C9 | 1.392 (2) |
| C15—C16 | 1.393 (2) | C14—C2 | 1.498 (2) |
| C20—H20 | 0.9500 | C1—C2 | 1.396 (2) |
| C20—C19 | 1.386 (2) | C1—C6 | 1.383 (2) |
| C23—H23 | 0.9500 | C2—C3 | 1.388 (2) |
| C23—C24 | 1.378 (2) | C6—H6 | 0.9500 |
| C27—H27 | 0.9500 | C6—C5 | 1.387 (2) |
| C27—C26 | 1.389 (2) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| C24—C25 | 1.378 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.375 (2) |
| C26—H26 | 0.9500 | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C26—C25 | 1.383 (2) | C12—C11 | 1.383 (2) |
| C25—H25 | 0.9500 | C3—H3 | 0.9500 |
| C19—H19 | 0.9500 | C3—C4 | 1.385 (2) |
| C19—C18 | 1.382 (2) | C10—C11 | 1.378 (2) |
| C18—H18 | 0.9500 | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| C18—C17 | 1.387 (2) | C5—H5 | 0.9500 |
| C17—H17 | 0.9500 | C5—C4 | 1.381 (3) |
| C17—C16 | 1.391 (2) | C4—H4 | 0.9500 |
| C21—N2—H2 | 121.3 (12) | C7—N1—H1 | 120.6 (11) |
| C21—N2—C15 | 121.57 (12) | C7—N1—C1 | 122.97 (12) |
| C15—N2—H2 | 115.8 (12) | C1—N1—H1 | 115.8 (11) |
| O2—C21—N2 | 121.88 (12) | O1—C7—N1 | 122.38 (13) |
| O2—C21—C22 | 120.67 (12) | O1—C7—C8 | 121.14 (13) |
| N2—C21—C22 | 117.41 (12) | N1—C7—C8 | 116.45 (12) |
| C23—C22—C21 | 116.60 (12) | C8—C13—H13 | 120.0 |
| C23—C22—C27 | 119.84 (13) | C12—C13—H13 | 120.0 |
| C27—C22—C21 | 123.51 (13) | C12—C13—C8 | 120.07 (14) |
| F5—C28—F7 | 105.63 (11) | C13—C8—C7 | 122.83 (13) |
| F5—C28—C16 | 112.95 (11) | C9—C8—C7 | 117.21 (12) |
| F6—C28—F5 | 106.38 (11) | C9—C8—C13 | 119.90 (13) |
| F6—C28—F7 | 106.41 (11) | F1—C14—C2 | 112.80 (12) |
| F6—C28—C16 | 112.65 (11) | F3—C14—F1 | 105.76 (11) |
| F7—C28—C16 | 112.27 (11) | F3—C14—C2 | 113.12 (11) |
| C20—C15—N2 | 119.58 (12) | F2—C14—F1 | 105.87 (11) |
| C20—C15—C16 | 119.81 (13) | F2—C14—F3 | 106.14 (11) |
| C16—C15—N2 | 120.58 (12) | F2—C14—C2 | 112.54 (12) |
| C15—C20—H20 | 119.9 | C2—C1—N1 | 119.57 (12) |
| C19—C20—C15 | 120.13 (13) | C6—C1—N1 | 120.87 (13) |
| C19—C20—H20 | 119.9 | C6—C1—C2 | 119.52 (13) |
| C22—C23—H23 | 120.8 | C1—C2—C14 | 119.84 (12) |
| C24—C23—C22 | 118.46 (13) | C3—C2—C14 | 120.09 (13) |
| C24—C23—H23 | 120.8 | C3—C2—C1 | 120.06 (13) |
| C22—C27—H27 | 120.1 | C1—C6—H6 | 119.8 |
| C26—C27—C22 | 119.85 (14) | C1—C6—C5 | 120.40 (15) |
| C26—C27—H27 | 120.1 | C5—C6—H6 | 119.8 |
| F8—C24—C23 | 118.46 (14) | C8—C9—H9 | 120.9 |
| F8—C24—C25 | 118.60 (13) | C10—C9—C8 | 118.16 (14) |
| C25—C24—C23 | 122.93 (14) | C10—C9—H9 | 120.9 |
| C27—C26—H26 | 119.6 | C13—C12—H12 | 119.8 |
| C25—C26—C27 | 120.80 (14) | C11—C12—C13 | 120.45 (14) |
| C25—C26—H26 | 119.6 | C11—C12—H12 | 119.8 |
| C24—C25—C26 | 118.10 (13) | C2—C3—H3 | 120.1 |
| C24—C25—H25 | 121.0 | C4—C3—C2 | 119.71 (15) |
| C26—C25—H25 | 121.0 | C4—C3—H3 | 120.1 |
| C20—C19—H19 | 119.9 | F4—C10—C9 | 118.27 (14) |
| C18—C19—C20 | 120.20 (13) | F4—C10—C11 | 118.59 (14) |
| C18—C19—H19 | 119.9 | C9—C10—C11 | 123.14 (15) |
| C19—C18—H18 | 120.0 | C12—C11—H11 | 120.9 |
| C19—C18—C17 | 120.04 (13) | C10—C11—C12 | 118.26 (14) |
| C17—C18—H18 | 120.0 | C10—C11—H11 | 120.9 |
| C18—C17—H17 | 120.0 | C6—C5—H5 | 120.1 |
| C18—C17—C16 | 119.99 (14) | C4—C5—C6 | 119.84 (14) |
| C16—C17—H17 | 120.0 | C4—C5—H5 | 120.1 |
| C15—C16—C28 | 120.12 (12) | C3—C4—H4 | 119.8 |
| C17—C16—C28 | 120.05 (13) | C5—C4—C3 | 120.45 (14) |
| C17—C16—C15 | 119.82 (13) | C5—C4—H4 | 119.8 |
| F5—C28—C16—C15 | 54.98 (17) | F1—C14—C2—C1 | −64.46 (17) |
| F5—C28—C16—C17 | −126.11 (14) | F1—C14—C2—C3 | 115.45 (14) |
| F6—C28—C16—C15 | 175.54 (12) | F3—C14—C2—C1 | 55.52 (17) |
| F6—C28—C16—C17 | −5.54 (18) | F3—C14—C2—C3 | −124.56 (14) |
| F7—C28—C16—C15 | −64.33 (16) | F2—C14—C2—C1 | 175.83 (12) |
| F7—C28—C16—C17 | 114.58 (14) | F2—C14—C2—C3 | −4.26 (19) |
| O2—C21—C22—C23 | −12.78 (18) | O1—C7—C8—C13 | 157.12 (13) |
| O2—C21—C22—C27 | 164.63 (13) | O1—C7—C8—C9 | −19.98 (19) |
| N2—C21—C22—C23 | 169.55 (12) | F4—C10—C11—C12 | −178.75 (14) |
| N2—C21—C22—C27 | −13.04 (19) | N1—C7—C8—C13 | −20.83 (19) |
| N2—C15—C20—C19 | 177.07 (13) | N1—C7—C8—C9 | 162.08 (13) |
| N2—C15—C16—C28 | 1.5 (2) | N1—C1—C2—C14 | 3.9 (2) |
| N2—C15—C16—C17 | −177.37 (13) | N1—C1—C2—C3 | −176.01 (13) |
| F8—C24—C25—C26 | −178.96 (13) | N1—C1—C6—C5 | 176.39 (14) |
| C21—N2—C15—C20 | 68.06 (18) | C7—N1—C1—C2 | −115.64 (15) |
| C21—N2—C15—C16 | −113.80 (15) | C7—N1—C1—C6 | 66.89 (19) |
| C21—C22—C23—C24 | 176.07 (13) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 177.40 (13) |
| C21—C22—C27—C26 | −175.71 (13) | C13—C8—C9—C10 | 0.2 (2) |
| C22—C23—C24—F8 | −179.84 (13) | C13—C12—C11—C10 | −0.4 (2) |
| C22—C23—C24—C25 | 0.0 (2) | C8—C13—C12—C11 | −0.8 (2) |
| C22—C27—C26—C25 | −0.4 (2) | C8—C9—C10—F4 | 178.85 (14) |
| C15—N2—C21—O2 | 2.8 (2) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −1.5 (2) |
| C15—N2—C21—C22 | −179.58 (12) | C14—C2—C3—C4 | 179.50 (14) |
| C15—C20—C19—C18 | 0.8 (2) | C1—N1—C7—O1 | −1.2 (2) |
| C20—C15—C16—C28 | 179.68 (13) | C1—N1—C7—C8 | 176.74 (12) |
| C20—C15—C16—C17 | 0.8 (2) | C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.6 (2) |
| C20—C19—C18—C17 | −0.1 (2) | C1—C6—C5—C4 | −0.3 (2) |
| C23—C22—C27—C26 | 1.6 (2) | C2—C1—C6—C5 | −1.1 (2) |
| C23—C24—C25—C26 | 1.2 (2) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.8 (2) |
| C27—C22—C23—C24 | −1.4 (2) | C6—C1—C2—C14 | −178.59 (13) |
| C27—C26—C25—C24 | −1.0 (2) | C6—C1—C2—C3 | 1.5 (2) |
| C19—C18—C17—C16 | −0.2 (2) | C6—C5—C4—C3 | 1.2 (2) |
| C18—C17—C16—C28 | −179.05 (13) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 1.6 (3) |
| C18—C17—C16—C15 | −0.1 (2) | C12—C13—C8—C7 | −176.08 (13) |
| C16—C15—C20—C19 | −1.1 (2) | C12—C13—C8—C9 | 0.9 (2) |
(I) 3-Fluoro-N-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]benzamide . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···O2 | 0.87 (2) | 2.01 (2) | 2.8239 (16) | 157 (1) |
| N2—H2···O1i | 0.89 (2) | 1.99 (2) | 2.8303 (16) | 158 (1) |
| C5—H5···O2ii | 0.95 | 2.35 | 3.2861 (18) | 167 |
| C12—H12···O1iii | 0.95 | 2.45 | 3.3172 (17) | 152 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+1, y, z; (ii) x, y, z+1; (iii) x, y, z−1.
(II) 3-Bromo-N-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]benzamide . Crystal data
| C14H9BrF3NO | Prism |
| Mr = 344.13 | Dx = 1.760 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Melting point: 369 K |
| a = 12.9456 (6) Å | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å |
| b = 4.7377 (2) Å | Cell parameters from 132 reflections |
| c = 21.9025 (10) Å | θ = 6.4–64.4° |
| β = 104.770 (2)° | µ = 4.63 mm−1 |
| V = 1298.94 (10) Å3 | T = 173 K |
| Z = 4 | Prism, colourless |
| F(000) = 680 | 0.28 × 0.24 × 0.20 mm |
(II) 3-Bromo-N-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]benzamide . Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2114 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1986 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.039 |
| phi and φ scans | θmax = 64.4°, θmin = 6.4° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009) | h = −14→15 |
| Tmin = 0.315, Tmax = 0.396 | k = −5→4 |
| 8466 measured reflections | l = −24→25 |
(II) 3-Bromo-N-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]benzamide . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.034 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.090 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.05 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0627P)2 + 0.3564P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2114 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 185 parameters | Δρmax = 0.62 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Δρmin = −0.34 e Å−3 |
(II) 3-Bromo-N-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]benzamide . Special details
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
(II) 3-Bromo-N-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]benzamide . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| H1 | 1.167 (2) | 0.262 (5) | 0.0800 (14) | 0.022 (7)* | |
| Br1 | 0.85044 (2) | 0.78177 (6) | 0.240898 (12) | 0.02952 (16) | |
| F3 | 1.32385 (11) | 0.0139 (3) | 0.09354 (7) | 0.0309 (4) | |
| F1 | 1.46295 (12) | 0.0991 (4) | 0.06107 (8) | 0.0414 (4) | |
| O1 | 1.10042 (14) | 0.8797 (4) | 0.07865 (8) | 0.0262 (4) | |
| C12 | 1.1116 (2) | 0.2628 (5) | 0.25054 (12) | 0.0254 (6) | |
| H12 | 1.1500 | 0.1231 | 0.2784 | 0.031* | |
| F2 | 1.41294 (13) | 0.3932 (3) | 0.12181 (7) | 0.0379 (4) | |
| C14 | 1.3768 (2) | 0.2193 (5) | 0.07210 (13) | 0.0249 (6) | |
| C13 | 1.1429 (2) | 0.3313 (5) | 0.19641 (12) | 0.0240 (5) | |
| H13 | 1.2016 | 0.2364 | 0.1869 | 0.029* | |
| C3 | 1.3518 (2) | 0.4176 (6) | −0.03571 (12) | 0.0285 (6) | |
| H3 | 1.4176 | 0.3321 | −0.0371 | 0.034* | |
| N1 | 1.16903 (15) | 0.4434 (4) | 0.07018 (9) | 0.0210 (4) | |
| C9 | 1.0021 (2) | 0.6762 (5) | 0.17009 (12) | 0.0232 (5) | |
| H9 | 0.9649 | 0.8205 | 0.1431 | 0.028* | |
| C8 | 1.08811 (17) | 0.5397 (5) | 0.15593 (11) | 0.0199 (5) | |
| C1 | 1.21188 (18) | 0.4948 (5) | 0.01743 (11) | 0.0207 (5) | |
| C11 | 1.0248 (2) | 0.3955 (5) | 0.26468 (11) | 0.0267 (5) | |
| H11 | 1.0030 | 0.3468 | 0.3016 | 0.032* | |
| C6 | 1.1575 (2) | 0.6606 (5) | −0.03303 (12) | 0.0254 (5) | |
| H6 | 1.0908 | 0.7434 | −0.0328 | 0.030* | |
| C10 | 0.97086 (18) | 0.6007 (5) | 0.22362 (11) | 0.0232 (5) | |
| C5 | 1.2015 (2) | 0.7035 (6) | −0.08358 (13) | 0.0297 (6) | |
| H5 | 1.1646 | 0.8180 | −0.1178 | 0.036* | |
| C2 | 1.31040 (18) | 0.3751 (5) | 0.01629 (11) | 0.0217 (5) | |
| C4 | 1.2976 (2) | 0.5838 (6) | −0.08530 (12) | 0.0317 (6) | |
| H4 | 1.3264 | 0.6155 | −0.1205 | 0.038* | |
| C7 | 1.11912 (18) | 0.6373 (5) | 0.09788 (11) | 0.0201 (5) |
(II) 3-Bromo-N-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]benzamide . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br1 | 0.0248 (2) | 0.0363 (2) | 0.0329 (2) | 0.00046 (9) | 0.01727 (14) | −0.00145 (10) |
| F3 | 0.0284 (7) | 0.0269 (8) | 0.0370 (8) | 0.0009 (6) | 0.0073 (6) | 0.0084 (6) |
| F1 | 0.0305 (8) | 0.0536 (11) | 0.0446 (9) | 0.0194 (8) | 0.0177 (7) | 0.0089 (8) |
| O1 | 0.0314 (9) | 0.0173 (9) | 0.0350 (10) | 0.0019 (7) | 0.0179 (7) | 0.0024 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0288 (15) | 0.0243 (13) | 0.0234 (14) | 0.0018 (10) | 0.0071 (11) | 0.0019 (9) |
| F2 | 0.0466 (9) | 0.0294 (8) | 0.0297 (8) | −0.0022 (7) | −0.0048 (7) | −0.0037 (6) |
| C14 | 0.0235 (13) | 0.0246 (13) | 0.0281 (14) | 0.0012 (10) | 0.0093 (11) | −0.0042 (9) |
| C13 | 0.0218 (12) | 0.0228 (12) | 0.0286 (13) | −0.0004 (10) | 0.0085 (10) | −0.0024 (10) |
| C3 | 0.0260 (12) | 0.0333 (15) | 0.0295 (13) | −0.0006 (11) | 0.0134 (10) | −0.0044 (11) |
| N1 | 0.0236 (10) | 0.0167 (10) | 0.0262 (10) | 0.0021 (8) | 0.0130 (8) | 0.0024 (8) |
| C9 | 0.0239 (12) | 0.0191 (11) | 0.0283 (13) | −0.0015 (9) | 0.0100 (10) | −0.0013 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0180 (11) | 0.0183 (11) | 0.0250 (12) | −0.0041 (9) | 0.0085 (9) | −0.0012 (9) |
| C1 | 0.0223 (11) | 0.0181 (11) | 0.0234 (11) | −0.0035 (9) | 0.0093 (9) | −0.0035 (9) |
| C11 | 0.0305 (13) | 0.0291 (14) | 0.0207 (12) | −0.0075 (11) | 0.0066 (10) | −0.0018 (10) |
| C6 | 0.0247 (12) | 0.0238 (12) | 0.0278 (13) | 0.0004 (10) | 0.0069 (10) | −0.0005 (10) |
| C10 | 0.0204 (11) | 0.0241 (13) | 0.0281 (12) | −0.0037 (10) | 0.0117 (10) | −0.0042 (10) |
| C5 | 0.0359 (16) | 0.0322 (14) | 0.0207 (14) | −0.0005 (11) | 0.0066 (11) | 0.0026 (10) |
| C2 | 0.0211 (11) | 0.0214 (12) | 0.0235 (12) | −0.0008 (10) | 0.0076 (9) | −0.0037 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0349 (14) | 0.0394 (15) | 0.0249 (13) | −0.0041 (12) | 0.0151 (11) | −0.0005 (11) |
| C7 | 0.0176 (11) | 0.0176 (12) | 0.0264 (12) | −0.0039 (9) | 0.0077 (9) | −0.0016 (9) |
(II) 3-Bromo-N-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]benzamide . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Br1—C10 | 1.900 (2) | N1—C1 | 1.424 (3) |
| F3—C14 | 1.342 (3) | N1—H1 | 0.89 (3) |
| F1—C14 | 1.328 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.381 (3) |
| O1—C7 | 1.226 (3) | C9—C8 | 1.390 (3) |
| C12—C13 | 1.386 (4) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| C12—C11 | 1.389 (4) | C8—C7 | 1.500 (3) |
| C12—H12 | 0.9500 | C1—C6 | 1.392 (3) |
| F2—C14 | 1.350 (3) | C1—C2 | 1.402 (3) |
| C14—C2 | 1.497 (4) | C11—C10 | 1.386 (4) |
| C13—C8 | 1.394 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| C13—H13 | 0.9500 | C6—C5 | 1.383 (4) |
| C3—C4 | 1.380 (4) | C6—H6 | 0.9500 |
| C3—C2 | 1.392 (3) | C5—C4 | 1.376 (4) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C5—H5 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C7 | 1.353 (3) | C4—H4 | 0.9500 |
| C13—C12—C11 | 121.0 (2) | C6—C1—C2 | 119.5 (2) |
| C13—C12—H12 | 119.5 | C6—C1—N1 | 121.2 (2) |
| C11—C12—H12 | 119.5 | C2—C1—N1 | 119.3 (2) |
| F1—C14—F3 | 106.3 (2) | C10—C11—C12 | 118.4 (2) |
| F1—C14—F2 | 105.9 (2) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.8 |
| F3—C14—F2 | 105.3 (2) | C12—C11—H11 | 120.8 |
| F1—C14—C2 | 113.4 (2) | C5—C6—C1 | 119.4 (2) |
| F3—C14—C2 | 113.9 (2) | C5—C6—H6 | 120.3 |
| F2—C14—C2 | 111.5 (2) | C1—C6—H6 | 120.3 |
| C12—C13—C8 | 119.8 (2) | C9—C10—C11 | 121.6 (2) |
| C12—C13—H13 | 120.1 | C9—C10—Br1 | 118.99 (19) |
| C8—C13—H13 | 120.1 | C11—C10—Br1 | 119.40 (18) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 120.1 (2) | C4—C5—C6 | 121.4 (2) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.9 | C4—C5—H5 | 119.3 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.9 | C6—C5—H5 | 119.3 |
| C7—N1—C1 | 125.2 (2) | C3—C2—C1 | 119.9 (2) |
| C7—N1—H1 | 120 (2) | C3—C2—C14 | 118.6 (2) |
| C1—N1—H1 | 114 (2) | C1—C2—C14 | 121.4 (2) |
| C10—C9—C8 | 119.6 (2) | C5—C4—C3 | 119.7 (2) |
| C10—C9—H9 | 120.2 | C5—C4—H4 | 120.1 |
| C8—C9—H9 | 120.2 | C3—C4—H4 | 120.1 |
| C9—C8—C13 | 119.6 (2) | O1—C7—N1 | 123.9 (2) |
| C9—C8—C7 | 116.6 (2) | O1—C7—C8 | 120.5 (2) |
| C13—C8—C7 | 123.7 (2) | N1—C7—C8 | 115.6 (2) |
| C11—C12—C13—C8 | 1.2 (4) | N1—C1—C2—C3 | 178.3 (2) |
| C10—C9—C8—C13 | −1.0 (3) | C6—C1—C2—C14 | 173.9 (2) |
| C10—C9—C8—C7 | −178.6 (2) | N1—C1—C2—C14 | −6.4 (3) |
| C12—C13—C8—C9 | −0.3 (4) | F1—C14—C2—C3 | −10.1 (3) |
| C12—C13—C8—C7 | 177.1 (2) | F3—C14—C2—C3 | −131.8 (2) |
| C7—N1—C1—C6 | −40.8 (3) | F2—C14—C2—C3 | 109.3 (3) |
| C7—N1—C1—C2 | 139.5 (2) | F1—C14—C2—C1 | 174.5 (2) |
| C13—C12—C11—C10 | −0.7 (4) | F3—C14—C2—C1 | 52.8 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.2 (4) | F2—C14—C2—C1 | −66.1 (3) |
| N1—C1—C6—C5 | −179.5 (2) | C6—C5—C4—C3 | −0.1 (4) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | 1.5 (4) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | −1.1 (4) |
| C8—C9—C10—Br1 | −178.14 (17) | C1—N1—C7—O1 | 3.6 (4) |
| C12—C11—C10—C9 | −0.6 (4) | C1—N1—C7—C8 | −175.5 (2) |
| C12—C11—C10—Br1 | 178.98 (18) | C9—C8—C7—O1 | 27.0 (3) |
| C1—C6—C5—C4 | 0.5 (4) | C13—C8—C7—O1 | −150.5 (2) |
| C4—C3—C2—C1 | 1.8 (4) | C9—C8—C7—N1 | −153.9 (2) |
| C4—C3—C2—C14 | −173.6 (2) | C13—C8—C7—N1 | 28.5 (3) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −1.4 (3) |
(II) 3-Bromo-N-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]benzamide . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···O1i | 0.89 (2) | 2.00 (2) | 2.835 (2) | 156 (3) |
Symmetry code: (i) x, y−1, z.
(III) 3-Iodo-N-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]benzamide . Crystal data
| C14H9F3INO | Prism |
| Mr = 391.12 | Dx = 1.908 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Melting point: 393 K |
| a = 13.3358 (6) Å | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å |
| b = 4.7471 (2) Å | Cell parameters from 131 reflections |
| c = 22.3558 (10) Å | θ = 6.2–64.3° |
| β = 105.848 (2)° | µ = 18.78 mm−1 |
| V = 1361.47 (10) Å3 | T = 173 K |
| Z = 4 | Prism, colourless |
| F(000) = 752 | 0.27 × 0.22 × 0.18 mm |
(III) 3-Iodo-N-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]benzamide . Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2223 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2124 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.053 |
| phi and φ scans | θmax = 64.3°, θmin = 6.2° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009) | h = −15→14 |
| Tmin = 0.081, Tmax = 0.133 | k = −5→5 |
| 7120 measured reflections | l = −25→25 |
(III) 3-Iodo-N-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]benzamide . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.043 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.109 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.09 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0788P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2223 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 185 parameters | Δρmax = 1.84 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Δρmin = −1.41 e Å−3 |
(III) 3-Iodo-N-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]benzamide . Special details
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
(III) 3-Iodo-N-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]benzamide . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C12 | 1.1208 (4) | 0.7461 (9) | 0.2483 (2) | 0.0187 (10) | |
| H12 | 1.1593 | 0.8842 | 0.2760 | 0.022* | |
| H1 | 1.167 (4) | 0.751 (7) | 0.081 (2) | 0.017 (13)* | |
| I1 | 0.85495 (2) | 0.21117 (7) | 0.240621 (11) | 0.02136 (18) | |
| F1 | 1.32578 (18) | 0.9967 (6) | 0.09091 (11) | 0.0280 (6) | |
| F3 | 1.4613 (2) | 0.8794 (9) | 0.06351 (14) | 0.0448 (8) | |
| C13 | 1.1487 (4) | 0.6826 (9) | 0.19429 (19) | 0.0196 (9) | |
| H13 | 1.2047 | 0.7794 | 0.1847 | 0.024* | |
| O1 | 1.1058 (2) | 0.1341 (7) | 0.07951 (13) | 0.0225 (7) | |
| C3 | 1.3480 (3) | 0.5671 (12) | −0.03282 (19) | 0.0270 (11) | |
| H3 | 1.4136 | 0.6425 | −0.0335 | 0.032* | |
| F2 | 1.4039 (2) | 0.6087 (7) | 0.12348 (11) | 0.0360 (6) | |
| C9 | 1.0116 (3) | 0.3381 (9) | 0.16847 (18) | 0.0177 (8) | |
| H9 | 0.9745 | 0.1950 | 0.1417 | 0.021* | |
| C8 | 1.0943 (3) | 0.4774 (9) | 0.15463 (16) | 0.0147 (8) | |
| C14 | 1.3742 (4) | 0.7780 (9) | 0.0729 (2) | 0.0202 (10) | |
| N1 | 1.1697 (2) | 0.5723 (8) | 0.06981 (14) | 0.0165 (7) | |
| C11 | 1.0390 (3) | 0.6134 (10) | 0.26236 (17) | 0.0204 (9) | |
| H11 | 1.0203 | 0.6594 | 0.2992 | 0.025* | |
| C6 | 1.1542 (3) | 0.3508 (10) | −0.03154 (19) | 0.0216 (9) | |
| H6 | 1.0877 | 0.2776 | −0.0320 | 0.026* | |
| C7 | 1.1231 (3) | 0.3789 (10) | 0.09730 (18) | 0.0165 (9) | |
| C10 | 0.9841 (3) | 0.4115 (9) | 0.22197 (17) | 0.0167 (8) | |
| C1 | 1.2104 (3) | 0.5142 (9) | 0.01811 (16) | 0.0154 (8) | |
| C5 | 1.1976 (5) | 0.2967 (10) | −0.0806 (2) | 0.0277 (11) | |
| H5 | 1.1602 | 0.1826 | −0.1143 | 0.033* | |
| C2 | 1.3078 (3) | 0.6222 (10) | 0.01769 (17) | 0.0184 (8) | |
| C4 | 1.2923 (4) | 0.4035 (12) | −0.08166 (18) | 0.0302 (11) | |
| H4 | 1.3197 | 0.3651 | −0.1158 | 0.036* |
(III) 3-Iodo-N-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]benzamide . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C12 | 0.016 (2) | 0.022 (3) | 0.017 (2) | 0.0021 (16) | 0.0033 (19) | −0.0030 (16) |
| I1 | 0.0206 (2) | 0.0284 (3) | 0.0216 (2) | 0.00032 (9) | 0.01687 (16) | 0.00060 (9) |
| F1 | 0.0282 (13) | 0.0237 (15) | 0.0317 (12) | −0.0011 (11) | 0.0074 (11) | −0.0056 (11) |
| F3 | 0.0302 (15) | 0.067 (2) | 0.0431 (16) | −0.0210 (16) | 0.0205 (13) | −0.0115 (17) |
| C13 | 0.027 (2) | 0.018 (3) | 0.017 (2) | 0.0013 (18) | 0.0107 (18) | 0.0035 (16) |
| O1 | 0.0341 (17) | 0.0156 (17) | 0.0265 (15) | −0.0004 (14) | 0.0233 (13) | −0.0033 (13) |
| C3 | 0.025 (2) | 0.044 (3) | 0.0185 (19) | 0.008 (2) | 0.0166 (17) | 0.006 (2) |
| F2 | 0.0484 (16) | 0.0305 (17) | 0.0216 (12) | 0.0002 (13) | −0.0034 (11) | 0.0045 (12) |
| C9 | 0.019 (2) | 0.019 (2) | 0.0179 (19) | 0.0030 (17) | 0.0096 (16) | 0.0005 (16) |
| C8 | 0.0173 (17) | 0.016 (2) | 0.0145 (16) | 0.0041 (16) | 0.0104 (14) | 0.0004 (15) |
| C14 | 0.020 (3) | 0.026 (3) | 0.017 (2) | −0.0005 (17) | 0.0094 (19) | 0.0018 (16) |
| N1 | 0.0217 (16) | 0.017 (2) | 0.0167 (15) | −0.0002 (14) | 0.0150 (13) | −0.0016 (14) |
| C11 | 0.022 (2) | 0.028 (3) | 0.0143 (18) | 0.0093 (19) | 0.0097 (16) | −0.0019 (18) |
| C6 | 0.024 (2) | 0.024 (3) | 0.0190 (19) | 0.0005 (19) | 0.0092 (17) | −0.0009 (18) |
| C7 | 0.0177 (19) | 0.017 (2) | 0.0181 (19) | 0.0047 (18) | 0.0108 (15) | 0.0015 (18) |
| C10 | 0.0164 (17) | 0.020 (2) | 0.0187 (18) | 0.0016 (17) | 0.0133 (15) | 0.0041 (17) |
| C1 | 0.0194 (18) | 0.017 (2) | 0.0130 (16) | 0.0061 (16) | 0.0099 (15) | 0.0036 (15) |
| C5 | 0.040 (3) | 0.033 (3) | 0.011 (2) | 0.004 (2) | 0.009 (2) | −0.0045 (17) |
| C2 | 0.024 (2) | 0.019 (2) | 0.0157 (18) | 0.0059 (18) | 0.0097 (16) | 0.0016 (17) |
| C4 | 0.037 (2) | 0.044 (3) | 0.0166 (19) | 0.010 (2) | 0.0203 (18) | 0.002 (2) |
(III) 3-Iodo-N-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]benzamide . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C12—H12 | 0.9500 | C9—C10 | 1.387 (5) |
| C12—C13 | 1.390 (6) | C8—C7 | 1.509 (5) |
| C12—C11 | 1.368 (7) | C14—C2 | 1.502 (6) |
| I1—C10 | 2.106 (4) | N1—H1 | 0.89 (3) |
| F1—C14 | 1.342 (5) | N1—C7 | 1.348 (6) |
| F3—C14 | 1.326 (6) | N1—C1 | 1.431 (4) |
| C13—H13 | 0.9500 | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| C13—C8 | 1.382 (6) | C11—C10 | 1.382 (6) |
| O1—C7 | 1.230 (6) | C6—H6 | 0.9500 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C6—C1 | 1.393 (6) |
| C3—C2 | 1.400 (5) | C6—C5 | 1.397 (6) |
| C3—C4 | 1.380 (7) | C1—C2 | 1.399 (6) |
| F2—C14 | 1.356 (5) | C5—H5 | 0.9500 |
| C9—H9 | 0.9500 | C5—C4 | 1.368 (8) |
| C9—C8 | 1.391 (6) | C4—H4 | 0.9500 |
| C13—C12—H12 | 119.4 | C12—C11—H11 | 120.6 |
| C11—C12—H12 | 119.4 | C12—C11—C10 | 118.9 (3) |
| C11—C12—C13 | 121.2 (5) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.6 |
| C12—C13—H13 | 120.3 | C1—C6—H6 | 120.7 |
| C8—C13—C12 | 119.5 (4) | C1—C6—C5 | 118.7 (4) |
| C8—C13—H13 | 120.3 | C5—C6—H6 | 120.7 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.9 | O1—C7—C8 | 119.9 (4) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.9 | O1—C7—N1 | 124.4 (3) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 120.1 (4) | N1—C7—C8 | 115.6 (4) |
| C8—C9—H9 | 120.5 | C9—C10—I1 | 118.7 (3) |
| C10—C9—H9 | 120.5 | C11—C10—I1 | 120.0 (2) |
| C10—C9—C8 | 119.0 (4) | C11—C10—C9 | 121.3 (4) |
| C13—C8—C9 | 120.1 (3) | C6—C1—N1 | 120.7 (3) |
| C13—C8—C7 | 123.5 (4) | C6—C1—C2 | 119.8 (3) |
| C9—C8—C7 | 116.3 (4) | C2—C1—N1 | 119.5 (3) |
| F1—C14—F2 | 105.2 (3) | C6—C5—H5 | 119.1 |
| F1—C14—C2 | 113.8 (4) | C4—C5—C6 | 121.9 (4) |
| F3—C14—F1 | 106.3 (4) | C4—C5—H5 | 119.1 |
| F3—C14—F2 | 106.2 (4) | C3—C2—C14 | 119.0 (4) |
| F3—C14—C2 | 113.2 (4) | C1—C2—C3 | 119.8 (4) |
| F2—C14—C2 | 111.5 (4) | C1—C2—C14 | 121.0 (3) |
| C7—N1—H1 | 117 (3) | C3—C4—H4 | 120.2 |
| C7—N1—C1 | 124.1 (4) | C5—C4—C3 | 119.7 (4) |
| C1—N1—H1 | 118 (3) | C5—C4—H4 | 120.2 |
| C12—C13—C8—C9 | 0.7 (6) | N1—C1—C2—C14 | 5.1 (6) |
| C12—C13—C8—C7 | −175.6 (4) | C11—C12—C13—C8 | −1.4 (7) |
| C12—C11—C10—I1 | −178.2 (3) | C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.4 (6) |
| C12—C11—C10—C9 | 1.2 (6) | C6—C1—C2—C14 | −174.7 (4) |
| F1—C14—C2—C3 | 129.8 (4) | C6—C5—C4—C3 | 0.7 (8) |
| F1—C14—C2—C1 | −55.0 (5) | C7—N1—C1—C6 | 43.4 (6) |
| F3—C14—C2—C3 | 8.3 (6) | C7—N1—C1—C2 | −136.4 (4) |
| F3—C14—C2—C1 | −176.5 (4) | C10—C9—C8—C13 | 0.9 (6) |
| C13—C12—C11—C10 | 0.5 (7) | C10—C9—C8—C7 | 177.4 (4) |
| C13—C8—C7—O1 | 148.7 (4) | C1—N1—C7—O1 | −3.5 (6) |
| C13—C8—C7—N1 | −29.7 (6) | C1—N1—C7—C8 | 174.8 (3) |
| F2—C14—C2—C3 | −111.3 (5) | C1—C6—C5—C4 | −1.1 (7) |
| F2—C14—C2—C1 | 63.9 (5) | C5—C6—C1—N1 | −179.2 (4) |
| C9—C8—C7—O1 | −27.7 (5) | C5—C6—C1—C2 | 0.6 (6) |
| C9—C8—C7—N1 | 153.9 (4) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.4 (8) |
| C8—C9—C10—I1 | 177.5 (3) | C4—C3—C2—C14 | 174.4 (4) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | −1.9 (6) | C4—C3—C2—C1 | −0.9 (7) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −179.8 (4) |
(III) 3-Iodo-N-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]benzamide . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···O1i | 0.89 (3) | 1.99 (4) | 2.826 (5) | 156 (5) |
Symmetry code: (i) x, y+1, z.
References
- Abdou, I. M., Saleh, A. M. & Zohdi, H. F. (2004). Molecules, 9, 109–116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2009). APEX2, SADABS, SAINT-Plus and XPREP. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Gowda, B. T., Usha, K. M. & Jayalakshmi, K. L. (2003). Z. Naturforsch. Teil A, 58, 801–806.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Hathwar, V. R., Chopra, D., Panini, P. & Guru Row, T. N. (2014). Cryst. Growth Des. 14, 5366–5369.
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Manojkumar, K. E., Sreenivasa, S., Mohan, N. R., Madhuchakrapani Rao, T. & Harikrishna, T. (2013a). J. Appl. Chem, 2, 730–737.
- Manojkumar, K. E., Sreenivasa, S., Shivaraja, G. & Madhuchakrapani Rao, T. (2013b). Molbank, M803, doi: 10.3390/M803.
- Panini, P. & Chopra, D. (2012). CrystEngComm, 14, 1972–1989.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, II, III, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016007866/su5298sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016007866/su5298Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016007866/su5298IIsup3.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) III. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016007866/su5298IIIsup4.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016007866/su5298Isup5.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016007866/su5298IIsup6.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016007866/su5298IIIsup7.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report










