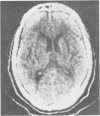
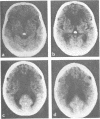
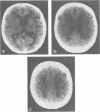
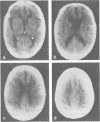
Abstract
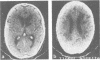
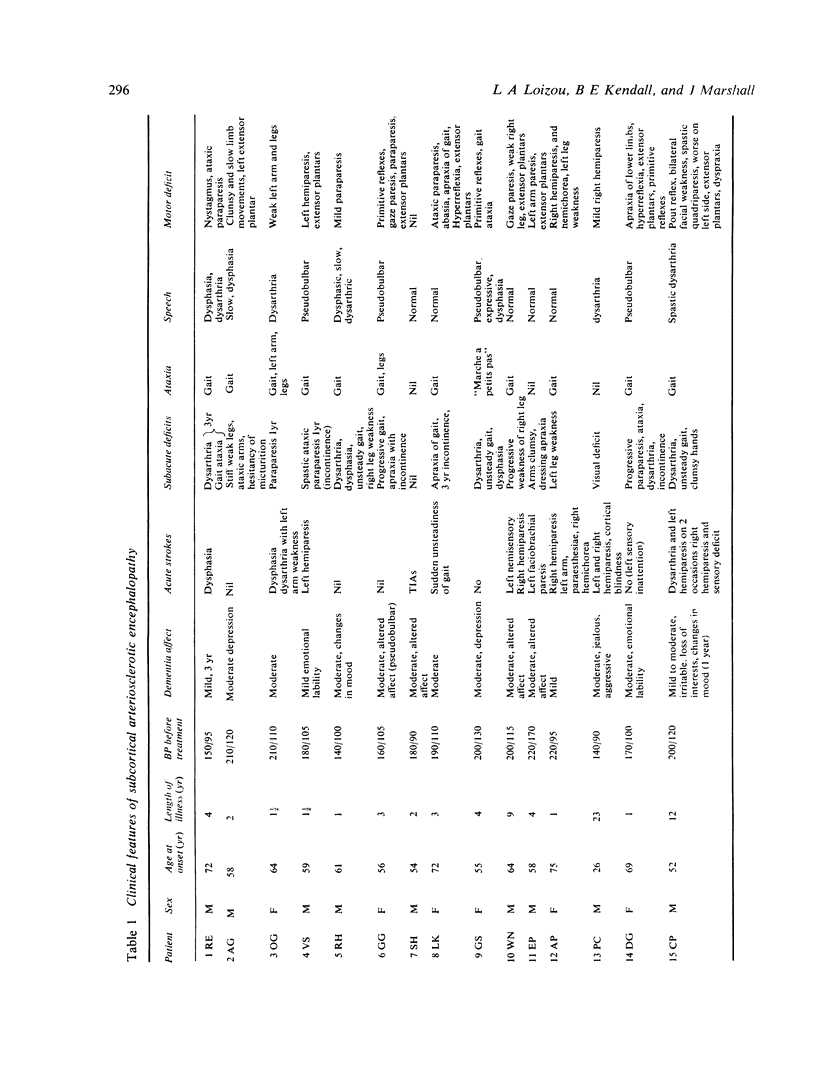
Subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy (Binswanger's type) was diagnosed in a group of patients with hypertension or arteriosclerosis, who showed acute and subacute neurological deficits, dementia, reduced cerebral blood flow, and white matter low attenuation with mild atrophy and infarcts as the predominant CT scan features. This set of clinical and radiological criteria could be used to make the diagnosis in life, as confirmed neuropathologically in one patient.
Full text
PDF

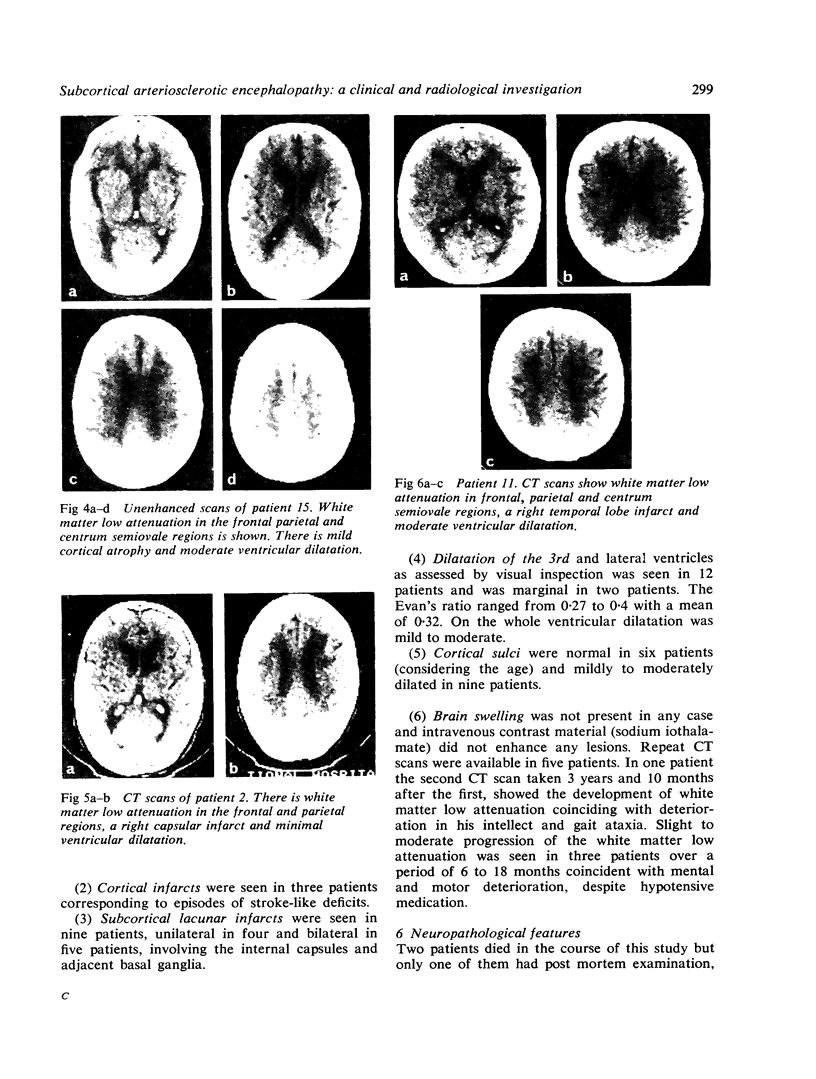





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronson S. M., Perl D. P. Clinical neuropathological conference. A 58-year-old concrete worker was amitted to the hospital because of slowly progressive dementia. Dis Nerv Syst. 1974 Jun;35(6):286–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biemond A. On Binswanger's subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy and the possibility of its clinical recognition. Psychiatr Neurol Neurochir. 1970 Nov-Dec;73(6):413–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger P. C., Burch J. G., Kunze U. Subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy (Binswanger's disease). A vascular etiology of dementia. Stroke. 1976 Nov-Dec;7(6):626–631. doi: 10.1161/01.str.7.6.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan L. R., Schoene W. C. Clinical features of subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy (Binswanger disease). Neurology. 1978 Dec;28(12):1206–1215. doi: 10.1212/wnl.28.12.1206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole F. M., Yates P. O. Comparative incidence of cerebrovascular lesions in normotensive and hypertensive patients. Neurology. 1968 Mar;18(3):255–259. doi: 10.1212/wnl.18.3.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnest M. P., Fahn S., Karp J. H., Rowland L. P. Normal pressure hydrocephalus and hypertensive cerebrovascular disease. Arch Neurol. 1974 Oct;31(4):262–266. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1974.00490400076009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEIGIN I., POPOFF N. NEUROPATHOLOGICAL CHANGES LATE IN CEREBRAL EDEMA: THE RELATIONSHIP TO TRAUMA, HYPERTENSIVE DISEASE AND BINSWANGER'S ENCEPHALOPATHY. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1963 Jul;22:500–511. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196307000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigin I., Budzilovich G., Weinberg S., Ogata J. Degeneration of white matter in hypoxia, acidosis and edema. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1973 Jan;32(1):125–143. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197301000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher C. M. The arterial lesions underlying lacunes. Acta Neuropathol. 1968 Dec 18;12(1):1–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00685305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES W., DODGSON M. C., MACLENNAN D. C. Chronic cerebral hypertensive disease. Lancet. 1954 Oct 16;267(6842):770–774. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(54)92498-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hachinski V. C., Iliff L. D., Zilhka E., Du Boulay G. H., McAllister V. L., Marshall J., Russell R. W., Symon L. Cerebral blood flow in dementia. Arch Neurol. 1975 Sep;32(9):632–637. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1975.00490510088009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hachinski V. C., Lassen N. A., Marshall J. Multi-infarct dementia. A cause of mental deterioration in the elderly. Lancet. 1974 Jul 27;2(7874):207–210. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91496-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison M. J., Thomas D. J., Du Boulay G. H., Marshall J. Multi-infarct dementia. J Neurol Sci. 1979 Feb;40(2-3):97–103. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(79)90195-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishino H., Higashi H., Hayahara T., Ikeda H., Otsuki S. A case of subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy (Binswanger's disease). Folia Psychiatr Neurol Jpn. 1972 Jan;26(1):39–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1819.1972.tb01110.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JELLINGER K., NEUMAYER E. PROGRESSIVE SUBCORTICALE VASCULAERE ENCEPHALOPATHIE BINSWANGER. EINE KLINISCH-NEUROPATHOLOGISCHE STUDIE. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr. 1964 Aug 6;205:523–554. doi: 10.1007/BF00352748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladurner G., Sager W. D., Iliff L. D., Lechner H. A correlation of clinical findings and CT in ischaemic cerebrovascular disease. Eur Neurol. 1979;18(5):281–288. doi: 10.1159/000115091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley I. F., Radü E. W. Factors influencing the development of periventricular lucencies in patients with raised intracranial pressure. Neuroradiology. 1979 Feb 26;17(2):65–69. doi: 10.1007/BF00556020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. F., Pullicino P., Kendall B. E., Marshall J. Computed tomography in patients presenting with lacunar syndromes. Stroke. 1980 May-Jun;11(3):256–261. doi: 10.1161/01.str.11.3.256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLSZEWSKI J. Subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy. Review of the literature on the so-called Binswanger's disease and presentation of two cases. World Neurol. 1962 May;3:359–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okeda R. Morphometrische Verleichsuntersuchungen an Hirnarterien bei Binswangerscher Encephalopathie und Hochdruckencephalopathie. Acta Neuropathol. 1973;26(1):23–43. doi: 10.1007/BF00685521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radue E. W., du Boulay G. H., Harrison M. J., Thomas D. J. Comparison of angiographic and CT findings between patients with multi-infarct dementia and those with dementia due to primary neuronal degeneration. Neuroradiology. 1978;16:113–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00395221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg G. A., Kornfeld M., Stovring J., Bicknell J. M. Subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy (Binswanger): computerized tomography. Neurology. 1979 Aug;29(8):1102–1106. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.8.1102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. J., Zilkha E., Redmond S., Du Boulay G. H., Marshall J., Russell R. W., Symon L. An intravenous 133xenon clearance technique for measuring cerebral blood flow. J Neurol Sci. 1979 Jan;40(1):53–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(79)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson B. E., Blessed G., Roth M. Observations on the brains of demented old people. J Neurol Sci. 1970 Sep;11(3):205–242. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(70)90063-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentine A. R., Moseley I. F., Kendall B. E. White matter abnormality in cerebral atrophy: clinicoradiological correlations. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1980 Feb;43(2):139–142. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.43.2.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisberg L. A. Computed tomography and pure motor hemiparesis. Neurology. 1979 Apr;29(4):490–495. doi: 10.1212/wnl.29.4.490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. C. Periodic EEG activity in subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy (Binswanger's type). Arch Neurol. 1979 Aug;36(8):485–489. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1979.00500440055010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wodarz R. Watershed infarctions and computed tomography. A topographical study in cases with stenosis or occlusion of the carotid artery. Neuroradiology. 1980;19(5):245–248. doi: 10.1007/BF00347803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeumer H., Schonsky B., Sturm K. W. Predominant white matter involvement in subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy (Binswanger disease). J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1980 Feb;4(1):14–19. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198002000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]