In the title compounds, N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds lead to dimers; the dimers are linked by weak interactions into a three-dimensional network in one case and chains in the other.
Keywords: crystal structure, N-(arylsulfonyl)arylamides, N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, C—H⋯O interactions, C—H⋯π interactions
Abstract
The crystal structures of two N-(arylsulfonyl)arylamides, namely N-(3-fluorobenzoyl)benzenesulfonamide, C13H10FNO3S, (I), and N-(3-fluorobenzoyl)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide, C14H12FNO3S, (II), are described and compared with related structures. The dihedral angle between the benzene rings is 82.73 (10)° in (I) compared to 72.60 (12)° in (II). In the crystal of (I), the molecules are linked by C—H⋯O and C—H⋯π interactions, resulting in a three-dimensional grid-like architecture, while C—H⋯O interactions lead to one-dimensional ribbons in (II). The crystals of both (I) and (II) feature strong but non-structure-directing N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds with R 2 2(8) ring motifs. The structure of (I) also features π–π stacking interactions.
Chemical context
N-(Arylsulfonyl)arylamides have received much attention as they constitute an important class of drugs for Alzheimers disease (Hasegawa et al., 2000 ▸), antibacterial inhibitors of tRNA synthetases (Banwell et al., 2000 ▸), antagonists for angiotensin II (Chang et al., 1994 ▸) and as leukotriene D4-receptors (Musser et al., 1990 ▸). Further, N-(arylsulfonyl)arylamides are known to be potent antitumour agents against a broad spectrum of human tumour xenografts (colon, lung, breast, ovary and prostate) in nude mice (Mader et al., 2005 ▸). As part of our ongoing work on the synthesis and crystal structures of this class of compound (Gowda et al., 2009a
▸,b
▸; Sreenivasa et al., 2014 ▸; Suchetan et al., 2010 ▸, 2012 ▸), compounds (I) and (II) were synthesized and their crystal structures were determined.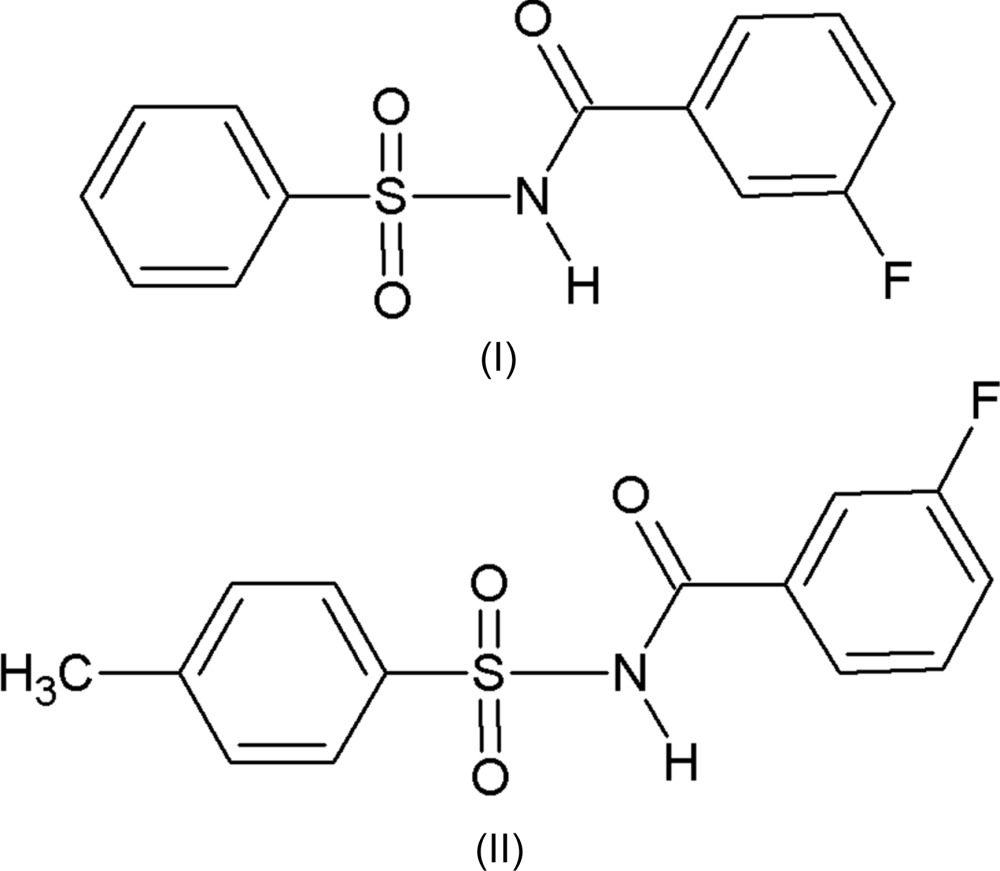
Structural commentary
The meta-fluoro substitution on the benzoyl ring of (I) (Fig. 1 ▸) is syn to the N—H bond in the central –C—SO2—N—C(=O)– segment. By contrast, in (II) (Fig. 2 ▸), the conformation of the N—H bond is anti with respect to the meta-fluoro substitution on the benzoyl ring. The dihedral angle between the benzene rings is 82.73 (10)° in (I), while, in (II) the value is slightly less [72.60 (12)°]. Further, in (I), the dihedral angle between the benzoic acid ring and the central C8—C7(O3)—N1—S1 segment is 16.54 (10)°, while that between the sulfonamide ring and the C7(O3)—N1—S1—C1 segment is 81.87 (12)°. The corresponding values in (II) are slightly less than those observed in (I), being 12.12 (12) and 57.58 (13)°, respectively.
Figure 1.
A view of the molecular structure of (I), with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level.
Figure 2.
A view of the molecular structure of (II), with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level.
Supramolecular features
The crystal structure of (I) features strong N1—H1⋯O1 hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▸) that connect the molecules into  (8) dimers (Fig. 3 ▸). These dimers are further interconnected by C9—H9⋯O1 interactions, forming
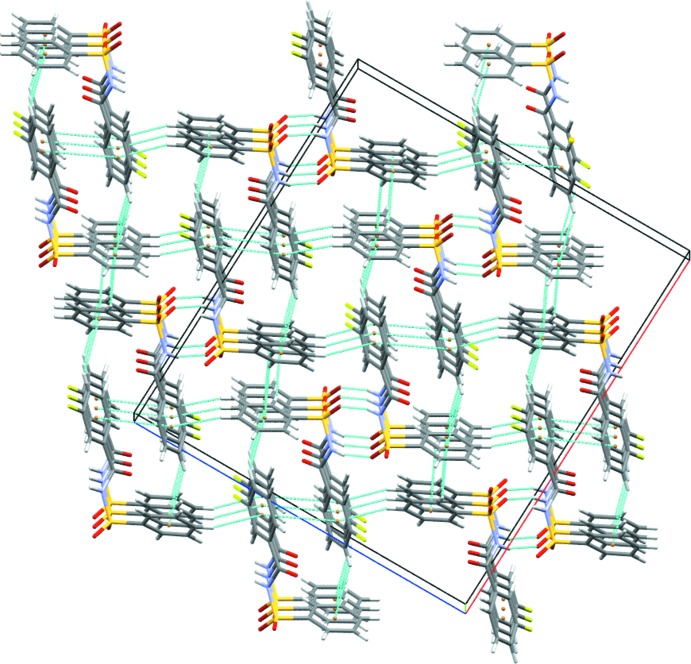
(8) dimers (Fig. 3 ▸). These dimers are further interconnected by C9—H9⋯O1 interactions, forming  (14) ring motifs. C6—H6⋯O3 interactions connect these dimers into C7 chains, forming columns propagating along the b-axis direction (Fig. 3 ▸). In addition, C4—H4⋯πaryl (π system of the fluorobenzoyl ring) interactions link the molecules into chains along the c axis. These chains are interconnected via C2—H2⋯πaryl (π system of the sulfonylbenzene ring) and C11—H11⋯πaryl (π system of the sulfonylbenzene ring) interactions, forming a three-dimensional grid-like structure (Fig. 4 ▸). The crystal structure also features π–π (π system of the fluorobenzoyl ring) stacking interactions. It is notable that the N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds present in the crystal structure of (I) has no structure-directing properties (leading only to dimers), while one of the C—H⋯O and the three C—H..πaryl interactions have structure-directing characteristics.
(14) ring motifs. C6—H6⋯O3 interactions connect these dimers into C7 chains, forming columns propagating along the b-axis direction (Fig. 3 ▸). In addition, C4—H4⋯πaryl (π system of the fluorobenzoyl ring) interactions link the molecules into chains along the c axis. These chains are interconnected via C2—H2⋯πaryl (π system of the sulfonylbenzene ring) and C11—H11⋯πaryl (π system of the sulfonylbenzene ring) interactions, forming a three-dimensional grid-like structure (Fig. 4 ▸). The crystal structure also features π–π (π system of the fluorobenzoyl ring) stacking interactions. It is notable that the N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds present in the crystal structure of (I) has no structure-directing properties (leading only to dimers), while one of the C—H⋯O and the three C—H..πaryl interactions have structure-directing characteristics.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (I) .
Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the sulfonyl and benzoyl rings, respectively.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯O1i | 0.81 (3) | 2.08 (3) | 2.883 (2) | 171 (3) |
| C9—H9⋯O1i | 0.93 | 2.42 | 3.244 (3) | 148 |
| C6—H6⋯O3ii | 0.93 | 2.50 | 3.294 (3) | 143 |
| C2—H2⋯Cg1iii | 0.93 | 2.82 | 3.474 (2) | 129 |
| C4—H4⋯Cg2iv | 0.93 | 2.84 | 3.582 (2) | 137 |
| C11—H11⋯Cg1v | 0.93 | 2.97 | 3.756 (3) | 143 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  ; (v)
; (v)  .
.
Figure 3.
Crystal packing of (I), displaying N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and C—H⋯O interactions, which result in columns along the b axis.
Figure 4.
Three-dimensional grid-like architecture formed by various C—H⋯πaryl interactions in (I).
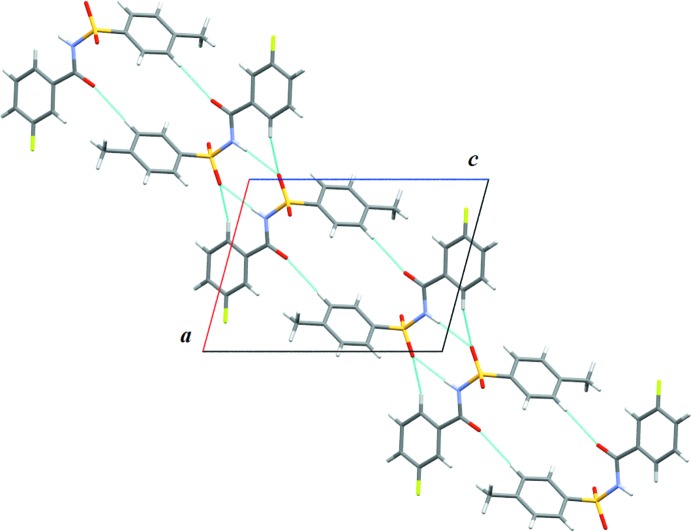
Similar to that observed in the crystal structure of (I), in (II) strong N1—H1⋯O1 hydrogen bonds (Table 2 ▸) result in the formation of  (8) dimers (Fig. 5 ▸). The molecules constituting these dimers are interconnected into
(8) dimers (Fig. 5 ▸). The molecules constituting these dimers are interconnected into  (14) ring motifs via C13—H13⋯O1 interactions, as observed in (I). Adjacent dimers are interconnected via C5—H5⋯O3 interactions into
(14) ring motifs via C13—H13⋯O1 interactions, as observed in (I). Adjacent dimers are interconnected via C5—H5⋯O3 interactions into  (16) rings, thus forming ribbons along the diagonal of the ac plane (Fig. 5 ▸). The overall supramolecular architecture displayed in (II) is one-dimensional, in contrast to the three-dimensional architecture displayed in (I).
(16) rings, thus forming ribbons along the diagonal of the ac plane (Fig. 5 ▸). The overall supramolecular architecture displayed in (II) is one-dimensional, in contrast to the three-dimensional architecture displayed in (I).
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (II) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯O1i | 0.87 (4) | 2.06 (4) | 2.937 (3) | 177 (3) |
| C5—H5⋯O3ii | 0.93 | 2.46 | 3.375 (3) | 168 |
| C13—H13⋯O1i | 0.93 | 2.47 | 3.285 (3) | 147 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Figure 5.
One-dimensional ribbons formed in the crystal structure of (II) via N—H⋯O dimeric pairs and various C—H⋯O dimeric pairs.
Database survey
The crystal structures of five related N-(arylsulfonyl)arylamides, namely N-(benzoyl)benzenesulfonamide (III), N-(3-chlorobenzoyl)benzenesulfonamide (IV), N-(3-methylbenzoyl)benzenesulfonamide (V), N-(benzoyl)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide (VI) and N-(3-methylbenzoyl)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide (VII) have previously been reported. A comparison of the dihedral angle between the two benzene rings in these closely related structures indicates that introducing a methyl substituent into the para position of the benzenesulfonyl ring lowers the dihedral angle with compound (VII) being an exception. The dihedral angle values are 80.3 (1)° in (III) (Gowda et al., 2009a ▸), 87.5 (1)° in (IV) (Gowda et al., 2009b ▸), 83.3 (2), 84.4 (2) and 87.6 (2)° in the three molecules of (V) (Suchetan et al., 2012 ▸), 79.4 (1)° in (VI) (Suchetan et al., 2010 ▸) and 89.6 (2)° in (VII) (Sreenivasa et al., 2014 ▸). This effect is the same as that observed in the present two structures (I) and (II). Furthermore, in (I)–(VII) the conformation of the N—H bond in the central segment is anti to the meta substituent on the benzoyl ring in the presence of a methyl substituent either on the benzoyl ring or the benzenesulfonyl ring. Otherwise, the conformation is syn as observed in (I) and (IV). A comparison of the crystal structures of (I) and (II) with those previously reported shows that fluoro substitution on the benzoyl ring appears to have a significant effect on the supramolecular architecture, and also on the type and nature of the intermolecular interactions displayed. For instance, in all the reported structures except (VII), the molecules are linked into one-dimensional infinite C(4) chains via strong structure-directing N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. The structures do not feature any other type of interactions. However, in (I) and (II), the N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds lead to dimers and, in addition, both of them feature other structure-directing interactions of the type C—H⋯O or C—H⋯πaryl. Furthermore, introducing the methyl substituent into the benzenesulfonyl ring of (I) to form (III) reduces the three-dimensional grid-like architecture into a one-dimensional ribbon architecture. However, in (III)–(VII), the introduction of a methyl substituent into the benzenesulfonyl ring results in no change to the supramolecular architecture.
Synthesis and crystallization
Compounds (I) and (II) were prepared by refluxing a mixture of 3-fluorobenzoic acid, the corresponding substituted benzenesulfonamides and phosphorus oxychloride for 3 h on a water bath. The resultant mixtures were cooled and poured into ice-cold water. The solids obtained were filtered, washed thoroughly with water and then dissolved in sodium bicarbonate solutions. The compounds were later reprecipitated by acidifying the filtered solutions with dilute HCl. They were filtered, dried and recrystallized; m.p = 442–444 K for (I) and 422–423 K for (II). Prism-like, colourless single crystals of (I) and (II) were obtained by slow evaporation of the respective solutions of the compounds in methanol (with a few drops of water).
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. The H atoms of the NH groups in (I) and (II) were located in a difference map and later refined freely. The other H atoms were positioned with idealized geometry using a riding model with C—H = 0.93–0.96 Å, and with U iso = 1.2 or 1.5U eq(parent atom). To improve considerably the values of R1, wR2 and GOOF, reflections with very bad agreement (−20 0 0), (−20 0 10) and (−19 1 15) in (I) and (0 6 0) in (II) were omitted from the final refinements.
Table 3. Experimental details.
| (I) | (II) | |
|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | ||
| Chemical formula | C13H10FNO3S | C14H12FNO3S |
| M r | 279.28 | 293.31 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, C2/c | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 173 | 173 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 21.4036 (8), 5.7673 (2), 19.5525 (7) | 9.0376 (4), 12.2912 (5), 12.1377 (5) |
| β (°) | 92.135 (1) | 105.107 (2) |
| V (Å3) | 2411.90 (15) | 1301.70 (9) |
| Z | 8 | 4 |
| Radiation type | Cu Kα | Cu Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 2.56 | 2.40 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.28 × 0.24 × 0.19 | 0.28 × 0.22 × 0.18 |
| Data collection | ||
| Diffractometer | Bruker APEXII | Bruker APEXII |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009 ▸) | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.512, 0.614 | 0.557, 0.649 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 8647, 1985, 1846 | 8422, 2115, 1796 |
| R int | 0.037 | 0.056 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.587 | 0.583 |
| Refinement | ||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.042, 0.133, 0.98 | 0.050, 0.152, 1.05 |
| No. of reflections | 1985 | 2115 |
| No. of parameters | 176 | 186 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.39, −0.38 | 0.45, −0.47 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, II, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016003248/hb7565sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016003248/hb7565Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016003248/hb7565IIsup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016003248/hb7565Isup4.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016003248/hb7565IIsup5.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Institution of Excellence, Vijnana Bhavana, University of Mysore, Mysore, for providing the single-crystal X-ray diffraction data. GMS thanks the Vision Group on Science and Technology (VGST), Karnataka, India, for financial support under its SPiCE project scheme.
supplementary crystallographic information
(I) N-(3-Fluorobenzoyl)benzenesulfonamide . Crystal data
| C13H10FNO3S | Prism |
| Mr = 279.28 | Dx = 1.538 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, C2/c | Melting point: 442 K |
| Hall symbol: -C 2yc | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å |
| a = 21.4036 (8) Å | Cell parameters from 123 reflections |
| b = 5.7673 (2) Å | θ = 4.1–64.8° |
| c = 19.5525 (7) Å | µ = 2.56 mm−1 |
| β = 92.135 (1)° | T = 173 K |
| V = 2411.90 (15) Å3 | Prism, colourless |
| Z = 8 | 0.28 × 0.24 × 0.19 mm |
| F(000) = 1152 |
(I) N-(3-Fluorobenzoyl)benzenesulfonamide . Data collection
| Bruker APEXII diffractometer | 1846 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.037 |
| Graphite monochromator | θmax = 64.8°, θmin = 4.1° |
| phi and φ scans | h = −24→24 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009) | k = −6→5 |
| Tmin = 0.512, Tmax = 0.614 | l = −22→22 |
| 8647 measured reflections | 1 standard reflections every 1 reflections |
| 1985 independent reflections | intensity decay: 0.1% |
(I) N-(3-Fluorobenzoyl)benzenesulfonamide . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.042 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.133 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 0.98 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.105P)2 + 2.9874P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 1985 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 176 parameters | Δρmax = 0.39 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.38 e Å−3 |
(I) N-(3-Fluorobenzoyl)benzenesulfonamide . Special details
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
(I) N-(3-Fluorobenzoyl)benzenesulfonamide . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.26504 (2) | 0.47902 (9) | 0.41244 (2) | 0.0162 (2) | |
| F1 | 0.46178 (7) | 0.8164 (3) | 0.66939 (7) | 0.0325 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.24567 (7) | 0.2440 (3) | 0.40478 (8) | 0.0220 (4) | |
| O1 | 0.21912 (7) | 0.6490 (3) | 0.42975 (8) | 0.0230 (4) | |
| O3 | 0.38206 (7) | 0.2258 (3) | 0.43259 (8) | 0.0233 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.31971 (9) | 0.5057 (3) | 0.47405 (10) | 0.0174 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.41781 (9) | 0.4102 (4) | 0.53566 (11) | 0.0175 (5) | |
| C7 | 0.37286 (10) | 0.3690 (3) | 0.47665 (11) | 0.0176 (5) | |
| C3 | 0.33096 (10) | 0.4990 (4) | 0.22344 (12) | 0.0205 (5) | |
| H3 | 0.3305 | 0.4048 | 0.1848 | 0.025* | |
| C9 | 0.41783 (10) | 0.6094 (4) | 0.57623 (11) | 0.0195 (5) | |
| H9 | 0.3885 | 0.7264 | 0.5684 | 0.023* | |
| C5 | 0.36070 (10) | 0.8565 (4) | 0.27931 (12) | 0.0215 (5) | |
| H5 | 0.3808 | 0.9994 | 0.2782 | 0.026* | |
| C2 | 0.30217 (10) | 0.4254 (4) | 0.28191 (11) | 0.0180 (5) | |
| H2 | 0.2828 | 0.2811 | 0.2831 | 0.022* | |
| C6 | 0.33094 (9) | 0.7874 (4) | 0.33818 (11) | 0.0188 (5) | |
| H6 | 0.3300 | 0.8840 | 0.3762 | 0.023* | |
| C10 | 0.46279 (10) | 0.6266 (4) | 0.62832 (11) | 0.0215 (5) | |
| C1 | 0.30264 (9) | 0.5700 (4) | 0.33854 (10) | 0.0153 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.36042 (10) | 0.7129 (4) | 0.22245 (12) | 0.0217 (5) | |
| H4 | 0.3802 | 0.7605 | 0.1833 | 0.026* | |
| C11 | 0.50814 (11) | 0.4618 (4) | 0.64123 (12) | 0.0247 (5) | |
| H11 | 0.5383 | 0.4820 | 0.6762 | 0.030* | |
| C13 | 0.46262 (10) | 0.2394 (4) | 0.54849 (12) | 0.0228 (5) | |
| H13 | 0.4623 | 0.1061 | 0.5217 | 0.027* | |
| C12 | 0.50767 (11) | 0.2653 (4) | 0.60072 (13) | 0.0268 (6) | |
| H12 | 0.5376 | 0.1504 | 0.6085 | 0.032* | |
| H1 | 0.3091 (14) | 0.591 (5) | 0.5042 (17) | 0.035 (8)* |
(I) N-(3-Fluorobenzoyl)benzenesulfonamide . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0155 (4) | 0.0201 (4) | 0.0130 (3) | 0.00064 (18) | −0.0003 (2) | −0.00239 (18) |
| F1 | 0.0361 (8) | 0.0312 (8) | 0.0295 (8) | −0.0004 (6) | −0.0089 (6) | −0.0093 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0238 (8) | 0.0243 (9) | 0.0178 (8) | −0.0059 (7) | −0.0004 (6) | 0.0001 (6) |
| O1 | 0.0178 (8) | 0.0339 (9) | 0.0173 (8) | 0.0065 (7) | −0.0013 (6) | −0.0070 (6) |
| O3 | 0.0233 (8) | 0.0233 (8) | 0.0233 (9) | 0.0036 (6) | 0.0000 (6) | −0.0069 (7) |
| N1 | 0.0185 (10) | 0.0213 (10) | 0.0124 (9) | 0.0031 (7) | −0.0009 (8) | −0.0035 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0152 (10) | 0.0203 (11) | 0.0171 (11) | 0.0004 (9) | 0.0026 (8) | 0.0027 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0187 (10) | 0.0160 (11) | 0.0183 (11) | −0.0003 (8) | 0.0029 (8) | 0.0014 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0194 (11) | 0.0257 (12) | 0.0165 (11) | 0.0020 (8) | 0.0009 (9) | −0.0024 (8) |
| C9 | 0.0170 (10) | 0.0211 (11) | 0.0205 (11) | 0.0006 (8) | 0.0015 (8) | 0.0021 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0194 (11) | 0.0164 (11) | 0.0286 (12) | 0.0014 (8) | −0.0020 (9) | 0.0040 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0182 (11) | 0.0167 (10) | 0.0190 (11) | 0.0022 (9) | −0.0024 (8) | −0.0022 (9) |
| C6 | 0.0183 (10) | 0.0172 (11) | 0.0208 (11) | 0.0026 (8) | −0.0023 (8) | −0.0026 (9) |
| C10 | 0.0224 (11) | 0.0218 (12) | 0.0203 (11) | −0.0042 (9) | 0.0008 (9) | −0.0006 (9) |
| C1 | 0.0132 (10) | 0.0178 (10) | 0.0149 (10) | 0.0041 (8) | −0.0007 (8) | 0.0006 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0166 (10) | 0.0281 (12) | 0.0207 (12) | 0.0027 (9) | 0.0018 (8) | 0.0084 (9) |
| C11 | 0.0172 (11) | 0.0336 (13) | 0.0229 (12) | −0.0031 (9) | −0.0037 (9) | 0.0070 (10) |
| C13 | 0.0193 (11) | 0.0223 (11) | 0.0268 (12) | 0.0024 (9) | 0.0020 (9) | 0.0001 (9) |
| C12 | 0.0189 (11) | 0.0288 (13) | 0.0323 (13) | 0.0066 (9) | −0.0032 (9) | 0.0041 (10) |
(I) N-(3-Fluorobenzoyl)benzenesulfonamide . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—O2 | 1.4238 (16) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| S1—O1 | 1.4375 (16) | C5—C4 | 1.386 (3) |
| S1—N1 | 1.6549 (19) | C5—C6 | 1.394 (3) |
| S1—C1 | 1.760 (2) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| F1—C10 | 1.358 (3) | C2—C1 | 1.386 (3) |
| O3—C7 | 1.215 (3) | C2—H2 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C7 | 1.383 (3) | C6—C1 | 1.392 (3) |
| N1—H1 | 0.81 (3) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| C8—C13 | 1.391 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.375 (3) |
| C8—C9 | 1.396 (3) | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| C8—C7 | 1.494 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.383 (4) |
| C3—C2 | 1.385 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.386 (3) | C13—C12 | 1.386 (3) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C9—C10 | 1.378 (3) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| O2—S1—O1 | 118.36 (9) | C3—C2—C1 | 119.0 (2) |
| O2—S1—N1 | 111.12 (9) | C3—C2—H2 | 120.5 |
| O1—S1—N1 | 103.67 (9) | C1—C2—H2 | 120.5 |
| O2—S1—C1 | 109.75 (10) | C1—C6—C5 | 118.3 (2) |
| O1—S1—C1 | 109.12 (10) | C1—C6—H6 | 120.9 |
| N1—S1—C1 | 103.73 (9) | C5—C6—H6 | 120.9 |
| C7—N1—S1 | 122.13 (16) | F1—C10—C11 | 118.4 (2) |
| C7—N1—H1 | 125 (2) | F1—C10—C9 | 117.97 (19) |
| S1—N1—H1 | 112 (2) | C11—C10—C9 | 123.7 (2) |
| C13—C8—C9 | 119.6 (2) | C2—C1—C6 | 121.9 (2) |
| C13—C8—C7 | 116.5 (2) | C2—C1—S1 | 119.10 (17) |
| C9—C8—C7 | 123.80 (19) | C6—C1—S1 | 119.01 (16) |
| O3—C7—N1 | 121.08 (19) | C3—C4—C5 | 120.6 (2) |
| O3—C7—C8 | 122.62 (19) | C3—C4—H4 | 119.7 |
| N1—C7—C8 | 116.29 (18) | C5—C4—H4 | 119.7 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.1 (2) | C10—C11—C12 | 118.1 (2) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.0 | C10—C11—H11 | 120.9 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.0 | C12—C11—H11 | 120.9 |
| C10—C9—C8 | 117.7 (2) | C8—C13—C12 | 120.8 (2) |
| C10—C9—H9 | 121.2 | C8—C13—H13 | 119.6 |
| C8—C9—H9 | 121.2 | C12—C13—H13 | 119.6 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.2 (2) | C11—C12—C13 | 120.0 (2) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.9 | C11—C12—H12 | 120.0 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.9 | C13—C12—H12 | 120.0 |
| O2—S1—N1—C7 | 51.25 (19) | C5—C6—C1—C2 | −1.5 (3) |
| O1—S1—N1—C7 | 179.42 (17) | C5—C6—C1—S1 | 179.79 (15) |
| C1—S1—N1—C7 | −66.61 (19) | O2—S1—C1—C2 | 7.79 (19) |
| S1—N1—C7—O3 | 1.5 (3) | O1—S1—C1—C2 | −123.41 (16) |
| S1—N1—C7—C8 | −179.26 (14) | N1—S1—C1—C2 | 126.59 (16) |
| C13—C8—C7—O3 | −16.3 (3) | O2—S1—C1—C6 | −173.49 (15) |
| C9—C8—C7—O3 | 162.1 (2) | O1—S1—C1—C6 | 55.31 (18) |
| C13—C8—C7—N1 | 164.44 (19) | N1—S1—C1—C6 | −54.69 (18) |
| C9—C8—C7—N1 | −17.2 (3) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.9 (3) |
| C13—C8—C9—C10 | −0.5 (3) | C6—C5—C4—C3 | −0.3 (3) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | −178.80 (19) | F1—C10—C11—C12 | 177.9 (2) |
| C4—C3—C2—C1 | 0.9 (3) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −1.6 (4) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 1.5 (3) | C9—C8—C13—C12 | −0.6 (3) |
| C8—C9—C10—F1 | −177.86 (19) | C7—C8—C13—C12 | 177.9 (2) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | 1.6 (3) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.5 (4) |
| C3—C2—C1—C6 | 0.3 (3) | C8—C13—C12—C11 | 0.6 (4) |
| C3—C2—C1—S1 | 179.00 (16) |
(I) N-(3-Fluorobenzoyl)benzenesulfonamide . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the sulfonyl and benzoyl rings, respectively.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···O1i | 0.81 (3) | 2.08 (3) | 2.883 (2) | 171 (3) |
| C9—H9···O1i | 0.93 | 2.42 | 3.244 (3) | 148 |
| C6—H6···O3ii | 0.93 | 2.50 | 3.294 (3) | 143 |
| C2—H2···Cg1iii | 0.93 | 2.82 | 3.474 (2) | 129 |
| C4—H4···Cg2iv | 0.93 | 2.84 | 3.582 (2) | 137 |
| C11—H11···Cg1v | 0.93 | 2.97 | 3.756 (3) | 143 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1/2, −y+3/2, −z+1; (ii) x, y+1, z; (iii) x, −y−1, z−1/2; (iv) x, −y, z+1/2; (v) −x, −y, −z.
(II) N-(3-Fluorobenzoyl)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide . Crystal data
| C14H12FNO3S | Prism |
| Mr = 293.31 | Dx = 1.497 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Melting point: 423 K |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å |
| a = 9.0376 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 142 reflections |
| b = 12.2912 (5) Å | θ = 5.1–64.1° |
| c = 12.1377 (5) Å | µ = 2.40 mm−1 |
| β = 105.107 (2)° | T = 173 K |
| V = 1301.70 (9) Å3 | Prism, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.28 × 0.22 × 0.18 mm |
| F(000) = 608 |
(II) N-(3-Fluorobenzoyl)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide . Data collection
| Bruker APEXII diffractometer | 1796 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.056 |
| Graphite monochromator | θmax = 64.1°, θmin = 5.1° |
| phi and φ scans | h = −10→10 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009) | k = −14→14 |
| Tmin = 0.557, Tmax = 0.649 | l = −10→13 |
| 8422 measured reflections | 1 standard reflections every 1 reflections |
| 2115 independent reflections | intensity decay: 0.1% |
(II) N-(3-Fluorobenzoyl)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.050 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.152 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.05 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.1104P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2115 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.023 |
| 186 parameters | Δρmax = 0.45 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.47 e Å−3 |
(II) N-(3-Fluorobenzoyl)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide . Special details
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
(II) N-(3-Fluorobenzoyl)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.86791 (7) | 0.55562 (5) | 0.81354 (5) | 0.0171 (3) | |
| F1 | 0.17463 (17) | 0.30702 (14) | 0.94022 (13) | 0.0303 (4) | |
| O1 | 1.0242 (2) | 0.55041 (16) | 0.88113 (15) | 0.0231 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.7956 (2) | 0.65901 (15) | 0.79047 (14) | 0.0240 (5) | |
| O3 | 0.5443 (2) | 0.48889 (17) | 0.75791 (15) | 0.0260 (5) | |
| N1 | 0.7768 (2) | 0.47863 (18) | 0.88728 (19) | 0.0183 (5) | |
| C8 | 0.5545 (3) | 0.3863 (2) | 0.9263 (2) | 0.0169 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.9568 (3) | 0.4058 (2) | 0.6775 (2) | 0.0205 (6) | |
| H2 | 1.0292 | 0.3827 | 0.7426 | 0.025* | |
| C9 | 0.3950 (3) | 0.3781 (2) | 0.8985 (2) | 0.0199 (6) | |
| H9 | 0.3346 | 0.4151 | 0.8360 | 0.024* | |
| C13 | 0.6429 (3) | 0.3294 (2) | 1.0197 (2) | 0.0192 (6) | |
| H13 | 0.7492 | 0.3351 | 1.0387 | 0.023* | |
| C12 | 0.5722 (3) | 0.2640 (2) | 1.0844 (2) | 0.0206 (6) | |
| H12 | 0.6318 | 0.2251 | 1.1457 | 0.025* | |
| C5 | 0.7362 (3) | 0.4729 (2) | 0.4840 (2) | 0.0214 (6) | |
| H5 | 0.6619 | 0.4947 | 0.4193 | 0.026* | |
| C3 | 0.9501 (3) | 0.3593 (2) | 0.5727 (2) | 0.0204 (6) | |
| H3 | 1.0200 | 0.3053 | 0.5672 | 0.024* | |
| C10 | 0.3296 (3) | 0.3141 (2) | 0.9655 (2) | 0.0207 (6) | |
| C4 | 0.8399 (3) | 0.3922 (2) | 0.4747 (2) | 0.0210 (6) | |
| C11 | 0.4148 (3) | 0.2562 (2) | 1.0587 (2) | 0.0212 (6) | |
| H11 | 0.3671 | 0.2134 | 1.1026 | 0.025* | |
| C6 | 0.7415 (3) | 0.5214 (2) | 0.5878 (2) | 0.0189 (6) | |
| H6 | 0.6718 | 0.5754 | 0.5931 | 0.023* | |
| C7 | 0.6213 (3) | 0.4561 (2) | 0.8499 (2) | 0.0191 (6) | |
| C1 | 0.8532 (3) | 0.4879 (2) | 0.6840 (2) | 0.0169 (6) | |
| C14 | 0.8314 (4) | 0.3399 (2) | 0.3606 (2) | 0.0299 (7) | |
| H14A | 0.7802 | 0.2710 | 0.3563 | 0.045* | |
| H14B | 0.9331 | 0.3291 | 0.3524 | 0.045* | |
| H14C | 0.7754 | 0.3864 | 0.3006 | 0.045* | |
| H1 | 0.833 (4) | 0.469 (3) | 0.957 (3) | 0.033 (9)* |
(II) N-(3-Fluorobenzoyl)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0170 (4) | 0.0203 (4) | 0.0131 (4) | −0.0036 (2) | 0.0024 (3) | −0.0003 (2) |
| F1 | 0.0154 (8) | 0.0438 (11) | 0.0311 (9) | −0.0039 (7) | 0.0050 (6) | 0.0043 (7) |
| O1 | 0.0181 (10) | 0.0340 (12) | 0.0153 (9) | −0.0082 (8) | 0.0011 (7) | −0.0010 (7) |
| O2 | 0.0298 (10) | 0.0223 (10) | 0.0204 (10) | −0.0003 (8) | 0.0075 (8) | −0.0008 (7) |
| O3 | 0.0173 (10) | 0.0386 (12) | 0.0184 (10) | −0.0005 (8) | −0.0019 (8) | 0.0092 (8) |
| N1 | 0.0152 (11) | 0.0245 (12) | 0.0127 (11) | −0.0033 (9) | −0.0006 (9) | 0.0027 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0159 (12) | 0.0170 (13) | 0.0172 (12) | −0.0003 (10) | 0.0032 (9) | −0.0031 (10) |
| C2 | 0.0161 (12) | 0.0251 (15) | 0.0181 (13) | −0.0024 (11) | 0.0004 (10) | 0.0029 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0175 (12) | 0.0233 (14) | 0.0169 (13) | 0.0008 (11) | 0.0012 (10) | 0.0015 (10) |
| C13 | 0.0164 (12) | 0.0210 (14) | 0.0192 (13) | 0.0010 (10) | 0.0030 (10) | −0.0021 (10) |
| C12 | 0.0250 (13) | 0.0183 (14) | 0.0167 (12) | 0.0011 (11) | 0.0020 (10) | 0.0015 (10) |
| C5 | 0.0216 (13) | 0.0255 (14) | 0.0141 (13) | −0.0027 (11) | −0.0005 (10) | 0.0027 (10) |
| C3 | 0.0204 (13) | 0.0188 (13) | 0.0227 (13) | −0.0006 (11) | 0.0070 (10) | 0.0005 (10) |
| C10 | 0.0128 (12) | 0.0273 (15) | 0.0215 (13) | −0.0009 (10) | 0.0035 (10) | −0.0044 (10) |
| C4 | 0.0242 (14) | 0.0212 (14) | 0.0186 (13) | −0.0070 (11) | 0.0074 (10) | −0.0004 (10) |
| C11 | 0.0252 (13) | 0.0207 (14) | 0.0201 (13) | −0.0025 (11) | 0.0101 (11) | −0.0010 (10) |
| C6 | 0.0183 (13) | 0.0199 (13) | 0.0170 (13) | −0.0014 (11) | 0.0020 (10) | 0.0008 (10) |
| C7 | 0.0176 (13) | 0.0224 (15) | 0.0173 (13) | −0.0005 (11) | 0.0048 (11) | −0.0018 (10) |
| C1 | 0.0165 (13) | 0.0187 (13) | 0.0161 (13) | −0.0044 (10) | 0.0054 (10) | 0.0001 (10) |
| C14 | 0.0428 (17) | 0.0295 (16) | 0.0189 (13) | −0.0069 (13) | 0.0103 (12) | −0.0024 (11) |
(II) N-(3-Fluorobenzoyl)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—O2 | 1.423 (2) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| S1—O1 | 1.4383 (19) | C12—C11 | 1.378 (4) |
| S1—N1 | 1.661 (2) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| S1—C1 | 1.753 (2) | C5—C6 | 1.383 (4) |
| F1—C10 | 1.356 (3) | C5—C4 | 1.389 (4) |
| O3—C7 | 1.220 (3) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C7 | 1.387 (3) | C3—C4 | 1.398 (4) |
| N1—H1 | 0.87 (4) | C3—H3 | 0.9300 |
| C8—C13 | 1.393 (4) | C10—C11 | 1.388 (4) |
| C8—C9 | 1.396 (4) | C4—C14 | 1.510 (4) |
| C8—C7 | 1.500 (4) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.382 (4) | C6—C1 | 1.392 (4) |
| C2—C1 | 1.393 (4) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C14—H14A | 0.9600 |
| C9—C10 | 1.371 (4) | C14—H14B | 0.9600 |
| C9—H9 | 0.9300 | C14—H14C | 0.9600 |
| C13—C12 | 1.391 (4) | ||
| O2—S1—O1 | 118.99 (11) | C2—C3—C4 | 120.9 (2) |
| O2—S1—N1 | 110.36 (11) | C2—C3—H3 | 119.5 |
| O1—S1—N1 | 102.63 (11) | C4—C3—H3 | 119.5 |
| O2—S1—C1 | 108.91 (11) | F1—C10—C9 | 118.8 (2) |
| O1—S1—C1 | 108.91 (11) | F1—C10—C11 | 118.2 (2) |
| N1—S1—C1 | 106.26 (11) | C9—C10—C11 | 123.0 (2) |
| C7—N1—S1 | 122.65 (19) | C5—C4—C3 | 118.9 (2) |
| C7—N1—H1 | 125 (2) | C5—C4—C14 | 120.3 (2) |
| S1—N1—H1 | 111 (2) | C3—C4—C14 | 120.8 (2) |
| C13—C8—C9 | 119.8 (2) | C12—C11—C10 | 118.0 (2) |
| C13—C8—C7 | 123.5 (2) | C12—C11—H11 | 121.0 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 116.7 (2) | C10—C11—H11 | 121.0 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 118.9 (2) | C5—C6—C1 | 118.9 (2) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.5 | C5—C6—H6 | 120.6 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.5 | C1—C6—H6 | 120.6 |
| C10—C9—C8 | 118.5 (2) | O3—C7—N1 | 121.4 (2) |
| C10—C9—H9 | 120.8 | O3—C7—C8 | 121.9 (2) |
| C8—C9—H9 | 120.8 | N1—C7—C8 | 116.6 (2) |
| C12—C13—C8 | 119.9 (2) | C6—C1—C2 | 121.1 (2) |
| C12—C13—H13 | 120.0 | C6—C1—S1 | 118.8 (2) |
| C8—C13—H13 | 120.0 | C2—C1—S1 | 120.01 (19) |
| C11—C12—C13 | 120.8 (2) | C4—C14—H14A | 109.5 |
| C11—C12—H12 | 119.6 | C4—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C13—C12—H12 | 119.6 | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 121.2 (2) | C4—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.4 | H14A—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.4 | H14B—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| O2—S1—N1—C7 | 55.4 (2) | C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.1 (4) |
| O1—S1—N1—C7 | −176.8 (2) | S1—N1—C7—O3 | 2.7 (4) |
| C1—S1—N1—C7 | −62.5 (2) | S1—N1—C7—C8 | −179.31 (17) |
| C13—C8—C9—C10 | 0.6 (4) | C13—C8—C7—O3 | 166.5 (3) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | 179.3 (2) | C9—C8—C7—O3 | −12.1 (4) |
| C9—C8—C13—C12 | 0.4 (4) | C13—C8—C7—N1 | −11.5 (4) |
| C7—C8—C13—C12 | −178.2 (2) | C9—C8—C7—N1 | 169.9 (2) |
| C8—C13—C12—C11 | −1.3 (4) | C5—C6—C1—C2 | −1.1 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −1.2 (4) | C5—C6—C1—S1 | 175.79 (19) |
| C8—C9—C10—F1 | 179.0 (2) | C3—C2—C1—C6 | 1.7 (4) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | −0.9 (4) | C3—C2—C1—S1 | −175.14 (18) |
| C6—C5—C4—C3 | 0.6 (4) | O2—S1—C1—C6 | −19.8 (2) |
| C6—C5—C4—C14 | 179.7 (2) | O1—S1—C1—C6 | −150.97 (19) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.0 (4) | N1—S1—C1—C6 | 99.1 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C14 | −179.0 (2) | O2—S1—C1—C2 | 157.1 (2) |
| C13—C12—C11—C10 | 1.0 (4) | O1—S1—C1—C2 | 25.9 (2) |
| F1—C10—C11—C12 | −179.7 (2) | N1—S1—C1—C2 | −84.0 (2) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | 0.1 (4) |
(II) N-(3-Fluorobenzoyl)-4-methylbenzenesulfonamide . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···O1i | 0.87 (4) | 2.06 (4) | 2.937 (3) | 177 (3) |
| C5—H5···O3ii | 0.93 | 2.46 | 3.375 (3) | 168 |
| C13—H13···O1i | 0.93 | 2.47 | 3.285 (3) | 147 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, −y+1, −z+2; (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1.
References
- Banwell, M. G., Crasto, C. F., Easton, C. J., Forrest, A. K., Karoli, T., March, D. R., Mensah, L., Nairn, M. R., O’Hanlon, P. J., Oldham, M. D. & Yue, W. (2000). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 10, 2263–2266. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2009). APEX2, SADABS and SAINT-Plus. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Chang, L. L., Ashton, W. T., Flanagan, K. L., Chen, T. B., O’Malley, S. S., Zingaro, G. J., Siegl, P. K. S., Kivlighn, S. D., Lotti, V. J., Chang, R. S. L. & & Greenlee, W. J. (1994). J. Med. Chem. 37, 4464–4478. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Gowda, B. T., Foro, S., Suchetan, P. A. & Fuess, H. (2009a). Acta Cryst. E65, o2516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Gowda, B. T., Foro, S., Suchetan, P. A. & Fuess, H. (2009b). Acta Cryst. E65, o2750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, T. & Yamamoto, H. (2000). Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn, 73, 423–428.
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Mader, M., Shih, C., Considine, E., Dios, A. D., Grossman, C., Hipskind, P., Lin, H., Lobb, K., Lopez, B., Lopez, J., Cabrejas, L., Richett, M., White, W., Cheung, Y., Huang, Z., Reilly, J. & Dinn, S. (2005). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 15, 617–620. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Musser, J. H., Kreft, A. F., Bender, R. H. W., Kubrak, D. M., Grimes, D., Carlson, R. P., Hand, J. M. & Chang, J. (1990). J. Med. Chem. 33, 240–245. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sreenivasa, S., Mohan, N. R., Manojkumar, K. E. & Suchetan, P. A. (2014). J. Appl. Chem. 3, 551–559.
- Suchetan, P. A., Foro, S. & Gowda, B. T. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Suchetan, P. A., Gowda, B. T., Foro, S. & Fuess, H. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, II, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016003248/hb7565sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016003248/hb7565Isup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) II. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016003248/hb7565IIsup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016003248/hb7565Isup4.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016003248/hb7565IIsup5.cml
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report