Abstract
Objectives:
The objective of this study was to evaluate the prevalence and severity of clozapine-induced hypersalivation, and assess the impact hypersalivation has on global functioning.
Methods:
Participants attending a dedicated clozapine clinic were invited to undertake a structured interview regarding their experiences of clozapine-induced hypersalivation. Two psychometric instruments to measure hypersalivation, the Nocturnal Hypersalivation Rating Scale and the Drooling Severity and Frequency Scale were used.
Results:
Clozapine-induced hypersalivation was experienced by 92% of participants, with nocturnal hypersalivation more prevalent compared to daytime hypersalivation (85% versus 48%). Daytime drooling was severe in 18% of cases and was present on a frequent or constant basis for 20% of individuals. Hypersalivation had at least a moderate impact on the quality of life of 15% of study participants.
Conclusions:
Clozapine-induced hypersalivation is the most prevalent adverse effect experienced by patients treated with clozapine and negatively impacts on quality of life, particularly if daytime drooling is present. The development of further strategies to ameliorate this adverse effect is required given the demonstrated lack of success to date in managing this condition.
Keywords: clozapine, drooling, frequency, hypersalivation, incidence, prevalence, quality, life schizophrenia, severity, sialorrhea, sialorrhoea
Introduction
Clozapine has consistently been demonstrated to have the greatest efficacy amongst all antipsychotic agents in the management of psychosis [Asenjo Lobos et al. 2010], with beneficial effects for positive symptoms, negative symptoms and cognitive symptoms demonstrated [Burton, 2006]. Clozapine has also been shown to significantly improve patients functioning [Wheeler et al. 2009] and quality of life [Kim et al. 2006; Lewis et al. 2006]. However, its potential for inducing profound neutropenia has predominantly limited its use to treatment-resistant schizophrenia [Crilly, 2007]. Clozapine is also associated with a wide array of more prevalent, albeit predominantly less severe, adverse effects many of which impact on individuals’ quality of life. One of the most prevalent of these is hypersalivation, although wide variance in prevalence rates (30–80%) has been reported [Syed et al. 2008]. In addition, hypersalivation has been found to be under-reported to clinicians [Yusufi et al. 2007]. Consequently, not only may the rates of clozapine-induced hypersalivation be high, the effect on patient’s quality of life may also be under-estimated [Nielsen et al. 2010].
Limited data are present pertaining to the severity of hypersalivation experienced by patients treated with clozapine. Existing studies predominantly investigate either the prevalence of numerous adverse effects experienced, of which hypersalivation is one [Syed et al. 2008] or investigate salivary flow rates in the context of antipsychotic-induced hypersalivation [Ben-Aryeh et al. 1996]. Consequently in this study we wanted to ascertain, through structured interviews, the prevalence of hypersalivation at a specialized clozapine clinic. In addition, we wanted to ascertain: (1) the severity of hypersalivation experienced by patients, (2) the impact of hypersalivation on individuals’ quality of life, (3) patients perspectives in relation to how hypersalivation ranked amongst other adverse effects experienced, (4) if hypersalivation was associated with treatment dose or plasma levels of clozapine, (5) if any previous management strategies had alleviated this adverse effect and (6) participants’ views in relation to their mental health care team’s perspective regarding hypersalivation.
Method
Participants
This study was undertaken at a dedicated clozapine clinic in Galway University Hospital, Ireland. Consecutive participants attending for their routine blood tests (full blood count) were invited to participate. Exclusion criteria included individuals <18 years of age, the presence of an intellectual disability (intelligence quotient <70), a diagnosis of dementia and the presence of acute psychosis. Of the 161 individuals attending, 1 individual was excluded due to experiencing acute psychosis and 62 individuals refused to participate. Thus, the study consisted of a sample size of 98 (61%) individuals who provided written informed consent to participate in this study (see Figure 1). Ethical approval was attained from the Galway University Hospital Research Ethics Committee and the study was conducted in accordance with the Helsinki declaration on research ethics.
Figure 1.
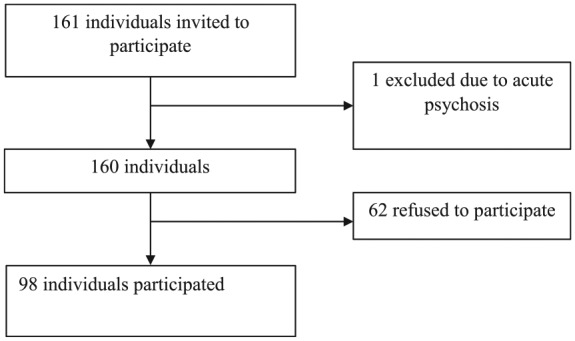
Flow diagram.
Structured interview and measures
Demographic data collected included gender, age, employment, and marital and domiciliary status. Clinical data included diagnosis, time on clozapine (in years), clozapine dose and most recent clozapine plasma level at the time of interview. We utilized two psychometric instruments to measure hypersalivation, the Nocturnal Hypersalivation Rating Scale (NHRS) [Spivak et al. 1997] and the Drooling Severity and Frequency Scale (DSFS) [Rashnoo and Daniel, 2015]. The NHRS is a validated five-item scale utilized to ascertain the severity of nocturnal salivation. Scores range from no nocturnal hypersalivation to being awoken at least three times per night due to hypersalivation [Spivak et al. 1997]. Due to the anticipated number of participants that might score ‘1’ (patient has saliva on pillow in the morning) but who were not awoken because of this, we also enquired if participants had to change their pillow more frequently or had to cover their pillow with a towel due to hypersalivation [Bai et al. 2001]. The DSFS a validated instrument to assess the severity of daytime drooling [Rashnoo and Daniel, 2015]. Drooling severity is graded on a five-point scale with scores ranging from no drooling to profuse drooling, where drool drips off the body onto objects and furniture. Drooling frequency is assessed on a four-point scale from no drooling to constant drooling. The two scores are then summed together to give the drooling severity and frequency score.
Impact of hypersalivation on quality of life was measured on a five-point scale ranging from ‘no impact’ on quality of life to ‘single biggest problem’ in life. In addition, participants were directly asked about the presence of 16 additional side effects (see Table 3), and asked to rank the side effects experienced depending on their impact on quality of life to a maximum of 3. This could include side effects other than the 16 listed. Participants who were currently experiencing hypersalivation were also asked if they perceived that their treating team was aware of the impact that hypersalivation had on their quality of life. All interviews were conducted by one researcher who was not involved in patients’ clinical care (all patients were fully aware of this).
Table 3.
Adverse effects experienced.
| Adverse effects |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Experienced n (%) | Most significant n (%) | One of 3 most significant n (%) | |
| Clozapine-induced side-effects | |||
| Hypersalivation | 90 (91.8) | 7 (7.1) | 24 (24.5) |
| Drowsiness | 61 (62.2) | 13 (13.3) | 30 (30.6) |
| Fatigue | 55 (56.1) | 11 (11.2) | 23 (23.5) |
| Weight gain | 47 (48.0) | 13 (13.3) | 26 (26.5) |
| Gastrointestinal upset | 31 (31.6) | 6 (6.1) | 14 (14.3) |
| Dizziness | 29 (29.6) | 3 (3.1) | 9 (9.2) |
| Restless legs | 22 (22.4) | 2 (2.0) | 6 (6.1) |
| Urinary incontinence or retention | 20 (20.4) | 1 (1.0) | 5 (5.1) |
| Tachycardia | 17 (17.3) | 2 (2.0) | 3 (3.1) |
| Tremor | 15 (15.3) | 1 (1.0) | 3 (3.1) |
| Rigidity | 14 (14.3) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.0) |
| Agitation | 11 (11.2) | 2 (2.0) | 4 (4.1) |
| Headache | 10 (10.2) | 1 (1.0) | 4 (4.1) |
| Hypertension | 8 (8.2) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.0) |
| Seizures | 7 (7.1) | 2 (2.0) | 2 (2.0) |
| Skin reactions | 7 (7.1) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Other* | 7 (7.1) | 2 (2.0) | 7 (7.1) |
Included sexual dysfunction, insomnia, dysphagia, reduced appetite or abnormal taste in mouth.
Statistical analysis was performed using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences 21.0 for Windows (SPSS Inc., IBM, New York, USA). We utilized the Student’s t-test for parametric data and the Chi-square test for nonparametric categorical data where appropriate. The Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient (nonparametric) was used to determine the correlations between quality of life and indices of hypersalivation severity.
Results
Demographic and clinical data
Demographic and clinical data are described in Table 1. Of note, 70 individuals (71.4%) were male and the mean age of participants was 41.4 years (SD = 12.1). The most common relationship status was single (80.6%), with most participants either living alone (25.2%) or with siblings or parents (39.8%) and the most common socioeconomic class (SEC) was SEC V (60.2%). All individuals had either a DSM-5 diagnosis of treatment-resistant schizophrenia (90.8%) or schizoaffective disorder (9.2%). Clozapine was augmented with additional antipsychotic agents in 33 individuals (33.7%), with aripiprazole or amisulpride employed in all but 7 individuals. Clozapine treatment was also augmented with mood-stabilizing agents (21.4%) and antidepressants (18.4%). Treatments to ameliorate hypersalivation had been employed in 17 individuals (17.3%) with three of these participants noting a modest benefit, which was independently corroborated by medical and clozapine nursing staff.
Table 1.
Demographic and clinical characteristics.
| Variable | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Gender | |
| Male | 70 (71.4%) |
| Female | 28 (28.6%) |
| Employment status | |
| 3rd level education | 8 (8.2) |
| Employed | 26 (26.5) |
| Unemployed | 64 (65.3) |
| Relationship status | |
| Single | 79 (80.6) |
| In a relationship | 4 (4.1) |
| Married | 12 (12.2) |
| Divorced / separated | 3 (3.1) |
| Living arrangements | |
| Alone | 25 (25.2) |
| With parents or siblings | 39 (39.8) |
| With partner or spouse | 13 (13.3) |
| In supported accommodation* | 21 (21.4) |
| Socioeconomic class | |
| I or II | 10 (10.2) |
| III | 21 (21.4) |
| IV | 8 (8.2) |
| V | 59 (60.2) |
| Diagnosis | |
| Schizophrenia | 89 (90.8) |
| Schizoaffective disorder | 9 (9.2) |
| Additional antipsychotic agents | |
| Amisulpride | 12 (12.2) |
| Aripiprazole | 14 (14.3) |
| Olanzapine | 3 (3.1) |
| Risperidone | 1 (1.0) |
| Haloperidol | 1 (1.0) |
| Flupenthixol decanoate | 1 (1.0) |
| Zuclopenthixol decanoate | 1 (1.0) |
| None | 65 (66.3) |
| Mood stabiliser medications** | |
| Sodium valproate | 12 (12.2) |
| Lamotrigine | 6 (6.1) |
| Lithium | 5 (5.1) |
| None | 77 (78.6) |
| Antidepressants | |
| Yes | 18 (18.4) |
| No | 80 (81.6) |
| Treatments utilized to reduce hypersalivation | |
| Hyoscine hydrobromide | 13 (13.3) |
| Scopolamine patch | 2 (2.0) |
| Pirenzipine | 1 (1.0) |
| Procyclidine | 1 (1.0) |
| None | 81 (82.7) |
| Mean (SD), range | |
| Age | 41.4 (12.1), 18–83 |
| Clozapine treatment | |
| Dose (mg/day) | 354.1 (159.4), 75–925 |
| Serum level | 0.41 (0.24), 0.1–1.4 |
| Duration of treatment (years) | 7.3 (6.7), 0.2–21.5 |
Accommodation provided by mental health or homeless services.
Two participants were on two mood-stabilizing medications.
Clozapine-induced hypersalivation
Hypersalivation was experienced by 90 individuals (91.8%) (Table 2), with 83 individuals (84.7%) experiencing nocturnal hypersalivation and 47 individuals (48.0%) experiencing daytime drooling at the time the study was conducted. Of those individuals with nocturnal hypersalivation, 31 individuals (31.6%) were awoken from sleep. A total of 50% of individuals with nocturnal hypersalivation who were not awoken (mild on NHRS) changed their pillow frequently or used a towel at night due to significant drooling. In relation to daytime drooling, 20 individuals (20.4%) experienced either frequent or constant drooling and 18 individuals (18.4%) experienced drool dripping onto their clothes or objects.
Table 2.
Clozapine-induced hypersalivation.
| Measure of hypersalivation | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Presence of hypersalivation | |
| Yes | 90 (91.8) |
| No | 8 (8.2) |
| NHRS | |
| Absent | 15 (15.3) |
| Minimal (saliva on pillow) | 52 (53.1) |
| Mild (wakes patient once per night) | 15 (15.3) |
| Moderate (wakes patient twice per night) | 9 (9.2) |
| Severe (wakes patient three times or more) | 7 (7.1) |
| DSFS: drooling severity | |
| Nil | 51 (52) |
| Mild drooling (wets lips) | 16 (16.3) |
| Moderate drooling (drool reaches lips and chin) | 13 (13.3) |
| Severe drooling (drool drips onto clothing) | 15 (15.3) |
| Profuse drooling (drool drips onto furniture or objects) | 3 (3.1) |
| DSFS: drooling frequency | |
| No drooling | 51 (52) |
| Occasional drooling | 27 (27.6) |
| Frequent drooling | 11 (11.2) |
| Constant drooling | 9 (9.2) |
| Impact of hypersalivation on quality of life | |
| No effect | 36 (42.4) |
| Minor effect | 33 (38.8) |
| Moderate effect | 7 (8.2) |
| Major effect | 5 (5.9) |
| Profound effect (greatest difficulty in life at present) | 1 (1.2) |
| Perceived awareness of hypersalivation by treating team* | |
| Fully aware | 52 (61.2) |
| Underestimated or minimal awareness | 8 (9.4) |
| Totally unaware | 13 (15.3) |
DSFS, Drooling Severity and Frequency Scale; NHRS, Nocturnal Hypersalivation Rating Scale.
Some participants chose not to answer this question (n = 17).
A total of 13 individuals (15.3%) suffering from clozapine-induced hypersalivation at the time of the study believed it had at least a moderate impact on their quality of life (see Table 2). Modest correlations were noted between total DSFS score (r = 0.38, p < 0.001), drooling frequency (r = 0.38, p < 0.001), drooling severity (r = 0.39, p < 0.001) and NHRS score (r = 0.21, p = 0.06) and impact on quality of life. Two individuals had previously experienced hypersalivation with antipsychotic medications and this became even more severe with clozapine treatment. The presence of hypersalivation was not significantly correlated with duration of treatment (r = -0.41, p = 0.70), clozapine dose (r = 0.12,p = 0.27) or plasma level of clozapine (r = -0.11, p = 0.34). The presence or severity of hypersalivation was not affected by treatment with additional antipsychotic (r = -0.04, p = 0.73) or other psychotropic agents (r = -0.14, p = 0.20).
A majority of participants believed their treating clinician or clozapine nurse had a good awareness of their experience of hypersalivation (71.2%).
Other adverse effects
A mean of 4.6 (SD = 2.9) adverse effects were experienced by participants, with particularly high rates of clozapine-induced drowsiness (62.2%), fatigue (56.1%) and weight gain (48.0%) noted (Table 3). Hypersalivation was ranked as the most significant adverse effect by 7.1% of participants and was ranked as one of the three most significant adverse effects by 24 participants (24.5%). Clozapine-induced drowsiness (13.3%), weight gain (13.3%) and fatigue (11.2%) were the most significant adverse effects reported by participants.
Discussion
Our principle finding in this study is a very high rate (92%) of hypersalivation secondary to treatment with clozapine. This finding is consistent with some studies [Qurashi et al. 2015; Essali et al. 2009] but higher than several other previous studies [Davydov and Botts, 2000; Syed et al. 2008]. In contrast to some of these studies, we utilized two validated instruments to measure rates of hypersalivation. Previous estimates of lower rates might be due to nonreporting by patients who were not questioned directly about this adverse effect [Yusifi et al. 2007].
One potential reason for participants to not report hypersalivation may relate to participants not perceiving this adverse effect as having the greatest impact on their quality of life. A total of 29% of individuals in this study believed their clinicians were either partially or fully unaware of this adverse effect. Although less frequently reported in this study, drowsiness, fatigue and weight gain were rated as having a greater impact on quality of life. While hypersalivation (nocturnal and daytime) impacted on quality of life in this study, only daytime drooling demonstrated statistical significance in this regard. This finding is in contrast to a recent study [Qurashi et al. 2015] where nocturnal hypersalivation was also found to impact statistically on quality of life. However, unlike Qurashi and colleagues [Qurashi et al. 2015] who undertook a comparison of clozapine-induced hypersalivation compared to previous antipsychotic-induced hypersalivation; we undertook no such comparison, as hypersalivation has consistently been reported as more prevalent secondary to clozapine than other antipsychotic agents [Asenjo Lobos, 2010]. Indeed, only two participants stated that this was a significant adverse effect for them previously with other psychotropic agents. Our study was also based in a different setting (general adult service versus a forensic service) and included a larger cohort of patients.
Hypersalivation is a paradoxical side effect of clozapine given its potent anticholinergic effects. Although several proposed mechanisms exist, management strategies based on such mechanisms have demonstrated minimal efficacy to date. Proposed mechanisms include clozapine agonism at the M4 muscarinic receptor [Zorn et al. 1994], alpha-2 antagonism [Corrigan et al. 1995] unopposed beta adrenoceptors activity secondary to alpha-1 and alpha-2 antagonism [Rogers and Shamkro, 2000] and decreased laryngeal peristalsis [Praharaj et al. 2006]. Pharmacotherapeutic strategies employed based on these mechanisms include the use of antimuscarinic agent, scopolamine [Takeuchi et al. 2015], pirenzepine [Rogers and Shramko, 2000] and atropine [Chu et al. 2015], alpha-2 agonists such as clonidine [Praharaj et al. 2005; Praharaj et al. 2006] and a variety of other agents including minocycline [Qurashi et al. 2014], amisulpride [Kreinin et al. 2006] and botulinum toxin [Kahl et al. 2004]. Reviews of all available treatments to date have largely concluded that sample sizes are too small or of insufficient study quality to clearly inform or change clinical practice [Rogers and Shramko, 2000; Sockalingam et al. 2007; Syed et al. 2008]. In this study, only three participants demonstrated any benefit with such treatment, with this effect only modest in nature. No association was ascertained between hypersalivation and either dose or plasma level of clozapine. Thus, dose alteration or augmentation of clozapine with other agents may not be strategies that confer a significant benefit for this adverse effect, albeit this study was not longitudinal in design and thus caution is required with such an interpretation.
There are a number of limitations with this study. First, the assessor was not blinded to current patient management; however, he was not involved in the clinical management of any patient which was made explicit to participants. Second, a relatively large sample (37.3%) refused to engage with this study; however no statistical difference in diagnosis, treatment or other demographic or clinical factors were noted between the groups. Third, approximately one-third of participants were on additional antipsychotic agents with other participants treated additionally with mood-stabilizing or antidepressant agents. However, no difference in the rates or severity of hypersalivation was identified between individuals attaining clozapine monotherapy and those attaining prescribed psychotropic agents.
Conclusion
Clozapine-induced hypersalivation is the most prevalent adverse effect suffered by patients treated with clozapine with daytime drooling, in particular negatively impacting on patients’ quality of life. We believe, based on the findings of this study that the NHRS and DSS should be employed routinely for the measurement of hypersalivation for patients treated with clozapine. In addition, information regarding the effect of hypersalivation on patients’ quality of life should be attained. The development of further strategies to ameliorate hypersalivation would be welcomed given the lack of effective treatment strategies to date. Such strategies may be associated with improved quality of life and increased levels of treatment adherence.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to all participants for their input into this study. We also wish to thank staff members Esther Courtney, Elaine Callinan, Allison Dunne, Elaine Maloney and Nigel Conneely working in the clozapine service for their assistance with this project.
Footnotes
Funding: This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Contributor Information
Senan Maher, National University of Ireland Galway, Clinical Sciences Institute, Galway, Ireland.
Aoife Cunningham, National University of Ireland Galway, Ireland.
Niamh O’Callaghan, National University of Ireland Galway, Ireland.
Fintan Byrne, National University of Ireland Galway, Ireland.
Colm Mc Donald, National University of Ireland Galway, Ireland.
Shane McInerney, National University of Ireland Galway, Ireland.
Brian Hallahan, National University of Ireland Galway, Ireland.
References
- Asenjo Lobos C., Komossa K., Rummel-Kluge C., Hunger H., Schmid F., Schwarz S., et al. (2010) Clozapine versus other atypical antipsychotics for schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev CD006633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bai Y., Lin C., Chen J., Liu W. (2001) Therapeutic effect of pirenzepine for clozapine-induced hypersalivation: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over study. J Clin Psychopharmacol 21: 608–611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Aryeh H., Jungerman T., Szargel R., Klein E., Laufer D. (1996) Salivary flow-rate and composition in schizophrenic patients on clozapine: Subjective reports and laboratory data. Biol Psychiatry 39: 946–949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrigan F., MacDonald S., Reynolds G. (1995) Clozapine-induced hypersalivation and the alpha2 adrenoceptor. Br J Psychiatry 167: 412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu S., Qurashi I., Campbell N., Stephenson P., Massey R., Drake R., Husain N. (2016) A natural study of the efficacy of replacement medications for the treatment of clozapine-induced hypersalivation. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol 29 June 2015. (ePub ahead of print). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crilly J. (2007) The history of clozapine and its emergence in the US market: a review and analysis. Hist Psychiatr 18: 39–60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davydov L., Botts S. (2000) Clozapine-induced hypersalivation. Ann Pharmacother 34: 662–665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Essali A., Al-Haj Hassan N., Li C., Rathbone J. (2009) Clozapine versus typical neuroleptic medication for schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev CD000059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahl K. G., Hagenah J., Zapf S., Trillenberg P., Klein C., Lencer R. (2004) Botulinum toxin as an effective treatment of clozapine-induced hypersalivation. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 173: 229–230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krenin A., Novitski D., Weizman A. (2006) Amisulpride treatment of clozapine-induced hypersalivation in schizophrenia patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled cross-over study. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 21: 99–103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Kim S., Ahn Y., Kim Y. (2006) Subjective response to clozapine and risperidone treatment in outpatients with schizophrenia. Prog NeuroPsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatr 30: 301–305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S., Barnes T., Davies L., Murray R., Dunn G., Hayhurst K., et al. (2006) Randomized controlled trial of effect of prescription of clozapine versus other second-generation antipsychotic drugs in resistant schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 32: 715–723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J., Dahm M., Lublin H., Taylor D. (2010) Psychiatrists’ attitude towards and knowledge of clozapine treatment. J Psychopharmacol 24: 965–971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Praharj S., Arora M., Gandotra S. (2006) Clozapine-induced sialorrhea: pathophysiology and management strategies. Psychopharmacology 185: 265–273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Praharaj S., Verma P., Roy D., Singh A. (2005) Is clonidine useful for treatment of clozapine-induced sialorrhea? J Psychopharmacol 19: 426–428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qurashi I., Collins J., Chaudhry I., Husain N. (2014) Promising use of minocycline augmentation with clozapine in treatment-resistant schizophrenia.J Psychopharmacol 28: 707–708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qurashi I., Stephenson P., Chu S., Duffy C., Husain N., Chaudry I. (2015) An evaluation of subjective experiences, effects and overall satisfaction with clozapine treatment in a UK forensic service. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol 5: 146–150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rashnoo P., Daniel S. (2015) Drooling quantification: correlation of different techniques. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 79: 1201–1205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers D., Shramko J. (2000) Therapeutic options in the treatment of clozapine-induced sialorrhea. Pharmacotherapy 20: 1092–1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socklingham S., Shammi C., Remington G. (2007) Clozapine-induced hypersalivation: a review of treatment strategies. Can J Psychiatry 52: 377–384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spivak B., Adlersberg S., Rosen L., Gonen N., Mester R., Weizman A. (1997) Trihexyphenidyl treatment of clozapine-induced hypersalivation. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 12: 213–215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syed R., Au K., Cahill C., Duggan L., He Y., Udu V., Xia J. (2008) Pharmacological interventions for clozapine-induced hypersalivation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev CD005579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi I., Suzuki T., Kishi T., Kanamori D., Hanya M., Uno J., et al. (2015) Effect of scopolamine butylbromide on clozapine-induced hypersalivation in schizophrenic patients: a case series. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci 13: 109–112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler A., Humberstone V., Robinson G. (2009) Outcomes for schizophrenia patients with clozapine treatment: how good does it get? Journal of Psychopharmacology, 23: 957–965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yusufi B., Mukherjee S., Flanagan R., Paton C., Dunn G., Page E., Barnes T. (2007) Prevalence and nature of side effects during clozapine maintenance treatment and the relationship with clozapine dose and plasma concentration. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 22: 238–243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorn S., Jones S., Ward K., Liston D. (1994) Clozapine is a potent and selective muscarinic M4 receptor agonist. Eur J Pharmacol 269: R1–R2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


