Figure 5.
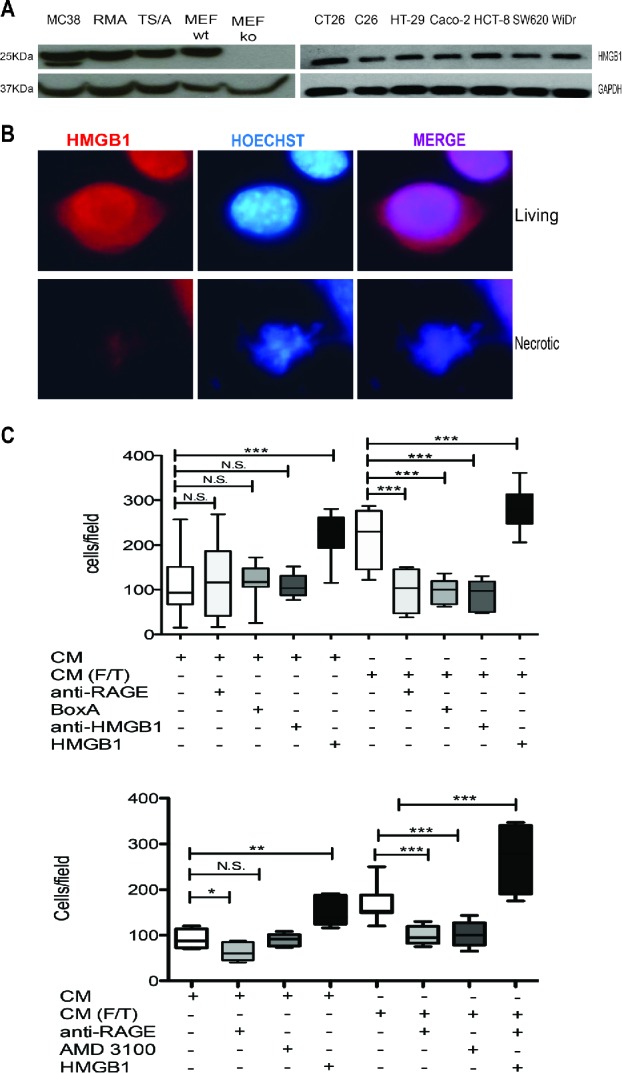
Colon cancer cell HMGB1 expression and biological activity. (A) Western Blot analysis of HMGB1 in murine colon carcinoma cells (MC-38); H-2b mouse lymphoma cells (RMA); mouse mammary adenocarcinoma cell line (TS/A); wild-type mouse Embryonic Fibroblast cells (MEF-wt) and Hmgb1 Knock Out Murine Embryonic Fibroblast cells (MEF-ko); murine colon adenocarcinoma cell lines (CT-26; C-26) and human colon adenocarcinoma cell lines (HT-29; Caco-2; HCT8; SW 620; WiDr). GAPDH was used as loading control. (B) HMGB1 expression (red) was revealed by immunofuorescence in living or freezed-thawed necrotic (F/T) MC-38 cells. Nuclei were counterstained with HOECHST (blue). (C) Murine bone-marrow-derived macrophage migration was assessed in a Boyden Chamber assay in response to conditioned media (CM) of living or necrotic (F/T) MC-38 cells, in the presence or the absence of HMGB1, anti-RAGE antibodies, Box A, anti-HMGB1 antibodies, and (E) the CXCR4 antagonist, AMD3100 as indicated. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.005; ***p < 0.001; significantly different from control (Unpaired T test).
