Abstract
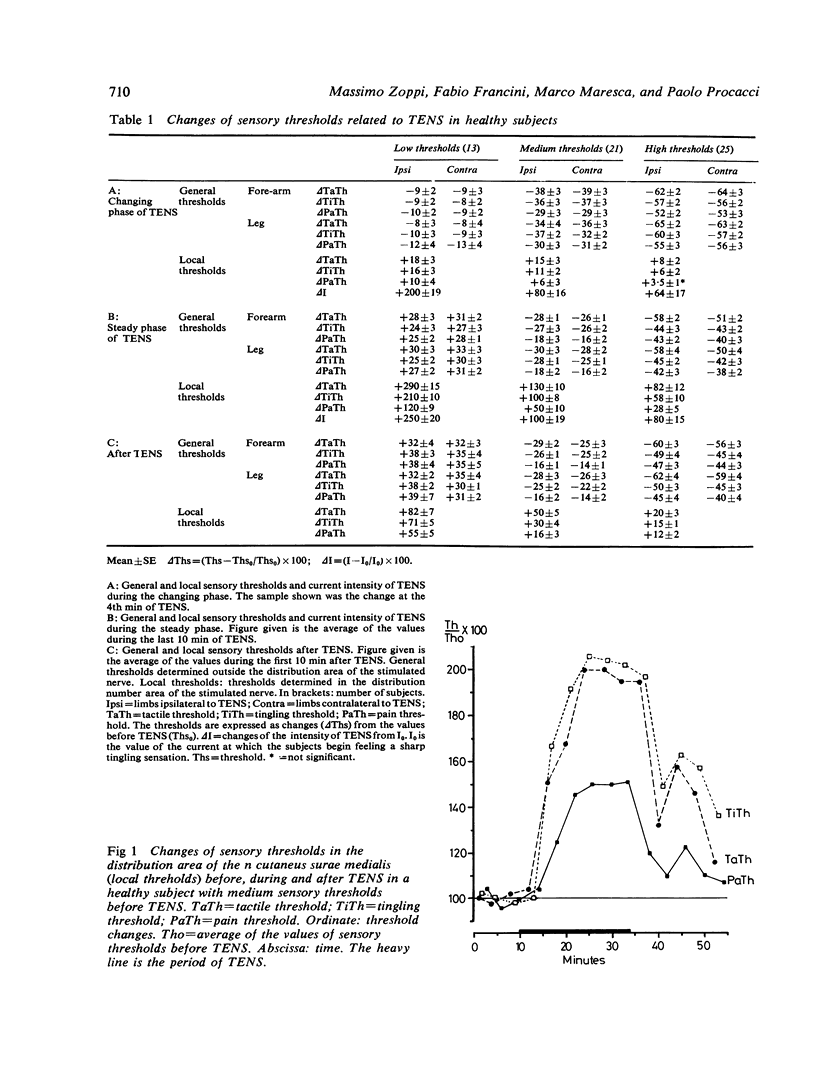
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) of the nervi cutaneus surae medialis was applied to 59 healthy subjects and 30 patients suffering from chronic myofascial pain in one lower limb, with an intensity of current that induced a well tolerated tingling sensation. Each period of stimulation lasted 24 minutes. The thresholds of the tactile, tingling and painful sensations were tested at fixed intervals before, during and after stimulation. Trains of constant current square waves in the distribution area of the stimulated nerve (local thresholds) and in other areas (general thresholds) were used. In all subjects repeated changes of the current were necessary in order to maintain constant tingling during the first period of TENS (changing phase); after that few if any changes of the current were necessary (steady phase). There were changes in thresholds within the territory of the electrically stimulated nerve, and marked changes elsewhere and generally in the body. In healthy subjects local thresholds increased during both phases of TENS; general thresholds decreased during the changing phase and increased during the steady phase. After TENS, thresholds showed the same trend as during the steady phase. Trends of the sensory thresholds during and after TENS differed in different subjects according to their thresholds before TENS. Thresholds did not return to normal for more than 20 minutes after TENS. In the group of 30 patients there was a significant difference between thresholds on the two sides of the body. The difference between the two sides was reduced by TENS. Pain relief induced by TENS may be related to this fact.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bates J. A., Nathan P. W. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation for chronic pain. Anaesthesia. 1980 Aug;35(8):817–822. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1980.tb03926.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callaghan M., Sternbach R. A., Nyquist J. K., Timmermans G. Changes in somatic sensitivity during transcutaneous electrical analgesia. Pain. 1978 Aug;5(2):115–127. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(78)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman C. R., Wilson M. E., Gehrig J. D. Comparative effects of acupuncture and transcutaneous stimulation on the perception of painful dental stimuli. Pain. 1976 Sep;2(3):265–283. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(76)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francini F., Zoppi M., Maresca M., Procacci P. Skin potential and EMG changes induced by cutaneous electrical stimulation. I. Normal man in arousing and non-arousing environment. Appl Neurophysiol. 1979;42(3):113–124. doi: 10.1159/000102355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long D. M., Hagfors N. Electrical stimulation in the nervous system: the current status of electrical stimulation of the nervous system for relief of pain. Pain. 1975 Jun;1(2):109–123. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(75)90096-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAINTAL A. S. Participation by pressure-pain receptors of mammalian muscles in the flexion reflex. J Physiol. 1961 May;156:498–514. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Procacci P., Francini F., Maresca M., Zoppi M. Skin potential and EMG changes induced by cutaneous electrical stimulation. II. Subjects with reflex sympathetic dystrophies. Appl Neurophysiol. 1979;42(3):125–134. doi: 10.1159/000102356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Procacci P., Francini F., Zoppi M., Maresca M. Cutaneous pain threshold changes after sympathetic block in reflex dystrophies. Pain. 1975 Jun;1(2):167–175. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(75)90100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Procacci P., Zoppi M., Dorigo B., Voegelin M. R., Pampanini A., Bolletti A., Bartoli V. La soglia del dolore cutaneo negli arti inferiori determinata con l'algometria termica. Studio comparativo in soggetti normali, mialgici e arteriopatici. Minerva Cardioangiol. 1971 Nov;19(11):593–598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall P. D., Sweet W. H. Temporary abolition of pain in man. Science. 1967 Jan 6;155(3758):108–109. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3758.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



