Abstract
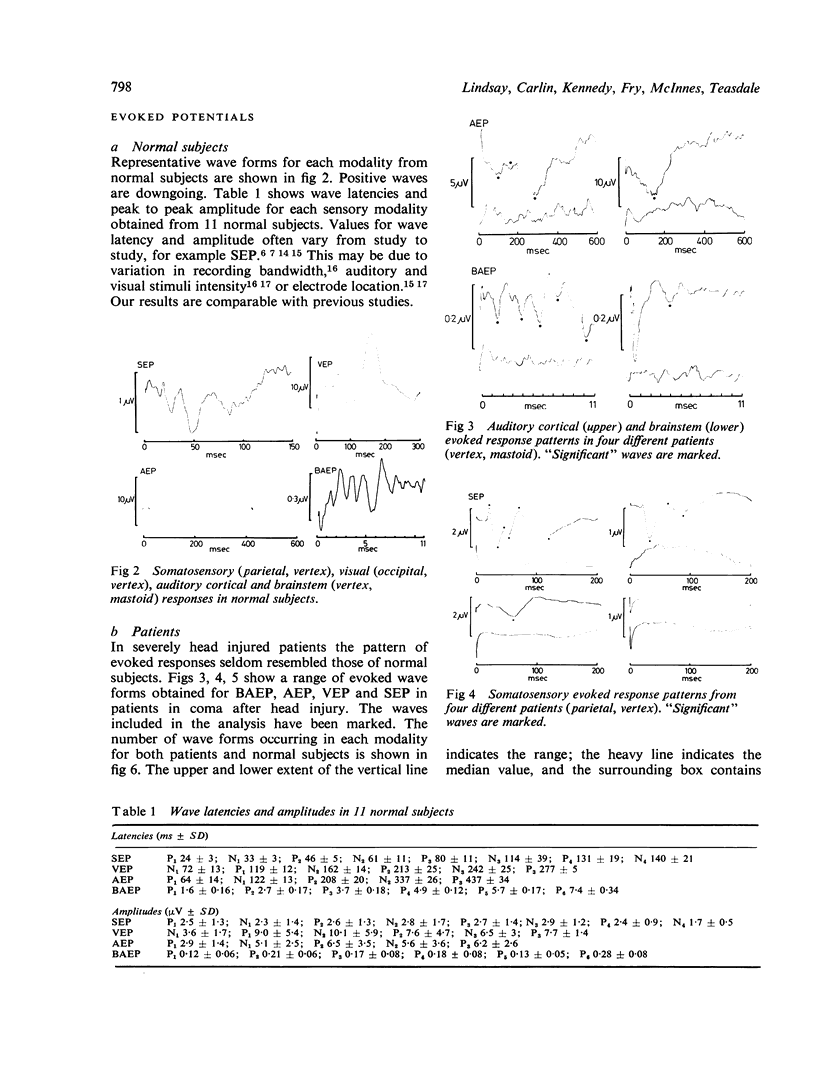
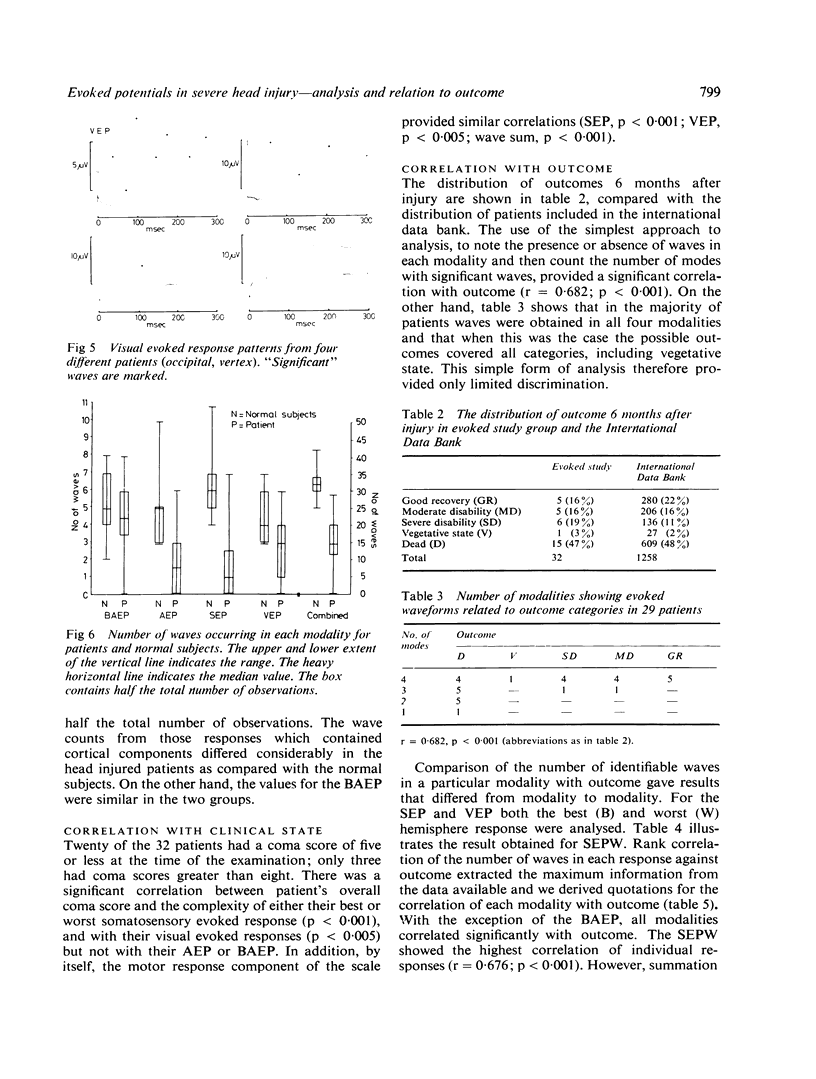
Somatosensory, visual and auditory cortical and brainstem evoked responses were obtained from 32 patients with severe head injury. A simple count of the number of waves present in the various responses provided the optimum method of analysing the data. The results of each cortical response, but not of the brainstem response, correlated with outcome, and a combined assessment gave the highest correlation. The data provided only slight improvement on predictions based upon clinical features.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braakman R., Gelpke G. J., Habbema J. D., Maas A. I., Minderhoud J. M. Systematic selection of prognostic features in patients with severe head injury. Neurosurgery. 1980 Apr;6(4):362–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De La Torre J. C., Trimble J. L., Beard R. T., Hanlon K., Surgeon J. W. Somatosensory evoked potentials for the prognosis of coma in humans. Exp Neurol. 1978 Jun;60(2):304–317. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(78)90085-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinsod M., Auerbach E. Electrophysiological examinations of the visual system in the acute phase after head injury. Eur Neurol. 1973;9(1):56–64. doi: 10.1159/000114201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff G. D., Matsumiya Y., Allison T., Goff W. R. The scalp topography of human somatosensory and auditory evoked potentials. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1977 Jan;42(1):57–76. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(77)90151-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg R. P., Becker D. P., Miller J. D., Mayer D. J. Evaluation of brain function in severe human head trauma with multimodality evoked potentials. Part 2: Localization of brain dysfunction and correlation with posttraumatic neurological conditions. J Neurosurg. 1977 Aug;47(2):163–177. doi: 10.3171/jns.1977.47.2.0163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg R. P., Mayer D. J., Becker D. P., Miller J. D. Evaluation of brain function in severe human head trauma with multimodality evoked potentials. Part 1: Evoked brain-injury potentials, methods, and analysis. J Neurosurg. 1977 Aug;47(2):150–162. doi: 10.3171/jns.1977.47.2.0150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennett B., Bond M. Assessment of outcome after severe brain damage. Lancet. 1975 Mar 1;1(7905):480–484. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92830-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennett B., Teasdale G., Braakman R., Minderhoud J., Heiden J., Kurze T. Prognosis of patients with severe head injury. Neurosurgery. 1979 Apr;4(4):283–289. doi: 10.1227/00006123-197904000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennett B., Teasdale G., Braakman R., Minderhoud J., Knill-Jones R. Predicting outcome in individual patients after severe head injury. Lancet. 1976 May 15;1(7968):1031–1034. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92215-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson S. J., Sances A., Jr, Ackmann J. J., Reigel D. H. Noninvasive evaluation of head trauma patients. Surgery. 1973 Jul;74(1):34–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibasaki H., Yamashita Y., Tsuji S. Somatosensory evoked potentials. Diagnostic criteria and abnormalities in cerebral lesions. J Neurol Sci. 1977 Dec;34(3):427–439. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(77)90159-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr A., Schwartzkroin P. Cochlear-microphonic and middle-ear pressure changes during nitrous oxide anesthesia in cats. J Acoust Soc Am. 1972 Apr;51(4):1367–1369. doi: 10.1121/1.1912985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr A. Sensory evoked potentials in clinical disorders of the nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1978;1:103–127. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.01.030178.000535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teasdale G., Jennett B. Assessment and prognosis of coma after head injury. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1976;34(1-4):45–55. doi: 10.1007/BF01405862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teasdale G., Murray G., Parker L., Jennett B. Adding up the Glasgow Coma Score. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien) 1979;28(1):13–16. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-4088-8_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsubokawa T., Nishimoto H., Yamamoto T., Kitamura M., Katayama Y., Moriyasu N. Assessment of brainstem damage by the auditory brainstem response in acute severe head injury. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1980 Nov;43(11):1005–1011. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.43.11.1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson P. D., Goff W. R., Allison T. Somato-sensory evoked responses in patients with unilateral cerebral lesions. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1970 Jun;28(6):566–575. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(70)90198-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


