Abstract
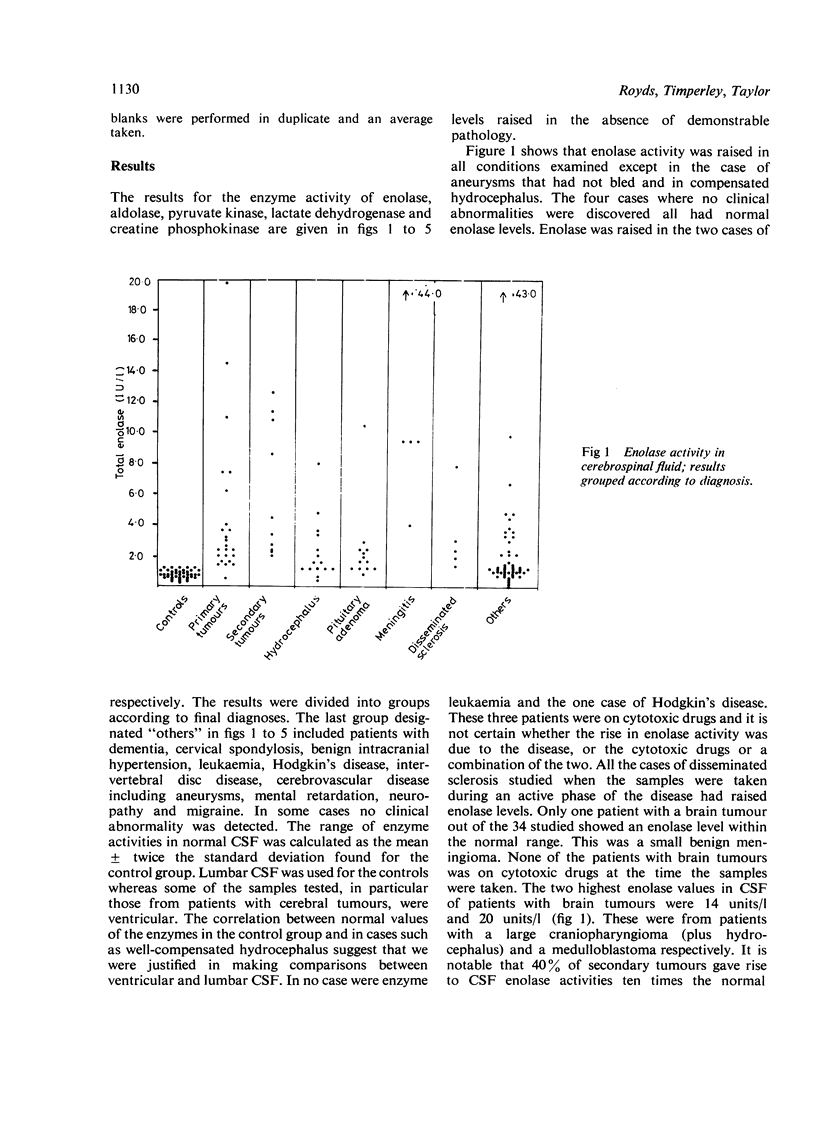
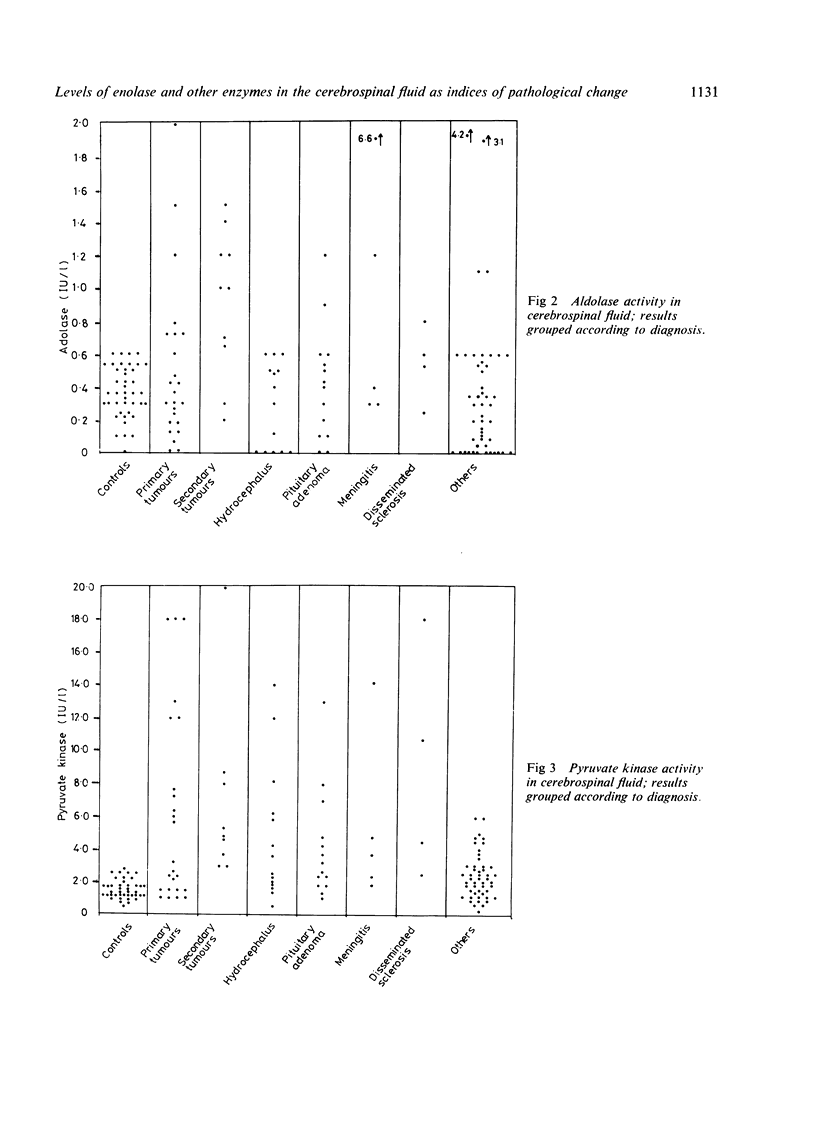
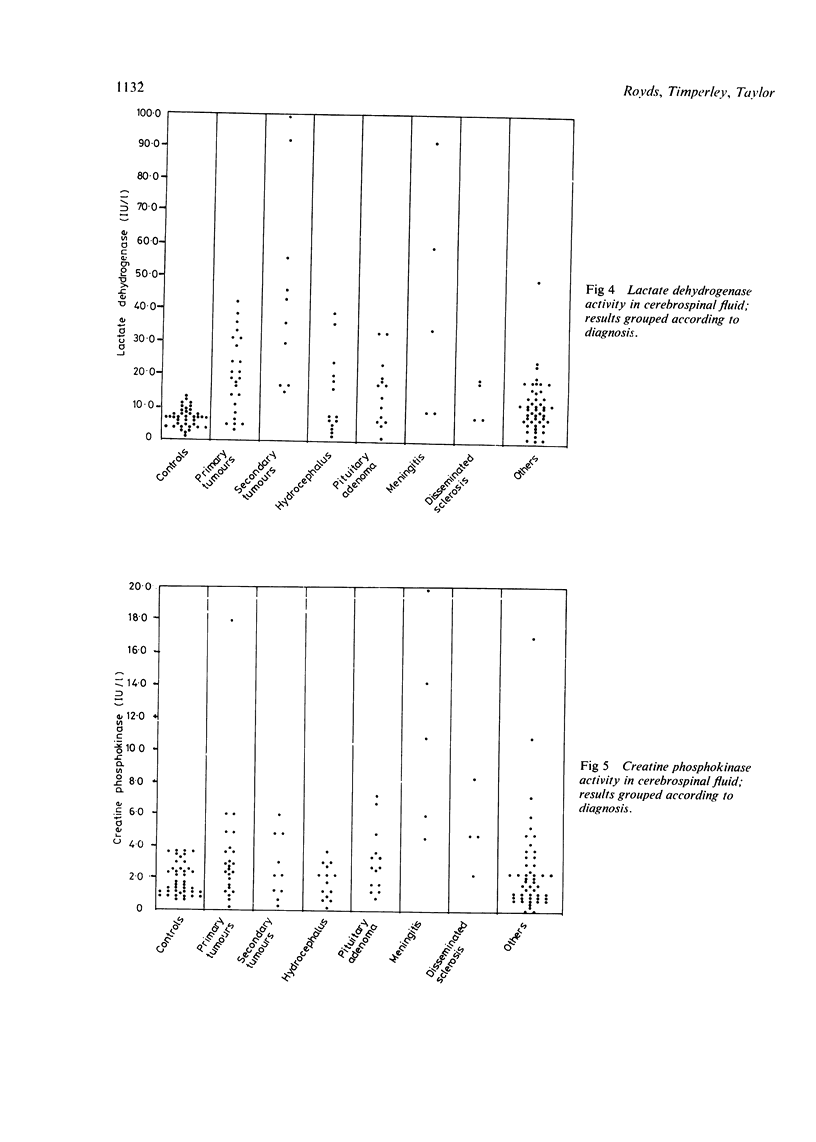
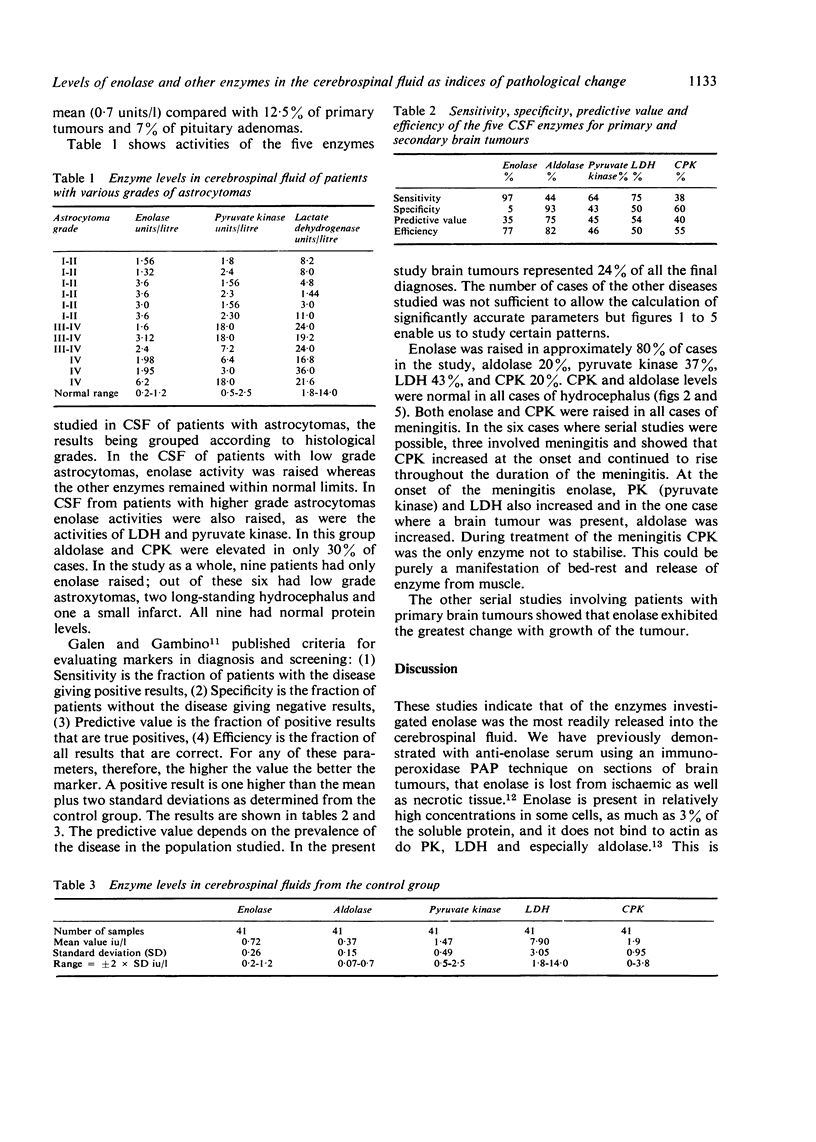
The activities of enolase, aldolase, pyruvate kinase, lactate dehydrogenase and creatine phosphokinase were measured in cerebrospinal fluid of 121 patients presenting with a range of disorders of the central nervous system. The results from 41 patients undergoing myelography were used as controls. An assessment was made of the relative merits of these five enzymes as markers of brain damage with special reference to brain tumours. Enolase was the most sensitive marker of pathological change and was the only enzyme raised in the CSF of patients with low grade astrocytomas.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clarke F. M., Masters C. J., Winzor D. J. The different adsorption of aldolase isoenzymes in rat brain. Biochem J. 1970 Jun;118(2):325–327. doi: 10.1042/bj1180325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies-Jones G. A. Lactate dehydrogenase and glutamic oxalacetic transaminase of the cerebrospinal fluid in neurological disease. J Neurol Sci. 1970 Dec;11(6):583–591. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(70)90108-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maas A. I. Cerebrospinal fluid enzymes in acute brain injury. 3. Effect of hypotension on increase of CSF enzyme activity after cold injury in cats. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1977 Sep;40(9):896–900. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.40.9.896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez Barrero F., Nieto Vales J. M., Rodríguez Navarro I. La actividad enzimática del líquido cefalorraquídeo en las vasculopatías encefálicas. Su interés diagnóstico y pronóstico. Rev Clin Esp. 1974 Sep 15;134(5):425–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. V., Carey W. F., Pollard A. C. Diagnostic significance and source of lactate dehydrogenase and its isoenzymes in cerebrospinal fluid of children with a variety of neurological disorders. J Clin Pathol. 1975 Oct;28(10):828–833. doi: 10.1136/jcp.28.10.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rider C. C., Taylor C. B. Enolase isoenzymes in rat tissues. Electrophoretic, chromatographic, immunological and kinetic properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Sep 13;365(1):285–300. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90273-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidenfeld J., Marton L. J. Biochemical markers of central nervous system tumors measured in cerebrospinal fluid and their potential use in diagnosis and patient management: a review. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1979 Oct;63(4):919–931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UNDERWOOD A. H., NEWSHOLME E. A. SOME PROPERTIES OF FRUCTOSE 1,6-DIPHOSPHATASE OF RAT LIVER AND THEIR RELATION TO THE CONTROL OF GLUCONEOGENESIS. Biochem J. 1965 Jun;95:767–774. doi: 10.1042/bj0950767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viallard J. L., Gaulme J., Dalens B., Dastugue B. Cerebrospinal fluid enzymology: creatine kinase, lactate dehydrogenase activity and isozyme pattern as a brain damage index. Clin Chim Acta. 1978 Nov 1;89(3):405–409. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(78)90402-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willson V. J., Graham J. G., McQueen I. N., Thompson R. J. Immunoreactive aldolase C in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with neurological disorders. Ann Clin Biochem. 1980 May;17(3):110–113. doi: 10.1177/000456328001700302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



