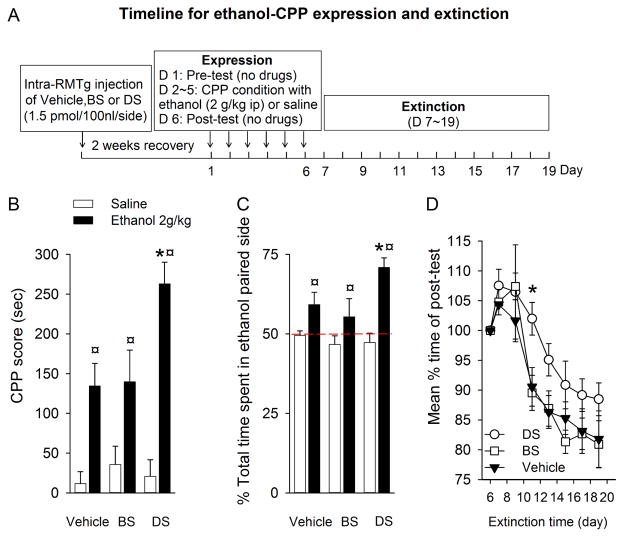
Fig. 4.
Intra-RMTg DS injection significantly enhances the expression of ethanol-induced CPP, slows the extinction, and attenuates the expression of ethanol CPA. Panel (A) depicts the timeline for the expression of ethanol induced CPP and extinction. During the post-test session, all rats conditioned with ethanol (2 g/kg) spent a longer time (B) and a greater percentage of time (C) in the ethanol-paired chamber than the rats conditioned with saline only. Furthermore, RMTg area lesions by DS markedly enhanced ethanol-induced CPP expression compared to BS and vehicle. (D) During the extinction phase, rats injected with DS extinguished slower than those in the BS- or vehicle-injected rats. ¤ p < 0.001, compared respectively to Vehicle-, BS- and DS-treated rats that conditioned with saline only; * p < 0.05, compared to BS and vehicle treated rats that conditioned with ethanol. (n=8 in each group).