Abstract
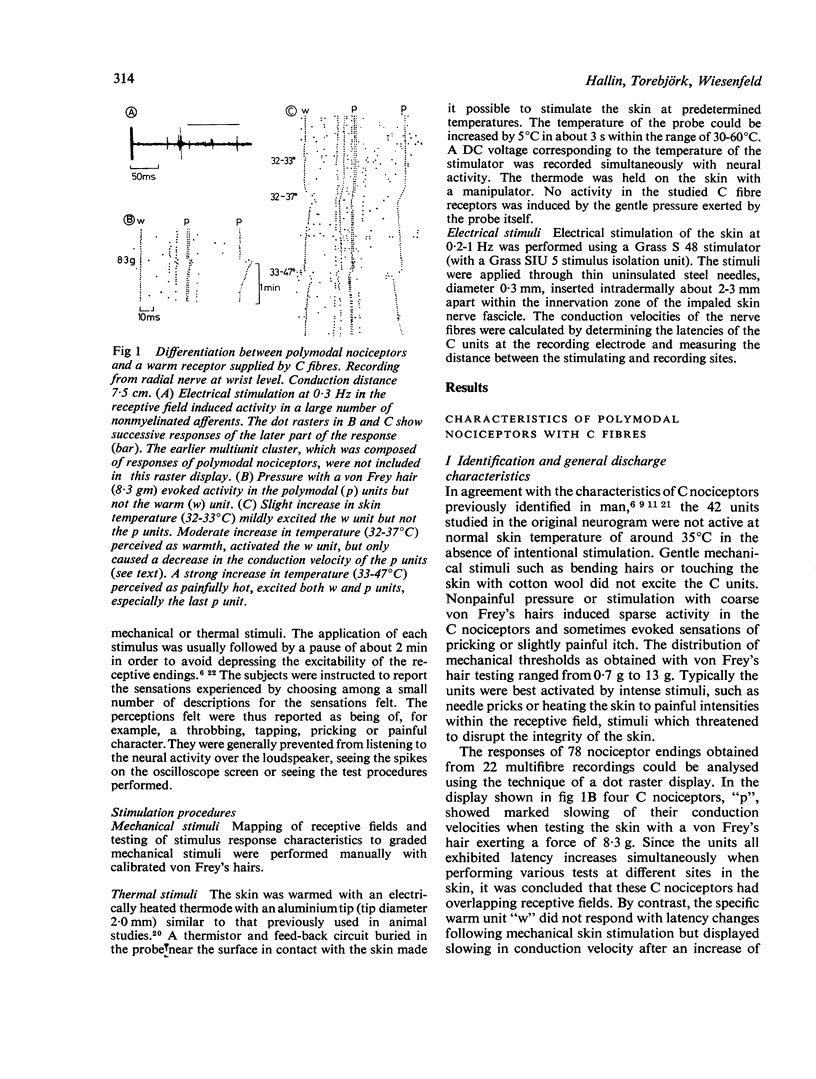
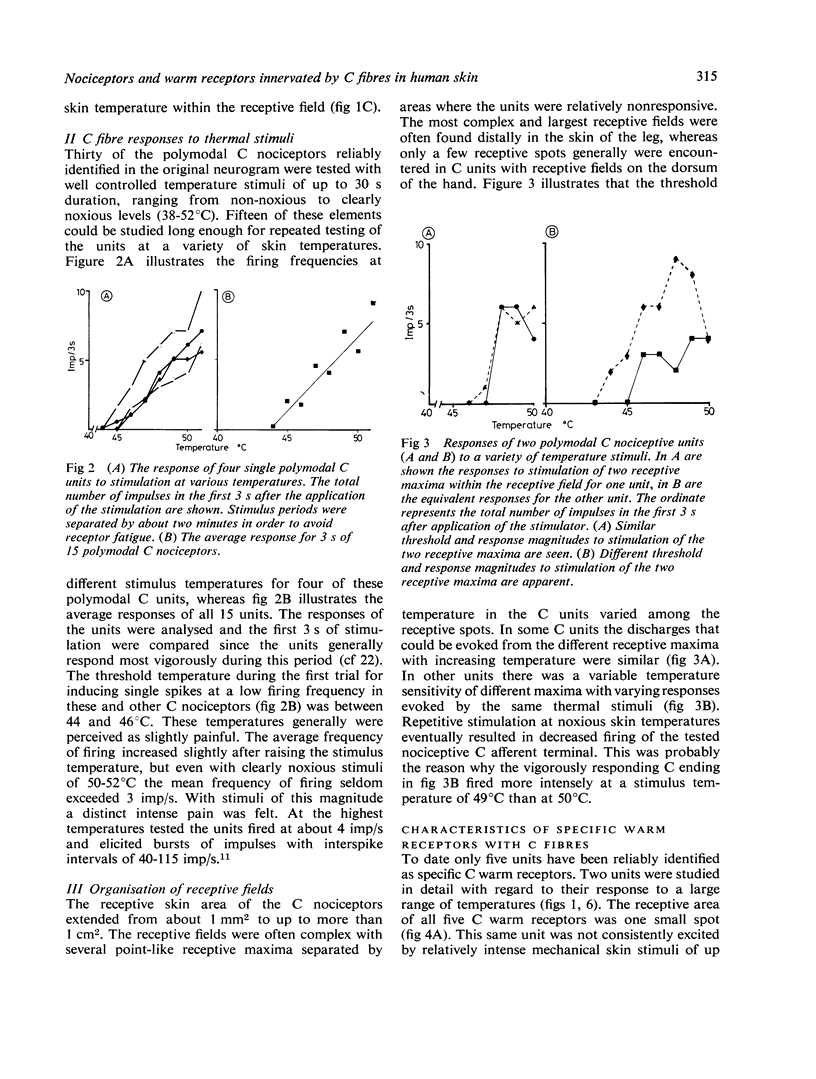
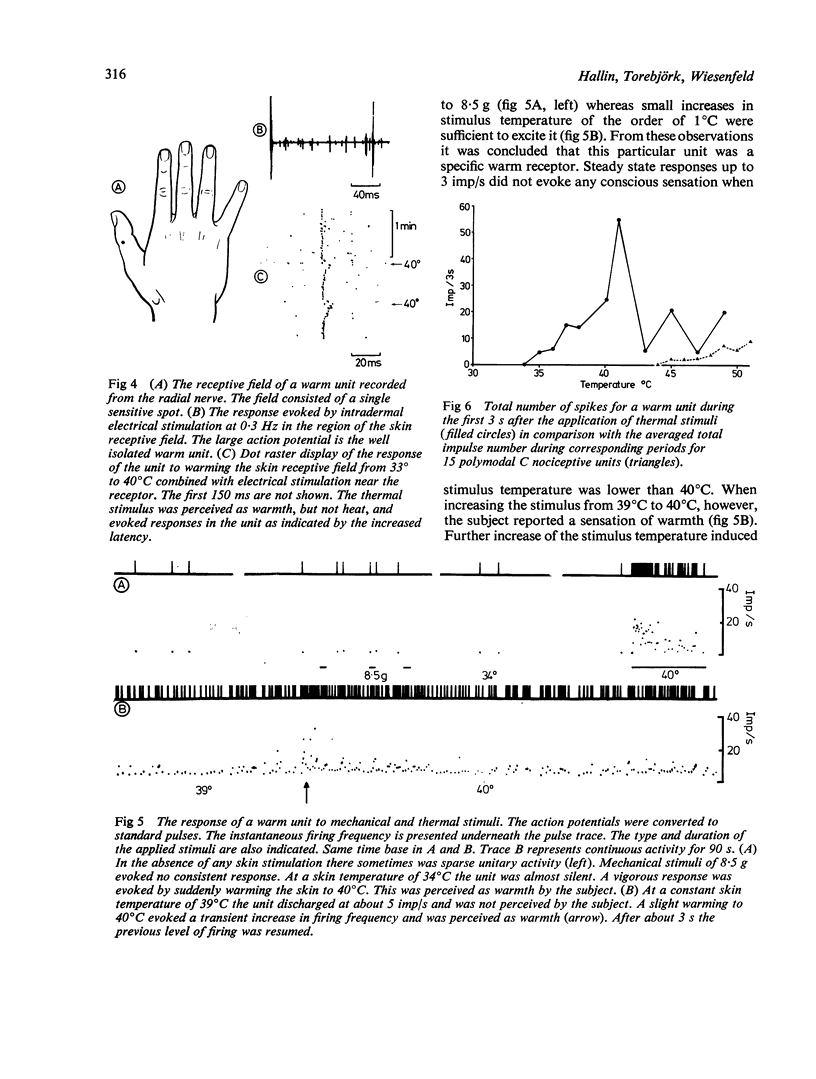
The properties of 125 C fibre units recorded from the peripheral nerves of conscious man were studied. On the basis of receptive field properties and responses to natural stimulation, 120 of the units were classified as polymodal C nociceptors. Five of the units were identified as specific C warm receptors. In contrast to the polymodal nociceptors, which often had comparatively large and complex receptive fields with several receptive maxima, receptive fields of the thermo-receptors consisted of one single spot. Polymodal nociceptors responded readily to moderately intense and noxious mechanical stimuli whereas the warm receptors produced inconsistent responses to even intense mechanical skin stimulation. Thermal stimulation in the innocuous range, perceived as warmth, optimally excited the thermoreceptors whereas the polymodal C nociceptors fired most intensely to noxious painful heat.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adriaensen H., Gybels J., Handwerker H. O., Van Hees J. Latencies of chemically evoked discharges in human cutaneous nociceptors and of the concurrent subjective sensations. Neurosci Lett. 1980 Oct 20;20(1):55–59. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90233-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beitel R. E., Dubner R. Response of unmyelinated (C) polymodal nociceptors to thermal stimuli applied to monkey's face. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Nov;39(6):1160–1175. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.6.1160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessou P., Burgess P. R., Perl E. R., Taylor C. B. Dynamic properties of mechanoreceptors with unmyelinated (C) fibers. J Neurophysiol. 1971 Jan;34(1):116–131. doi: 10.1152/jn.1971.34.1.116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessou P., Perl E. R. Response of cutaneous sensory units with unmyelinated fibers to noxious stimuli. J Neurophysiol. 1969 Nov;32(6):1025–1043. doi: 10.1152/jn.1969.32.6.1025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess P. R., Perl E. R. Myelinated afferent fibres responding specifically to noxious stimulation of the skin. J Physiol. 1967 Jun;190(3):541–562. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLINS W. R., Jr, NULSEN F. E., RANDT C. T. Relation of peripheral nerve fiber size and sensation in man. Arch Neurol. 1960 Oct;3:381–385. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1960.00450040031003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS W. W., RITCHIE J. M., STRAUB R. W. The role of nonmyelinated fibres in signalling cooling of the skin. J Physiol. 1960 Feb;150:266–283. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EMMELIN N., ENGSTROM J. On the existence of specific secretory sympathetic fibres for the cat's submaxillary gland. J Physiol. 1960 Aug;153:1–8. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopoulos A. P. Functional properties of primary afferent units probably related to pain mechanisms in primate glabrous skin. J Neurophysiol. 1976 Jan;39(1):71–83. doi: 10.1152/jn.1976.39.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gybels J., Handwerker H. O., Van Hees J. A comparison between the discharges of human nociceptive nerve fibres and the subject's ratings of his sensations. J Physiol. 1979 Jul;292:193–206. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagbarth K. E., Hongell A., Hallin R. G., Torebjörk H. E. Afferent impulses in median nerve fascicles evoked by tactile stimuli of the human hand. Brain Res. 1970 Dec 18;24(3):423–442. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90183-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallin R. G. Blocking effects of a topical anesthetic composition containing Ketocaine on cutaneous C receptor responses in alert man. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1974;18(4):306–317. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1974.tb01184.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallin R. G., Torebjôrk H. E. Methods to differentiate electrically induced afferent and sympathetic C unit responses in human cutaneous nerves. Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 Nov;92(3):318–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05750.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallin R. G., Torebjörk H. E. Afferent and efferent C units recorded from human skin nerves in situ. A preliminary report. Acta Soc Med Ups. 1970;75(5-6):277–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallin R. G., Torebjörk H. E. C-fibre components in electrically evoked compound potentials recorded from human median nerve fascicles in situ. A preliminary report. Acta Soc Med Ups. 1970;75(1-2):77–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallin R. G., Torebjörk H. E. Electrically induced A and C fibre responses in intact human skin nerves. Exp Brain Res. 1973 Jan 29;16(3):309–320. doi: 10.1007/BF00233333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallin R. G., Torebjörk H. E. Single unit sympathetic activity in human skin nerves during rest and various manoeuvres. Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 Nov;92(3):303–317. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05749.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensel H., Iggo A. Analysis of cutaneous warm and cold fibres in primates. Pflugers Arch. 1971;329(1):1–8. doi: 10.1007/BF00586896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IGGO A. Cutaneous heat and cold receptors with slowly conducting (C) afferent fibres. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1959 Oct;44:362–370. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1959.sp001417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IGGO A. Cutaneous mechanoreceptors with afferent C fibres. J Physiol. 1960 Jul;152:337–353. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iggo A. Cutaneous thermoreceptors in primates and sub-primates. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):403–430. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iriki M., Dorward P., Korner P. I. Baroreflex "resetting" by arterial hypoxia in the renal and cardiac sympathetic nerves of the rabbit. Pflugers Arch. 1977 Jul 29;370(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00707938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konietzny F., Hensel H. Letters and notes: Warm fiber activity in human skin nerves. Pflugers Arch. 1975 Sep 9;359(3):265–267. doi: 10.1007/BF00587384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumazawa T., Perl E. R. Primate cutaneous sensory units with unmyelinated (C) afferent fibers. J Neurophysiol. 1977 Nov;40(6):1325–1338. doi: 10.1152/jn.1977.40.6.1325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMotte R. H., Campbell J. N. Comparison of responses of warm and nociceptive C-fiber afferents in monkey with human judgments of thermal pain. J Neurophysiol. 1978 Mar;41(2):509–528. doi: 10.1152/jn.1978.41.2.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackenzie R. A., Burke D., Skuse N. F., Lethlean A. K. Fibre function and perception during cutaneous nerve block. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975 Sep;38(9):865–873. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.38.9.865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torebjörk H. E. Afferent C units responding to mechanical, thermal and chemical stimuli in human non-glabrous skin. Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 Nov;92(3):374–390. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05755.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torebjörk H. E., Hallin R. G. C-fibre units recorded from human sensory nerve fascicles in situ. A preliminary report. Acta Soc Med Ups. 1970;75(1-2):81–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torebjörk H. E., Hallin R. G. Identification of afferent C units in intact human skin nerves. Brain Res. 1974 Mar 8;67(3):387–403. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90489-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torebjörk H. E., Hallin R. G. Perceptual changes accompanying controlled preferential blocking of A and C fibre responses in intact human skin nerves. Exp Brain Res. 1973 Jan 29;16(3):321–332. doi: 10.1007/BF00233334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torebjörk H. E., Hallin R. G. Responses in human A and C fibres to repeated electrical intradermal stimulation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1974 Jun;37(6):653–664. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.37.6.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallbo A. B., Hagbarth K. E. Activity from skin mechanoreceptors recorded percutaneously in awake human subjects. Exp Neurol. 1968 Jul;21(3):270–289. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(68)90041-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Hees J., Gybels J. M. Pain related to single afferent C fibers from human skin. Brain Res. 1972 Dec 24;48:397–400. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90198-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


