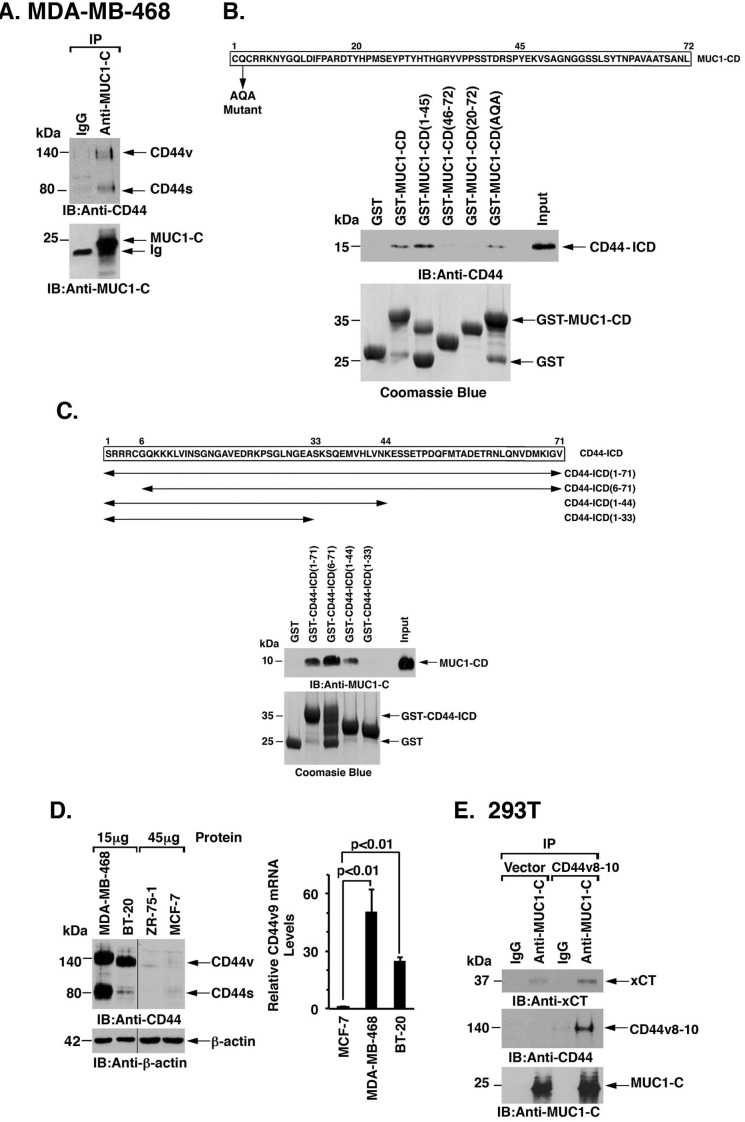
Figure 2. MUC1-C interacts with CD44v.
A. Lysates from MDA-MB-468 cells were precipitated with anti-MUC1-C or a control IgG. The precipitates were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. B. Amino acid sequence of the MUC1 cytoplasmic domain (MUC1-CD). GST, GST-MUC1-CD or the indicated GST-MUC1-CD fragments were incubated with His-CD44-ICD. The adsorbates were immunoblotted with anti-CD44. Input of the GST proteins was assessed by Coomassie blue staining. C. Amino acid sequence of the CD44-ICD. GST, GST-CD44-ICD or the indicated GST-CD44-ICD fragments were incubated with MUC1-CD. The adsorbates were immunoblotted with anti-MUC1-C. Input of the GST proteins was assessed by Coomassie blue staining. D. Lysates (15 and 45 μg) from MDA-MB-468, BT-20, ZR-75-1 and MCF-7 cells were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies (left). CD44v9 mRNA levels in the indicated cells were determined by qRT-PCR (right). The results (mean±SD of 4 determinations) are expressed as relative CD44v9 mRNA levels as compared with that obtained for MCF-7 cells (assigned a value of 1). E. Lysates from 293T/MUC1-C cells transfected with an empty vector or one expressing CD44v8-10 were precipitated with anti-MUC1-C or a control IgG. The precipitates were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies.