Abstract
Kinema, an ethnic fermented, non-salted and sticky soybean food is consumed in the eastern part of India. The stickiness is one of the best qualities of good kinema preferred by consumers, which is due to the production of poly-γ-glutamic acid (PGA). Average load of Bacillus in kinema was 107 cfu/g and of lactic acid bacteria was 103 cfu/g. Bacillus spp. were screened for PGA-production and isolates of lactic acid bacteria were also tested for degradation of PGA. Only Bacillus produced PGA, none of lactic acid bacteria produced PGA. PGA-producing Bacillus spp. were identified by phenotypic characterization and also by 16S rRNA gene sequencing as Bacillus subtilis, B. licheniformis and B. sonorensis.
Keywords: Kinema, Bacillus, fermented soybean, poly-glutamic acid
Introduction
Poly-γ-polyglutamic acid (PGA), an amino acid polymer, is not synthesized by ribosomal proteins (Oppermann-Sanio and Steinbüchel, 2002); but is synthesized by Gram-positive bacteria (Yao et al., 2009) and few Gram-negative bacteria (Candela et al., 2009) produced as a polymer outside of the cell (Moraes et al., 2013). PGA-producing bacteria are mainly Bacillus subtilis, B. anthracis, B. licheniformis, B. thuringensis, B. cereus, B. pumilus, B. amyloliquefaciens, B. mojavensis, B. atrophaeus, B. megaterium, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Natrialba aegyptiaca, Lysinibacillus sphaericus, and Fusobacterium nucleatum (Kambourova et al., 2001; Cachat et al., 2008; Meerak et al., 2008; Candela et al., 2009; Cao et al., 2011). PGA is one of the functional properties of microorganisms present in fermented soybean foods (Tamang et al., 2016a). PGA is an anionic, biodegradable, water-soluble, non-toxic, and edible (Yoon et al., 2000; Zhang et al., 2011). Structurally there are two types of PGA: γ-PGA and α-PGA, which are composed of glutamic acids joined by γ or α linkages, respectively (Goto and Kunioka, 1992). γ-PGA has a structure of 5,000–10,000 units of D- and L-glutamic acids that generate a highly viscous solution when it accumulates in the culture medium (Ashiuchi et al., 2001; Tanimoto et al., 2001). PGA produced by Bacillus spp. has potential applications as thickener, cryoprotectant, humectant, drug carrier, biological adhesive, heavy metal absorbent, etc., with biodegradability in the fields of food, cosmetics, medicine, and water treatments (Bajaj and Singhal, 2011; Ogunleye et al., 2015).
Ethnic people of North East India consume spontaneously fermented soybean foods as side dish in meals, which include kinema, tungrymbai, hawaijar, bekang, aakhone, and peruyaan (Tamang, 2015). Kinema is a naturally fermented, sticky, mild-ammoniacal flavor and non-salted soybean food of Sikkim and Darjeeling in India, east Nepal and west Bhutan. It is similar to natto of Japan, and chungkokjang of Korea. PGA is produced by Bacillus spp. in many Asian fermented soybean products giving the characteristic of a sticky texture to the product (Urushibata et al., 2002; Nishito et al., 2010) such as natto of Japan (Nagai, 2012; Kada et al., 2013), chungkokjang of Korea (Lee et al., 2010), tungrymbai and bekang of India (Chettri and Tamang, 2014), and thau nao of Thailand (Chunhachart et al., 2006). One of the criteria for good quality of kinema is high stickiness of the product preferred by consumers (Tamang and Nikkuni, 1996). Relative viscosity and stickiness are probably due to production of PGA by Bacillus spp. (Nagai et al., 1994; Tamang and Nikkuni, 1996). B. subtilis KK3:B4, isolated from naturally fermented kinema of India, produced high amount of relative viscosity of 20.1 (Tamang and Nikkuni, 1996). PGA-producing Bacillus strain was isolated from kinema of Nepal (Hara et al., 1995). Though several species of Bacillus such as B. subtilis, B. licheniformis, B. cereus, B. circulans, B. thuringiensis, and B. sphaericus were previously isolated from kinema using phenotypic characterization (Sarkar et al., 1994, 2002; Tamang, 2003; Tamang et al., 2016b); however, there has been no further report on PGA-producing strains/species of Bacillus, isolated from kinema samples of India. Hence we conducted this experiment. The present study was to screen PGA-producing species of Bacillus from kinema and to identify species of Bacillus by 16S rRNA sequencing.
Materials and Methods
Sample Collection
Fresh samples of kinema were collected from different markets of Sikkim in India. Samples were collected aseptically in pre-sterile bottles, sealed, labeled, kept in an ice-box and were transported immediately to the laboratory. Samples were stored at 4°C for further microbial and biochemical analyses.
Isolation of Microorganisms
Ten gram of sample was homogenized in 90 mL sterile physiological saline in a stomacher lab-blender (400, Seward, UK) for 1 min and a serial dilution was made. The diluents were heated at 100°C for 2 min for inactivation of vegetative cells of endospore bacteria (Tamang and Nikkuni, 1996), were isolated and enumerated on nutrient agar (MM012, HiMedia, India), and incubated for 24 h at 37°C. Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) were isolated on plates of MRS agar (M641, HiMedia, India) supplemented with 1% CaCO3 and incubated at 30°C in an anaerobic gas-jar (LE002, HiMedia, India) for 48–72 h. Total viable counts were determined on plate count agar (M091A, HiMedia, India) incubated at 30°C for 48–72 h. Isolated colonies were purified and were preserved in 15% (v/v) glycerol at -20°C for further analysis.
Phenotypic Characterization
Cell morphology and motility of isolates were observed using a phase contrast microscope (Olympus CH3-BH-PC, Japan). Isolates were Gram-stained and tested for production of catalase, carbon dioxide from glucose, ammonia from arginine, growth at different temperatures, in different concentrations of NaCl and pH in nutrient broth (M002, HiMedia, India) following the method of Schillinger and Lücke (1987). Voges–Proskauer test, nitrate reduction, starch hydrolysis, casein hydrolysis, citrate utilization test, bile salt tolerance, anaerobic growth, and sugar fermentations were determined following the method of Duc et al. (2004). Taxonomic key of Slepecky and Hemphill (2006) was followed for identification of Bacillus spp.
Measurement of Stickiness
Cultures were grown on phytone agar (Nagai et al., 1994) at 37°C for 24 h were pulled by touching with an inoculating needle and the stickiness was measured by the length of the thread using scale in cm.
Screening of PGA
Screening of PGA by bacteria was done with a slightly modification of the method described by Nagai et al. (1997) and Meerak et al. (2007). Bacillus isolates were grown at 37°C for 24 h in a conical flask containing 100 ml of PGA medium that consisted of sodium glutamate 2.0%, glucose 2.0%, (NH4)2SO4 1.0%, Na2HPO4 0.1%, KH2PO4 0.1%, MgSO4⋅7H2O 0.05%, Mn(Cl2)4.H2O 0.002%, FeCl3⋅7H2O 0.005% (Kunioka and Goto, 1994). The culture after incubation was centrifuged to obtain a supernatant that contained insoluble material. An equal volume of ethanol was added to the supernatant to get fibrous precipitate presumbly the PGA (Nagai et al., 1997).
Efficiency of PGA of the isolates were tested in different pH (5, 7.5, and 9) and temperature (30 and 45°C) following the method of Meerak et al. (2007).
Degradation of PGA
Screening of LAB for degradation of PGA was performed following the method described by Tanaka et al. (1993). Strains were grown in MRS broth (M369, HiMedia, India), for 18-24 h at 30°C. The isolates were streaked on MRS agar plates containing 0.5% pure PGA (Sigma) solution (pH 4.5), and incubated at 30°C for 2–3 days. The plates were flooded with 5 ml of 18 N H2SO4 and allowed to stand for 30 min at room temperature. The presence of halo around the colony determines the degradation of PGA.
Genomic DNA Isolation
Genomic DNA was isolated according to the method of Wilson (2001). Amplified 16S rDNA was obtained from each strain by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) with the universal primers; forward 5′-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3′ and reverse 5′-AAGGAGGTGATCCAGCCGCA-3′ (Weisburg et al., 1991). The amplicons sizes ranged from 914 BP to 1814 BP.
Gel Electrophoresis
The amplified DNA fragments were separated through gel electrophoresis by applying 10 μL of each PCR product with 1.5 μL of loading dye [(6×), DV4371, Promega, USA] into the wells of 1.5% agarose (V3125, Promega) gel containing 1.5 μL/mL ethidium bromide (H5041, Promega). DNA size markers (RMBD135, Genei; G5711, Promega) were added as standard for the calculation of size of the DNA fragments. The gel was run and photographed using gel documentation system (GelDoc FQ, Biorad, USA).
16S rDNA Sequence Analysis
The sequencing reactions were performed using ABI PRISM 3100 Genettic Analyzers (Applied Biosystems) in both direction with universal primers used for amplification. The electrophenogram data for 16S rDNA sequence was validated using Chromas 2.33 software.1 Sequences obtained were matched with previously published bacterial 16S rDNA sequences available in the GenBank database using BLAST and the Ribosomal Database Project (RDP).
Phylogenetic Analysis
For phylogenetic analysis, 16S rDNA sequence of the isolates and reference sequence retrieved from NCBI-GenBank database were aligned with Clustal Omega. The resulting alignment were analysed with MEGA 6.0 to construct the phylogenetic tree. Phylogenetic tree was inferred with neighbor-joining (NJ) method (Saitou and Nei, 1987). Sequence divergence among the strain were quantified using Kimura-2-paramater distance model (Kimura, 1980). A total of 1,000 bootstrap replication were calculated for evaluation of the tree topology.
Results and Discussion
Phenotypic Identification
The average population of Bacillus spp. in kinema was 107 cfu/g, LAB was 103 cfu/g and total viable counts were 10 cfu/g, respectively (data not shown). Thirty-nine isolates of Bacillus were isolated from 10 samples of kinema. Based on phenotypic characterization (data not shown) five species of Bacillus were identified from 10 samples of kinema as B. subtilis, B. licheniformis, B. pumulis, B. sphaericus and B. cereus (Table 1). About 90% of the total bacterial population found in kinema was Bacillus, indicating that Bacillus is the dominant bacterium in kinema. Sarkar and Tamang (1994) also reported that Bacillus is the predominant bacterium in kinema. B. subtilis, B. licheniformis, B. cereus, B. circulans, B. thuringiensis, and B. sphaericus were reported from kinema sample earlier (Sarkar et al., 1994, 2002; Nout et al., 1998; Tamang, 2003).
Table 1.
Screening of stickiness, and PGA production at different pH and temperatures.
| Organisms | Strain code | Stickiness (cm) | PGA production |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH 7.5 | 30°C | |||
| Bacillus subtilis (n = 13) | KAS:B5 | 16 | ++ | +++ |
| KAS:B6 | 18 | ++ | +++ | |
| KAS:B18 | 6 | + | + | |
| KAS:B29 | 16 | ++ | +++ | |
| KAS:B36 | 4 | + | + | |
| KAS:B39 | 15 | ++ | +++ | |
| KLM:B68 | 3 | + | + | |
| KLM:B78 | 3 | + | + | |
| KLM:B86 | 4 | + | + | |
| KLM:B98 | 4 | + | + | |
| KAS:B102 | 20 | ++ | +++ | |
| KLM:B112 | 23 | ++ | +++ | |
| KLM:B114 | 2 | + | + | |
| B. licheniformis (n = 4) | KAS:B46 | 4 | + | + |
| KAS:B56 | 20 | ++ | +++ | |
| KLM:B92 | 21 | ++ | +++ | |
| KLM:B108 | 2 | + | + | |
| B. pumulis (n = 5) | KAS:B15 | 3 | + | + |
| KAS:B48 | 5 | + | + | |
| KLM:B73 | 5 | + | + | |
| KLM:B93 | 6 | + | + | |
| KLM:B106 | 4 | + | + | |
| B. sphaericus (n = 8) | KAS:B9 | 2 | + | + |
| KAS:B16 | 4 | + | + | |
| KAS:B19 | 5 | + | + | |
| KAS:B49 | 6 | + | + | |
| KLM:B66 | 3 | + | + | |
| KLM:B72 | 2 | + | + | |
| KLM:B82 | 2 | + | + | |
| KLM:B96 | 2 | + | + | |
| B. cereus (n = 9) | KAS:B8 | 2 | _ | _ |
| KAS:B10 | 1 | _ | _ | |
| KAS:B38 | 2 | _ | _ | |
| KAS:B58 | 2 | _ | _ | |
| KLM:B74 | 2 | _ | _ | |
| KLM:B84 | 2 | _ | _ | |
| KLM:B85 | 2 | _ | _ | |
| KLM:B88 | 3 | _ | _ | |
| KLM:B104 | 1 | _ | _ | |
n, number of isolates in parenthesis. +++, high clumping of insoluble precipitate; ++, more clumping of precipitate; +, moderate clumping of precipitate; -, no clumping of precipitate. No precipitate was observed in pH 5 and 9, and at 45°C.
Screening of PGA Production
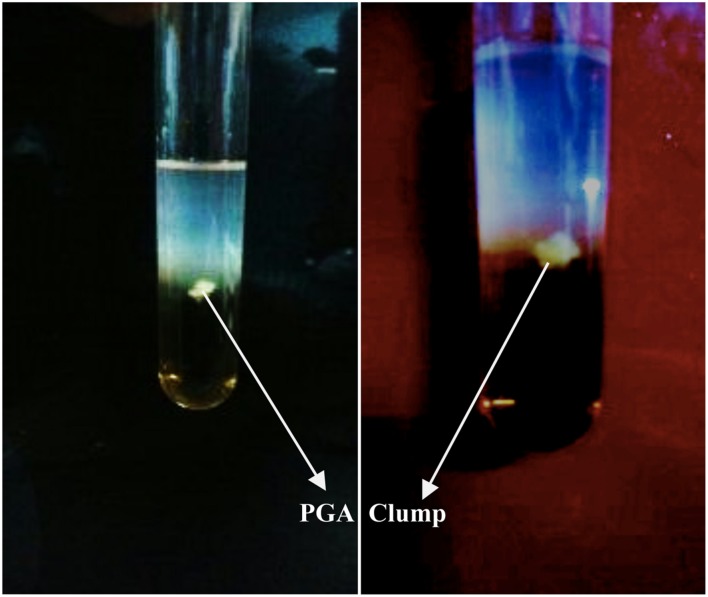
Stickiness of 39 isolates of Bacillus was measured (Table 1). The ability of 39 isolates of Bacillus were tested for production of PGA in PGA medium (Kunioka and Goto, 1994) in pH 5, 7.5, and 9, and at 30C and 45°C (Table 1). The isolates formed an insoluble material or fibrous precipitate after addition of equal volume of ethanol into the PGA medium (Figure 1) presumbly PGA biopolymer (Nagai et al., 1997; Ashiuchi et al., 2001). All species of Bacillus showed fibrous precipitate indicating the absence of PGA production except B. cereus.
FIGURE 1.
Clumping of insoluble material presumably PGA biopolymer produced by Bacillus subtilis KAS:B5 after addition of ethanol into PGA medium.
We tested 25 isolates of LAB isolated from kinema for their ability to degrade poly-glutamic acid (PGA) to know whether LAB also produce PGA in kinema (data not shown). All LAB isolates were found to degrade PGA, indicating that they have no role in PGA production. Similar observations of degradation of PGA by LAB in fermented soybean were made earlier (Kimura and Fujimoto, 2010; Chettri and Tamang, 2014).
Molecular Characterization
On the basis of high (+++) fibrous precipitate at 30o C and pH 7.5, and stickiness of >15 cm (Table 1), 8 strains of Bacillus viz. KAS:B5, KAS:B29, KAS:B39, KAS:B56, KAS:B102, KAS:B6, KAS:B92, and KAS:B112 were selected and were identified by 16S rRNA sequencing. Based on the similarity search with blastN and EzTaxon server the strain KAS:B5 was identified as B. subtilis, KAS:B6 as B. licheniformis, KAS:B29 as B. licheniformis, KAS:B39 as B. licheniformis, KAS:B56 as B. subtilis, KAS:B92 as B. licheniformis, KAS:B102 as B. licheniformis and KAS:B112 as B. sonorensis. Recovery of B. sonorensis from kinema is the first report.
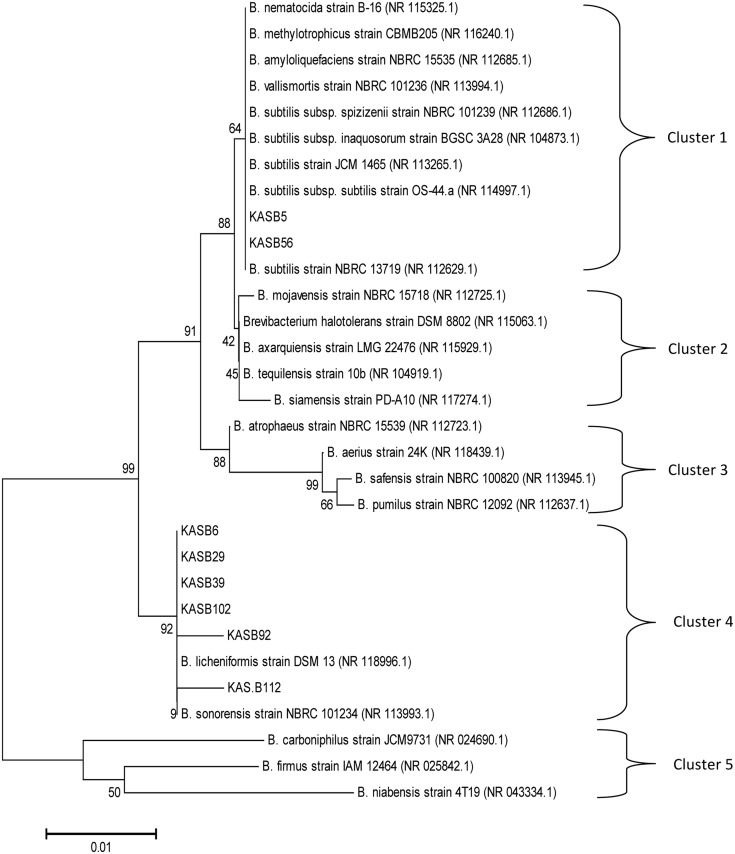
Phylogenetic tree was constructed with neighbor joining method based on the evolutionary distance calculated from 1,000 replicates has showed 5 distinct clusters (Figure 2), which were separated on a scale of 0.01 nucleotide substitution. The homogeny similarity of Bacillus spp. and accession numbers were shown in Table 2. Out of 8 PGA-producing strains KAS:B5 and KAS:B56 showed similarities with B. substilis strain NBRC13719, B. subtilis subsp. subtilis strain OS44a and other strains of subtilis like JCM1465, NBRC 101236, NBRC 101239, and BGSC 3A28 with 64% of similarity percentage in cluster 1. KAS:B6, KAS:B29, KAS:B39, KAS:B102, and KAS:B92 were found in same clade of cluster 4 showing similarities with B. licheniformis DSM12 with 92% similarity and KAS:B112 showed similarities with B. sonorensis strain NBRC 101234 with 90% similarity. Strains KAS:B92 and KAS:B112 were found to show a distance gap between the other species of cluster 4 indicating the difference in nucleotide sequence and evolutionary lineage. In this paper, we could find that B. subtilis and B. licheniformis are PGA-producing bacteria in kinema. B. subtilis and B. licheniformis are the most widely used industrial producers of γ-PGA (Kambourova et al., 2001; Stanley and Lazazzera, 2005; Zhang et al., 2011).
FIGURE 2.
Evolutionary relationships of the analyzed strains with their closest known taxa. The evolutionary history was inferred using the Neighbor-Joining method. The tree was constructed based on the evolutionary distance calculated from 16S rRNA gene sequences using Kimura 2-parameter method. The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (1,000 replicates) are shown next to the branches. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances.
Table 2.
Homogeny of PGA-producing Bacillus isolated from kinema.
| Strain code | Bacillus | Accession number | Homogeny (% similarity) |
|---|---|---|---|
| KAS:B5 | Bacillus subtilis | KX262911 | 96 |
| KAS:B6 | B. licheniformis | KX262910 | 98 |
| KAS:B29 | B. licheniformis | KX261423 | 94 |
| KAS:B39 | B. licheniformis | KX261424 | 97 |
| KAS:B56 | B. subtilis | KX262912 | 97 |
| KAS:B92 | B. licheniformis | KX261426 | 97 |
| KAS:B102 | B. licheniformis | KX261425 | 96 |
| KAS:B112 | B. sonorensis | KX262913 | 97 |
Conclusion
Consumers prefer slimy texture of kinema as good quality product. Presumably slimy material in fermented soybean food is polyglutamic acid, which has been reported from several Asian fermented foods produced by Bacillus spp. PGA, has several applications as foods as well as non-foods. The present study revealed that some species of Bacillus produced PGA in kinema. Further investigation is needed to characterize and purify PGA produced by Bacillus spp. during natural fermentation of kinema.
Author Contributions
RC: screening of PGA-producing Bacillus from kinema, molecular identification of Bacillus, screening go PGA, stickiness, and preparation of draft paper. MOB: phenotypic identification. JPT: analysis of data, compilation and finalization of paper.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Footnotes
References
- Ashiuchi M., Kamei T., Baek D. H., Shin S. Y., Sung M. H., Soda K., et al. (2001). Isolation of Bacillus subtilis (chungkookjang), a poly-γ-glutamate producer with high genetic competence. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 57 764–769. 10.1007/s00253-001-0848-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajaj I., Singhal R. (2011). Poly (glutamic acid) an emerging biopolymer of commercial interest. Bioresour. Technol. 102 5551–5561. 10.1016/j.biortech.2011.02.047 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cachat E., Barker M., Read T. D., Priest F. G. (2008). A Bacillus thuringiensis strain producing a polyglutamate capsule resembling that of Bacillus anthracis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 285 220–226. 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2008.01231.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Candela T., Moya M., Haustant M., Fouet A. (2009). Fusobacterium nucleatum, the first Gram-negative bacterium demonstrated to produce polyglutamate. Can. J. Microbiol. 55 627–632. 10.1139/w09-003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao M., Geng W., Liu L., Song C., Xie H., Guo W., et al. (2011). Glutamic acid independent production of poly-γ-glutamic acid by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens LL3 and cloning of pgsBCA genes. Bioresour. Technol. 102 4251–4257. 10.1016/j.biortech.2010.12.065 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chettri R., Tamang J. P. (2014). Functional properties of Tungrymbai and Bekang, naturally fermented soybean foods of North East India. Int. J. Ferment. Foods 3 87–103. 10.5958/2321-712X.2014.01311.8 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Chunhachart O., Itoh T., Sukchotiratana M., Tanimoto H., Tahara Y. (2006). Characterization of ©-glutamyl hydrolase produced by Bacillus sp. isolated from Thai thua-nao. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 70 2779–2782. 10.1271/bbb.60280 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duc L. H., Hong H. A., Barbosa T. M., Henriques A. O., Cutting S. M. (2004). Characterization of Bacillus probiotics available for human use. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 70 2161–2171. 10.1128/AEM.70.4.2161-2171.2004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto A., Kunioka M. (1992). Biosynthesis and hydrolysis of poly(γ-glutamic acid) from Bacillus subtilis IFO3335. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 56 1031–1035. 10.1271/bbb.56.1031 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara T., Saito H., Iwamoto N., Kaneko S. (1995). Plasmid analysis in Polyglutamate producing Bacillus strain isolated from non-salty fermented soybean food, “Kinema” in Nepal. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 41 3–9. 10.2323/jgam.41.3 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kada S., Ishikawa A., Ohshima Y., Yoshida K. (2013). Alkaline serine protease AprE plays an essential role in poly-γ-glutamate production during natto fermentation. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 77 802–809. 10.1271/bbb.120965 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kambourova M., Tangney M., Priest F. G. (2001). Regulation of polyglutamic acid synthesis by glutamate in Bacillus licheniformis and Bacillus subtilis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67 1004–1007. 10.1128/AEM.67.2.1004-1007.2001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura K., Fujimoto Z. (2010). “Enzymatic degradation of poly-gamma-glutamic acid,” in Amino-Acid Homopolymers Occurring in Nature, 95 Microbiology Monographs 15 ed. Hamano Y. (Berlin: Springer-Verlag; ), 25–116. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M. (1980). A simple method for estimating evolutionary rate of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 16 111–120. 10.1007/BF01731581 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunioka M., Goto A. (1994). Biosynthesis of poly (γ-glutamic acid) from L-glutamic acid, citric acid, and ammonium sulfate in Bacillus subtilis IFO3335. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 40 867–872. 10.1007/BF00173990 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H., Chang M. J., Kim S. H. (2010). Effects of poly-gamma-glutamic acid on serum and brain concentrations of glutamate and GABA in diet-induced obese rats. Nutr. Res. Pract. 4 23–29. 10.4162/nrp.2010.4.1.23 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meerak J., Lida H., Watanabe Y., Miyashita M., Sato H., Nakagawa Y., et al. (2007). Phylogeny of poly-γ-glutamic acid-producing Bacillus strains isolated from fermented soybean foods manufactured in Asian countries. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 53 315–323. 10.2323/jgam.53.315 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meerak J., Yukphan P., Miyashita M., Sato H., Nakagawa Y., Tahara Y. (2008). Phylogeny of (-polyglutamic acid-producing Bacillus strains isolated from a fermented locust bean product manufactured in West Africa. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 54 159–166. 10.2323/jgam.54.159 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moraes L. P., Brito P. N., Alegre R. M. (2013). The existing studies on biosynthesis of poly(γ-glutamic acid) by fermentation. Food Public Health 3 28–36. [Google Scholar]
- Nagai T. (2012). Overview of studies on Bacillus subtilis (natto) bacteriophages and the prospects. JARQ 46 305–310. 10.6090/jarq.46.305 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai T., Koguchi K., Itoh Y. (1997). Chemical analysis of poly-(-glutamic acid produced by plasmid-free Bacillus subtilis (natto): evidence that plasmids are not involved in poly-glutamic acid production. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 43 139–143. 10.2323/jgam.43.139 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai T., Nishimura K., Suzuki H., Banba Y., Sasaki H., Kiuchi K. (1994). Isolation and characterization of Bacillus subtilis strain producing natto with strong umami-taste and high viscosity. Nippon Shokuhin Kogyo Gakkaishi 41 123–128. 10.3136/nskkk1962.41.123 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Nishito Y., Osana Y., Hachiya T., Popendorf K., Toyoda A., Fujiyama A., et al. (2010). Whole genome assembly of a natto production strain Bacillus subtilis natto from very short read data. BMC Genomics 11:243 10.1186/1471-2164-11243 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nout M. J. R., Bakshi D., Sarkar P. K. (1998). Microbiological safety of Kinema, a fermented soyabean food. Food Control 9 357–362. 10.1016/S0956-7135(98)00126-1 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Ogunleye A., Bhat A., Irorere V. U., Hill D., Williams C., Radecka I. (2015). Poly-γ-glutamic acid: production, properties and applications. Microbiology 161 1–17. 10.1099/mic.0.081448-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppermann-Sanio F. B., Steinbüchel A. (2002). Occurrence, functions and biosynthesis of polyamides in microorganisms and biotechnological production. Naturwissenschaften 89 11–22. 10.1007/s00114-001-0280-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitou N., Nei M. (1987). The Neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4 406–425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar P. K., Hasenack B., Nout M. J. R. (2002). Diversity and functionality of Bacillus and related genera isolated from spontaneously fermented soybeans (Indian Kinema) and locust beans (African Soumbala). Int. J. Food Microbiol. 77 175–186. 10.1016/S0168-1605(02)00124-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar P. K., Tamang J. P. (1994). The influence of process variables and inoculum composition on the sensory quality of kinema. Food Microbiol. 11 317–325. 10.1006/fmic.1994.1036 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar P. K., Tamang J. P., Cook P. E., Owens J. D. (1994). Kinema-a traditional soybean fermented food: proximate composition and microflora. Food Microbiol. 11 47–55. 10.1006/fmic.1994.1007 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Schillinger U., Lücke F. K. (1987). Identification of lactobacilli from meat and meat products. Food Microbiol. 4 199–208. 10.1016/0740-0020(87)90002-5 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Slepecky R. A., Hemphill H. E. (2006). “The genus Bacillus-nonmedical,” in The Prokaryotes, A Handbook on the Biology of Bacteria: Bacteria, Firmicutes, Cyanobacteria 3rd Edn Vol. 4 eds Dworkin M., Falkow S., Rosenberg E., Schleifer K.-H., Stackebrandt E. (New York, NY: Springer-Verlag; ), 530–562. [Google Scholar]
- Stanley N. R., Lazazzera B. A. (2005). Defining the genetic differences between wild and domestic strains of Bacillus subtilis that affect poly-γ-dl-glutamic acid production and biofilm formation. Mol. Microbiol. 57 1143–1158. 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04746.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamang J. P. (2003). Native microorganisms in fermentation of kinema. Indian J. Microbiol. 43 127–130. [Google Scholar]
- Tamang J. P. (2015). Naturally fermented ethnic soybean foods of India. J. Ethnic Foods 2 8–17. 10.1016/j.jef.2015.02.003 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Tamang J. P., Nikkuni S. (1996). Selection of starter culture for production of kinema, fermented soybean food of the Himalaya. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 12 629–635. 10.1007/BF00327727 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamang J. P., Shin D. H., Jung S. J., Chae S. W. (2016a). Functional properties of microorganisms in fermented foods. Front. Microbiol. 7:578 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00578 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamang J. P., Watanabe K., Holzapfel W. H. (2016b). Review: diversity of microorganisms in global fermented foods and beverages. Front. Microbiol. 7:377 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00377 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Yaguchi T., Hiruta O., Futamura T., Uotani K., Satoh A., et al. (1993). Screening for microorganisms having poly (-glutamic acid) endohydrolase activity and the enzyme production by Myrothecium sp.TM-4222. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 57 1809–1810. 10.1271/bbb.57.1809 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Tanimoto H., Mori M., Motoki M., Torii K., Kadowaki M., Noguchi T. (2001). Natto mucilage containing poly-γ-glutamic acid increases soluble calcium in the rat small intestine. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 65 516–521. 10.1271/bbb.65.516 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urushibata Y., Tokuyama S., Tahara Y. (2002). Characterization of the Bacillus subtilis ywsC gene, involved in gamma-polyglutamic acid production. J. Bacteriol. 184 337–343. 10.1128/JB.184.2.337-343 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisburg W. G., Barns S. M., Pelletier D. A., Lane D. J. (1991). 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J. Bacteriol. 173 697–703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. (2001). Preparation of genomic DNA from bacteria. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. Chap. 2 Unit 2.4 10.1002/0471142727.mb0204s56 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao J., Jing J., Xu H., Liang J., Wu Q., Feng X., et al. (2009). Investigation on enzymatic degradation of γ-polyglutamic acid from Bacillus subtilis NX-2. J. Mol. Catal. B 56 158–164. 10.1016/j.molcatb.2007.12.027 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon S., Do J., Lee S., Chag H. (2000). Production of poly-δ-glutamic acid by fed-batch culture of Bacillus licheniformis. Biotechnol. Lett. 22 585–588. 10.1023/A:1005610400511 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang D., Xu Z., Xu H., Feng X., Li S., Cai H., et al. (2011). Improvement of poly(γ-glutamic acid) biosynthesis and quantitative metabolic flux analysis of a two-stage strategy for agitation speed control in the culture of Bacillus subtilis NX-2. Biotechnol. Bioprocess. Eng. 16 1144–1151. 10.1007/s12257-011-0074-y [DOI] [Google Scholar]