Abstract
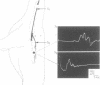
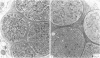
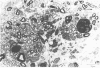
Dogs exposed to acrylamide develop a sensorimotor peripheral neuropathy and megaoesophagus. The presence of neuropathy was confirmed electrophysiologically and histologically. Hindlimb motor conduction velocity was reduced and there was a loss of large diameter myelinated fibres in the dorsal common digital nerve and the tibial nerve. The conduction velocity of vagal motor fibres innervating the thoracic oesophagus was not decreased; there was a reduction in the conduction velocity of the mixed nerve action potential of the vagus. Degenerating nerve fibres were observed in the vagus in the midthoracic region. The damage to vagal nerve fibres may be an important factor in the causation of megaoesophagus.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COOPER W. C., GREEN I. J., WANG S. P. CEREBRAL SALT-WASTING ASSOCIATED WITH THE GUILLAIN-BARR'E SYNDROME. Arch Intern Med. 1965 Jul;116:113–119. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1965.03870010115014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clifford D. H., Lee M. O., Byun K. W., Lee D. C. Effects of autonomic drugs on the cardiovascular system: dogs with achalasia (under halothane anesthesia). Am J Vet Res. 1977 Mar;38(3):323–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALY M. D., EVANS D. H. Functional and histological changes in the vagus nerve of the cat after degenerative section at various levels. J Physiol. 1953 Jun 29;120(4):579–595. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamant N., Szczepanski M., Mui H. Manometric characteristics of idiopathic megaesophagus in the dog: an unsuitable animal model for achalasia in man. Gastroenterology. 1973 Aug;65(2):216–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan G., Johnson R. H., Lambie D. G., Whiteside E. A. Evidence of vagal neuropathy in chronic alcoholics. Lancet. 1980 Nov 15;2(8203):1053–1057. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92275-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan I. D., Griffiths I. R., Carmichael S., Henderson S. Inherited canine giant axonal neuropathy. Muscle Nerve. 1981 May-Jun;4(3):223–227. doi: 10.1002/mus.880040309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS D. H., MURRAY J. G. Histological and functional studies on the fibre composition of the vagus nerve of the rabbit. J Anat. 1954 Jul;88(3):320–337. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullerton P. M., Barnes J. M. Peripheral neuropathy in rats produced by acrylamide. Br J Ind Med. 1966 Jul;23(3):210–221. doi: 10.1136/oem.23.3.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. W. Acute experiments on neuroeffector function in canine esophageal achalasia. Am J Vet Res. 1974 Aug;35(8):1075–1081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths I. R., Duncan I. D., Swallow J. S. Peripheral polyneuropathies in dogs: a study of five cases. J Small Anim Pract. 1977 Feb;18(2):101–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollis J. B., Castell D. O., Braddom R. L. Esophageal function in diabetes mellitus and its relation to peripheral neuropathy. Gastroenterology. 1977 Nov;73(5):1098–1102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins A. P., Gilliatt R. W. Motor and sensory nerve conduction velocity in the baboon: normal values and changes during acrylamide neuropathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1971 Aug;34(4):415–426. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.34.4.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins A. The effect of acrylamide on the peripheral nervous system of the baboon. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1970 Dec;33(6):805–816. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.33.6.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. F., Bowen J. M. Evaluation of motor nerve conduction velocity in the dog. Am J Vet Res. 1970 Aug;31(8):1361–1366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandelstam P., Siegel C. I., Lieber A., Siegel M. The swallowing disorder in patients with diabetic neuropathy-gastroenteropathy. Gastroenterology. 1969 Jan;56(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post E. J., McLeod J. G. Acrylamide autonomic neuropathy in the cat. Part 1. Neurophysiological and histological studies. J Neurol Sci. 1977 Sep;33(3):353–374. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(77)90133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers W. A., Fenner W. R., Sherding R. G. Electromyographic and esophagomanometric findings in clinically normal dogs and in dogs with idiopathic megaesophagus. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1979 Jan 15;174(2):181–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satchell P. M., McLeod J. G. Megaoesophagus due to acrylamide neuropathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1981 Oct;44(10):906–913. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.44.10.906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strombeck D. R., Troya L. Evaluation of lower motor neuron function in two dogs with megaesophagus. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1976 Aug 15;169(4):411–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winship D. H., Caflisch C. R., Zboralske F. F., Hogan W. J. Deterioration of esophageal peristalsis in patients with alcoholic neuropathy. Gastroenterology. 1968 Aug;55(2):173–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]