Abstract
Mutations were identified in the catalytic subunit (C) of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase (EC 2.7.1.37) that block inactivation by regulatory subunit (R) without compromising catalytic activity. Randomly mutagenized mouse C expression vectors were screened functionally for clones that stimulated gene induction in the presence of excess R. Point mutations in the C coding sequence were identified that result in a His----Gln substitution at amino acid 87 (His87Gln) and a Trp----Arg change at amino acid 196 (Trp196Arg). In contrast to wild-type C, both mutants retained partial activity in the presence of excess R isoform RI alpha, although only Trp196Arg retained partial activity in the presence of excess R isoform RII alpha. A C expression vector that included both mutations was fully active in promoting gene induction and was virtually unaffected by an 80-fold excess of either RI alpha or RII alpha. These results demonstrate that mutations at His-87 and Trp-196 alter R interactions with C at a site that is not involved in substrate recognition or enzymatic activity. In contrast to these randomly generated mutations, a site-specific alteration of the autophosphorylated Thr-197 to an Ala resulted in an 80% loss of biological activity and partial resistance to R inhibition. The location and proximity of His-87 and Trp-196 in the crystal structure of C suggest a surface domain that may interact with a region of R that is outside of the substrate/pseudosubstrate site.
Full text
PDF
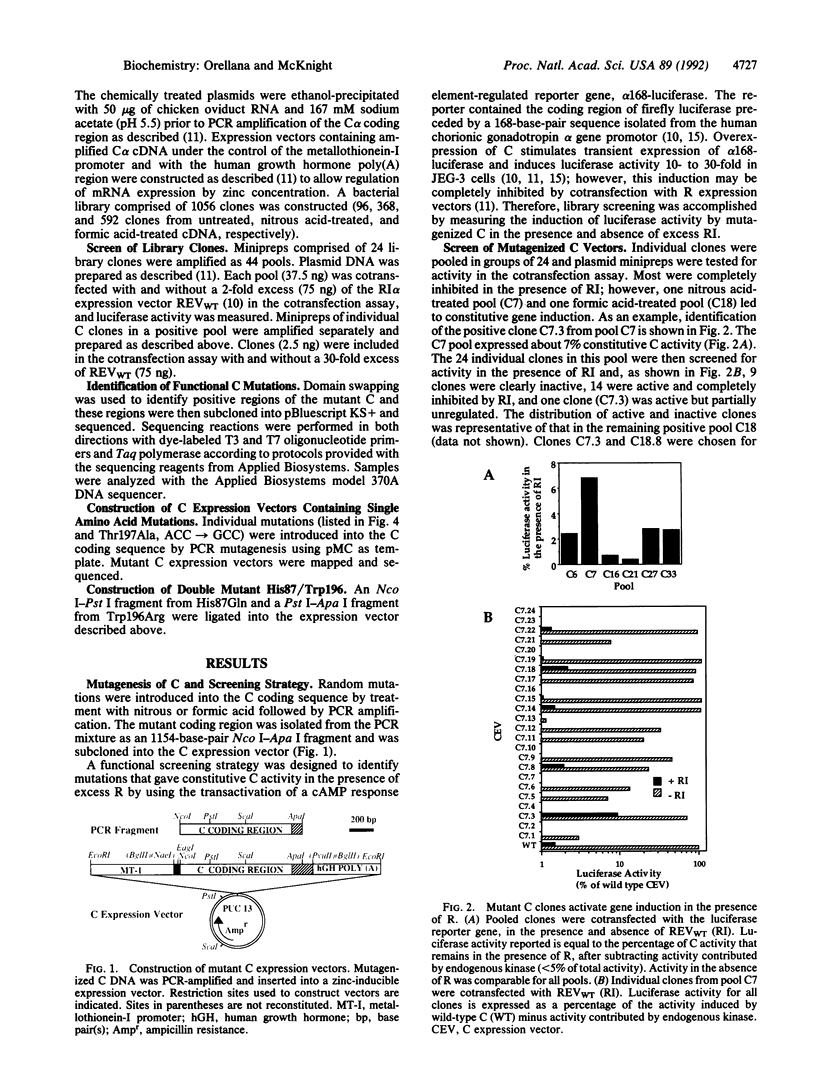

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bourne H. R., Landis C. A., Masters S. B. Hydrolysis of GTP by the alpha-chain of Gs and other GTP binding proteins. Proteins. 1989;6(3):222–230. doi: 10.1002/prot.340060304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Sugden P. H., West L., Flockhart D. A., Lincoln T. M., McCarthy D. Studies on the properties and mode of action of the purified regulatory subunit of bovine heart adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):3997–4003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correll L. A., Woodford T. A., Corbin J. D., Mellon P. L., McKnight G. S. Functional characterization of cAMP-binding mutations in type I protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16672–16678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ducommun B., Brambilla P., Félix M. A., Franza B. R., Jr, Karsenti E., Draetta G. cdc2 phosphorylation is required for its interaction with cyclin. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3311–3319. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04895.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlund T., Walker M. D., Barr P. J., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression of the rat insulin gene: evidence for role of two distinct 5' flanking elements. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):912–916. doi: 10.1126/science.3904002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flockhart D. A., Corbin J. D. Regulatory mechanisms in the control of protein kinases. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1982 Feb;12(2):133–186. doi: 10.3109/10409238209108705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flockhart D. A., Watterson D. M., Corbin J. D. Studies on functional domains of the regulatory subunit of bovine heart adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4435–4440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Moreno S., Owen D. J., Sazer S., Nurse P. Phosphorylation at Thr167 is required for Schizosaccharomyces pombe p34cdc2 function. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3297–3309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04894.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huggenvik J. I., Collard M. W., Stofko R. E., Seasholtz A. F., Uhler M. D. Regulation of the human enkephalin promoter by two isoforms of the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jul;5(7):921–930. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-7-921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Graves D. J., Benjamini E., Krebs E. G. Role of multiple basic residues in determining the substrate specificity of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4888–4894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Zheng J. H., Ten Eyck L. F., Ashford V. A., Xuong N. H., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M. Crystal structure of the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):407–414. doi: 10.1126/science.1862342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Zheng J. H., Ten Eyck L. F., Xuong N. H., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M. Structure of a peptide inhibitor bound to the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):414–420. doi: 10.1126/science.1862343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin L. R., Kuret J., Johnson K. E., Powers S., Cameron S., Michaeli T., Wigler M., Zoller M. J. A mutation in the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase that disrupts regulation. Science. 1988 Apr 1;240(4848):68–70. doi: 10.1126/science.2832943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight G. S., Cadd G. G., Clegg C. H., Otten A. D., Correll L. A. Expression of wild-type and mutant subunits of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 1):111–119. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P. L., Clegg C. H., Correll L. A., McKnight G. S. Regulation of transcription by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4887–4891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orellana S. A., McKnight G. S. The S49 Kin- cell line transcribes and translates a functional mRNA coding for the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3048–3053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otten A. D., McKnight G. S. Overexpression of the type II regulatory subunit of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase eliminates the type I holoenzyme in mouse cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20255–20260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne D. M., Rossomando A. J., Martino P., Erickson A. K., Her J. H., Shabanowitz J., Hunt D. F., Weber M. J., Sturgill T. W. Identification of the regulatory phosphorylation sites in pp42/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAP kinase). EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):885–892. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08021.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. S. cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Model for an enzyme family. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8443–8446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhler M. D., Carmichael D. F., Lee D. C., Chrivia J. C., Krebs E. G., McKnight G. S. Isolation of cDNA clones coding for the catalytic subunit of mouse cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1300–1304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh D. A., Perkins J. P., Krebs E. G. An adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependant protein kinase from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 10;243(13):3763–3765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y. H., Scott J. D., McKnight G. S., Krebs E. G. A constitutively active holoenzyme form of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2446–2450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein L. S., Shenker A., Gejman P. V., Merino M. J., Friedman E., Spiegel A. M. Activating mutations of the stimulatory G protein in the McCune-Albright syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1991 Dec 12;325(24):1688–1695. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199112123252403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]