Abstract
In many exocytic systems, micromolar concentrations of intracellular Ca2+ trigger fusion. We find that aggregates of secretory granules isolated from sea urchin eggs fuse together when perfused with greater than or equal to 10 microM free Ca2+. Mixing of membrane components was demonstrated by transfer of fluorescent lipophilic dye, and melding of granule contents was seen with differential interference microscopy. A technique based upon light scattering was developed to conveniently detect fusion. Two protein modifiers, trypsin and N-ethylmaleimide, inhibit granule-granule fusion at concentrations similar to those that inhibit granule-plasma membrane fusion. We suggest that molecular machinery sufficient for Ca(2+)-triggered fusion resides on secretory granules as purified and that at least some of these essential components are proteinaceous.
Full text
PDF

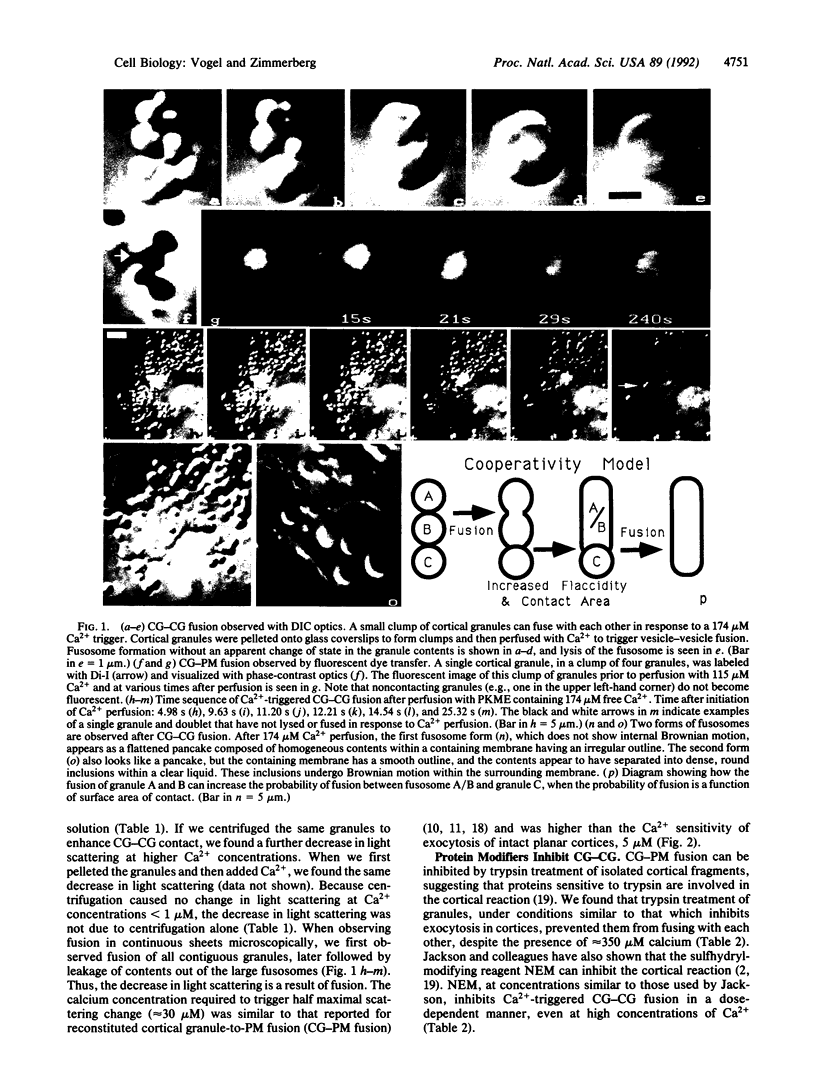
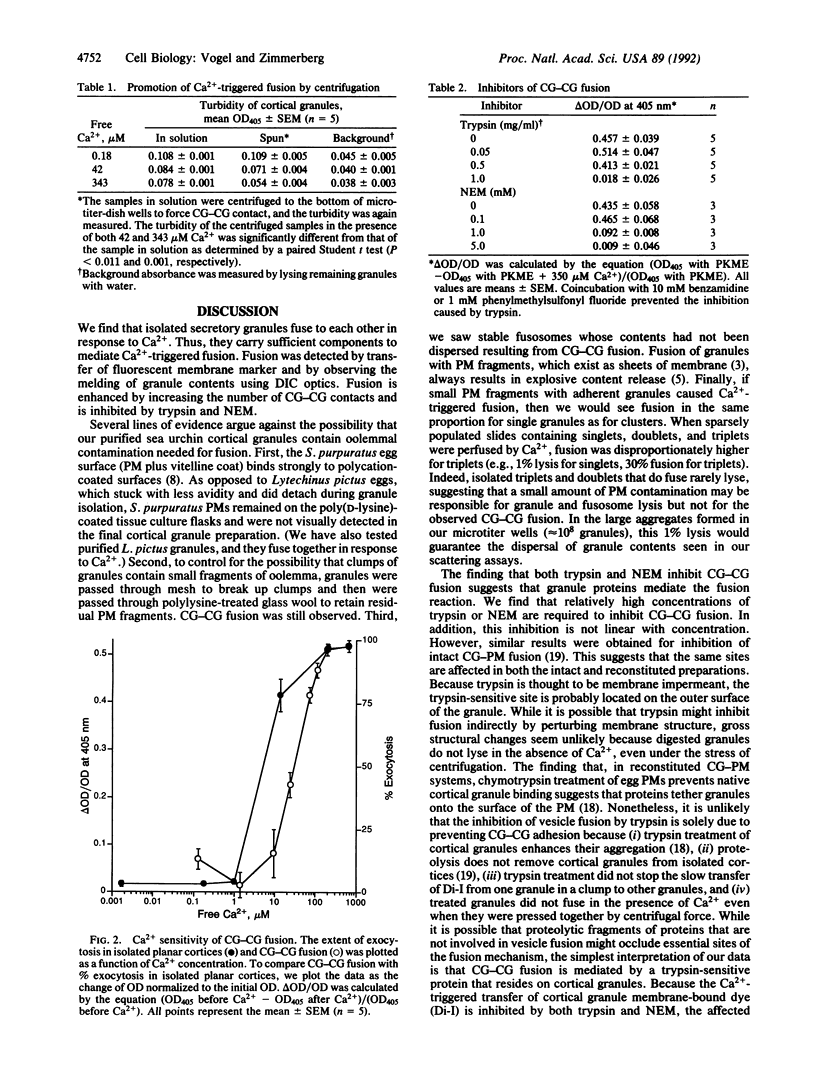

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker P. F., Whitaker M. J. Influence of ATP and calcium on the cortical reaction in sea urchin eggs. Nature. 1978 Nov 30;276(5687):513–515. doi: 10.1038/276513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler D. E., Heuser J. E. Arrest of membrane fusion events in mast cells by quick-freezing. J Cell Biol. 1980 Aug;86(2):666–674. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.2.666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabb J. H., Jackson R. C. In vitro reconstitution of exocytosis from plasma membrane and isolated secretory vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2263–2273. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creutz C. E. cis-Unsaturated fatty acids induce the fusion of chromaffin granules aggregated by synexin. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):247–256. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl G., Ekerdt R., Gratzl M. Models for exocytotic membrane fusion. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1979;33:349–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Calculator programs for computing the composition of the solutions containing multiple metals and ligands used for experiments in skinned muscle cells. J Physiol (Paris) 1979;75(5):463–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gratzl M., Dahl G., Russell J. T., Thorn N. A. Fusion of neurohypophyseal membranes in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Oct 3;470(1):45–57. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haggerty J. G., Jackson R. C. Release of granule contents from sea urchin egg cortices. New assay procedures and inhibition by sulfhydryl-modifying reagents. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1819–1825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. C., Modern P. A. Reassociation of cortical secretory vesicles with sea urchin egg plasma membrane: assessment of binding specificity. J Membr Biol. 1990 Apr;115(1):83–93. doi: 10.1007/BF01869108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. C., Ward K. K., Haggerty J. G. Mild proteolytic digestion restores exocytotic activity to N-ethylmaleimide-inactivated cell surface complex from sea urchin eggs. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;101(1):6–11. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.1.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagayama M., Douglas W. W. Electron microscope evidence of calcium-induced exocytosis in mast cells treated with 48-80 or the ionophores A-23187 and X-537A. J Cell Biol. 1974 Aug;62(2):519–526. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.2.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadin C. Y., Rogers J., Tomlinson S., Edwardson J. M. A specific interaction in vitro between pancreatic zymogen granules and plasma membranes: stimulation by G-protein activators but not by Ca2+. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2801–2808. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornberg R. L., Reese T. S. Comparison of compound with plasmalemmal exocytosis in Limulus amebocytes. Methods Cell Biol. 1981;23:301–311. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61505-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki H., Epel D. Cortical vesicle exocytosis in isolated cortices of sea urchin eggs: description of a turbidometric assay and its utilization in studying effects of different media on discharge. Dev Biol. 1983 Aug;98(2):327–337. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90363-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki H. Modulation of calcium sensitivity by a specific cortical protein during sea urchin egg cortical vesicle exocytosis. Dev Biol. 1984 Jan;101(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90123-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon W., Carafoli E. Design, properties, and applications of neutral ionophores. Methods Enzymol. 1979;56:439–448. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)56043-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhardt R. A., Epel D. Activation of sea-urchin eggs by a calcium ionophore. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1915–1919. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhardt R., Zucker R., Schatten G. Intracellular calcium release at fertilization in the sea urchin egg. Dev Biol. 1977 Jul 1;58(1):185–196. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90084-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Rink T. J. Neutral carrier ion-selective microelectrodes for measurement of intracellular free calcium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul;599(2):623–638. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90205-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vacquier V. D. The isolation of intact cortical granules from sea urchin eggs: calcium lons trigger granule discharge. Dev Biol. 1975 Mar;43(1):62–74. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(75)90131-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalley T., Whitaker M. Exocytosis reconstituted from the sea urchin egg is unaffected by calcium pretreatment of granules and plasma membrane. Biosci Rep. 1988 Aug;8(4):335–343. doi: 10.1007/BF01115224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker M. J., Baker P. F. Calcium-dependent exocytosis in an in vitro secretory granule plasma membrane preparation from sea urchin eggs and the effects of some inhibitors of cytoskeletal function. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1983 Jul 22;218(1213):397–413. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1983.0047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Kielian M., Helenius A. Membrane fusion proteins of enveloped animal viruses. Q Rev Biophys. 1983 May;16(2):151–195. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerberg J., Curran M., Cohen F. S., Brodwick M. Simultaneous electrical and optical measurements show that membrane fusion precedes secretory granule swelling during exocytosis of beige mouse mast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1585–1589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerberg J., Liu J. Ionic and permeability requirements for exocytosis in vitro in sea urchin eggs. J Membr Biol. 1988 Mar;101(3):199–207. doi: 10.1007/BF01872835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerberg J., Sardet C., Epel D. Exocytosis of sea urchin egg cortical vesicles in vitro is retarded by hyperosmotic sucrose: kinetics of fusion monitored by quantitative light-scattering microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2398–2410. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




