Abstract
Septins are a conserved family of GTPases that form hetero–oligomeric complexes and perform diverse functions in higher eukaryotes, excluding plants. Our previous studies in the human fungal pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus revealed that the core septin, AspB, a CDC3 ortholog, is required for septation, conidiation, and conidial cell wall organization. Although AspB is important for these cellular functions, nothing is known about the role of kinases or phosphatases in the posttranslational regulation and localization of septins in A. fumigatus. In this study, we assessed the function of the Gin4 and Cla4 kinases and the PP2A regulatory subunit ParA, in the regulation of AspB using genetic and phosphoproteomic approaches. Gene deletion analyses revealed that Cla4 and ParA are indispensable for hyphal extension, and Gin4, Cla4, and ParA are each required for conidiation and normal septation. While deletion of gin4 resulted in larger interseptal distances and hypervirulence, a phenotype mimicking aspB deletion, deletion of cla4 and parA caused hyperseptation without impacting virulence, indicating divergent roles in regulating septation. Phosphoproteomic analyses revealed that AspB is phosphorylated at five residues in the GTPase domain (S134, S137, S247, T297, and T301) and two residues at its C-terminus (S416 and S461) in the wild-type, Δgin4 and Δcla4 strains. However, concomitant with the differential localization pattern of AspB and hyperseptation in the ΔparA strain, AspB remained phosphorylated at two additional residues, T68 in the N-terminal polybasic region and S447 in the coiled-coil domain. Generation of nonphosphorylatable and phosphomimetic strains surrounding each differentially phosphorylated residue revealed that only AspBmt-T68E showed increased interseptal distances, suggesting that dephosphorylation of T68 is important for proper septation. This study highlights the importance of septin phosphorylation/dephosphorylation in the regulation of A. fumigatus hyphal septation.
Keywords: Aspergillus fumigatus, septin, phosphorylation, kinase, phosphatase
Introduction
Septins, a conserved family of GTPases, are involved in a variety of critical cellular functions, ranging from cell division to cell wall maintenance (Momany et al., 2001; Alvarez-Tabares and Perez-Martin, 2010; Kozubowski and Heitman, 2010; Lindsey et al., 2010; Hernandez-Rodriguez et al., 2012, 2014). The number of septin-encoding genes varies amongst all organisms. In the pathogenic fungus Candida albicans there are seven septin genes, all of which have orthologs in the model yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, while Aspergillus fumigatus has only five septin genes (Warenda and Konopka, 2002; Pan et al., 2007; Juvvadi et al., 2011b). A. fumigatus aspA, aspB, aspC, and aspD are orthologous to S. cerevisiae CDC11, CDC3, CDC12, and CDC10, respectively; while aspE is absent in S. cerevisiae (Pan et al., 2007; Lindsey et al., 2010; Juvvadi et al., 2011b). Deletion analyses in A. fumigatus revealed that none of the septins are required for growth under basal conditions, yet septins AspA, AspB, AspC, and AspE play a key role in regular septation and AspA, AspB, AspC, and AspD regulate conidiation (Vargas-Muniz et al., 2015). Deletion of aspB resulted in hypervirulence in an invertebrate model of invasive aspergillosis, as well as increased susceptibility and AspB mislocalization following exposure to anti-cell wall agents.
Septins function through formation of heteropolymeric complexes; however, regulation of the formation of these complexes is unclear (Gladfelter, 2010). Multiple lines of evidence suggest that posttranslational modification, such as phosphorylation, regulates the formation, and stability of septin complexes. For example, posttranslational modification of septins in S. cerevisiae is key in controlling the assembly of septins into higher-order structures (Tang and Reed, 2002; Garcia et al., 2011). Septin Cdc3, Cdc10, Cdc11, Cdc12, and Shs1 are also phosphorylated in the filamentous hemiascomycete Ashbya gossypii (Meseroll et al., 2013). Phosphomimetic mutation of A. gossypii septin Cdc12 and Shs1 phosphorylation sites resulted in lethality, supporting the notion of septin phosphorylation as a key regulator of proper septin function (Meseroll et al., 2013).
Kinases Gin4, and Cla4 have been shown to phosphorylate septins in hemiascomycetes (Longtine et al., 1998; Kadota et al., 2004; Versele and Thorner, 2004; Wightman et al., 2004; Sinha et al., 2007; DeMay et al., 2009; Li et al., 2012). In S. cerevisiae, Gin4 co-purifies with and is regulated by the septins (Barral et al., 1998; Mortensen et al., 2002). Gin4 requires this interaction with the septin complex in order to be activated by hyperphosphorylation and subsequently phosphorylates the non-core septin SHS1 (Barral et al., 1998; Mortensen et al., 2002). This co-dependence between Gin4 and septins has also been demonstrated in C. albicans, where deletion of gin4 eliminates septin ring formation (Wightman et al., 2004). Another important regulator of septins in S. cerevisiae is the PAK kinase Cla4. In the S. cerevisiaeΔcla4 strain, septins form a band at the tip of the bud instead of localizing at the bud neck (Cvrekova et al., 1995). Furthermore, Cla4 is capable of interacting in vitro with and phosphorylating septins Cdc3 and Cdc10. Cla4 phosphorylates Cdc10 on two serine residues (S256 and S312), and alanine substitution of serine 256 resulted in an elongated bud at 37°C, indicating that this phosphorylation site is required for proper Cdc10 function (Versele and Thorner, 2004). Although the essential roles of Gin4 and Cla4 in septin phosphorylation have been described in hemiascomycetes, their role as potential septin regulators has not been explored in filamentous ascomycetes. Recent work in the model filamentous fungi Neurospora crassa and A. nidulans has shown that Cla4 is involved in hyphal extension, polarity, and asexual and sexual reproduction (Park et al., 2011; De Souza et al., 2013). The filamentous plant pathogen Magnaporthe oryzae cla4 ortholog (CHM1) is also involved in hyphal extension, polarized growth, new growth foci limitation, conidiation and pathogenesis (Li et al., 2004). In the basidiomycete Ustilago maydis, cla4 is involved in budding, cytokinesis, cell wall assembly, mating and pathogenesis (Leveleki et al., 2004).
Although some septin kinases have been explored, less is known of septin phosphatases. In S. cerevisiae, Rts1, a protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) subunit, regulates septin dephosphorylation during telophase, and this dephosphorylation contributes to cytokinesis (Dobbelaere et al., 2003). In A. nidulans, deletion of parA (RTS1 ortholog) resulted in hyperseptation and reduction in conidiation; however, the possible septin regulatory role was not defined (Zhong et al., 2014).
In this study, we built on our previous explorations of septins in the pathogen A. fumigatus and defined for the first time the phosphorylation status of the core septin AspB and the role of Gin4, Cla4, and ParA as AspB regulators in A. fumigatus growth and development. We found that ParA and Cla4 are indispensable for full hyphal extension, whereas Gin4, Cla4, and ParA are important for conidiation and required for proper localization of AspB. While deletion of gin4 resulted in increased interseptal distances, deletion of cla4 or parA resulted in hyperseptation in more basal compartments. Similar to the ΔaspB strain, the Δgin4 strain is hypervirulent in the Galleria mellonella invertebrate and murine models of invasive aspergillosis. Phosphoproteomic analyses revealed that AspB is phosphorylated in seven residues, five of which are located in the GTPase domain. Interestingly, although the deletion of kinases gin4 or cla4 did not affect the phosphorylation status of AspB, the deletion of the phosphatase subunit parA resulted in the phosphorylation of two additional sites, including one residue (S447) in the coiled-coil domain. Mutation of these residues to alanine (blocking phosphorylation) or glutamic acid (phosphomimetic) mislocalized AspB and caused an increase in interseptal distances in the AspBmt-T68E strain. Taken together, these important findings suggest that ParA is a potential direct regulator of AspB through dephosphorylation, while Cla4 and Gin4 could regulate AspB through a yet unknown indirect mechanism.
Materials and Methods
Strains, Media, and Culture Conditions
The A. fumigatus akuBKU80 pyrG- uracil/uridine auxotroph was used for deletion analyses and the akuBKU80 uracil/uridine prototroph was used as the wild-type strain (da Silva Ferreira et al., 2006; Table 1). Cultures were grown on glucose minimal media (GMM) at 37°C, except where otherwise specified. Escherichia coli DH5α competent cells were used for cloning.
Table 1.
Strains used in the present study.
| Strain | Parent strain | Genotype | Reference on source |
|---|---|---|---|
| akuBKU80 pyrG- | CEA17 pyrG+ | pyrG | da Silva Ferreira et al., 2006 |
| akuBKU80 | CEA17 | Wild-type | da Silva Ferreira et al., 2006 |
| aspB–egfp | akuBKU80 | ΔaspB::aspBpromo-aspB–egfp-hph | Vargas-Muniz et al., 2015 |
| Δgin4 | akuBKU80 pyrG- | Δgin4::pyrG | This study |
| Δcla4 | akuBKU80 pyrG- | Δcla4::pyrG | This study |
| ΔparA | akuBKU80 pyrG- | ΔparA::pyrG | This study |
| Δgin4 ΔaspB | Δgin4 | Δgin4::pyrG ΔaspB::ble | This study |
| Δgin4 aspB–egfp | Δgin4 | Δgin4::pyrG ΔaspB::aspBpromo-aspB–egfp-hph | This study |
| Δcla4 aspB–egfp | Δcla4 | Δcla4::pyrG ΔaspB::aspBpromo-aspB–egfp-hph | This study |
| ΔparA aspB–egfp | ΔparA | ΔparA::pyrGΔaspB::aspBpromo-aspB–egfp-hph | This study |
| aspBmt-S447A | akuBKU80 | ΔaspB::aspBpromo- aspBmt-S447A -egfp-hph | This study |
| aspBmt-S447E | akuBKU80 | ΔaspB::aspBpromo- aspBmt-S447E -egfp-hph | This study |
| aspBmt-T68A | akuBKU80 | ΔaspB::aspBpromo- aspBmt-T68A -egfp-hph | This study |
| aspBmt-T68E | akuBKU80 | ΔaspB::aspBpromo- aspBmt-T68E -egfp-hph | This study |
Construction of Septin Deletion Strains
Deletion of cla4 was performed by replacing the 2.6 kb cla4 gene (Afu5g05900)1 with the 2.4 kb pyrG gene from A. parasiticus. Approximately 1 kb of upstream and downstream flanking regions of cla4 were PCR-amplified from AF293 genomic DNA (Supplementary Table S1). pyrG was amplified from the pJW24 plasmid. The cla4 deletion construct was generated by fusion PCR and transformed into the akuBKU80 pyrG- strain, as previously described (Steinbach et al., 2006). Deletion of gin4 was performed by similarly replacing the 4.0 kb gin4 gene (Afu6g02300) with the 2.4 kb pyrG gene from A. parasiticus. Deletion of parA was attained by replacing the 2.5 kb parA gene (Afu5g02560) with the 3.0 kb A. parasiticus pyrG cassette, and the resulting plasmid was digested with NotI and SalI and transformed into akuBKU80 pyrG-. Each deletion strain was then transformed with the aspB–egfp construct as previously described (Vargas-Muniz et al., 2015). All gene deletions were confirmed by both PCR (data not shown) and Southern analyses (Supplementary Figure S1).
Radial Growth and Conidial Quantification
Conidia (104) from each strain were inoculated on GMM agar, incubated at 37°C, and radial growth measured every 24 h for 5 days. For conidial quantification, 104 conidia from each strain were inoculated on GMM agar, incubated for 5 days at 37°C, and conidia harvested in 10 ml of 0.05% Tween-80 and quantified using a hemocytometer as previously described (Lamoth et al., 2012). All assays were performed in triplicate. Student’s t-tests were performed using Graph Pad Prism (San Diego, CA, USA).
Aniline Blue Staining
Aniline blue stain was used for detection of cell wall β-glucan. 104 conidia of each strain were cultured on coverslips immersed in 10 ml of GMM + UU broth and incubated for 20 h at 37°C, as previously described (Juvvadi et al., 2011a). The coverslips were rinsed with GMM + UU broth, inverted over 500 μl of aniline blue stain, and incubated for 5 min at 25°C. Coverslips were rinsed once more briefly with GMM + UU broth and observed by fluorescence microscopy.
Galleria mellonella and Murine Invasive Aspergillosis Virulence Models
Virulence of the deletion strains was assessed in an iterative fashion using an invertebrate and then a murine model of invasive aspergillosis. For the initial invertebrate model, 20 larvae of the wax moth G. mellonella were infected with each of the A. fumigatus deletion strains or the wild-type strain, delivering 5 μl of a 1 × 108 conidia/ml of suspension with a total inoculum size of 2 × 105 conidia. Infected larvae were incubated at 37°C and survival scored daily for 5 days (Steinbach et al., 2006). For the murine model, male mice (CD1, Charles River Laboratory, Raleigh, NC, USA) were immunosuppressed with cyclophosphamide (175 mg/kg, intraperitoneally, days -2 and +3) and triamcinolone acetonide (40 mg/kg, subcutaneously, days -1 and +6). A total inoculum of 4 × 106 conidia was delivered intranasally using 40 μl of 108 conidia of the Δgin4, Δcla4, ΔparA, and akuBKU80 strains (Vargas-Muniz et al., 2015). Survival for both virulence models was plotted on a Kaplan–Meier curve and analyzed using log rank pair-wise comparison. Animal studies were carried out in accordance with all of the guidelines of the Duke University Medical Center Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) and in compliance with the United States Animal Welfare Act (Public Law 98-198). Duke University Medical Center IACUC approved all of the vertebrate studies. The studies were conducted in the Division of Laboratory Animal Resources (DLAR) facilities that are accredited by the Association for Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care (AAALAC).
Histopathology Analyses
To characterize in vivo disease histopathology, three additional mice per each single deletion strain were infected. Mice were euthanized on day +3 after inoculation and lungs were harvested. Lungs sections were stained with Gomori’s methenamine silver stain to stain fungal hyphae and hematoxylin and eosin stain to examine inflammation (Steinbach et al., 2006).
Fluorescence Microscopy
Conidia (104) of each aspB–egfp expressing strain were cultured on coverslips immersed in 10 ml of GMM broth and incubated for 20 h at 37°C, as previously described (Vargas-Muniz et al., 2015). Localization patterns were visualized using an Axioskop 2 plus microscope (Zeiss) equipped with AxioVision 4.6 imaging software.
Protein Extraction, AspB–EGFP Fusion Protein Purification and LC–MS/MS Analysis
Each A. fumigatus strain expressing the aspB–egfp fusion construct under the control of the aspB native promoter was grown in GMM broth for 24 h at 37°C. Biological replicates were prepared for each strain. Total cell lysate was obtained by homogenizing mycelia (600–650 mg wet weight) as previously described (Juvvadi et al., 2013). Total protein in the crude extract was quantified by the Bradford method and normalized to contain 10 mg of protein in the sample before purification using GFP-Trap® affinity purification (Chromotek). GFP-Trap® resin was equilibrated according to the manufacturer’s instructions and resuspended in 100 μl ice-cold dilution buffer (10 mM Tris–HCl pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 0.5 mM EDTA, 1 mM PMSF, 1:100 protease inhibitor cocktail). GFP-Trap® resin suspension was then added to the crude lysate containing the 10 mg of protein and incubated for 2 h at 4°C with gentle agitation. The suspension was centrifuged at 2000 rpm for 10 min at 4°C and the GFP-Trap® pellet was washed once with 500 μl of iced-cold dilution buffer and twice with 500 μl of wash buffer (10 mM Tris–HCl pH 7.5, 350 mM NaCl, 0.5 mM EDTA, 1 mM PMSF, 1:100 protease inhibitor cocktail). The resin was finally washed 3 times with 200 μl of 50 mM ammonium bicarbonate and resuspended in 30 μl of 50 mM ammonium bicarbonate.
Protein bound GFP-Trap® resins suspended in 30 μl 50 mM ammonium bicarbonate, pH 8.0, were supplemented with 0.1% Rapigest SF surfactant (Waters Corp). Samples were reduced with 5 mM dithiolthreitol for 30 min at 70°C and free sulfhydryls were alkylated with 10 mM iodoacetamide for 45 min at room temperature. Proteolytic digestion was accomplished by the addition of 500 ng sequencing grade trypsin (Promega) directly to the resin with incubation at 37°C for 18 h. Supernatants were collected following a 2 min centrifugation at 1,000 rpm, acidified to pH 2.5 with TFA and incubated at 60°C for 1 h to hydrolyze remaining Rapigest surfactant. Insoluble hydrolyzed surfactant was cleared by centrifugation at 15,000 rpm for 5 min. The sample was lyophilized to dryness and phosphopeptides were enriched using GL Biosciences p10 TiO2 derivatized tips according to manufacturer protocols. Extracted peptides were lyophilized to dryness and resuspended in 12 μL of 0.2% formic acid/2% acetonitrile.
Each sample was subjected to chromatographic separation on a Waters NanoAquity UPLC equipped with a 1.7 μm BEH130 C18 75 μm I.D. × 250 mm reversed-phase column. The mobile phase consisted of (A) 0.1% formic acid in water and (B) 0.1% formic acid in acetonitrile. Following a 4 μL injection, peptides were trapped for 3 min on a 5 μm Symmetry C18 180 μm I.D. X 20 mm column at 5 μl/min in 99.9% A. The analytical column was then switched in-line and a linear elution gradient of 5% B to 40% B was performed over 30 min at 400 nL/min. The analytical column was connected to a fused silica PicoTip emitter (New Objective, Cambridge, MA, USA) with a 10 μm tip orifice and coupled to a QExactive Plus mass spectrometer through an electrospray interface operating in a data-dependent mode of acquisition. The instrument was set to acquire a precursor MS scan from m/z 375–1675 with MS/MS spectra acquired for the ten most abundant precursor ions. For all experiments, HCD (higher energy collisional dissociation) energy settings were 27 v and a 120 s dynamic exclusion was employed for previously fragmented precursor ions.
Raw LC–MS/MS data files were processed in Proteome Discoverer (Thermo Scientific) and then submitted to independent Mascot searches (Matrix Science) against a RefSeq Aspergillus database containing both forward and reverse entries of each protein. Search tolerances were 5 ppm for precursor ions and 0.02 Da for product ions using trypsin specificity with up to two missed cleavages. Carbamidomethylation (+57.0214 Da on C) was set as a fixed modification, whereas oxidation (+15.9949 Da on M), deamidation (+0.98 Da on NQ), and phosphorylation (+79.99 Da on STY) were considered dynamic mass modifications. All searched spectra were imported into Scaffold (v4.3, Proteome Software) and scoring thresholds were set to achieve a peptide false discovery rate of 1% using the PeptideProphet algorithm. Peak area calculations from extracted ion chromatograms were generated within Skyline v3.5 (MacCoss Lab, University of Washington) following manual peak integration based on identification of retention time and accurate mass.
Results
Cla4 and ParA Are Required for Hyphal Extension
Our previous studies showed that A. fumigatus septins play a pleiotropic role in septation, conidiation, and response to anti-cell wall agents (Vargas-Muniz et al., 2015). In order to gain a further understanding into the regulation and function of AspB in septation, we characterized the possible regulators of AspB using a candidate approach. Based on the literature, we selected the non-essential kinases Gin4 and Cla4, as well as the protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) subunit ParA, and first defined their contributions to A. fumigatus growth and morphology. Deletion of cla4 or parA reduced hyphal extension by 2.9- and 1.5-fold, respectively (p < 0.001; Figure 1A). Deletion of aspB led to an increase in susceptibility to anti-cell wall agents. To test whether the kinases and the PP2A subunit deletion strains phenocopy this increase in susceptibility, the respective deletion strains were cultured in the presence of the cell wall stressor Congo Red as well as the β-glucan synthase inhibitor, caspofungin, and the chitin synthase inhibitor, nikkomycin Z. Only the ΔparA strain showed increased susceptibility to Congo Red; however, no increase in susceptibility was noted when the ΔparA strain was exposed to anti-cell wall agents in comparison to the akuBKU80 wild-type strain. (Figure 2).
FIGURE 1.
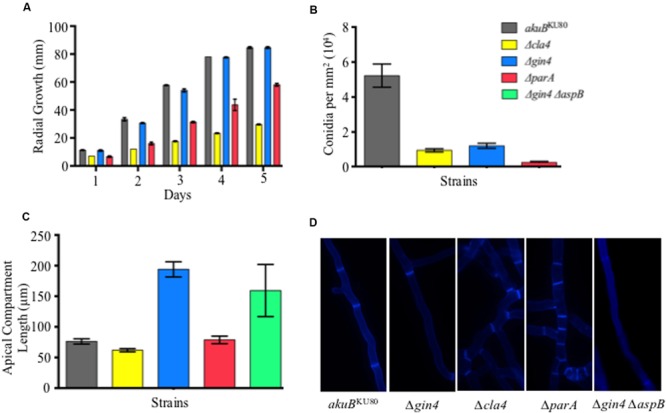
Septin regulators are required for hyphal extension, conidiation, and proper septation. (A) Deletion of parA and cla4 results in a 1.5- and 2.9-fold reduction in radial growth, respectively (p < 0.001). Conidia (104) from each septin deletion strain and wild-type strain were inoculated on glucose minimum media (GMM) and incubated for 5 days at 37°C. (B) Deletion of gin4, cla4, or parA genes resulted in a 4.4-, 5.6-, and 20.7-fold reduction in conidia production, respectively (p < 0.001). Conidia were harvested after 5 days of growth using 10 ml of 0.05% Tween-80 and the conidial count was normalized by fungal colony area. (C) Deletion of gin4 results in an increase in length of the apical compartments (p < 0.001). Apical compartments were measured following aniline blue staining by fluorescent microscopy after 20 h of incubation at 37°C. (D) Aniline blue staining revealed that strains lacking Cla4 or ParA are hyperseptated in basal compartments, while the strain lacking Gin4 contained a larger basal compartment compared to the wild-type strain. Error bars represent standard error of the mean.
FIGURE 2.
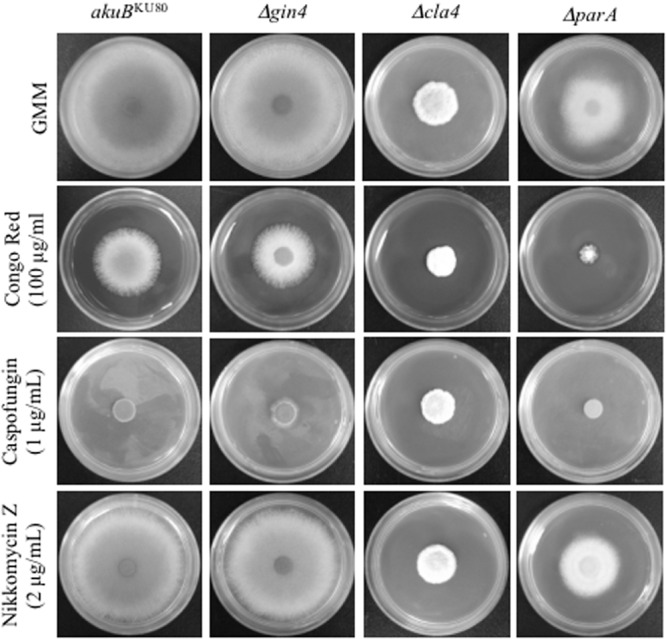
Deletion of parA increased susceptibility to Congo Red, but not to anti-cell wall drugs. Conidia (104) from each strain were inoculated into GMM agar, GMM agar containing Congo Red (100 μg), Caspofungin (1 μg/ml), or Nikkomycin Z (2 μg/ml), and incubated for 3 days at 37°C.
Gin4, ParA, and Cla4 Are Required for Proper Conidiation and Septation in A. fumigatus
Deletion of the A. fumigatus core septin AspB resulted in reduction of conidia production and delayed septation (Vargas-Muniz et al., 2015). To further understand the possible role of Cla4, Gin4, and ParA as septin regulators, we measured conidial production in the respective deletion backgrounds (Figure 1B). The Δcla4, Δgin4, and ΔparA strains showed a 5.6-, 4.4-, and 20.7-fold, reduction in conidiation, respectively, compared to the akuBKU80 wild-type strain (p < 0.005). Only the Δgin4 strain exhibited a significant increase in apical compartment lengths (2.5-fold, p < 0.001; Figure 1C). Due to the observed similarity in the apical compartment length between the Δgin4 and ΔaspB strains, we next generated a Δgin4 ΔaspB double deletion strain to determine if Gin4 and AspB were acting in the same pathway or were contributing to septation through different mechanisms. The Δgin4 ΔaspB strain apical compartment length was similar to that of both the Δgin4 and ΔaspB single deletion strains, indicating that AspB and Gin4 may contribute to septation through the same pathway. In the basal compartments, the Δcla4 and ΔparA strains exhibited a hyperseptation phenotype, while the Δgin4 strain and the Δgin4 ΔaspB double deletion strain maintained the increased interseptal distances (Figure 1D).
Deletion of gin4 Results in Hypervirulence in an Invertebrate and a Murine Model of Invasive Aspergillosis
We previously reported that the ΔaspB strain was hypervirulent in the G. mellonella model but not in a murine model of invasive aspergillosis. Similar to our findings with the ΔaspB strain, the Δgin4 strain resulted in a significantly increased mortality (100%) in G. mellonella by day +3 post infection, compared to the 70% mortality of the akuBKU80 wild-type strain (p < 0.001; Figure 3A). In contrast, the ΔparA strain had a significantly reduced mortality in this model compared to the wild-type strain, and only 45% mortality at day +5 (p < 0.001). The Δcla4 strain displayed no statistical difference in mortality compared to the wild-type strain (p = 0.7971). Building on these invertebrate model virulence results, we then examined these strains in an intranasal murine model of invasive aspergillosis. The Δgin4 strain hypervirulence was reproduced in the murine model, with 100% mortality on day +6 (p < 0.001), while the Δcla4 and ΔparA strains were not significantly different from the wild-type strain (50–65% survival; p > 0.05; Figure 3B). To further understand the contribution of these proteins to pathogenesis, we performed histopathology analysis of the murine lungs after day +3 of infection (Figure 3C). Concomitant with the hypervirulence exhibited by the Δgin4 strain, there was a significant increase in fungal burden via Gomori’s methenamine silver staining in the wild-type akuBKU80 and the Δgin4 strains. Although the Δcla4 and ΔparA strain mortality is similar to that of the wild-type strain, they differed in histopathology. The Δcla4 strain is defective in tissue invasion and only grew near the alveoli, while the ΔparA have a significant reduction in fungal burden. However, the Δcla4 and ΔparA strains infected mice presented symptoms of infection at the same level as the wild-type strain.
FIGURE 3.
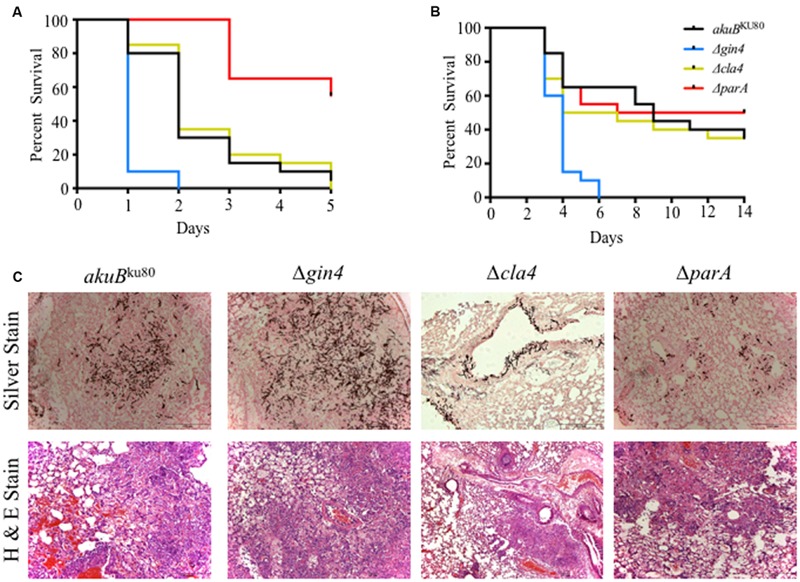
The Δgin4 strain is hypervirulent in both an invertebrate host model and in a persistently immunosuppressed intranasal murine model of invasive aspergillosis. (A) Infection with the Δgin4 strain yield a 100% mortality by day +2 compared to 70% mortality in wild-type strain in the Galleria mellonella model (p < 0.001). The ΔparA strain was hypovirulent (60% survival by day +5) compared to the wild-type strain (p < 0.001). A total of 20 waxmoth G. mellonella larvae were infected with each A. fumigatus strain with 5 μl of a 1 × 108 spores/ml spore suspension. Infected larvae were incubated at 37°C and survival was scored daily for 5 days. (B) Deletion of gin4 results in hypervirulence in a neutropenic murine model of invasive aspergillosis (p < 0.001). Mice were infected intranasally with a total of 4 × 106 conidia from each strain and survival monitored for 14 days. (C) Lung histopathology performed on day +3 days shows a significant increase in fungal burden (silver staining) and inflammation (H&E staining) between the wild-type and the Δgin4 strains.
AspB Exhibits Altered Localization Patterns in the Δgin4,Δcla4, and ΔparA Strains
During the multicellular growth stage, AspB localizes transiently at the septum, at possible septation sites (septal-like), as a ring, and in filaments and double bars (Figure 4) (Vargas-Muniz et al., 2015). Here, we found that AspB mislocalized in the Δgin4, Δcla4, and ΔparA backgrounds (Figure 4). In all the strains, including the wild-type strain, AspB localized as septal-like and double bars. In the ΔparA strain, the double bars had an intermediate length compared to the wild-type double bar localization. Although AspB in the wild type, Δgin4, and ΔparA strains localizes to ring-like structures, qualitative observation revealed that the rings in the Δgin4 and ΔparA background strains had a larger diameter compared to the rings observed in the wild-type strain. AspB localized into X-like structures in Δgin4 and ΔparA strains, similar to those observed in the wild-type strain after exposure to caspofungin. While AspB also localized in elongated X-like structures in the Δgin4 strain, it localized into intermediate length X-like structures in the ΔparA strain. In the Δgin4 and Δcla4 strains, AspB localized as a dot-like structure near the hyphal tip. Deletion of these kinases abolished the formation of AspB filaments, which remained present in the ΔparA strain. AspB in the Δgin4 strain localized into two different ring and bar structures, one that resembled the ring bar structures observed in the wild-type strain under caspofungin treatment, and another larger ring and bar that is unique to the Δgin4 strain. AspB localized at the majority of the hyphal tips in the Δcla4 strain, suggesting that the Cla4 kinase plays a role in excluding AspB from the hyphal tips. The structures described for each strain were commonly found throughout the mycelia. Compartments were observed to contain between 1-2 AspB structures, with the exception of multiple ring-like structures in the Δgin4 and ΔparA strains that were clumped together.
FIGURE 4.
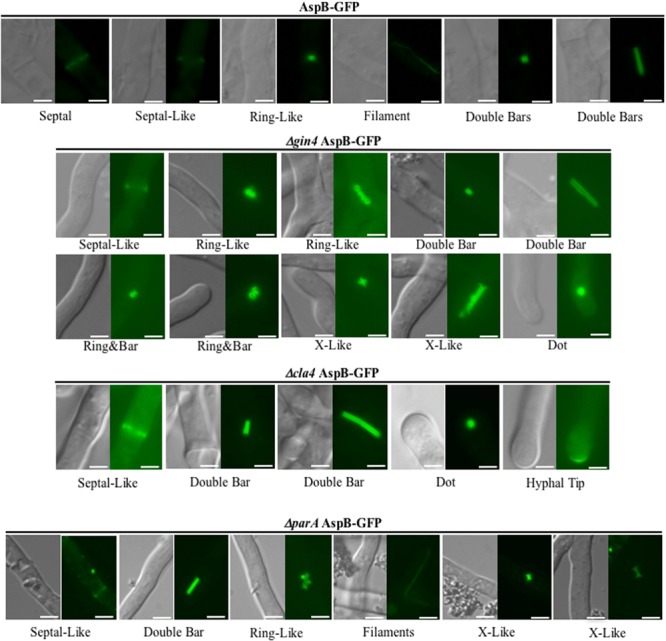
Deletion of gin4, cla4, or parA alters AspB localization pattern. Kinases Gin4 and Cla4, as well as the Protein Phosphatase 2A regulatory sub-unit ParA are required for proper localization of AspB under normal growth condition during the multicellular growth stage. The AspB–EGFP strain was grown in GMM broth for 20 h at 37°C and AspB–EGFP localization visualized by fluorescent microscopy. Scale bar, 2.5 μm.
AspB Is Differentially Phosphorylated in the ΔparA Strain
In order to determine the role of Gin4, Cla4, and ParA as AspB posttranslational regulators, we first determined the phosphorylation profile of AspB in the wild-type strain. AspB was phosphorylated in seven residues: five in the GTPase domain (S134, S137, S247, T297, and T301), and two in the carboxyl-terminus after the septin unique element (S416 and S461) (Table 2 and Figure 5A). We next defined the effect of the deletions of gin4, cla4, and parA on AspB phosphorylation in a comparative phosphoproteomic approach. This strategy revealed that only the parA deletion altered the AspB phosphorylation profile, with AspB phosphorylated at two additional sites: T68 and S447 (Figures 5B–E). Quantitative proteomic (Skyline) analyses showed that both ΔparA specific phosphoresidues had a sevenfold increase in the area under the curve of the spectrogram compared to the wild-type strain (Table 3).
Table 2.
Phosphorylation sites within AspB identified by TiO2 phospho-enrichment followed by LC–MS/MS analysis.
| Peptide sequence | Phosphorylated residue | Domain | m/z | Mascot ion score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TV[pS]IQSISADIEENGVR | S134 | GTPase | 82.16 + 0.1 | 22.4 |
| TVSIQ[pS]ISADIEENGVR | S137 | GTPase | 87.63 + 0.09 | 25.2 |
| ADTLTDEEI[pS]LFK | S247 | GTPase | 82.88 + 0.08 | 24.3 |
| VPFAVVGAN[pT]EVTTADGR | T297 | GTPase | 69.93 + 0.08 | 28.7 |
| VPFAVVGANTEVT[pT]ADGR | T301 | GTPase | 69.1 + 0.05 | 21.1 |
| LKQ[pS]EDEKYAR | S416 | 42.13 + 0.19 | 43.0 | |
| KGF[pS]LR | S461 | C-terminus | 44.16 + 0.25 | 33.2 |
FIGURE 5.

AspB is differentially phosphorylated in the ΔparA strain. (A) Schematic representation of AspB conserved domains and phosphorylation sites. Black bars indicate AspB phosphorylation sites in the wild-type strain and red bars indicate phosphorylation sites unique to the ΔparA strains. (B–E) AspB–EGFP and ΔparA AspB–EGFP strains were grown in GMM liquid for 24 h at 37°C. AspB–EGFP was purified using GFP-Trap® affinity purification, digested with trypsin and phospho-enriched using TiO2. LC–MS/MS was used to identify phosphopeptides. X-axis represents intensity of the signal, and Y-axis represents the retention time of the phosphopeptide in minutes after mixture injection to the liquid chromatography column. (B,C) Chromatogram for the KLTGYVGFANLPNQWHR peptide in (B) wild-type and (C) ΔparA strains. (C,D) LESGRPIEEK phosphopeptides chromatogram in (D) wild-type and (E) ΔparA strains. Area under the curve from each chromatogram peak was used for the Skyline analysis.
Table 3.
Differential phosphorylation of AspB in the ΔparA strain identified by Skyline Analysis of peaks obtained after TiO2 enrichment and LC–MS/MS.
| Peptide sequence | Phosphorylated residue | m/z | akuBKU80 Area | Δ parA Area | Fold change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL[pT]GYVGFANLPNQWHR | T68 | 76.06 ± 0.05 | 46987743 | 327294944 | 6.97 |
| LE[pS]GRPIEEK | S447 | 32.84 ± 0.12 | 55234844 | 8304621.5 | 6.65 |
To assess the role of these phosphorylated residues as possible posttranslational regulation sites, we next generated two non-phosphorylatable as well as two phosphomimetic mutant strains (T68A and T68E; S447A and S447E). Phenotypic analyses of these phosphomutant strains revealed that locking AspB in either a phosphorylation-mimic or non-phosphorylable state resulted in mislocalization of AspB (Figure 6). Similar to the wild-type and the ΔparA strains, AspB phosphomutants localized into rings and double bars. However, the length of the bars observed was different in each of the AspB phosphomutants, while the ring-like structures were similar to those found in the ΔparA strain. Although all four AspB phosphomutants showed the localization of AspB to dot-like structures associated with the hyphal tip, substitution of the serine or threonine to alanine resulted in a smaller dot structure compared to the dot structure in the glutamic acid substituted strain. AspBmt-T68E, AspBmt-S447A, and AspBmt-S447E localized in ring and bar structures, which is a localization pattern not observed in the ΔparA strain. AspBmt-T68A and AspBmt-T68E have septal-like localization, and only AspBmt-T68E localized transiently at septum. AspBmt-T68E and AspBmt-S447A did not abolish the AspB filament localization pattern. Similar to the ΔparA strain, each of these structures are fairly common across the respective AspB phosphomutant mycelia. However, mutation of these phosphorylation sites did not impact hyphal radial growth or conidiation (Supplementary Figures S2A,B). Additionally, the AspBmt-T68E strain had a 1.5-fold increase in interseptal distances when compared to the AspB–EGFP strain (p < 0.001; Supplementary Figure S2C).
FIGURE 6.
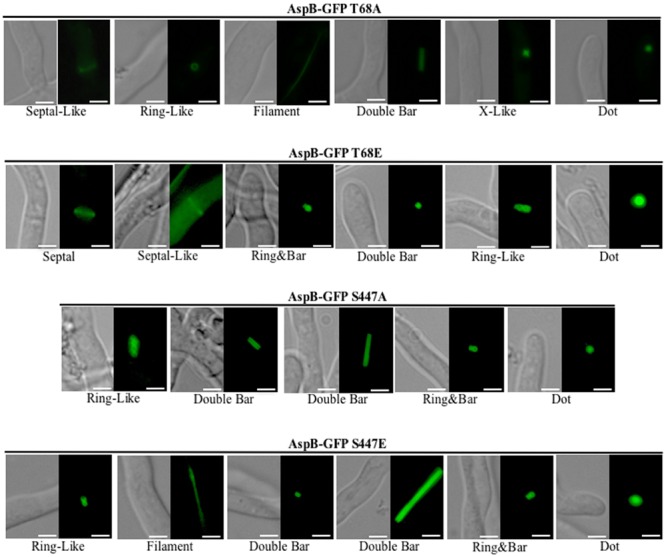
AspB localization patterns in different AspB phosphomutant strains. Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of T68 and S447 are required for proper localization of AspB under normal growth conditions during the multicellular growth stage. AspB–EGFP phosphomimetic (glutamic acid substitutions) or non-phosphorylatable (alanine substitutions) strains were grown in GMM broth for 20 h and AspB–EGFP localization visualized by fluorescent microscopy. Scale bar, 2.5 μm.
Discussion
We previously demonstrated that the A. fumigatus core septin AspB is required for critical cellular processes, including regular septation, conidiation, and conidial cell wall organization (Vargas-Muniz et al., 2015); however, regulation of AspB remains unclear. In S. cerevisiae, phosphorylation has been described as a possible mechanism of septin regulation (Tang and Reed, 2002; Garcia et al., 2011). Here, we explored the role of Gin4 and Cla4 kinases and the regulatory subunit of protein phosphatase 2A, ParA, as possible regulators of AspB. We found that AspB is phosphorylated at seven residues in vivo at the multicellular growth stage. Previously, core septins have been reported to be generally phosphorylated in the divergent amino- and carboxyl-termini, with the exception of S. cerevisiae Cdc10 (Hernandez-Rodriguez and Momany, 2012). However, most of the A. fumigatus AspB phosphorylation sites are within the GTPase domain. This is interesting because the majority of the known phosphorylation sites in septins are not present in the GTPase domain. While these residues are conserved across the filamentous ascomycetes, the same is not the case in other species. Due to the scattered pattern of septin phosphorylations observed in other species we expect no conservation in the residues phosphorylated (Hernandez-Rodriguez and Momany, 2012). However, further phosphoproteomic characterization is required to determine if phosphorylation of these residues is a conserved mechanism in other filamentous ascomycetes.
Aspergillus fumigatus Gin4 kinase is required for maintenance of proper interseptal distances and conidiation, similar to AspB. Deletion of aspB in the Δgin4 background exhibited a similar phenotype to the respective single deletion strains, suggesting that the Gin4 kinase and AspB may coordinately regulate septation. Nonetheless, AspB phosphorylation remains unchanged in the Δ gin4 strain. This suggests that: (i) AspB might recruit Gin4 to possible septation sites and Gin4 then regulates septation, (ii) Gin4 indirectly regulates AspB through the phosphorylation of another yet unidentified AspB interacting partner, or (iii) Gin4 regulates AspB in a kinase-independent manner. Previous studies in S. cerevisiae have suggested that septins are required for proper localization and function of Gin4, and Gin4 phosphorylates Shs1 (non-core septin) and has functions that are independent from its kinase activity (Barral et al., 1998; Carroll et al., 1998; Longtine et al., 1998; Mortensen et al., 2002; Asano et al., 2006). Gin4 has been shown to regulates septins in a cell-cycle dependent manner in S. cerevisiae (Mortensen et al., 2002). It is still possible that Gin4 contributes to septin phosphorylation; however, this would be in a low abundant subset of AspB that we were not able to detect. Additionally, A. nidulans septins form distinct complexes at different growth stages (Hernandez-Rodriguez et al., 2014). The results reported here only focus on the multicellular growth stage, and it is possible we missed key regulatory phosphorylation events in the other growth stages. While the ΔaspB strain exhibited hypervirulence in the Galleria model but had no effect on virulence in the murine model (Vargas-Muniz et al., 2015), the Δgin4 strain is hypervirulent in both the insect and murine model of invasive aspergillosis. This could be due to misregulation of septin function in general or a septin-independent role of Gin4.
Deletion of the gene encoding the Cla4 kinase resulted in a dramatic reduction in hyphal growth as well as loss of polarity and hyperbranching (data not shown). These phenotypes are similar to those previously described in fungal plant pathogens, suggesting a conserved role of Cla4 in regulating hyphal morphology (Leveleki et al., 2004; Li et al., 2004; Rolke and Tudzynski, 2008; Frieser et al., 2011; Tian et al., 2015). Although the apical compartment lengths are not different from that in the wild-type strain, the Δcla4 strain is hyperseptated in the basal hyphal region, suggesting that Cla4 might not have a direct role in septum formation but instead coordinate septum positioning. A similar phenotype was observed in M. oryzae, where the chm1 deletion strain had normal hyphal morphology but the hyphal compartment was significantly reduced (Li et al., 2004). In C. albicans, deletion of cla4 resulted in reduction in fungal burden and hyphal invasion in mouse kidneys, leading to a reduction in pathogenesis (Leberer et al., 1997). The A. fumigatus Δcla4 strain also showed decreased tissue invasion in the intranasal murine model of invasive aspergillosis, however; the Δcla4 strain remained as virulent as the akuBKU80 strain. The Δcla4 strain did not phenocopy the ΔaspB strain or alter the AspB phosphorylation profile. Nonetheless, the AspB localization pattern in the Δcla4 strain was altered. It is suggested that Cla4 is capable of regulating the actin cytoskeleton in some fungi, and Cla4 could have a similar role in A. fumigatus (Leveleki et al., 2004). Furthermore, previously we showed that septin localization is dependent on actin and microtubules, and one of the septins, AspE, interacts with actin and microtubules (Juvvadi et al., 2011b, 2013). Thus, this altered localization could be a result of mislocalization of actin due to the absence of the Cla4 kinase.
Similar to A. nidulans, A. fumigatus ParA is involved in hyphal growth, conidiation and septation (Zhong et al., 2014). The ΔparA strain was hypovirulent in the G. mellonella model; however, the survival and histopathological analyses of the ΔparA strain were similar to that of the wild-type strain in the murine model. This difference in virulence between the two models could be due to the immunosuppression used in the murine model to establish infection, compared to the immunocompetent invertebrate model with a rudimentary immune system. Therefore, ParA is dispensable for pathogenesis in an immunosuppressed mammalian host. The role of RTS1 (ParA ortholog) as a septin regulator has been previously explored in S. cerevisiae, where it coordinates the dynamics of the septin rings by Rts1-dependent dephosphorylation of Shs1 (Dobbelaere et al., 2003). In A. fumigatus, deletion of parA resulted in altered AspB localization and, most importantly, altered the phosphorylation profile of AspB revealing ParA-dependent dephosphorylation of AspB. AspB under normal growth conditions is phosphorylated in seven residues distributed across the GTPase domain and the C-terminal region. Deletion of parA resulted in two additional phosphorylation sites (T68 and S447) that are enriched sevenfold when compared to the control strain. Our preliminary studies on the AspB interactome using purification of the AspB–EGFP fusion protein using GFP-Trap affinity matrix and subsequent LC–MS/MS analysis revealed PP2A as one of the AspB interactants, suggesting that PP2A could be directly dephosphorylating these residues (data not shown). Although mutation of these sites (S447A, S447E, T68A, and T68E) altered the localization pattern of AspB, only apical compartment length was affected in the AspBmt-T68E. Interestingly, AspBmt-T68E localizes transiently at the septum, similar to wild-type AspB, and the defect in apical compartment length could be due to altered interaction with septation regulators due to locking AspB in a phosphomimetic state. T68 is in the analogous position to A. gossypii S91 that has also been reported to be phosphorylated in vivo (Meseroll et al., 2013). A phosphomimetic strain of S91 in A. gossypii also resulted in a modest phenotype with abnormal spore morphology; however, spores were viable and capable of germinating at the same rate as the wild type. More detailed characterization of these mutants, as well as phosphomutants of the other AspB phosphoresidues, will further our understanding on how AspB is regulated through phosphorylation and how these phosphorylation sites might affect AspB–protein interactions.
Author Contributions
JV and WS conceived and designed research; JV, HR, and AR performed research; JV, HR, AR, and YA performed virulence and histopathology analyses; JV GW, ES, and MM acquired and analyzed the phosphoproteomic data. JV, PJ, and WJ wrote the paper; JV, HR, AR, GW, ES, MM, YA, PJ, and WS approved the final submission.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Dr. Andrew Alspaugh’s laboratory (Duke University) for helpful experimental discussion and technical support. The authors also thank Katie Falloon for assisting with some of the experiments. Any opinion, findings, and conclusions expressed in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
Funding. JV was supported by National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship Program DGF 1106401. WS. and PJ. are supported in part by 1 R01 AI112595-01.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00997
References
- Alvarez-Tabares I., Perez-Martin J. (2010). Septins from the phytopathogenic fungus Ustilago maydis are required for proper morphogenesis but dispensable for virulence. PLoS ONE 5:e12933 10.1371/journal.pone.0012933 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asano S., Park J. E., Yu L. R., Zhou M., Sakchaisri K., Park C. J., et al. (2006). Direct phosphorylation and activation of a Nim1-related kinase Gin4 by Elm1 in budding yeast. J. Biol. Chem. 281 27090–27098. 10.1074/jbc.M601483200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barral Y., Parra M., Bidlinmaier S., Snyder M. (1998). Nim1-related kinases coordinate cell cycle progression with the organization of the peripheral cytoskeleton in yeast. Genes Dev. 13 176–187. 10.1101/gad.13.2.176 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll C. W., Altman R., Schieltz D., Yates J. R., Kellogg D. (1998). The septins are required for the mitosis-specific activation of the Gin4 kinase. J. Cell Biol. 143 709–717. 10.1083/jcb.143.3.709 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cvrekova F., De Virgilio C., Manser E., Pringle J. R., Kasmyth K. (1995). Ste20-like protein kinases are required for normal localization of cell growth and for cytokinesis in budding yeast. Cell Cycle 9 1817–1830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- da Silva Ferreira M. E., Kress M. R., Savoldi M., Goldman M. H., Hartl A., Heinekamp T., et al. (2006). The akuB(KU80) mutant deficient for nonhomologous end joining is a powerful tool for analyzing pathogenicity in Aspergillus fumigatus. Eukaryot. Cell 5 207–211. 10.1128/EC.5.1.207-211.2006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Souza C. P., Hashmi S. B., Osmani A. H., Andrews P., Ringelberg C. S., Dunlap J. C., et al. (2013). Functional analysis of the Aspergillus nidulans kinome. PLoS ONE 8:e58008 10.1371/journal.pone.0058008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMay B. S., Meseroll R. A., Occhipinti P., Gladfelter A. S. (2009). Regulation of distinct septin rings in a single cell by Elm1p and Gin4p kinases. Mol. Biol. Cell 20 2311–2326. 10.1091/mbc.E08-12-1169 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbelaere J., Gentry M. S., Hallberg R. L., Barral Y. (2003). Phosphorylation-dependent regulation of septin dynamics during the cell cycle. Dev. Cell 4 345–357. 10.1016/S1534-5807(03)00061-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frieser S. H., Hlubek A., Sandrock B., Bolker M. (2011). Cla4 kinase triggers destruction of the Rac1-GEF Cdc24 during polarized growth in Ustilago maydis. Mol. Biol. Cell 22 3253–3262. 10.1091/mbc.E11-04-0314 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia G. III, Bertin A., Li Z., Song Y., Mcmurray M. A., Thorner J., et al. (2011). Subunit-dependent modulation of septin assembly: budding yeast septin Shs1 promotes ring and gauze formation. J. Cell Biol. 195 993–1004. 10.1083/jcb.201107123 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladfelter A. S. (2010). Guides to the final frontier of the cytoskeleton: septins in filamentous fungi. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 13 720–726. 10.1016/j.mib.2010.09.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez-Rodriguez Y., Hastings S., Momany M. (2012). The septin AspB in Aspergillus nidulans forms bars and filaments and plays roles in growth emergence and conidiation. Eukaryot. Cell 11 311–323. 10.1128/EC.05164-11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez-Rodriguez Y., Masuo S., Johnson D., Orlando R., Smith A., Couto-Rodriguez M., et al. (2014). Distinct septin heteropolymers Co-exist during multicellular development in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus nidulans. PLoS ONE 9:e92819 10.1371/journal.pone.0092819 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez-Rodriguez Y., Momany M. (2012). Posttranslational modifications and assembly of septin heteropolymers and higher-order structures. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 15 660–668. 10.1016/j.mib.2012.09.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juvvadi P. R., Belina D., Soderblom E. J., Moseley M. A., Steinbach W. J. (2013). Filamentous fungal-specific septin AspE is phosphorylated in vivo and interacts with actin, tubulin and other septins in the human pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 431 547–553. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.01.020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juvvadi P. R., Fortwendel J. R., Rogg L. E., Burns K. A., Randell S. H., Steinbach W. J. (2011a). Localization and activity of the calcineurin catalytic and regulatory subunit complex at the septum is essential for hyphal elongation and proper septation in Aspergillus fumigatus. Mol. Microbiol. 82 1235–1259. 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07886.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juvvadi P. R., Fortwendel J. R., Rogg L. E., Steinbach W. J. (2011b). Differential localization patterns of septins during growth of the human fungal pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus reveal novel functions. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 405 238–243. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.01.017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadota J., Yamamoto T., Yoshiuchi S., Bi E., Tanaka K. (2004). Septin ring assembly requires concerted action of polarisome components, a PAK Kinase Cla4p, and the actin cytoskeleton in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Biol. Cell 15 5329–5345. 10.1091/mbc.E04-03-0254 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozubowski L., Heitman J. (2010). Septins enforce morphogenetic events during sexual reproduction and contribute to virulence of Cryptococcus neoformans. Mol. Microbiol. 75 658–675. 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06983.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamoth F., Juvvadi P. R., Fortwendel J. R., Steinbach W. J. (2012). Heat shock protein 90 is required for conidiation and cell wall integrity in Aspergillus fumigatus. Eukaryot. Cell 11 1324–1332. 10.1128/EC.00032-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leberer E., Ziegelbauer K., Schimidt A., Harcus D., Dignard D., Ash J., et al. (1997). Virulence and hyphal formation of Candida albicans require the Ste20p-like protein kinase CaCla4p. Curr. Biol. 7 539–546. 10.1016/S0960-9822(06)00252-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leveleki L., Mahlert M., Sandrock B., Bolker M. (2004). The PAK family kinase Cla4 is required for budding and morphogenesis in Ustilago maydis. Mol. Microbiol. 54 396–406. 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04296.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. R., Yong J. Y., Wang Y. M., Wang Y. (2012). CDK regulates septin organization through cell-cycle-dependent phosphorylation of the Nim1-related kinase Gin4. J. Cell Sci. 125 2533–2543. 10.1242/jcs.104497 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L., Xue C., Bruno K., Nishimura M., Xu J. (2004). Two PAK kinase genes, CHM1 and MST20, have distinct functions in Magnaporthe grisea. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 17 547–556. 10.1094/MPMI.2004.17.5.547 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsey R., Cowden S., Hernandez-Rodriguez Y., Momany M. (2010). Septins AspA and AspC are important for normal development and limit the emergence of new growth foci in the multicellular fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Eukaryot. Cell 9 155–163. 10.1128/EC.00269-09 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longtine M. S., Fares H., Pringle J. R. (1998). Role of the yeast Gin4p protein kinase in septin assembly and the relationship between septin assembly and septin function. J. Cell Biol. 143 719–736. 10.1083/jcb.143.3.719 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meseroll R. A., Occhipinti P., Gladfelter A. S. (2013). Septin phosphorylation and coiled-coil domains function in cell and septin ring morphology in the filamentous fungus Ashbya gossypii. Eukaryot. Cell 12 182–193. 10.1128/EC.00251-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momany M., Zhao J., Lindsey R., Westfall P. J. (2001). Characterization of the Aspergillus nidulans Septin (asp) Gene Family. Genetics 157 969–977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortensen E. M., Mcdonald H., Yates J. R., III, Kellogg D. R. (2002). Cell cycle-dependent assembly of a Gin4-Septin complex. Mol. Biol. Cell 13 2091–2105. 10.1091/mbc.01-10-0500 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan F., Malmberg R. L., Momany M. (2007). Analysis of septins across kingdoms reveals orthology and new motifs. BMC Evol. Biol. 7:103 10.1186/1471-2148-7-103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park G., Servin J. A., Turner G. E., Altamirano L., Colot H. V., Collopy P., et al. (2011). Global analysis of serine-threonine protein kinase genes in Neurospora crassa. Eukaryot. Cell 10 1553–1564. 10.1128/EC.05140-11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolke Y., Tudzynski P. (2008). The small GTPase Rac and the p21-activated kinase Cla4 in Claviceps purpurea: interaction and impact on polarity, development and pathogenicity. Mol. Microbiol. 68 405–423. 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06159.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha I., Wang Y. M., Philp R., Li C. R., Yap W. H., Wang Y. (2007). Cyclin-dependent kinases control septin phosphorylation in Candida albicans hyphal development. Dev. Cell 13 421–432. 10.1016/j.devcel.2007.06.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbach W. J., Cramer R. A., Jr., Perfect B. Z., Asfaw Y. G., Sauer T. C., Najvar L. K., et al. (2006). Calcineurin controls growth, morphology, and pathogenicity in Aspergillus fumigatus. Eukaryot. Cell 5 1091–1103. 10.1128/EC.00139-06 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang C. S. L., Reed S. I. (2002). Phosphorylation of the Septin Cdc3 in G1 by Cdc28 kinase is essential for efficient septin ring disassembly. Cell Cycle 1 42–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian H., Zhou L., Guo W., Wang X. (2015). Small GTPase Rac1 and its interaction partner Cla4 regulate polarized growth and pathogenicity in Verticillium dahliae. Fungal Genet. Biol. 74 21–31. 10.1016/j.fgb.2014.11.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vargas-Muniz J. M., Renshaw H., Richards A. D., Lamoth F., Soderblom E. J., Moseley M. A., et al. (2015). The Aspergillus fumigatus septins play pleiotropic roles in septation, conidiation, and cell wall stress, but are dispensable for virulence. Fungal Genet. Biol. 81 41–51. 10.1016/j.fgb.2015.05.014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Versele M., Thorner J. (2004). Septin collar formation in budding yeast requires GTP binding and direct phosphorylation by the PAK, Cla4. J. Cell Biol. 164 701–715. 10.1083/jcb.200312070 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warenda A. J., Konopka J. B. (2002). Septin Function in Candida albicans Morphogenesis. Mol. Biol. Cell 13 2732–2746. 10.1091/mbc.E02-01-0013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wightman R., Bates S., Amornrrattanapan P., Sudbery P. (2004). In Candida albicans, the Nim1 kinases Gin4 and Hsl1 negatively regulate pseudohypha formation and Gin4 also controls septin organization. J. Cell Biol. 164 581–591. 10.1083/jcb.200307176 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong G., Jiang P., Qiao W., Zhang Y., Wei W., Lu L. (2014). Protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) regulatory subunits ParA and PabA orchestrate septation and conidiation and are essential for PP2A activity in Aspergillus nidulans. Eukaryot. Cell 13 1494–1506. 10.1128/EC.00201-14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


