Abstract
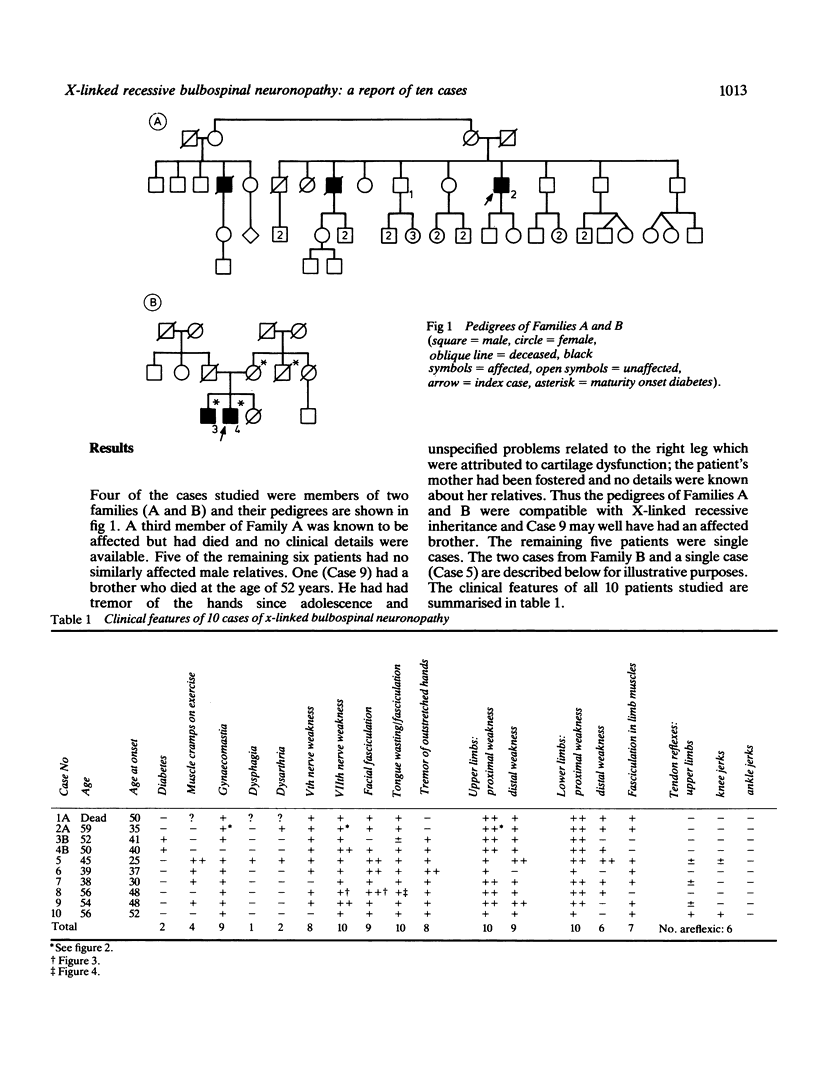
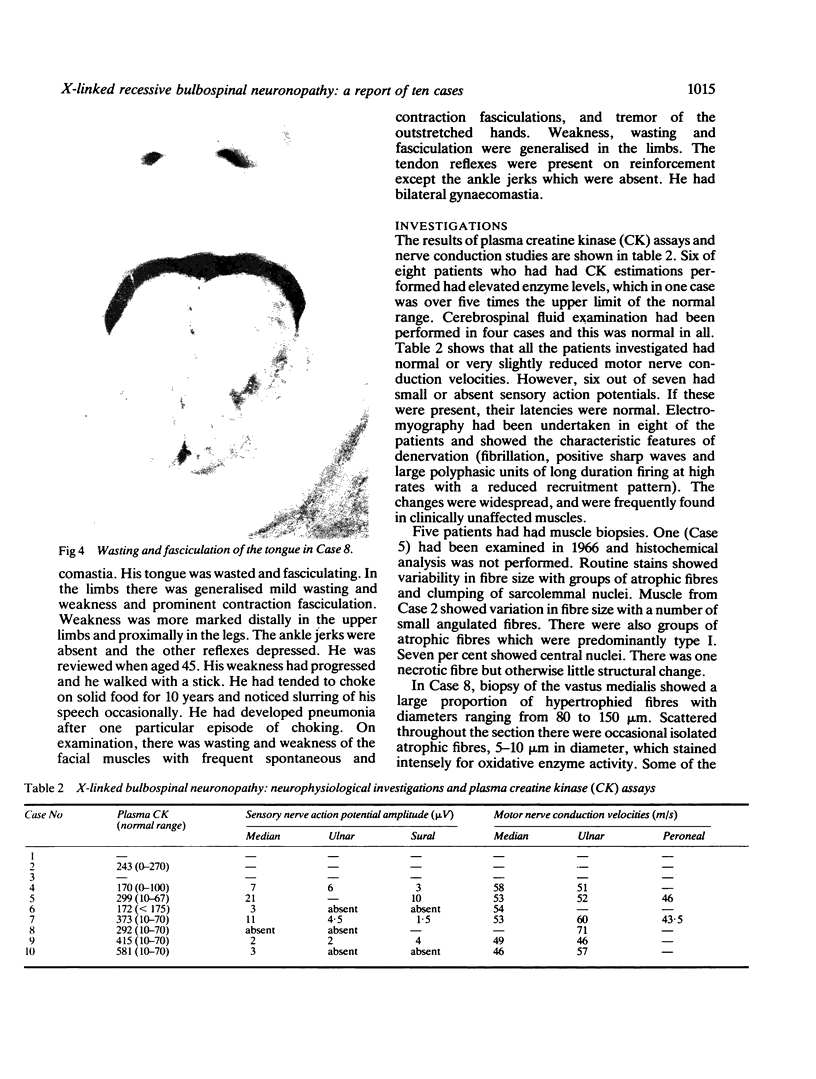
A form of adult onset 'bulbospinal muscular atrophy' of X-linked recessive inheritance is described in 10 patients from eight families. Muscle weakness in the limbs was mainly proximal and developed in the third to fifth decades of life, often preceded by muscle cramps on exertion and tremor of the hands. Weakness and fasciculation of the facial muscles and tongue were prominent. All the patients had gynaecomastia and some were infertile. Two had diabetes mellitus. Motor nerve conduction studies were normal but most patients had small or unrecordable sensory action potentials in the absence of clinical sensory loss. Plasma creatine kinase levels were considerably elevated and muscle biopsies showed neurogenic atrophy together with secondary myopathic changes. The importance of recognising this distinctive disorder in single cases (six of the present series) is emphasised.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bundey S., Lovelace R. E. A clinical and genetic study of chronic proximal spinal muscular atrophy. Brain. 1975 Sep;98(3):455–472. doi: 10.1093/brain/98.3.455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross M. Proximal spinal muscular atrophy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1966 Feb;29(1):29–34. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.29.1.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding A. E., Thomas P. K. Hereditary distal spinal muscular atrophy. A report on 34 cases and a review of the literature. J Neurol Sci. 1980 Mar;45(2-3):337–348. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(80)90177-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding A. E., Thomas P. K. The clinical features of hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy types I and II. Brain. 1980 Jun;103(2):259–280. doi: 10.1093/brain/103.2.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KURLAND L. T. Epidemiologic investigations of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. III. A genetic interpretation of incidence and geographic distribution. Proc Staff Meet Mayo Clin. 1957 Aug 21;32(17):449–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaeser H. E. Scapuloperoneal muscular atrophy. Brain. 1965 Jun;88(2):407–418. doi: 10.1093/brain/88.2.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy W. R., Alter M., Sung J. H. Progressive proximal spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy of late onset. A sex-linked recessive trait. Neurology. 1968 Jul;18(7):671–680. doi: 10.1212/wnl.18.7.671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGEE K. R. Familial progressive bulbar-spinal muscular atrophy. Neurology. 1960 Mar;10:295–305. doi: 10.1212/wnl.10.3.295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MULLER R. Progressive motor neuron disease in adults; a clinical study with special reference to the course of the disease. Acta Psychiatr Neurol Scand. 1952;27(1-2):137–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1952.tb04647.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod J. G., Prineas J. W. Distal type of chronic spinal muscular atrophy. Clinical, electrophysiological and pathological studies. Brain. 1971;94(4):703–714. doi: 10.1093/brain/94.4.703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearn J. H., Hudgson P., Walton J. N. A clinical and genetic study of spinal muscular atrophy of adult onset: the autosomal recessive form as a discrete disease entity. Brain. 1978 Dec;101(4):591–606. doi: 10.1093/brain/101.4.591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearn J. Autosomal dominant spinal muscular atrophy: a clinical and genetic study. J Neurol Sci. 1978 Sep;38(2):263–275. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(78)90072-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters H. A., Opitz J. M., Goto I., Reese H. H. The benign proximal spinal progressive muscular atrophies. Acta Neurol Scand. 1968;44(5):542–560. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1968.tb05591.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringel S. P., Lava N. S., Treihaft M. M., Lubs M. L., Lubs H. A. Late-onset X-linked recessive spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy. Muscle Nerve. 1978 Jul-Aug;1(4):297–307. doi: 10.1002/mus.880010406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH J. B., PATEL A. THE WOHLFART-KUGELBERG-WELANDER DISEASE; REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE AND REPORT OF A CASE. Neurology. 1965 May;15:469–473. doi: 10.1212/wnl.15.5.469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenen J., Delwaide P. J., Legros J. J., Franchimont P. Motoneuropathie héréditaire: la forme proximale de l'adulte lié au sexe (ou maladie de Kennedy). Observations cliniques et neuroendocrinologiques. J Neurol Sci. 1979 May;41(3):343–357. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(79)90094-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serratrice G., Gastaut J. L., Pellissier J. F., Pouget J. Amyotrotrophies scapulo-péronières chroniques de type Stark-Kaeser. (A propos de 10 observations) Rev Neurol (Paris) 1976 Dec;132(12):823–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanis C., Papapetropoulos T. h., Scarpalezos S., Lygidakis G., Panayiotopoulos C. P. X-linked spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy of late onset. A separate type of motor neuron disease? J Neurol Sci. 1975 Apr;24(4):493–403. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(75)90173-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSUKAGOSHI H., NAKANISHI T., KONDO K., TSUBAKI T. HEREDITARY PROXIMAL NEUROGENIC MUSCULAR ATROPHY IN ADULT. Arch Neurol. 1965 Jun;12:597–603. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1965.00460300045005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukagoshi H., Shoji H., Furukawa T. Proximal neurogenic muscular atrophy in adolescence and adulthood with X-linked recessive inheritance. Kugelberg-Welander disease and its variant of late onset in one pedigree. Neurology. 1970 Dec;20(12):1188–1193. doi: 10.1212/wnl.20.12.1188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







