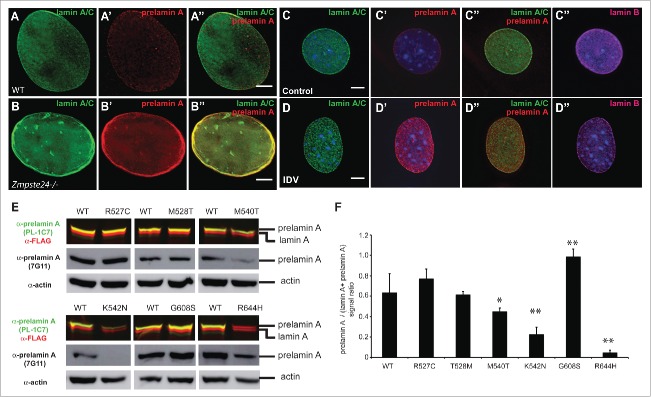
Figure 5.
Lack of ZMPSTE24 expression or activity increases prelamin A levels, but laminopathy -associated missense lamin A mutations exert different effects on prelamin A accumulation. (A) and (B). Zmpste24−/− and wild type MEFs were co-stained with anti-lamin A/C (green) and anti-prelamin A (Red) antibodies. Increased prelamin A levels can be observed in the absence of the sequence specific protease. (C) and (D). C2C12 cells were treated with the HIV protease inhibitor indinavir (IDV), which inhibits ZMPSTE24 activity. Cells were co-stained as described in A and including an anti-lamin B antibody as control. (E). Analysis of prelamin A accumulation in laminopathy-associated missense lamin A mutations. Dual infrared immunoblots of total proteins from cells transfected with 3XFLAG-tagged human LMNA constructs containing different laminopathy-associated mutations including: R527C, T528M, M540T, K542N, G608S and R644H. Blot shows the anti-prelamin A PL-1C7 antibody in green (800 nm channel) and a rabbit anti-FLAG antibody in red (700 nm channel). Membranes were re-blotted with anti-prelamin A 7G11 and β-actin antibodies (loading control) and evaluated by chemiluminescence. (F). Quantification of prelamin A levels in laminopathy-associated mutations. Ratio of prelamin A (800 nm channel)/ Total lamin A/prelamin A (700 nm channel) is shown. Values represent the mean +/− SD, * p< 0.005, ** p< 0.001. See also Fig. S4.