Abstract
A minimalist Cys2His2 zinc finger peptide, Lys-Tyr-Ala-Cys-Ala-Ala-Cys-Ala-Ala-Ala-Phe-Ala-Ala-Lys-Ala-Ala-Leu-Ala- Ala-His-Ala-Ala-Ala-His-Ala-Lys, has been synthesized. Metal binding studies using Co2+ as a probe indicated that this peptide forms a 1:1 peptide/metal complex with a dissociation constant comparable to that observed for other zinc finger peptides. At high peptide concentrations, a 2:1 peptide/metal complex also forms, with four cysteinates coordinated to Co2+. Additional studies with sequence variants in which the canonical hydrophobic residues were changed to alanine, or in which one of the residues between the cysteines and the histidines was deleted, revealed an even more pronounced formation of the 2:1 complex over the 1:1 complex. In addition, the absorption spectra of the 1:1 peptide/Co2+ complexes of the variant peptides are significantly different from those seen for complexes of the parent peptide or those of more typical zinc finger peptides. NMR studies revealed that the parent peptide folds in the presence of Zn2+ to a structure very similar to that observed for other zinc finger peptides of this class. Taken together, these results suggest that the metal-binding and canonical hydrophobic residues are necessary and sufficient to determine the structure of this class of zinc finger peptides.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anfinsen C. B. Principles that govern the folding of protein chains. Science. 1973 Jul 20;181(4096):223–230. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4096.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Proposed structure for the zinc-binding domains from transcription factor IIIA and related proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):99–102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Zinc finger domains: hypotheses and current knowledge. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1990;19:405–421. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.19.060190.002201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowie J. U., Reidhaar-Olson J. F., Lim W. A., Sauer R. T. Deciphering the message in protein sequences: tolerance to amino acid substitutions. Science. 1990 Mar 16;247(4948):1306–1310. doi: 10.1126/science.2315699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. S., Sander C., Argos P. The primary structure of transcription factor TFIIIA has 12 consecutive repeats. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 8;186(2):271–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80723-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeGrado W. F., Wasserman Z. R., Lear J. D. Protein design, a minimalist approach. Science. 1989 Feb 3;243(4891):622–628. doi: 10.1126/science.2464850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diakun G. P., Fairall L., Klug A. EXAFS study of the zinc-binding sites in the protein transcription factor IIIA. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):698–699. doi: 10.1038/324698a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Hollenberg S. M. Zinc fingers: gilt by association. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90522-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. D., Berg J. M., Pabo C. O. Metal-dependent folding of a single zinc finger from transcription factor IIIA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4841–4845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg A. M., King B. O., Roeder R. G. Xenopus 5S gene transcription factor, TFIIIA: characterization of a cDNA clone and measurement of RNA levels throughout development. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):479–489. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90455-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser E. T., Kézdy F. J. Amphiphilic secondary structure: design of peptide hormones. Science. 1984 Jan 20;223(4633):249–255. doi: 10.1126/science.6322295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klevit R. E., Herriott J. R., Horvath S. J. Solution structure of a zinc finger domain of yeast ADR1. Proteins. 1990;7(3):215–226. doi: 10.1002/prot.340070303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochoyan M., Havel T. F., Nguyen D. T., Dahl C. E., Keutmann H. T., Weiss M. A. Alternating zinc fingers in the human male associated protein ZFY: 2D NMR structure of an even finger and implications for "jumping-linker" DNA recognition. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 9;30(14):3371–3386. doi: 10.1021/bi00228a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. S., Cavanagh J., Wright P. E. Complete assignment of the 1H NMR spectrum of a synthetic zinc finger from Xfin. Sequential resonance assignments and secondary structure. FEBS Lett. 1989 Aug 28;254(1-2):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. S., Gippert G. P., Soman K. V., Case D. A., Wright P. E. Three-dimensional solution structure of a single zinc finger DNA-binding domain. Science. 1989 Aug 11;245(4918):635–637. doi: 10.1126/science.2503871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhaus D., Nakaseko Y., Nagai K., Klug A. Sequence-specific [1H]NMR resonance assignments and secondary structure identification for 1- and 2-zinc finger constructs from SW15. A hydrophobic core involving four invariant residues. FEBS Lett. 1990 Mar 26;262(2):179–184. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80184-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omichinski J. G., Clore G. M., Appella E., Sakaguchi K., Gronenborn A. M. High-resolution three-dimensional structure of a single zinc finger from a human enhancer binding protein in solution. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 9;29(40):9324–9334. doi: 10.1021/bi00492a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Párraga G., Horvath S. J., Eisen A., Taylor W. E., Hood L., Young E. T., Klevit R. E. Zinc-dependent structure of a single-finger domain of yeast ADR1. Science. 1988 Sep 16;241(4872):1489–1492. doi: 10.1126/science.3047872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Párraga G., Horvath S., Hood L., Young E. T., Klevit R. E. Spectroscopic studies of wild-type and mutant "zinc finger" peptides: determinants of domain folding and structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):137–141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
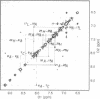
- Williamson M. P. Secondary-structure dependent chemical shifts in proteins. Biopolymers. 1990 Aug 15;29(10-11):1423–1431. doi: 10.1002/bip.360291009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]