Abstract
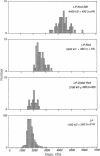
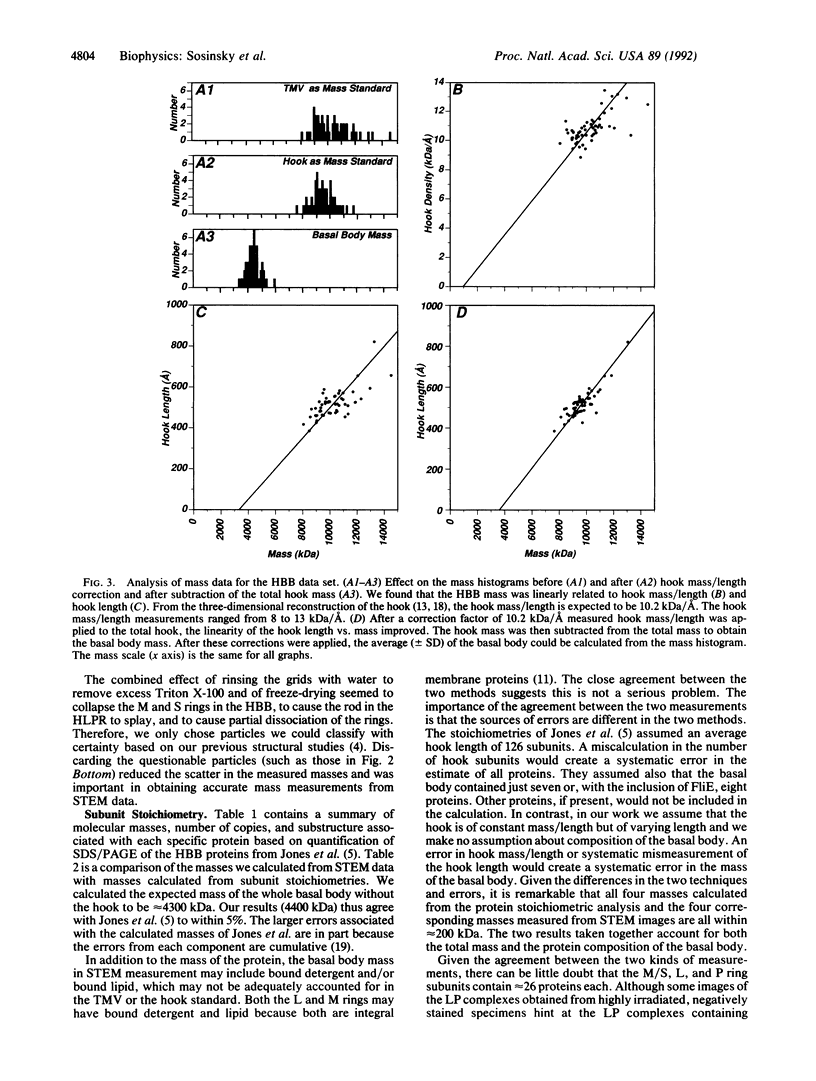
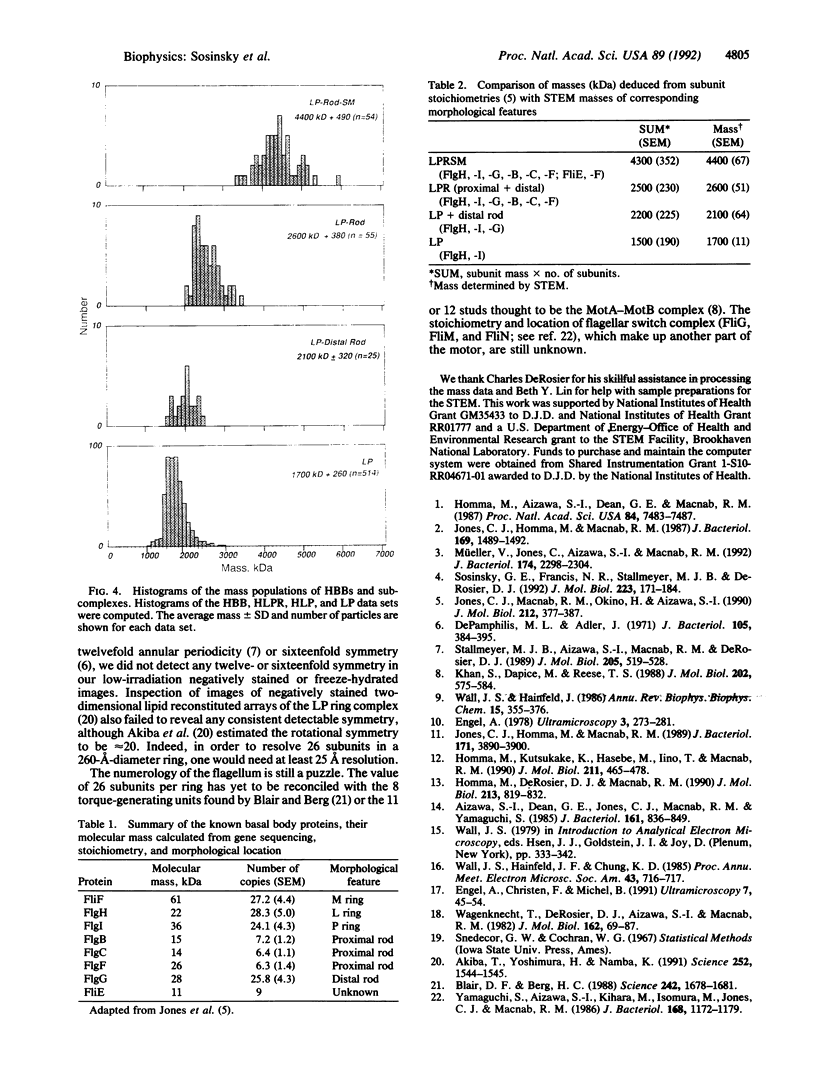
The basal body, a part of the rotary motor of the bacterial flagellum, is a multiprotein assembly that consists of four rings (denoted M, S, P, and L) and an axial rod (denoted R). From analysis of scanning transmission electron microscopy images of hook-basal body preparations isolated from Salmonella typhimurium, we have determined the masses of the basal body and three of its subcomplexes. The mass of the basal body (i.e., the four rings and rod) is 4400 +/- 490 kDa (mean +/- SD; n = 54). The mass of the LPR subcomplex (i.e., L and P rings and the whole rod) is 2600 +/- 380 kDa (n = 55), that of the L and P rings and the distal part of the rod is 2100 +/- 320 kDa (n = 25), and the mass of the L and P ring subcomplex is 1700 +/- 260 kDa (n = 514). These results, together with the masses of the component proteins, indicate that the rings contain approximately 26 subunits each and that the mass of the rod is consistent with a composition of approximately 6 copies each of three of the rod proteins FlgB, FlgC, and FlgF and approximately 26 copies of FlgG as determined by Jones et al. [Jones, C. J., Macnab, R. M., Okino, H. & Aizawa, S.-I. (1990) J. Mol. Biol. 212, 377-387] using quantitative gel electrophoresis. The results of Jones et al., together with ours, account for all proteins in the basal body to within approximately 5% (or 200 kDa).
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aizawa S. I., Dean G. E., Jones C. J., Macnab R. M., Yamaguchi S. Purification and characterization of the flagellar hook-basal body complex of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):836–849. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.836-849.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiba T., Yoshimura H., Namba K. Monolayer crystallization of flagellar L-P rings by sequential addition and depletion of lipid. Science. 1991 Jun 14;252(5012):1544–1546. doi: 10.1126/science.2047860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. F., Berg H. C. Restoration of torque in defective flagellar motors. Science. 1988 Dec 23;242(4886):1678–1681. doi: 10.1126/science.2849208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L., Adler J. Fine structure and isolation of the hook-basal body complex of flagella from Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):384–395. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.384-395.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. Molecular weight determination by scanning transmission electron microscopy. Ultramicroscopy. 1978;3(3):273–281. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3991(78)80037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Aizawa S., Dean G. E., Macnab R. M. Identification of the M-ring protein of the flagellar motor of Salmonella typhimurium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7483–7487. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., DeRosier D. J., Macnab R. M. Flagellar hook and hook-associated proteins of Salmonella typhimurium and their relationship to other axial components of the flagellum. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):819–832. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80266-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Kutsukake K., Hasebe M., Iino T., Macnab R. M. FlgB, FlgC, FlgF and FlgG. A family of structurally related proteins in the flagellar basal body of Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jan 20;211(2):465–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90365-S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. J., Homma M., Macnab R. M. Identification of proteins of the outer (L and P) rings of the flagellar basal body of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1489–1492. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1489-1492.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. J., Homma M., Macnab R. M. L-, P-, and M-ring proteins of the flagellar basal body of Salmonella typhimurium: gene sequences and deduced protein sequences. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3890–3900. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3890-3900.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. J., Macnab R. M., Okino H., Aizawa S. Stoichiometric analysis of the flagellar hook-(basal-body) complex of Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1990 Mar 20;212(2):377–387. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90132-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S., Dapice M., Reese T. S. Effects of mot gene expression on the structure of the flagellar motor. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 5;202(3):575–584. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90287-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller V., Jones C. J., Kawagishi I., Aizawa S., Macnab R. M. Characterization of the fliE genes of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium and identification of the FliE protein as a component of the flagellar hook-basal body complex. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(7):2298–2304. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.7.2298-2304.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sosinsky G. E., Francis N. R., Stallmeyer M. J., DeRosier D. J. Substructure of the flagellar basal body of Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jan 5;223(1):171–184. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90724-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stallmeyer M. J., Aizawa S., Macnab R. M., DeRosier D. J. Image reconstruction of the flagellar basal body of Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1989 Feb 5;205(3):519–528. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90223-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagenknecht T., DeRosier D. J., Aizawa S., Macnab R. M. Flagellar hook structures of Caulobacter and Salmonella and their relationship to filament structure. J Mol Biol. 1982 Nov 25;162(1):69–87. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90162-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi S., Aizawa S., Kihara M., Isomura M., Jones C. J., Macnab R. M. Genetic evidence for a switching and energy-transducing complex in the flagellar motor of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1172–1179. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1172-1179.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]