To the Editor
The search for specific autoantibodies in patients with multiple sclerosis has been an area of intensive research for decades, but the unequivocal identification of one or several autoantigens associated with the disease has remained elusive. However, considerable interest has been raised by a study showing the presence of serum autoantibodies to KIR4.1, an astrocytic inward-rectifying potassium channel, in 47% of adult patients with multiple sclerosis but not in patients with other neurologic diseases or in healthy controls.1 However, subsequent independent studies that were performed with the use of a cell-based assay or peptide antigen–based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) have not corroborated these find-ings.2-4 Consequently, the presence of KIR4.1 autoantibodies in patients with multiple sclerosis remains controversial.
A commonality among the studies that have contradicted the original report is that one of the three approaches that were originally used to measure the autoantibodies, a protein antigen–based ELISA, was not used. This ELISA procedure includes in vitro expression and purification of the full-length KIR4.1 protein, allowing for its native tetrameric assembly and the isolation of low-glycosylated KIR4.1 isoforms, both of which are reported to be critical for autoantibody binding.5 Accordingly, we sought to independently confirm the presence of these autoantibodies using this approach.
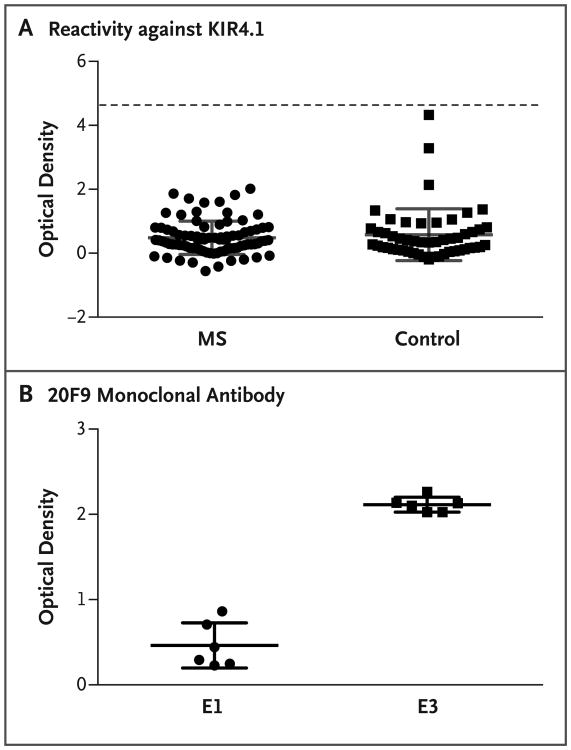
To this end, we performed the assay using detailed instructions provided by the authors of the original report during a visit to their laboratory as part of a collaborative scientific exchange. Moreover, we used a monoclonal antibody (20F9), which is specific for tetrameric and low-glycosylated isoforms of KIR4.1, to confirm enrichment of the antigenic form. We tested serum obtained from 86 clinic-based patients with multiple sclerosis and 51 healthy control donors at our center. None of the samples from either the multiple sclerosis group or the control group showed KIR4.1 reactivity, and no significant between-group difference (P>0.05) was established (Fig. 1A). The enrichment of low-glycosylated KIR4.1 tetramer isoforms was confirmed with the 20F9 monoclonal antibody (P = 0.002) (Fig. 1B).
Figure 1. Detection of KIR4.1 Protein in Samples from Patients with Multiple Sclerosis and Controls.
Panel A shows the results of a protein-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) that was used to detect serum autoantibodies against KIR4.1 in samples obtained from 86 patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) and 51 healthy controls. The MS samples included serum from 68 patients with relapsing–remitting disease, 8 with secondary progressive disease, 4 with primary progressive disease, and 6 with a clinically isolated syndrome. Purified KIR4.1 tetramers were covalently bound to the plates. The mean (±SD) optical density of the assays was 0.4844±0.5217 in the MS group and 0.5799±0.8107 in the control group (P>0.05 for all comparisons). Each serum sample was tested in duplicate. Positive reactivity (dashed line) was defined as 5 SD above the mean optical density of the control group. Elution 1 (E1) and elution 3 (E3) were obtained by applying increasing concentrations of imidazole and were enriched in high- and low-glycosylated KIR4.1 tetramers, respectively. E1 was therefore used to measure nonspecific binding, and E3, which contains the immunoreactive fraction of KIR4.1, was used to measure the specific autoantibodies. The optical density was measured by dividing the difference between E1 and E3 by E1. Panel B shows the results of an ELISA to evaluate the enrichment of low-glycosylated KIR4.1 tetramers in eluted fractions of histidine-tagged KIR4.1 from a cobalt-chelating column. Two wells of each plate that were used to generate the data in Panel A were incubated with 20F9 monoclonal antibody, which specifically binds to the KIR4.1 tetramers in their low-glycosylation state. The mean optical density was 0.4620±0.2648 for E1 and 2.114±0.08838 for E3 (P = 0.002). Each data point represents the value obtained in a single well. The optical densities in Panels A and B were all corrected for background by subtracting the value obtained at 540 nm from that obtained at 450 nm. The I bars in Panels A and B denote the SD. Statistical analyses were performed with the use of the Mann–Whitney U test.
Taken together, these results indicate that autoantibodies against KIR4.1 may not be specific for multiple sclerosis. Further support for this point of view is provided in this issue of the Journal by Pröbstel et al., who used approaches that were similar to ours and that produced similar results.6 However, our experience with the ELISA revealed considerable methodologic challenges and demands that are inherent to the assay — particularly, those associated with post-translational modifications and higher-order structure formation of the KIR4.1 protein. Additional study is required to better identify these technical issues and address discrepancies between investigations through cooperative sharing of specimens. We conclude that although there are technical challenges with measuring anti-KIR4.1 autoantibodies, future investigations are required to clarify their possible role in multiple sclerosis.
Acknowledgments
Supported by a grant from EMD Serono (to Dr. O'Connor) and by grants from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (AI045757, AI046130, AI070352, and AI039671), the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NS067305 and F31NS086434), the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (GM093080), the National Multiple Sclerosis Society (CA1061-A-18), the Penates Foundation, and the Nancy Taylor Foundation for Chronic Diseases (to Dr. Hafler).
Footnotes
Disclosure forms provided by the authors are available with the full text of this letter at NEJM.org.
References
- 1.Srivastava R, Aslam M, Kalluri SR, et al. Potassium channel KIR4.1 as an immune target in multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:115–23. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1110740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Brickshawana A, Hinson SR, Romero MF, et al. Investigation of the KIR4.1 potassium channel as a putative antigen in patients with multiple sclerosis: a comparative study. Lancet Neurol. 2014;13:795–806. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70141-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Nerrant E, Salsac C, Charif M, et al. Lack of confirmation of anti-inward rectifying potassium channel 4.1 antibodies as reliable markers of multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler. 2014;20:1699–703. doi: 10.1177/1352458514531086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Malyavantham K, Weinstock-Guttman B, Suresh L, et al. Humoral responses to diverse autoimmune disease-associated antigens in multiple sclerosis. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0129503. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0129503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hemmer B. Antibodies to the inward rectifying potassium channel 4.1 in multiple sclerosis: different methodologies — conflicting results? Mult Scler. 2015;21:537–9. doi: 10.1177/1352458514564493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Pröbstel AK, Kuhle J, Derfuss T. Multiple sclerosis and antibodies against KIR4.1. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:1496–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1507131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]