Abstract
Malignant glioma is the most common brain tumor. The molecular basis of glioma tumorigenicity has not been defined. Cultured glioma cells accumulate high levels of insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) transcripts. We asked whether IGF-I expression is coupled to tumorigenicity, using a combined in vivo/in vitro system employing antisense RNA for IGF-I. An antisense IGF-I expression construct in an expression vector that incorporates Epstein-Barr virus replicative signals and the ZnSO4-inducible metallothionein I transcriptional promoter was assembled. Stable glioma transfectants were derived from C6 glioma cells, which constitutively express IGF-I. B-104 neuroblastoma cells, derived originally from the same tumor but not expressing IGF-I, were also transfected as controls. In the absence of ZnSO4, the C6 transfectants expressed high levels of IGF-I mRNA and protein as detected by in situ hybridization and immunocytochemistry, respectively. Addition of ZnSO4 in the culture medium resulted in high levels of antisense transcript accumulation and dramatically decreased levels of endogenous IGF-I mRNA and IGF-I protein. Subcutaneous injection of either nontransfected C6 parental cells or C6 cells transfected with vector without IGF-I sequences into rats resulted in large tumors after 2 weeks, as did transfected and nontransfected B-104 cells. However, the rats injected with transfected C6 cells yielded no tumors after 40 weeks of observation. Two weeks after injection of the transfected C6 cells a small cyst was apparent in six rats. Histologic sections revealed a few glioma cells infiltrated by a large number of mononuclear cells. No infiltration of mononuclear cells was apparent in the glioma tumors resulting from injection of parental (nontransfected) cells, suggesting that the parental cells, but not the antisense IGF-I transfectants, escape the host immune response.
Full text
PDF



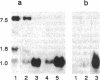
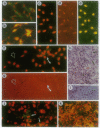
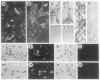
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blatt J., White C., Dienes S., Friedman H., Foley T. P., Jr Production of an insulin-like growth factor by osteosarcoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 30;123(1):373–376. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90423-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehm K. D., Kelley M. F., Ilan J., Ilan J. The interleukin 2 gene is expressed in the syncytiotrophoblast of the human placenta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):656–660. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelissen M. Nuclear and cytoplasmic sites for anti-sense control. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7203–7209. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daumas-Duport C., Scheithauer B., O'Fallon J., Kelly P. Grading of astrocytomas. A simple and reproducible method. Cancer. 1988 Nov 15;62(10):2152–2165. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19881115)62:10<2152::aid-cncr2820621015>3.0.co;2-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deiss L. P., Kimchi A. A genetic tool used to identify thioredoxin as a mediator of a growth inhibitory signal. Science. 1991 Apr 5;252(5002):117–120. doi: 10.1126/science.1901424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon Y. J., Johnson B., Romanowski E., Araullo-Cruz T. RNA complementary to herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP0 gene demonstrated in neurons of human trigeminal ganglia. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1832–1835. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1832-1835.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groger R. K., Morrow D. M., Tykocinski M. L. Directional antisense and sense cDNA cloning using Epstein-Barr virus episomal expression vectors. Gene. 1989 Sep 30;81(2):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90189-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hambor J. E., Hauer C. A., Shu H. K., Groger R. K., Kaplan D. R., Tykocinski M. L. Use of an Epstein-Barr virus episomal replicon for anti-sense RNA-mediated gene inhibition in a human cytotoxic T-cell clone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):4010–4014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.4010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauer C. A., Getty R. R., Tykocinski M. L. Epstein-Barr virus episome-based promoter function in human myeloid cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):1989–2003. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Westermark B. Growth factors as transforming proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Oct 1;184(3):487–496. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15041.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochberg F. H., Pruitt A. Assumptions in the radiotherapy of glioblastoma. Neurology. 1980 Sep;30(9):907–911. doi: 10.1212/wnl.30.9.907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff K. K., Kaufman D., Gabbay K. H., Spencer E. M., Lippman M. E., Dickson R. B. Secretion of an insulin-like growth factor-I-related protein by human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1986 Sep;46(9):4613–4619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izant J. G., Weintraub H. Constitutive and conditional suppression of exogenous and endogenous genes by anti-sense RNA. Science. 1985 Jul 26;229(4711):345–352. doi: 10.1126/science.2990048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen M., van Schaik F. M., Ricker A. T., Bullock B., Woods D. E., Gabbay K. H., Nussbaum A. L., Sussenbach J. S., Van den Brande J. L. Sequence of cDNA encoding human insulin-like growth factor I precursor. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):609–611. doi: 10.1038/306609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson T. R., Blossey B. K., Denko C. W., Ilan J. Expression of insulin-like growth factor I in cultured rat hepatocytes: effects of insulin and growth hormone. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Mar;3(3):580–587. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-3-580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson T. R., Trojan J., Rudin S. D., Blossey B. K., Ilan J., Ilan J. Effects of actinomycin D and cycloheximide on transcript levels of IGF-I, actin, and albumin in hepatocyte primary cultures treated with growth hormone and insulin. Mol Reprod Dev. 1991 Oct;30(2):95–99. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1080300204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsuki M., Sato M., Kimura M., Yokoyama M., Kobayashi K., Nomura T. Conversion of normal behavior to shiverer by myelin basic protein antisense cDNA in transgenic mice. Science. 1988 Jul 29;241(4865):593–595. doi: 10.1126/science.2456614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khochbin S., Lawrence J. J. An antisense RNA involved in p53 mRNA maturation in murine erythroleukemia cells induced to differentiate. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4107–4114. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08595.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khokha R., Waterhouse P., Yagel S., Lala P. K., Overall C. M., Norton G., Denhardt D. T. Antisense RNA-induced reduction in murine TIMP levels confers oncogenicity on Swiss 3T3 cells. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):947–950. doi: 10.1126/science.2465572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiess W., Lee L., Graham D. E., Greenstein L., Tseng L. Y., Rechler M. M., Nissley S. P. Rat C6 glial cells synthesize insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and express IGF-I receptors and IGF-II/mannose 6-phosphate receptors. Endocrinology. 1989 Apr;124(4):1727–1736. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-4-1727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. K., Wold B. J. Stable reduction of thymidine kinase activity in cells expressing high levels of anti-sense RNA. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):129–138. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelman D., Kirschner M. W. An antisense mRNA directs the covalent modification of the transcript encoding fibroblast growth factor in Xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):687–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystal G. W., Armstrong B. C., Battey J. F. N-myc mRNA forms an RNA-RNA duplex with endogenous antisense transcripts. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4180–4191. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahaley M. S., Jr, Mettlin C., Natarajan N., Laws E. R., Jr, Peace B. B. National survey of patterns of care for brain-tumor patients. J Neurosurg. 1989 Dec;71(6):826–836. doi: 10.3171/jns.1989.71.6.0826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martuza R. L., Malick A., Markert J. M., Ruffner K. L., Coen D. M. Experimental therapy of human glioma by means of a genetically engineered virus mutant. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):854–856. doi: 10.1126/science.1851332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minuto F., Del Monte P., Barreca A., Alama A., Cariola G., Giordano G. Evidence for autocrine mitogenic stimulation by somatomedin-C/insulin-like growth factor I on an established human lung cancer cell line. Cancer Res. 1988 Jul 1;48(13):3716–3719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollicone R., Trojan J., Oriol R. Appearance of H and B antigens in primary sensory cells of the rat olfactory apparatus and inner ear. Brain Res. 1985 Jan;349(1-2):275–279. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(85)90154-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munroe S. H. Antisense RNA inhibits splicing of pre-mRNA in vitro. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2523–2532. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03100.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemoto Y., Yamamoto T., Takada S., Matsui Y., Obinata M. Antisense RNA of the latent period gene (MER5) inhibits the differentiation of murine erythroleukemia cells. Gene. 1990 Jul 16;91(2):261–265. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90097-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nepveu A., Marcu K. B. Intragenic pausing and anti-sense transcription within the murine c-myc locus. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2859–2865. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04580.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Norstedt G., Gelinas R. E., Hammer R. E., Brinster R. L. Metallothionein-human GH fusion genes stimulate growth of mice. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):809–814. doi: 10.1126/science.6356363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C., Cuddy M., Haldar S., Croce C., Nowell P., Makover D., Bradley K. BCL2-mediated tumorigenicity of a human T-lymphoid cell line: synergy with MYC and inhibition by BCL2 antisense. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3660–3664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodermel S. R., Abbott M. S., Bogorad L. Nuclear-organelle interactions: nuclear antisense gene inhibits ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase enzyme levels in transformed tobacco plants. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):673–681. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90226-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen S. J., Daimon M., Wang C. Y., Jansen M., Ilan J. Isolation of an insulin-like growth factor II cDNA with a unique 5' untranslated region from human placenta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1947–1951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen S. J., Wang C. Y., Nelson K. K., Jansen M., Ilan J. Expression of insulin-like growth factor II in human placentas from normal and diabetic pregnancies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9179–9182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steel D. M., Harris H. The effect of antisense RNA to fibronectin on the malignancy of hybrids between melanoma cells and normal fibroblasts. J Cell Sci. 1989 Jul;93(Pt 3):515–524. doi: 10.1242/jcs.93.3.515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout J. T., Caskey C. T. Antisense RNA inhibition of HPRT synthesis. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1990 Jul;16(4):369–382. doi: 10.1007/BF01232465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart G. W., Searle P. F., Chen H. Y., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. A 12-base-pair DNA motif that is repeated several times in metallothionein gene promoters confers metal regulation to a heterologous gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7318–7322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trojan J., Naval J., Jusforgues H., Uriel J. Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in granulomatous inflammation of the mouse. Br J Exp Pathol. 1989 Aug;70(4):469–478. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trojan J., Uriel J., Deugnier M. A., Gaillard J. Immunocytochemical quantitative study of alpha-fetoprotein in normal and neoplastic neural development. Dev Neurosci. 1983;6(4-5):251–259. doi: 10.1159/000112352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. Y., Daimon M., Shen S. J., Engelmann G. L., Ilan J. Insulin-like growth factor-I messenger ribonucleic acid in the developing human placenta and in term placenta of diabetics. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Mar;2(3):217–229. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-3-217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitesell L., Rosolen A., Neckers L. M. Episome-generated N-myc antisense RNA restricts the differentiation potential of primitive neuroectodermal cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1360–1371. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. L., Warren N., Sugden B. Stable replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus in various mammalian cells. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):812–815. doi: 10.1038/313812a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]