Abstract
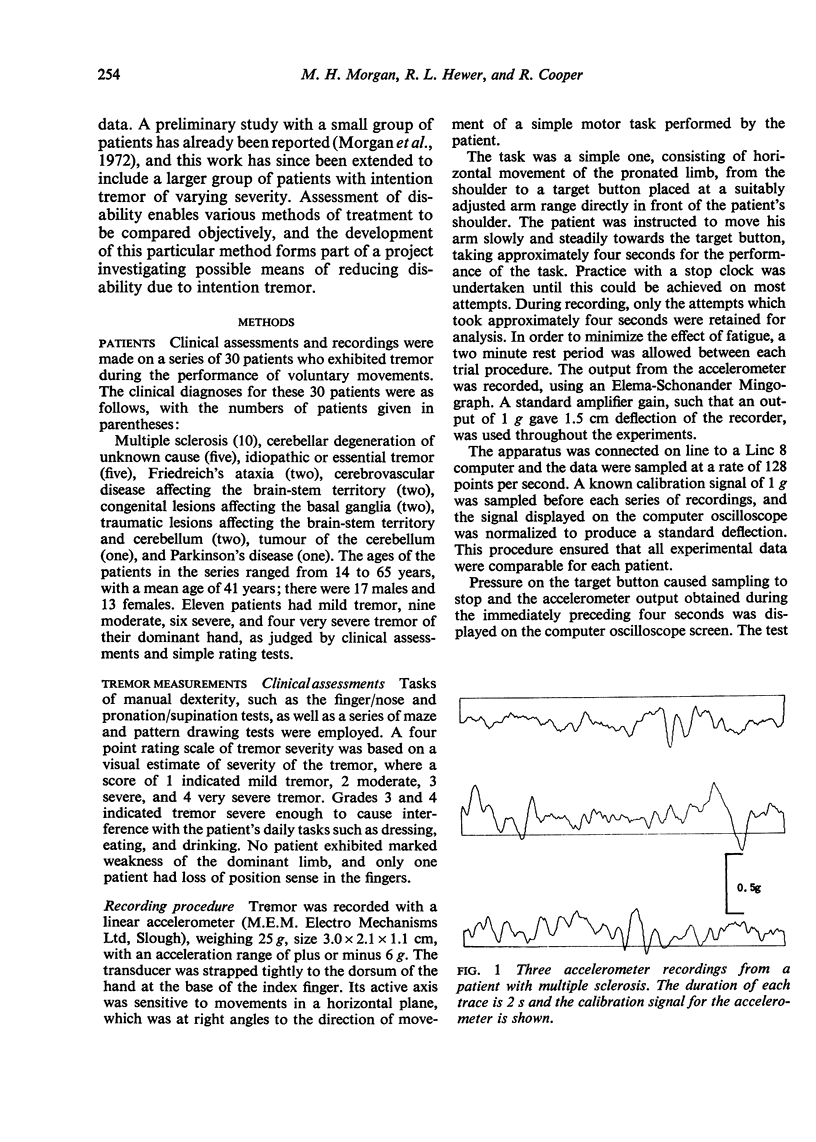
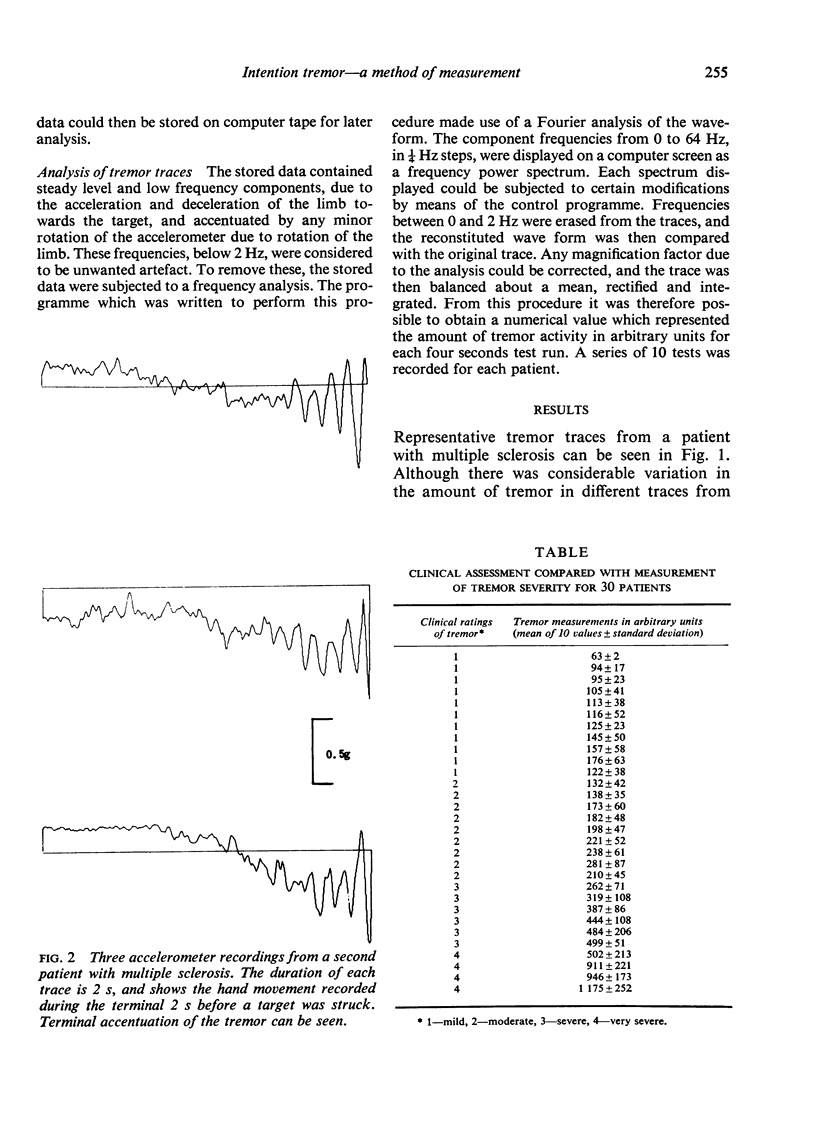
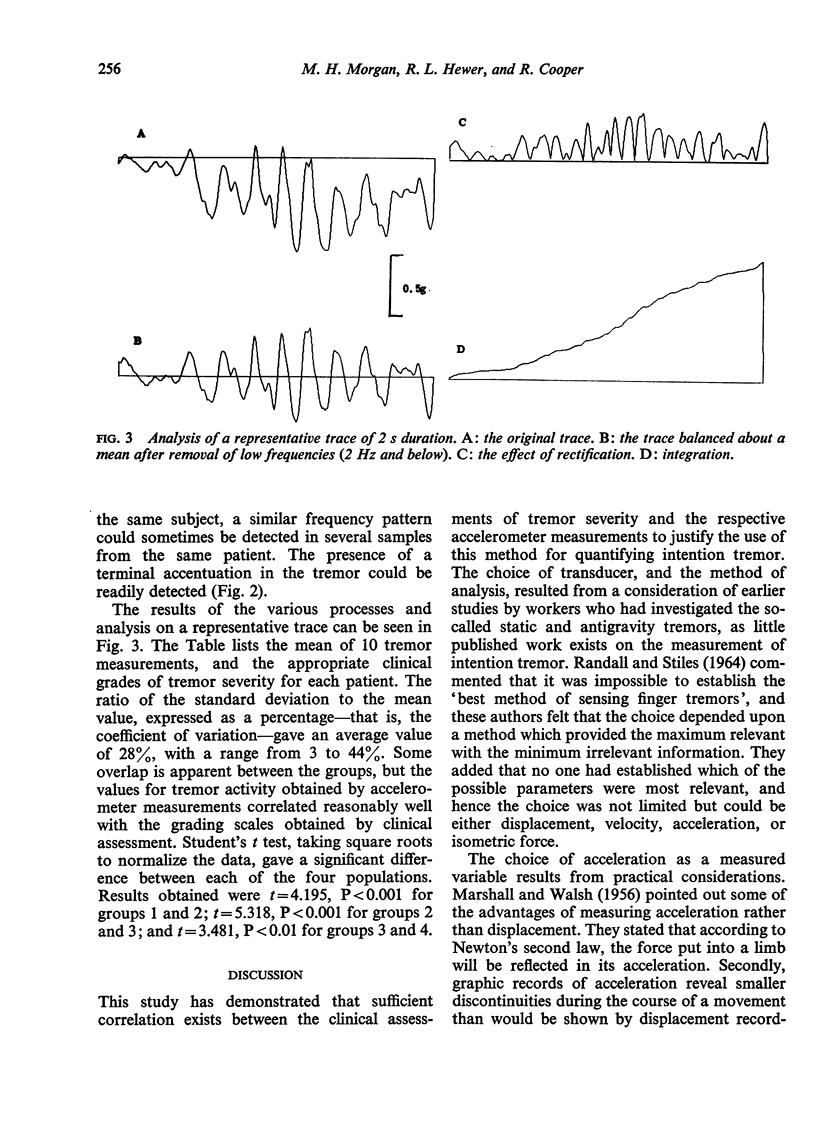
A method of measuring and analysing intention tremor using a linear accelerometer is described. Reasons are given for measuring this particular parameter of the tremor, for using this specific energy conversion device, and for employing the particular form of analysis. A comparison of the numerical values obtained for the amount of tremor activity, compared with a corresponding clinical grading, is made for 30 patients with intention tremor due to a variety of pathological causes. It is shown that the method gives clear correlation with the clinical assessments, although certain discrepancies are noted, and their importance discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRUMLIK J. On the nature of normal tremor. Neurology. 1962 Mar;12:159–179. doi: 10.1212/wnl.12.3.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase R. A., Cullen J. K., Jr, Sullivan S. A., Ommaya A. K. Modification of intention tremor in man. Nature. 1965 May 1;206(983):485–487. doi: 10.1038/206485a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper I. S. Clinical and physiologic implications of thalamic surgery for disorders of sensory communication. 2. Intention tremor, dystonia, Wilson's disease and torticollis. J Neurol Sci. 1965 Nov-Dec;2(6):520–553. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(65)90002-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowell T. K., Marsden C. D., Owen D. A. Objective measurement of parkinsonian tremor. Lancet. 1965 Dec 18;2(7425):1278–1279. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)92290-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIERSSEN G., LORENC M., SPITALERI R. M. A new method for graphic study of human movements. Neurology. 1961 Jul;11:610–618. doi: 10.1212/wnl.11.7.610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewer R. L., Cooper R., Morgan M. H. An investigation into the value of treating intention tremor by weighting the affected limb. Brain. 1972;95(3):579–590. doi: 10.1093/brain/95.3.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSHALL J., WALSH E. G. Physiological tremor. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1956 Nov;19(4):260–267. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.19.4.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D., Foley T. H., Owen D. A., McAllister R. G. Peripheral beta-adrenergic receptors concerned with tremor. Clin Sci. 1967 Aug;33(1):53–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D., Meadows J. C., Lange G. W., Watson R. S. Variations in human physiological finger tremor, with particular reference to changes with age. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1969 Aug;27(2):169–178. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(69)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan M. H., Hewer R. L., Cooper R. A method of recording and analysing intention tremor. Brain. 1972;95(3):573–578. doi: 10.1093/brain/95.3.573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANDALL J. E., METZGER J. M. Variance as a measure of tremor amplitude. J Appl Physiol. 1963 Mar;18:440–441. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1963.18.2.440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANDALL J. E., STILES R. N. POWER SPECTRAL ANALYSIS OF FINGER ACCELERATION TREMOR. J Appl Physiol. 1964 Mar;19:357–360. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1964.19.2.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall J. E. Analog and digital computers in the study of physiologic tremor. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1967 Sep;48(9):463–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Buskirk C., Wolbarsht M. L., Stecher K., Jr The nonnervous causes of normal physiologic tremor. Neurology. 1966 Feb;16(2):217–220. doi: 10.1212/wnl.16.2_part_1.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yap C. B., Boshes B. The frequency and pattern of normal tremor. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1967 Mar;22(3):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(67)90221-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


