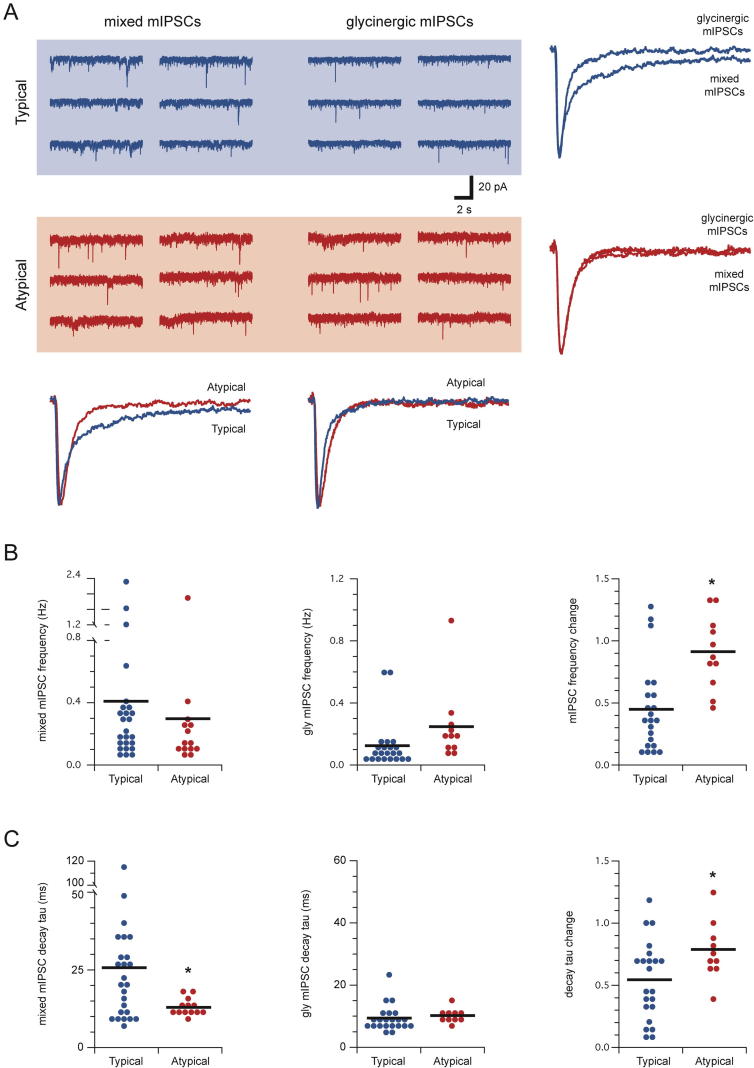
Fig. 4.
Typical CR-positive neurons receive a combination of ‘mixed’ GABAergic and glycinergic inhibition whereas glycinergic inhibition dominates in Atypical CR+ neurons. (A) Traces show continuous recordings of miniature inhibitory postsynaptic currents (mIPSCs) from Typical (upper) and Atypical CR+ (lower) neurons; before (mixed mIPSCs, left) and after (glycinergic mIPSCs, right) blocking GABAAergic mIPSCs with bicuculline (conc 10 μM). Overlaid currents (right and below) compare averaged mixed mIPSCs and glycinergic mIPSCs from Typical and Atypical CR+ neurons. Note mixed mIPSCs decay is significantly slower than glycinergic mIPSCs in Typical CR+ recordings, whereas Atypical CR+ mixed and glycinergic mIPSC decays are similar. (B) Plots comparing group data for mixed mIPSCs frequency, glycinergic mIPSCs frequency, and change in frequency for Typical and Atypical CR+ neurons in the absence and presence of bicuculline. Although the frequency of mixed and glycinergic mIPSCs was similar in the two populations, the change in mIPSC frequency differed significantly – mIPSC frequency was reduced by ∼50% in Typical CR+ neurons after the addition of bicuculline, whereas mIPSC frequency was similar under both conditions in Atypical CR+ neurons. (C) Left and middle plots compare single decay time constants fitted to mixed mIPSCs and glycinergic mIPSCs. Right plots show the change in mIPSC decay under the two recording conditions (mixed vs glycinergic mIPSCs) in Typical and Atypical CR+ neurons. The decay of mixed mIPSCs was slower in Typical CR+ neurons, whereas glycinergic mIPSC decay was similar in the two populations. mIPSC decay times in Typical CR+ neurons, when expressed as a change pre versus post bicuculline, were more dramatically affected than those from Atypical CR+ neurons (∼50% vs 20% change).