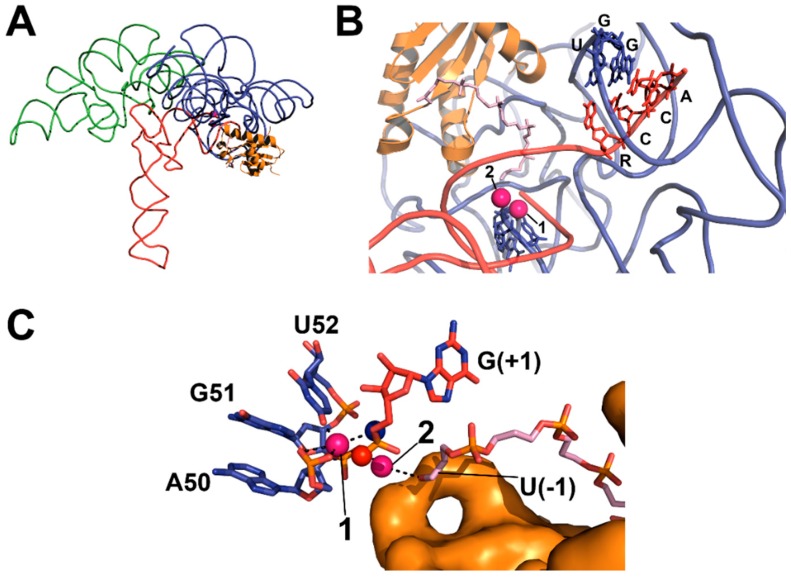
Figure 4.
X-ray crystal structure of T. maritima RNase P-tRNA-leader product complex (PDB 3q1r, PyMOL) [22]. (A) The holoenzyme-product complex of RNase P is shown, including C- (blue backbone) and S- (green backbone) domains, tRNA (red backbone), and RnpA (orange cartoon); (B) Topology of substrate contact sites in the catalytic domain (colored as in A), including the 5’ leader (light pink sticks) bound to RnpA and proposed divalent metal ions (pink spheres). Base-pairing between GGU residues in P RNA and the 3’ RCCA of tRNA (U256–R(73), G255–C(74), G254–C(75)) is shown; (C) Topology of the active site (colored as in A), including the active site residues (blue carbon atoms), product G(+1) (red carbon atoms), the 5’ leader (light pink carbon atoms) bound to RnpA (orange surface), proposed metal contacts (black dashed lines), and positions of the pro-RP (red sphere) and pro-SP (blue sphere) oxygens of the product 5’ phosphate.