Abstract
In studying the molecular defects responsible for cross-reacting material-positive hemophilia A, we have identified two patients in whom the nonfunctional factor VIII-like protein has abnormal, slower-moving heavy or light chains on SDS/PAGE. Both patients have severe hemophilia A (less than 1% of normal factor VIII activity) with a normal plasma level of factor VIII antigen. The molecular defects were identified by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis screening of PCR-amplified products of the factor VIII-coding DNA sequence followed by nucleotide sequencing of the abnormal PCR products. In patient ARC-21, a methionine-to-threonine substitution at position 1772 in the factor VIII light chain creates a potential new N-glycosylation site at asparagine-1770. In patient ARC-22, an isoleucine-to-threonine substitution at position 566 creates a potential new N-glycosylation site at asparagine-564 in the A2 domain of the factor VIII heavy chain. The mobility of these chains on SDS/PAGE was normal after N-Glycanase digestion and procoagulant activity was generated--to a maximum of 23% and 45% of control normal plasma. Abnormal N-glycosylation, blocking factor VIII procoagulant activity, represents a newly recognized mechanism for the pathogenesis of severe hemophilia A.
Full text
PDF
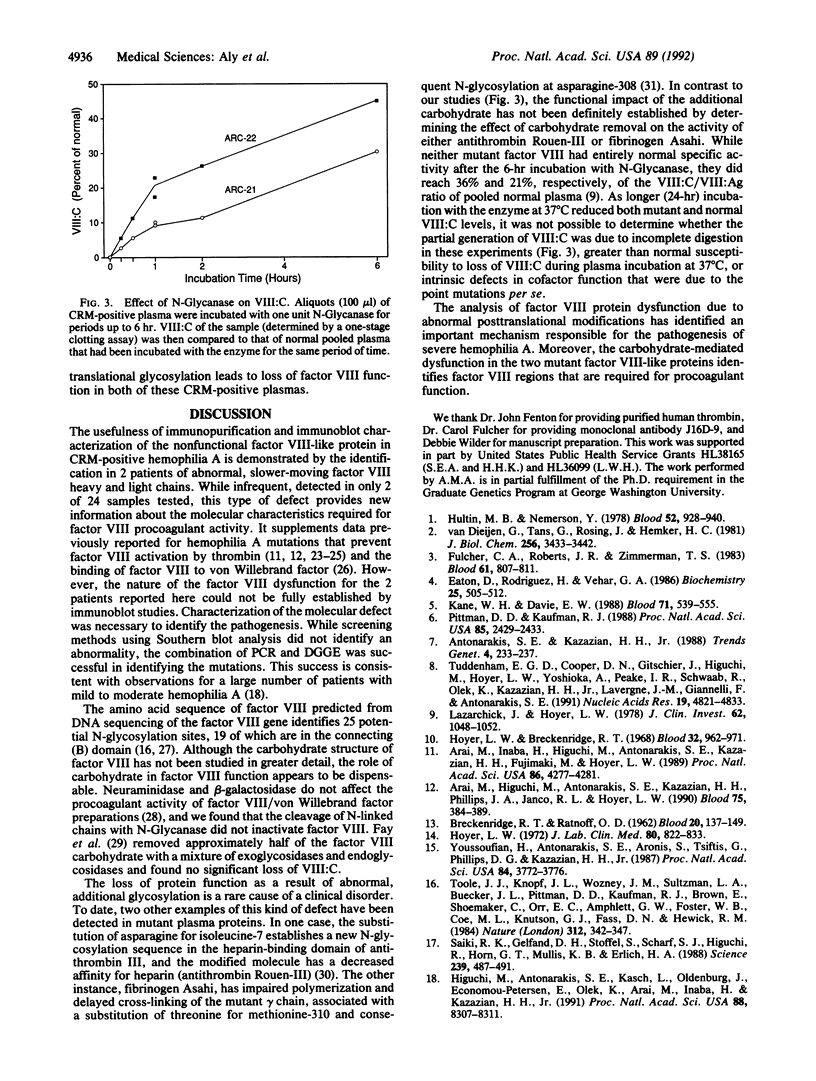

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonarakis S. E., Kazazian H. H., Jr The molecular basis of hemophilia A in man. Trends Genet. 1988 Aug;4(8):233–237. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90156-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai M., Higuchi M., Antonarakis S. E., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Phillips J. A., 3rd, Janco R. L., Hoyer L. W. Characterization of a thrombin cleavage site mutation (Arg 1689 to Cys) in the factor VIII gene of two unrelated patients with cross-reacting material-positive hemophilia A. Blood. 1990 Jan 15;75(2):384–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai M., Inaba H., Higuchi M., Antonarakis S. E., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Fujimaki M., Hoyer L. W. Direct characterization of factor VIII in plasma: detection of a mutation altering a thrombin cleavage site (arginine-372----histidine). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4277–4281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRECKENRIDGE R. T., RATNOFF C. D. Studies on the nature of the circulating anticoagulant directed against antihemophilic factor: with notes on an assay for anthemophilic factor. Blood. 1962 Aug;20:137–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan S. O., Borg J. Y., George P. M., Soria C., Soria J., Caen J., Carrell R. W. New carbohydrate site in mutant antithrombin (7 Ile----Asn) with decreased heparin affinity. FEBS Lett. 1988 Sep 12;237(1-2):118–122. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80183-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D., Rodriguez H., Vehar G. A. Proteolytic processing of human factor VIII. Correlation of specific cleavages by thrombin, factor Xa, and activated protein C with activation and inactivation of factor VIII coagulant activity. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 28;25(2):505–512. doi: 10.1021/bi00350a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fay P. J., Chavin S. I., Malone J. E., Schroeder D., Young F. E., Marder V. J. The effect of carbohydrate depletion on procoagulant activity and in vivo survival of highly purified human factor VIII. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jul 30;800(2):152–158. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(84)90054-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher C. A., Roberts J. R., Zimmerman T. S. Thrombin proteolysis of purified factor viii procoagulant protein: correlation of activation with generation of a specific polypeptide. Blood. 1983 Apr;61(4):807–811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitschier J., Kogan S., Levinson B., Tuddenham E. G. Mutations of factor VIII cleavage sites in hemophilia A. Blood. 1988 Sep;72(3):1022–1028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi M., Antonarakis S. E., Kasch L., Oldenburg J., Economou-Petersen E., Olek K., Arai M., Inaba H., Kazazian H. H., Jr Molecular characterization of mild-to-moderate hemophilia A: detection of the mutation in 25 of 29 patients by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8307–8311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi M., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Kasch L., Warren T. C., McGinniss M. J., Phillips J. A., 3rd, Kasper C., Janco R., Antonarakis S. E. Molecular characterization of severe hemophilia A suggests that about half the mutations are not within the coding regions and splice junctions of the factor VIII gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7405–7409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi M., Wong C., Kochhan L., Olek K., Aronis S., Kasper C. K., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Antonarakis S. E. Characterization of mutations in the factor VIII gene by direct sequencing of amplified genomic DNA. Genomics. 1990 Jan;6(1):65–71. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90448-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirani S., Bernasconi R. J., Rasmussen J. R. Use of N-glycanase to release asparagine-linked oligosaccharides for structural analysis. Anal Biochem. 1987 May 1;162(2):485–492. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90424-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W., Breckenridge R. T. Immunologic studies of antihemophilic factor (AHF, factor VIII): cross-reacting material in a genetic variant of hemophilia A. Blood. 1968 Dec;32(6):962–971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W. Immunologic studies of antihemophilic factor (AHF, factor VIII). IV. Radioimmunoassay of AHF antigen. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Dec;80(6):822–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultin M. B., Nemerson Y. Activation of factor X by factors IXa and VIII; a specific assay for factor IXa in the presence of thrombin-activated factor VIII. Blood. 1978 Nov;52(5):928–940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane W. H., Davie E. W. Blood coagulation factors V and VIII: structural and functional similarities and their relationship to hemorrhagic and thrombotic disorders. Blood. 1988 Mar;71(3):539–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Wasley L. C., Dorner A. J. Synthesis, processing, and secretion of recombinant human factor VIII expressed in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6352–6362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarchick J., Hoyer L. W. Immunoradiometric measurement of the factor VIII procoagulant antigen. J Clin Invest. 1978 Nov;62(5):1048–1052. doi: 10.1172/JCI109209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattinson J. K., McVey J. H., Boon M., Ajani A., Tuddenham E. G. CRM+ haemophilia A due to a missense mutation (372----Cys) at the internal heavy chain thrombin cleavage site. Br J Haematol. 1990 May;75(1):73–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb02618.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman D. D., Kaufman R. J. Proteolytic requirements for thrombin activation of anti-hemophilic factor (factor VIII). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2429–2433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shima M., Ware J., Yoshioka A., Fukui H., Fulcher C. A. An arginine to cysteine amino acid substitution at a critical thrombin cleavage site in a dysfunctional factor VIII molecule. Blood. 1989 Oct;74(5):1612–1617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodetz J. M., Pizzo S. V., McKee P. A. Relationship of sialic acid to function and in vivo survival of human factor VIII/von Willebrand factor protein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 10;252(15):5538–5546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toole J. J., Knopf J. L., Wozney J. M., Sultzman L. A., Buecker J. L., Pittman D. D., Kaufman R. J., Brown E., Shoemaker C., Orr E. C. Molecular cloning of a cDNA encoding human antihaemophilic factor. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):342–347. doi: 10.1038/312342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triolo G., Giardina E., Casiglia D., Scarantino G., Bompiani G. D. Detection of the terminal fluid-phase complement complex, SC5b-9, in the plasma of patients with insulin-dependent (type I) diabetes mellitus. Relation to increased urinary albumin excretion and plasma von Willebrand factor. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Apr;84(1):53–58. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuddenham E. G., Cooper D. N., Gitschier J., Higuchi M., Hoyer L. W., Yoshioka A., Peake I. R., Schwaab R., Olek K., Kazazian H. H. Haemophilia A: database of nucleotide substitutions, deletions, insertions and rearrangements of the factor VIII gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 25;19(18):4821–4833. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.18.4821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vehar G. A., Keyt B., Eaton D., Rodriguez H., O'Brien D. P., Rotblat F., Oppermann H., Keck R., Wood W. I., Harkins R. N. Structure of human factor VIII. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):337–342. doi: 10.1038/312337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C., Dowling C. E., Saiki R. K., Higuchi R. G., Erlich H. A., Kazazian H. H., Jr Characterization of beta-thalassaemia mutations using direct genomic sequencing of amplified single copy DNA. 1987 Nov 26-Dec 2Nature. 330(6146):384–386. doi: 10.1038/330384a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youssoufian H., Antonarakis S. E., Aronis S., Tsiftis G., Phillips D. G., Kazazian H. H., Jr Characterization of five partial deletions of the factor VIII gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3772–3776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dieijen G., Tans G., Rosing J., Hemker H. C. The role of phospholipid and factor VIIIa in the activation of bovine factor X. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3433–3442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]