Abstract
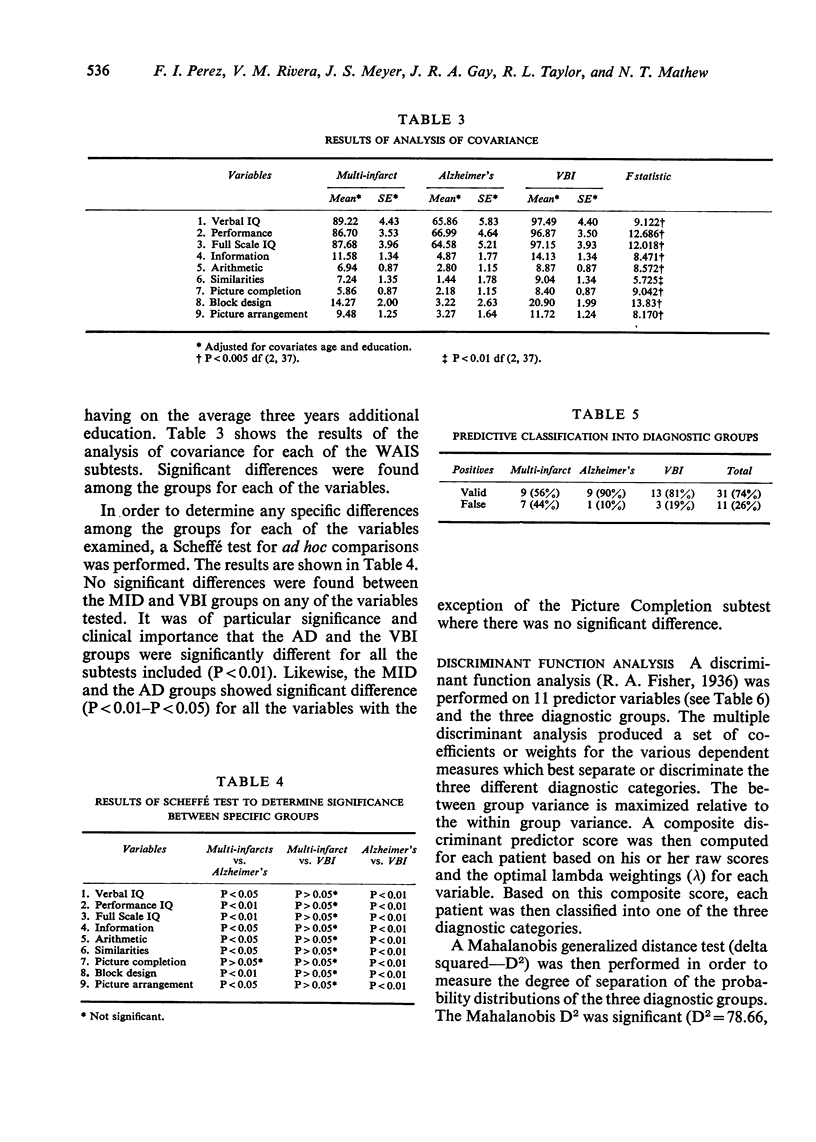
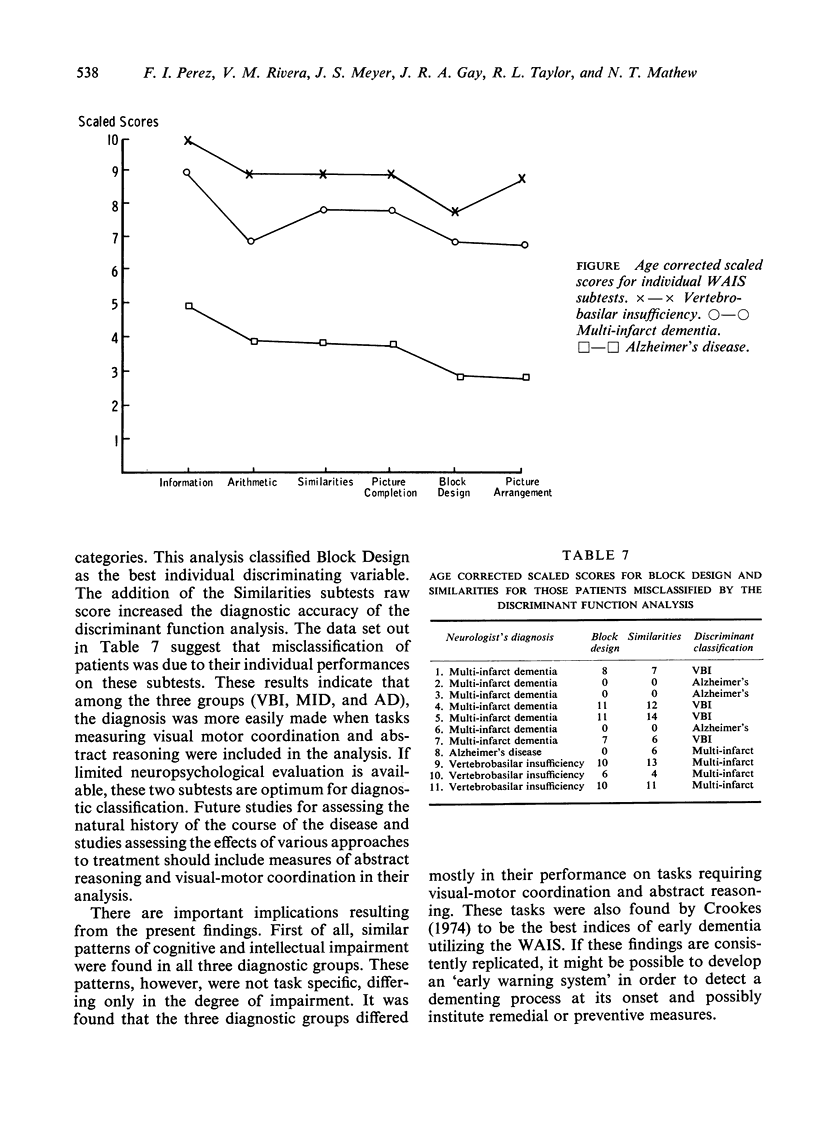
A prominent feature in dementia is intellectual deterioration. Review of the clinical literature indicates a lack of suitably quantitated studies of specific intellectual defects in dementia. The present study investigated the performance of patients with multi-infarct dementia (MID), dementia due to Alzheimer's disease (AD), and vertebrobasilar insufficiency (VBI) with dementia using the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS). Forty-two patients ranging in age from 45 to 85 years (x 66) were included. Significant differences in cognitive and intellectual performance were found between patients with dementia due to VBI and MID versus neuronal atrophy of the Alzheimer's type. The group with AD performed significantly and consistently lower on all measures. There were no significant differences between the two cerebrovascular disease groups, even though the MID group performed consistently more poorly than the VBI group. A discriminant function analysis classified 74% of the patients correctly based on the individual WAIS scores. The diagnosis was more easily made when tasks measuring visual motor coordination and abstract reasoning were included in the analysis.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crookes T. G. Indices of early dementia on WAIS. Psychol Rep. 1974 Jun;34(3):734–734. doi: 10.2466/pr0.1974.34.3.734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisk factors in stroke due to cerebral infarction. A statement for physicians. Stroke. 1971 Sep-Oct;2(5):423–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hachinski V. C., Lassen N. A., Marshall J. Multi-infarct dementia. A cause of mental deterioration in the elderly. Lancet. 1974 Jul 27;2(7874):207–210. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91496-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horenstein S. The clinical use of psychological testing in dementia. Contemp Neurol Ser. 1971;9:61–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew N. T., Meyer J. S. Pathogenesis and natural history of transient global amnesia. Stroke. 1974 May-Jun;5(3):303–311. doi: 10.1161/01.str.5.3.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivera V. M., Meyer J. S., Baer P. E., Faibish G. M., Mathew N. T., Hartmann A. Vertebrobasilar arterial insufficiency with dementia. Controlled trials of treatment with betahistine hydrochloride. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1974 Sep;22(9):397–406. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1974.tb05408.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


