Abstract
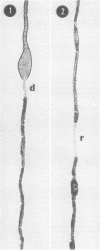
Chronic exposure of rats to 2,5-hexanedione (CH3COCH2CH2COCH3), a major metabolite of the neurotoxic industrial solvent methyl n-buryl ketone (CH3COCH2CH2CH2CH3), has been shown to cause a clinical peripheral neuropathy with dying-back peripheral and central nervous system degeneration characterized by giant axonal swellings filled with neurofilaments. This pattern of disease is similar to that produced by methyl n-butyl ketone.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asbury A. K., Gale M. K., Cox S. C., Baringer J. R., Berg B. O. Giant axonal neuropathy--a unique case with segmental neurofilamentous masses. Acta Neuropathol. 1972;20(3):237–247. doi: 10.1007/BF00686905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter S., Karpati G., Andermann F., Gold R. Giant axonal neuropathy. A clinically and morphologically distinct neurological disease. Arch Neurol. 1974 Nov;31(5):312–316. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1974.00490410060005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanagh J. B. The significance of the "dying back" process in experimental and human neurological disease. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1964;3:219–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckett S., Williams N., Francis S. Peripheral neuropathy associated with inhalation of methyl-n-butyl ketone. Experientia. 1974 Nov 15;30(11):1283–1284. doi: 10.1007/BF01945188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korobkin R., Asbury A. K., Sumner A. J., Nielsen S. L. Glue-sniffing neuropathy. Arch Neurol. 1975 Mar;32(3):158–162. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1975.00490450038004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendell J. R., Saida K., Ganansia M. F., Jackson D. B., Weiss H., Gardier R. W., Chrisman C., Allen N., Couri D., O'Neill J. Toxic polyneuropathy produced by methyl N-butyl ketone. Science. 1974 Aug 30;185(4153):787–789. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4153.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prineas J. The pathogenesis of dying-back polyneuropathies. I. An ultrastructural study of experimental tri-ortho-cresyl phosphate intoxication in the cat. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1969 Oct;28(4):571–597. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196910000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaumburg H. H., Wiśniewski H. M., Spencer P. S. Ultrastructural studies of the dying-back process. I. Peripheral nerve terminal and axon degeneration in systemic acrylamide intoxication. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1974 Apr;33(2):260–284. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197404000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer P. S., Schaumburg H. H. A review of acrylamide neurotoxicity. Part II. Experimental animal neurotoxicity and pathologic mechanisms. Can J Neurol Sci. 1974 Aug;1(3):152–169. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100119201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer P. S., Schaumburg H. H., Raleigh R. L., Terhaar C. J. Nervous system degeneration produced by the industrial solvent methyl n-butyl ketone. Arch Neurol. 1975 Apr;32(4):219–222. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1975.00490460035002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer P. S., Thomas P. K. Ultrastructural studies of the dying-back process. II. The sequestration and removal by Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes of organelles from normal and diseases axons. J Neurocytol. 1974 Dec;3(6):763–783. doi: 10.1007/BF01097197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]