Abstract
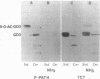
The respective roles of genetic and epigenetic factors in generation of pattern formation in the vertebrate nervous system are still poorly elucidated. The mammalian cerebellum is subdivided in parasagittal modules defined by anatomical, physiological, and biochemical criteria. Immunostaining of adult mouse cerebellum with two monoclonal antibodies, P-path, which recognizes 9-O-acetylated glycolipids, and Zebrin II, which recognizes a 36-kDa protein, reveals three classes of sagittally organized bands of Purkinje cells: two complementary groups distinctly immunoreactive to one antibody but not the other and a third group that contains double-labeled cells. No Purkinje cells could be detected that were unreactive to either antibody. The specific and reproducible topography of these three classes of Purkinje cells may be related to the compartmentation of the cerebellum into developmental genetic modules.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boegman R. J., Parent A., Hawkes R. Zonation in the rat cerebellar cortex: patches of high acetylcholinesterase activity in the granular layer are congruent with Purkinje cell compartments. Brain Res. 1988 May 17;448(2):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91261-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonafede D. M., Macala L. J., Constantine-Paton M., Yu R. K. Isolation and characterization of ganglioside 9-O-acetyl-GD3 from bovine buttermilk. Lipids. 1989 Aug;24(8):680–684. doi: 10.1007/BF02535204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnerot C., Grimber G., Briand P., Nicolas J. F. Patterns of expression of position-dependent integrated transgenes in mouse embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6331–6335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brochu G., Maler L., Hawkes R. Zebrin II: a polypeptide antigen expressed selectively by Purkinje cells reveals compartments in rat and fish cerebellum. J Comp Neurol. 1990 Jan 22;291(4):538–552. doi: 10.1002/cne.902910405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou D. K., Flores S., Jungalwala F. B. Identification of disialosyl paragloboside and O-acetyldisialosyl paragloboside in cerebellum and embryonic cerebrum. J Neurochem. 1990 May;54(5):1598–1607. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb01210.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantine-Paton M., Blum A. S., Mendez-Otero R., Barnstable C. J. A cell surface molecule distributed in a dorsoventral gradient in the perinatal rat retina. Nature. 1986 Dec 4;324(6096):459–462. doi: 10.1038/324459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd J., Solter D., Jessell T. M. Monoclonal antibodies against carbohydrate differentiation antigens identify subsets of primary sensory neurones. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):469–472. doi: 10.1038/311469a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doré L., Jacobson C. D., Hawkes R. Organization and postnatal development of zebrin II antigenic compartmentation in the cerebellar vermis of the grey opossum, Monodelphis domestica. J Comp Neurol. 1990 Jan 15;291(3):431–449. doi: 10.1002/cne.902910309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman L. M., Hawkes R. 5'-Nucleotidase and the mabQ113 antigen share a common distribution in the cerebellar cortex of the mouse. Neuroscience. 1989;31(1):231–235. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90045-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gravel C., Eisenman L. M., Sasseville R., Hawkes R. Parasagittal organization of the rat cerebellar cortex: direct correlation between antigenic Purkinje cell bands revealed by mabQ113 and the organization of the olivocerebellar projection. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Nov 8;265(2):294–310. doi: 10.1002/cne.902650211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gravel C., Hawkes R. Parasagittal organization of the rat cerebellar cortex: direct comparison of Purkinje cell compartments and the organization of the spinocerebellar projection. J Comp Neurol. 1990 Jan 1;291(1):79–102. doi: 10.1002/cne.902910107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. M., Boehm T., Sofroniew M. V., Keynes R. J., Barton S. C., Norris M. L., Surani M. A., Spillantini M. G., Rabbitts T. H. Segmental and developmental regulation of a presumptive T-cell oncogene in the central nervous system. Nature. 1990 Mar 8;344(6262):158–160. doi: 10.1038/344158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R., Leclerc N. Antigenic map of the rat cerebellar cortex: the distribution of parasagittal bands as revealed by monoclonal anti-Purkinje cell antibody mabQ113. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Feb 1;256(1):29–41. doi: 10.1002/cne.902560104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R., colonnier M., Leclerc N. Monoclonal antibodies reveal sagittal banding in the rodent cerebellar cortex. Brain Res. 1985 May 6;333(2):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91593-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclerc N., Doré L., Parent A., Hawkes R. The compartmentalization of the monkey and rat cerebellar cortex: zebrin I and cytochrome oxidase. Brain Res. 1990 Jan 1;506(1):70–78. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91200-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclerc N., Gravel C., Hawkes R. Development of parasagittal zonation in the rat cerebellar cortex: MabQ113 antigenic bands are created postnatally by the suppression of antigen expression in a subset of Purkinje cells. J Comp Neurol. 1988 Jul 15;273(3):399–420. doi: 10.1002/cne.902730310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. M., Beasley L., Stallcup W. B. The D1.1 antigen: a cell surface marker for germinal cells of the central nervous system. J Neurosci. 1984 Mar;4(3):820–831. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-03-00820.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberdick J., Smeyne R. J., Mann J. R., Zackson S., Morgan J. I. A promoter that drives transgene expression in cerebellar Purkinje and retinal bipolar neurons. Science. 1990 Apr 13;248(4952):223–226. doi: 10.1126/science.2109351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakic P., Suñer I., Williams R. W. A novel cytoarchitectonic area induced experimentally within the primate visual cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2083–2087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regan L. J., Dodd J., Barondes S. H., Jessell T. M. Selective expression of endogenous lactose-binding lectins and lactoseries glycoconjugates in subsets of rat sensory neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2248–2252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlosshauer B., Blum A. S., Mendez-Otero R., Barnstable C. J., Constantine-Paton M. Developmental regulation of ganglioside antigens recognized by the JONES antibody. J Neurosci. 1988 Feb;8(2):580–592. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-02-00580.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarting G. A., Crandall J. E. Subsets of olfactory and vomeronasal sensory epithelial cells and axons revealed by monoclonal antibodies to carbohydrate antigens. Brain Res. 1991 May 3;547(2):239–248. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90967-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeyne R. J., Oberdick J., Schilling K., Berrebi A. S., Mugnaini E., Morgan J. I. Dynamic organization of developing Purkinje cells revealed by transgene expression. Science. 1991 Nov 1;254(5032):719–721. doi: 10.1126/science.1948052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sotelo C., Bourrat F., Triller A. Postnatal development of the inferior olivary complex in the rat. II. Topographic organization of the immature olivocerebellar projection. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Jan 10;222(2):177–199. doi: 10.1002/cne.902220204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suchy S. F., Yamamoto M., Barbero L., Schwarting G. A. A monoclonal antibody, WCC4, recognizes a developmentally regulated ganglioside containing alpha-galactose and alpha-fucose present in the rat nervous system. Brain Res. 1988 Feb 2;440(1):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91155-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varki A., Hooshmand F., Diaz S., Varki N. M., Hedrick S. M. Developmental abnormalities in transgenic mice expressing a sialic acid-specific 9-O-acetylesterase. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90408-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassef M., Sotelo C., Cholley B., Brehier A., Thomasset M. Cerebellar mutations affecting the postnatal survival of Purkinje cells in the mouse disclose a longitudinal pattern of differentially sensitive cells. Dev Biol. 1987 Dec;124(2):379–389. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90490-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassef M., Sotelo C., Thomasset M., Granholm A. C., Leclerc N., Rafrafi J., Hawkes R. Expression of compartmentation antigen zebrin I in cerebellar transplants. J Comp Neurol. 1990 Apr 8;294(2):223–234. doi: 10.1002/cne.902940207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto M., Boyer A. M., Schwarting G. A. Fucose-containing glycolipids are stage- and region-specific antigens in developing embryonic brain of rodents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):3045–3049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.3045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]