Abstract
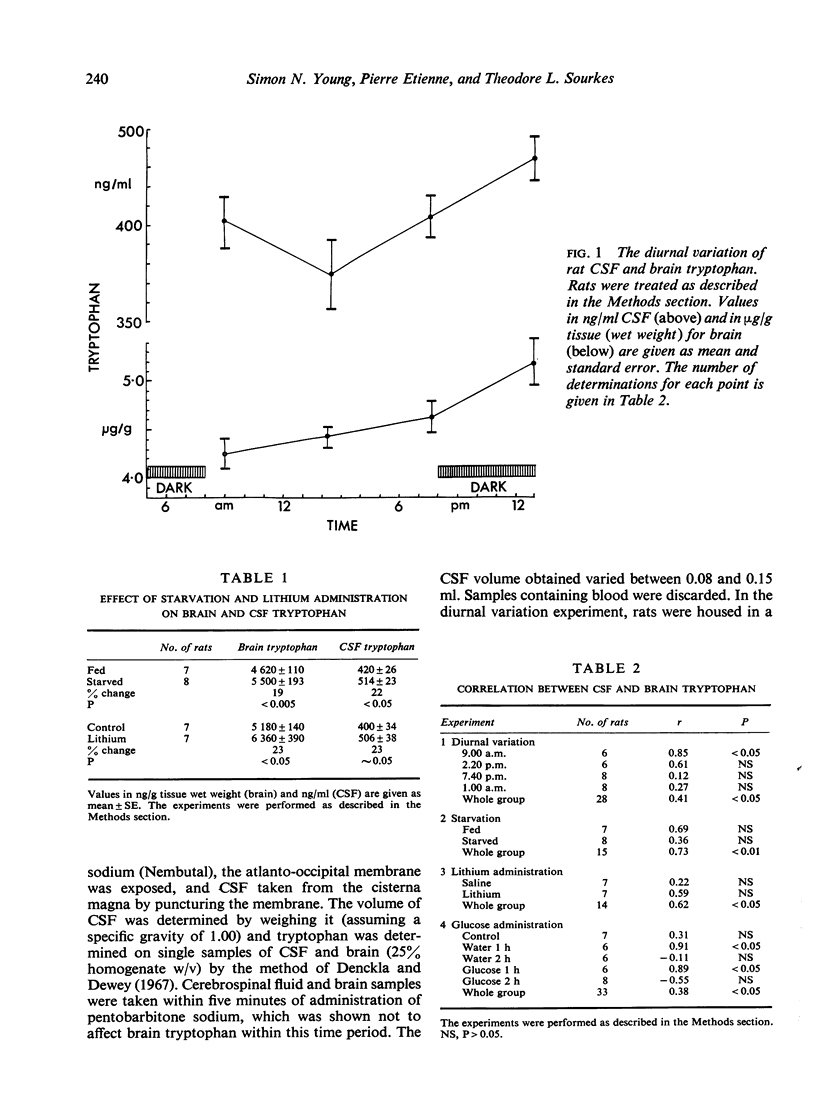
Tryptophan was measured in the cisternal CSF and brains of rats. In untreated rats there was a significant but not very close correlation between the tryptophan concentration in these two compartments. Factors that change the brain tryptophan concentration such as starvation, glucose feeding, and lithium treatment affected the CSF tryptophan in the same way as the brain tryptophan. Diurnal changes were parallel for brain and CSF. When we take into account our knowledge of the disposition of tryptophan in human CSF, these data suggest that measurement of lumbar CSF tryptophan in man may be a useful approach to the study of human brain tryptophan. However, because the correlation between brain and CSF is not very close, measurements on CSF tryptophan would be more meaningful in groups of patients than in individuals.
Full text
PDF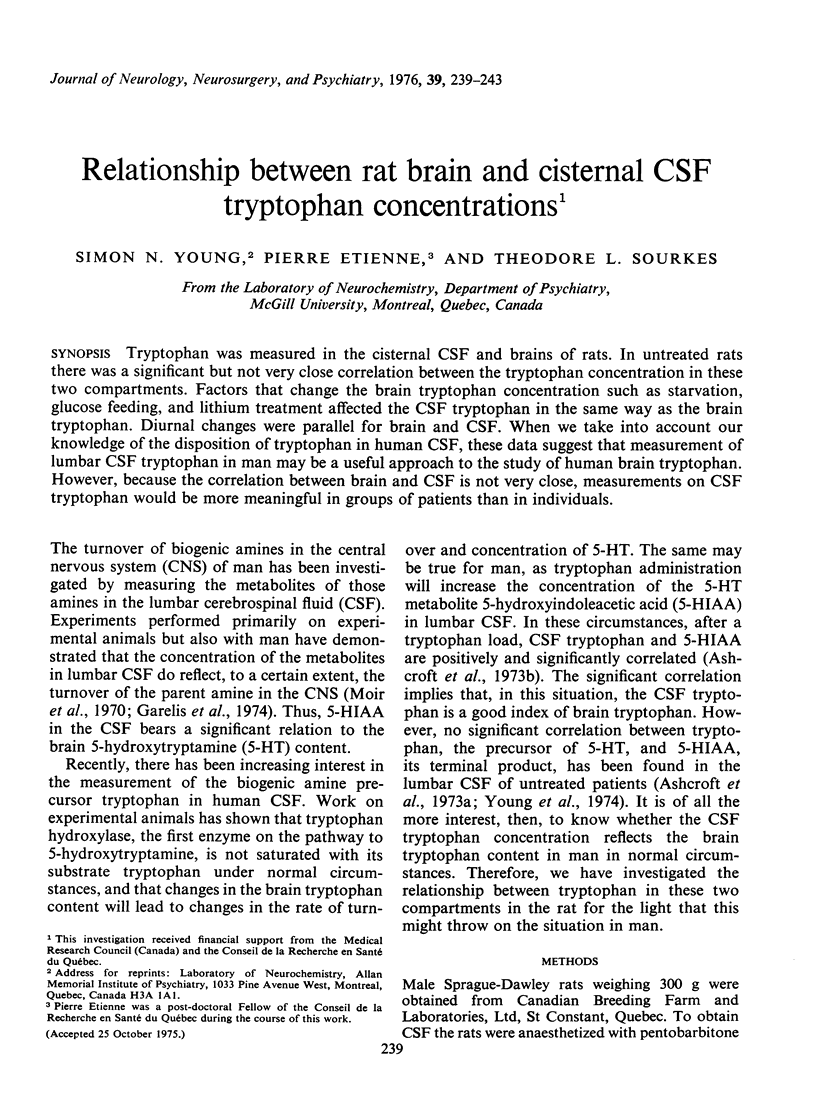


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashcroft G. W., Blackburn I. M., Eccleston D., Glen A. I., Hartley W., Kinloch N. E., Lonergan M., Murray L. G., Pullar I. A. Changes on recovery in the concentrations of tryptophan and the biogenic amine metabolites in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with affective illness. Psychol Med. 1973 Aug;3(3):319–325. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700049606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft G. W., Crawford T. B., Cundall R. L., Davidson D. L., Dobson J., Dow R. C., Eccleston D., Loose R. W., Pullar I. A. 5-Hydroxytryptamine metabolism in affective illness: the effect of tryptophan administration. Psychol Med. 1973 Aug;3(3):326–332. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700049618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppen A., Brooksbank B. W., Peet M. Tryptophan concentration in the cerebrospinal fluid of depressive patients. Lancet. 1972 Jun 24;1(7765):1393–1393. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)91123-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curzon G., Joseph M. H., Knott P. J. Effects of immobilization and food deprivation on rat brain tryptophan metabolism. J Neurochem. 1972 Aug;19(8):1967–1974. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01486.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denckla W. D., Dewey H. K. The determination of tryptophan in plasma, liver, and urine. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Jan;69(1):160–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccleston D., Ashcroft G. W., Crawford T. B. Effect of tryptophan administration on 5HIAA in cerebrospinal fluid in man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1970 Apr;33(2):269–272. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.33.2.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernstrom J. D., Wurtman R. J. Control of brain serotonin levels by the diet. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1974;11(0):133–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garelis E., Young S. N., Lal S., Sourkes T. L. Monoamine metabolites in lumbar CSF: the question of their origin in relation to clinical studies. Brain Res. 1974 Oct 11;79(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90562-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochwald G. M., Wald A., DiMattio J., Malhan C. The effects of serum osmolarity on cerebrospinal fluid volume flow. Life Sci. 1974 Oct 1;15(7):1309–1316. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90312-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madras B. K., Cohen E. L., Fernstrom J. D., Larin F., Munro H. N., Wurtman R. J. Letter: Dietary carbohydrate increases brain tryptophan and decreases free plasma tryptophan. Nature. 1973 Jul 6;244(5410):34–35. doi: 10.1038/244034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modigh K. The relationship between the concentrations of tryptophan and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in rat brain and cerebrospinal fluid. J Neurochem. 1975 Sep;25(3):351–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb06979.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moir A. T., Ashcroft G. W., Crawford T. B., Eccleston D., Guldberg H. C. Cerebral metabolites in cerebrospinal fluid as a biochemical approach to the brain. Brain. 1970;93(2):357–368. doi: 10.1093/brain/93.2.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Cruet J., Tagliamonte A., Tagliamonte P., Gessa G. L. Stimulation of serotonin synthesis by lithium. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Aug;178(2):325–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Cruet J., Chase T. N., Murphy D. L. Dietary regulation of brain tryptophan metabolism by plasma ratio of free tryptophan and neutral amino acids in humans. Nature. 1974 Apr 19;248(5450):693–695. doi: 10.1038/248693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagliamonte A., Tagliamonte P., Perez-Cruet J., Gessa G. L. Increase of brain tryptophan caused by drugs which stimulate serotonin synthesis. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jan 27;229(4):125–126. doi: 10.1038/newbio229125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. N., Garelis E., Lal S., Martin J. B., Molina-Negro P., Ethier R., Sourkes T. L. Tryptophan and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in human cerebrospinal fluid. J Neurochem. 1974 May;22(5):777–779. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb04294.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. N., Lal S., Martin J. B., Ford R. M., Sourkes T. L. 5-Hydroxyindoleacetic acid, homovanillic acid and tryptophan levels in CSF above and below a complete block of CSF flow. Psychiatr Neurol Neurochir. 1973 Nov-Dec;76(6):439–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. N., Lal S., Sourkes T. L., Feldmuller F., Aronoff A., Martin J. B. Relationships between tryptophan in serum and CSF, and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in CSF of man: effect of cirrhosis of liver and probenecid administration. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975 Apr;38(4):322–330. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.38.4.322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


