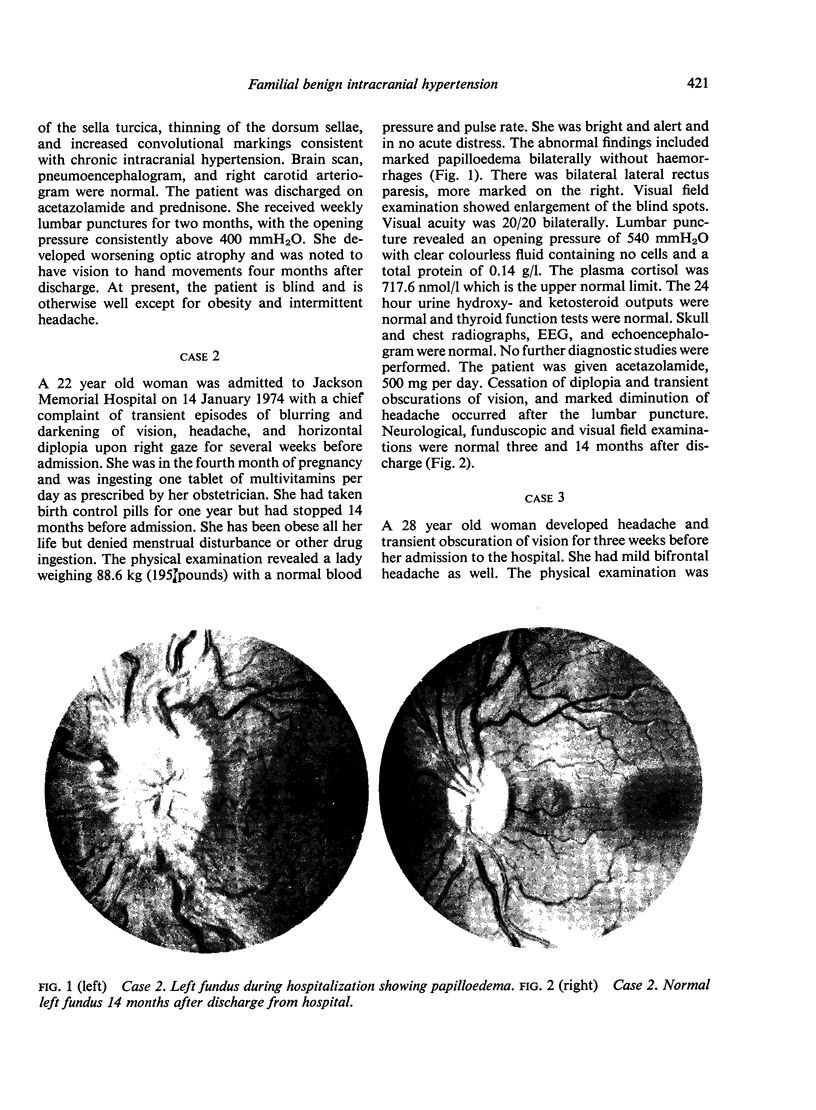
Abstract
Three sisters with benign intracranial hypertension are reported. This is the first documentation of benign intracranial hypertension in three family members. Obesity is a striking feature in these patients as well as five of the six previously reported patients with familial benign intracranial hypertension. Pregnancy and chronic dysfunctional uterine bleeding, well known predisposing factors in this syndrome when it occurs sporadically, were present in two of the sisters. A familial metabolic defect may be responsible for the intracranial hypertension in these patients.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buchheit W. A., Burton C., Haag B., Shaw D. Papilledema and idiopathic intracranial hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1969 Apr 24;280(17):938–942. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196904242801707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer M. Management of benign intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri). Clin Neurosurg. 1968;15:161–174. doi: 10.1093/neurosurgery/15.cn_suppl_1.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B. Disturbance of pituitary-adrenal interrelationships in benign intracranial hypertension (pseudotumor cerebri). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1966 Dec;26(12):1366–1369. doi: 10.1210/jcem-26-12-1366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothner A. D., Brust J. C. Pseudotumor cerebri. Report of a familial occurrence. Arch Neurol. 1974 Jan;30(1):110–111. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1974.00490310112021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]