Fig. 1.
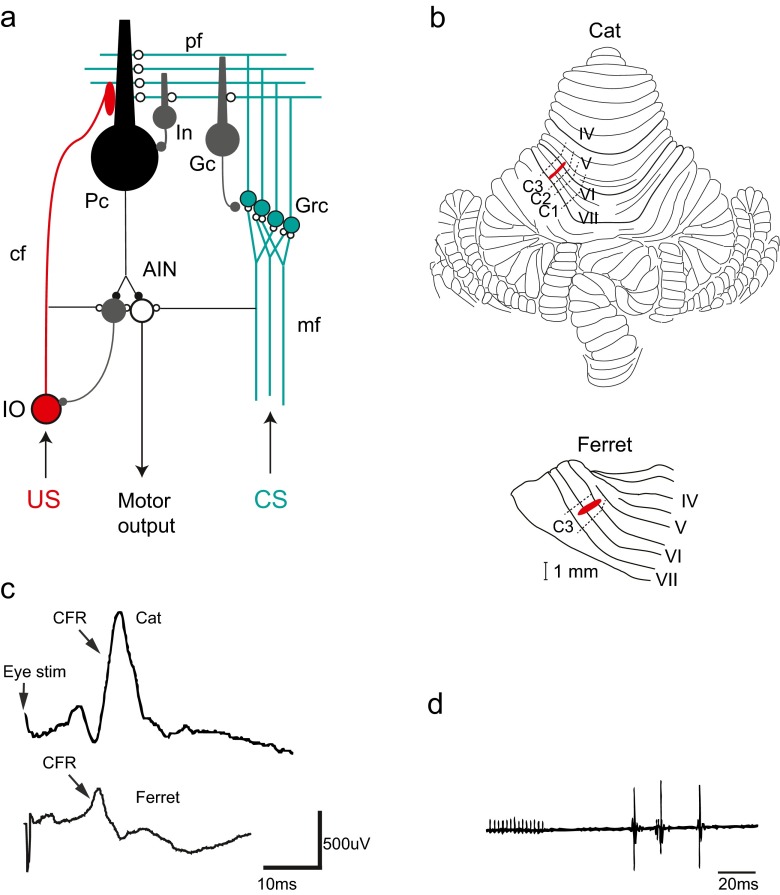
The cerebellar micro circuit and eyeblink microzones. a Neuronal circuitry in the cerebellum. Excitatory synapses are illustrated with open circles and inhibitory synapses are illustrated with filled circles. Purkinje cells (Pc), interneurons (In), Golgi cells (Gc), granule cells (Grc), anterior interpositus nucleus (AIN), inferior olive (IO), mossy fibres (mf), climbing fibres (cf). The conditional stimulus (CS, in green) activates mossy fibres (mf) from pre-cerebellar structures like pontine nuclei that transmit signals of different sensory modalities to the cerebellum. The mossy fibres form excitatory synapses onto granule cells (Grc) in the cerebellar cortex and in turn project axons that reach the cerebellar surface and diverge into parallel fibres (pf). The parallel fibres make excitatory synaptic contacts onto Golgi cells (Gc), interneurons (Int) and Purkinje cells (Pc). The unconditional stimulus (US, in red) activates the inferior olive that projects climbing fibres that converge with the parallel fibres (pf) on the dendrites of the Purkinje cell. Since the Purkinje cell is inhibitory (GABA-ergic), decreased activity in Purkinje cells will cause disinhibition of cells in the anterior interpositus nucleus (AIN) that in turn elicits motor output via downstream motor structures like the red nucleus and the facial nucleus in the case of the eyeblink response. A second population of neurons in the anterior interpositus nucleus (AIN) makes inhibitory (GABA-ergic) projections back to the inferior olivary cells that project to the microzone. b Localization of blink areas in cerebellar cortex in the cat and the ferret. Cerebellar lobules IV–VII are numbered according to Larsell [71]. Approximate borders between the C1, C2 and C3 zones are indicated by dashed lines. Areas in red illustrate the microzones identified in both species that control eyeblink muscles and also receive short-latency climbing fibre input from the periorbital area. Both of these microzones are located in the C3 zone in the respective species. c Climbing fibre field potential responses (CFR) recorded from the C3 eyeblink microzone. In the cat (upper trace), the CFR has an onset latency of 14 ms after stimulation of the periorbital skin. In the ferret (lower trace), the corresponding latency is 11–12 ms. d Delayed eyeblink responses (measured as electromyograms or EMGs) elicited by electrical stimulation of the C3 eyeblink microzone in the cat cerebellum (red area in panel b above). Adapted from [38, 49, 63]