Abstract
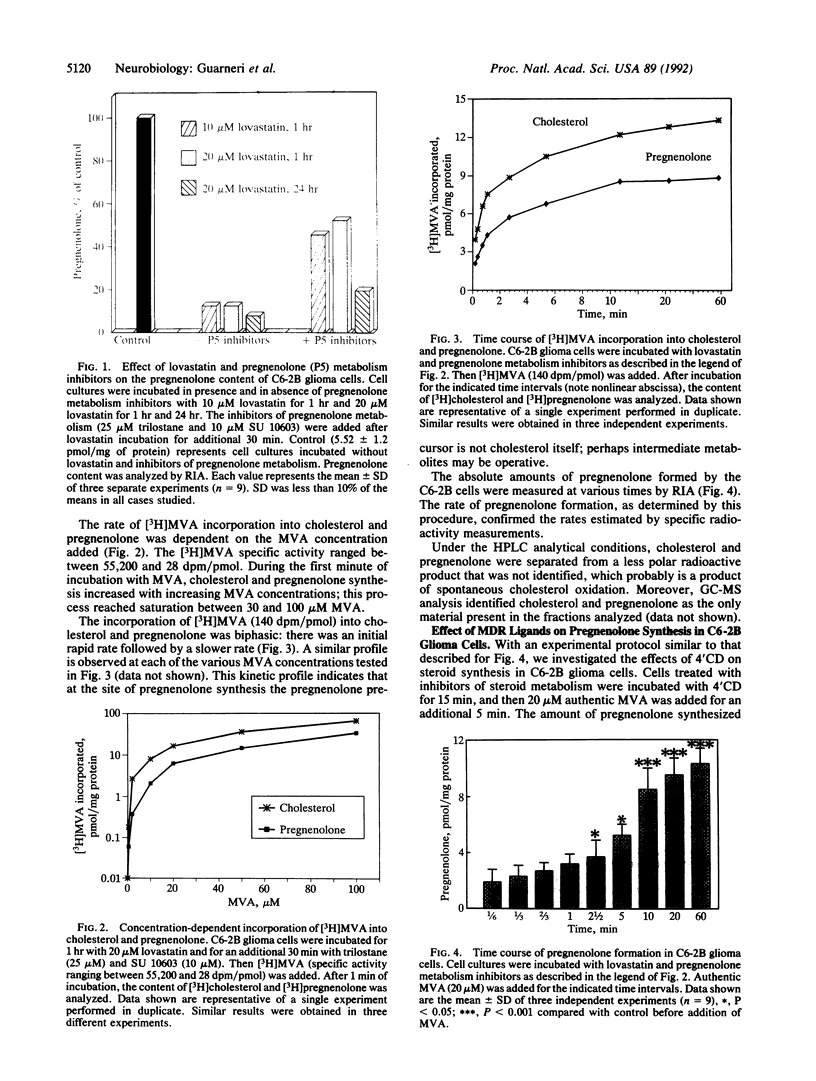
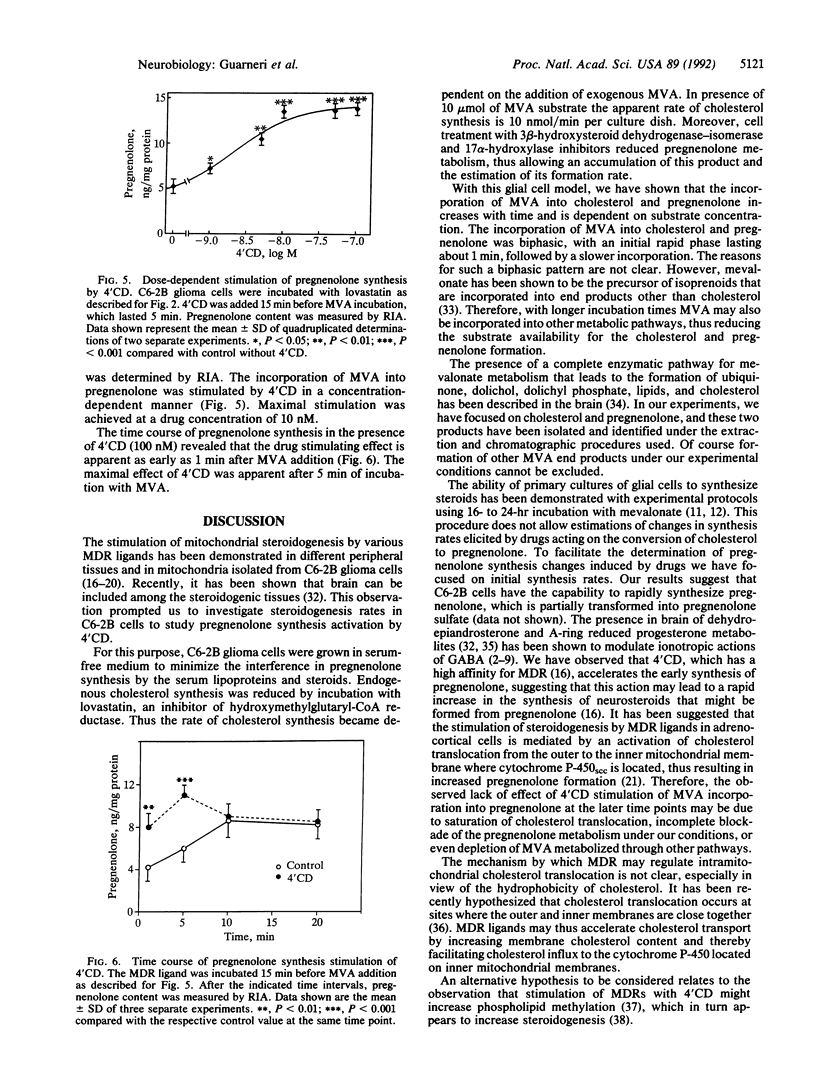
An experimental model to study synthesis of cholesterol and pregnenolone from the precursor mevalonolactone (MVA) was developed in C6-2B glioma cells. The steroidogenic capability of this cell line and the regulation of pregnenolone production by 4'-chlorodiazepam (4'CD), a specific ligand for the mitochondrial diazepam binding inhibitor (DBI) receptor (MDR), were investigated. Cells maintained in serum-free media were incubated with lovastatin (20 microM) and two inhibitors of pregnenolone metabolism, trilostane (25 microM) and 1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-4-oxo-7-chloro-2-naphthylpyridine (10 microM). Under these conditions the incorporation of [3H]MVA into cholesterol and pregnenolone formation was biphasic, with an initial rapid phase (within 1 min) followed by a slower phase. Cholesterol and pregnenolone were identified by coelution with authentic steroids from a Si 60 Lichrosorb column and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Pregnenolone synthesis in intact C6-2B glioma cells was stimulated by nanomolar concentrations of 4'CD after 5 min of incubation with MVA. The stimulatory effect was dependent on drug concentration and the maximal effect was achieved at 10 nM. The time course showed that the incorporation of MVA into pregnenolone is accelerated by the MDR ligand. Cholesterol synthesis is only slightly and not significantly affected by 4'CD. These results support the view that steroid synthesis occurs in a glioma cell line. Moreover, we provide evidence for a rapid steroid synthesis in C6-2B glioma cells, which in turn appears to be accelerated by 1-100 nM 4'CD, a MDR ligand.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baulieu E. E., Robel P. Neurosteroids: a new brain function? J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1990 Nov 20;37(3):395–403. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(90)90490-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Faust J. R., Goldstein J. L., Kaneko I., Endo A. Induction of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase activity in human fibroblasts incubated with compactin (ML-236B), a competitive inhibitor of the reductase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 25;253(4):1121–1128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards P. A., Popják G., Fogelman A. M., Edmond J. Control of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase by endogenously synthesized sterols in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1057–1063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust J. R., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Synthesis of ubiquinone and cholesterol in human fibroblasts: regulation of a branched pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Jan;192(1):86–99. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee K. W., Chang W. C., Brinton R. E., McEwen B. S. GABA-dependent modulation of the Cl- ionophore by steroids in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Apr 29;136(3):419–423. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90317-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):425–430. doi: 10.1038/343425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison N. L., Majewska M. D., Harrington J. W., Barker J. L. Structure-activity relationships for steroid interaction with the gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor complex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Apr;241(1):346–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Z. Y., Bourreau E., Jung-Testas I., Robel P., Baulieu E. E. Neurosteroids: oligodendrocyte mitochondria convert cholesterol to pregnenolone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8215–8219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeske D. J., Dietschy J. M. Regulation of rates of cholesterol synthesis in vivo in the liver and carcass of the rat measured using [3H]water. J Lipid Res. 1980 Mar;21(3):364–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung-Testas I., Hu Z. Y., Baulieu E. E., Robel P. Neurosteroids: biosynthesis of pregnenolone and progesterone in primary cultures of rat glial cells. Endocrinology. 1989 Oct;125(4):2083–2091. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-4-2083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger K. E., Papadopoulos V. Mitochondrial benzodiazepine receptors and the regulation of steroid biosynthesis. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1992;32:211–237. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.32.040192.001235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger K. E., Papadopoulos V. Peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptors mediate translocation of cholesterol from outer to inner mitochondrial membranes in adrenocortical cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):15015–15022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lan N. C., Chen J. S., Belelli D., Pritchett D. B., Seeburg P. H., Gee K. W. A steroid recognition site is functionally coupled to an expressed GABA(A)-benzodiazepine receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Jun 12;188(6):403–406. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(90)90201-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Goascogne C., Robel P., Gouézou M., Sananès N., Baulieu E. E., Waterman M. Neurosteroids: cytochrome P-450scc in rat brain. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1212–1215. doi: 10.1126/science.3306919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majewska M. D., Harrison N. L., Schwartz R. D., Barker J. L., Paul S. M. Steroid hormone metabolites are barbiturate-like modulators of the GABA receptor. Science. 1986 May 23;232(4753):1004–1007. doi: 10.1126/science.2422758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majewska M. D., Schwartz R. D. Pregnenolone-sulfate: an endogenous antagonist of the gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor complex in brain? Brain Res. 1987 Feb 24;404(1-2):355–360. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91394-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majewska M. D. Steroids and brain activity. Essential dialogue between body and mind. Biochem Pharmacol. 1987 Nov 15;36(22):3781–3788. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(87)90437-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mienville J. M., Vicini S. Pregnenolone sulfate antagonizes GABAA receptor-mediated currents via a reduction of channel opening frequency. Brain Res. 1989 Jun 5;489(1):190–194. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90024-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow A. L., Pace J. R., Purdy R. H., Paul S. M. Characterization of steroid interactions with gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor-gated chloride ion channels: evidence for multiple steroid recognition sites. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Feb;37(2):263–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow A. L., Suzdak P. D., Paul S. M. Steroid hormone metabolites potentiate GABA receptor-mediated chloride ion flux with nanomolar potency. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Oct 27;142(3):483–485. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90094-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukhin A. G., Papadopoulos V., Costa E., Krueger K. E. Mitochondrial benzodiazepine receptors regulate steroid biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9813–9816. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos V., Berkovich A., Krueger K. E., Costa E., Guidotti A. Diazepam binding inhibitor and its processing products stimulate mitochondrial steroid biosynthesis via an interaction with mitochondrial benzodiazepine receptors. Endocrinology. 1991 Sep;129(3):1481–1488. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-3-1481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos V., Guarneri P., Kreuger K. E., Guidotti A., Costa E. Pregnenolone biosynthesis in C6-2B glioma cell mitochondria: regulation by a mitochondrial diazepam binding inhibitor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):5113–5117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.5113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos V., Kamtchouing P., Drosdowsky M. A., Carreau S. Effects of the transmethylation inhibitor S-adenosyl-homocysteine and of the methyl donor S-adenosyl-methionine on rat Leydig cell function in vitro. J Steroid Biochem. 1987 Jan;26(1):93–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(87)90035-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos V., Mukhin A. G., Costa E., Krueger K. E. The peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor is functionally linked to Leydig cell steroidogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3772–3779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popják G., Cornforth J. W. Substrate stereochemistry in squalene biosynthesis: The first Ciba medal lecture. Biochem J. 1966 Dec;101(3):553.b4–553568. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potts G. O., Creange J. E., Hardomg H. R., Schane H. P. Trilostane, an orally active inhibitor of steroid biosynthesis. Steroids. 1978 Sep;32(2):257–267. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(78)90010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puia G., Santi M. R., Vicini S., Pritchett D. B., Purdy R. H., Paul S. M., Seeburg P. H., Costa E. Neurosteroids act on recombinant human GABAA receptors. Neuron. 1990 May;4(5):759–765. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90202-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackleton C. H. Profiling steroid hormones and urinary steroids. J Chromatogr. 1986 Jun 20;379:91–156. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)80683-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shikita M., Ogiso T., Tamaoki B. I. Effect of inhibitors on testicular microsomal steroid 17-alpha-hydroxylase and 17-alpha-hydroxypregnene C17-C20 lyase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Sep 20;105(3):516–522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens V. L., Tribble D. L., Lambeth J. D. Regulation of mitochondrial compartment volumes in rat adrenal cortex by ether stress. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Oct;242(1):324–327. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90508-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter W. J., Hirata F., Axelrod J., Mallorga P., Tallman J. F., Henneberry R. C. Benzodiazepine and beta-adrenergic receptor ligands independently stimulate phospholipid methylation. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):857–859. doi: 10.1038/282857a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagibashi K., Ohno Y., Nakamichi N., Matsui T., Hayashida K., Takamura M., Yamada K., Tou S., Kawamura M. Diazepam potentiates the corticoidogenic response of bovine adrenal fasciculata cells to dibutyryl cyclic AMP. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;51(3):347–355. doi: 10.1254/jjp.51.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




