Abstract
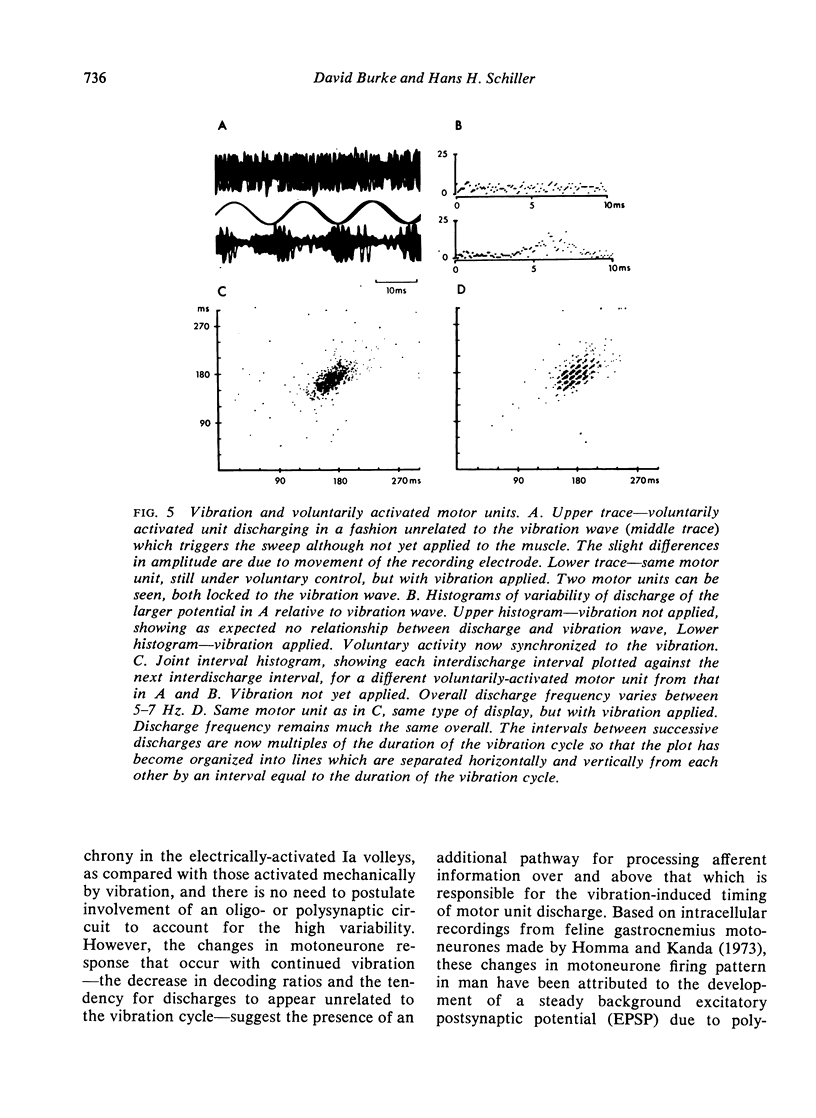
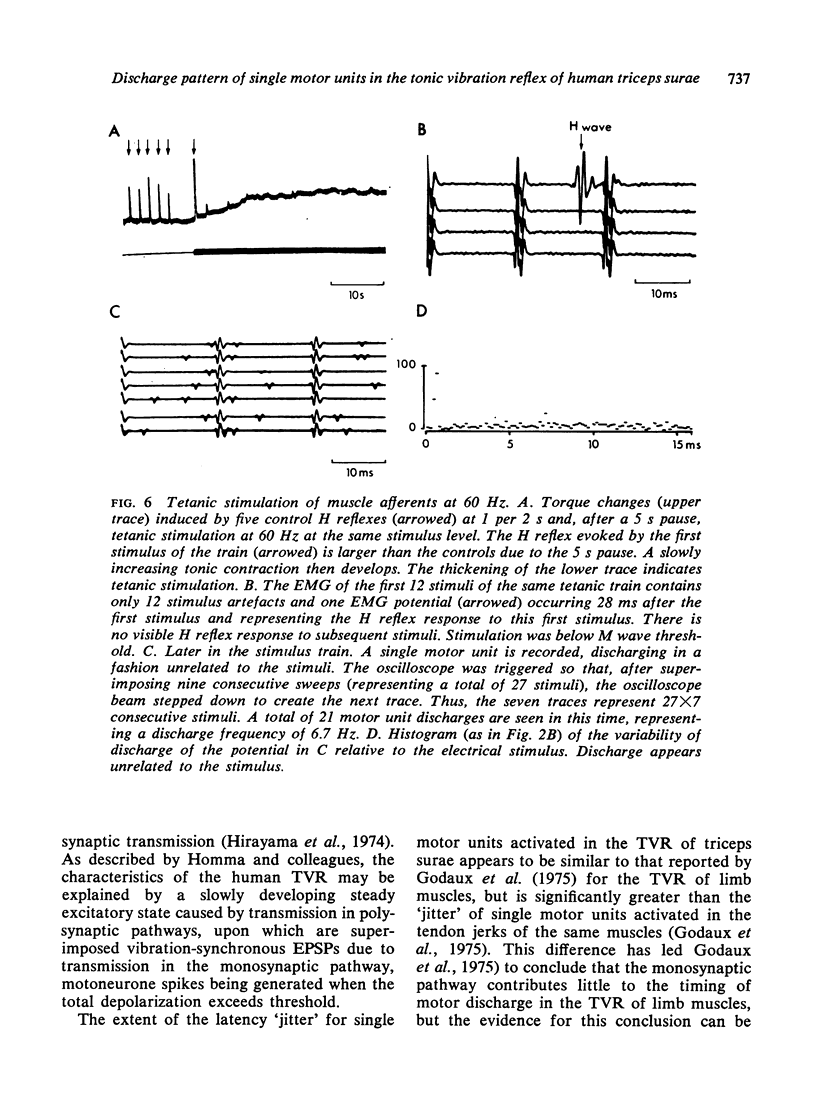
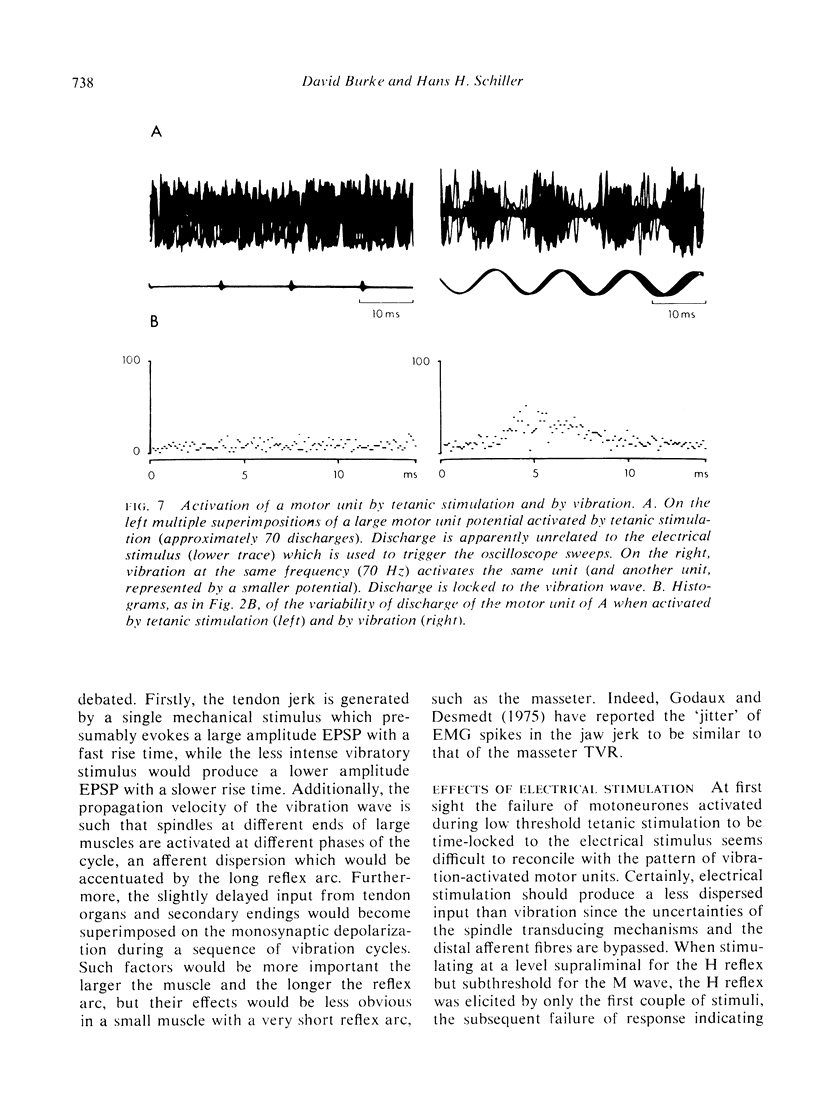
Using a single fibre EMG electrode the firing pattern of 46 motor units in the triceps surae has been studied during vibration of the Achilles tendon at frequencies of 25--200 Hz. Potentials activated in the tonic vibration reflex (TVR) were phase-locked to the vibration cycle but tended to become somewhat less so with continued vibration. The firing pattern of voluntarily activated motor units became locked to the waveform by the application of the vibrator. The discharges of 21 motor units were studied during low threshold (sub-M wave) tetanic stimulation of the tibial nerve at 25--100 Hz. No evidence was found of synchronization of potentials activated in the resulting tonic contraction. During weak voluntary contractions, stimulation also failed to regularize voluntarily activated motor units. The findings can be reconciled by postulating that, in normal man, vibration activates monosynaptic and polysynaptic pathways, the latter circuit being adequate to generate reflex contraction, while the former merely affects the temporal patterning of the motor outflow.
Full text
PDF


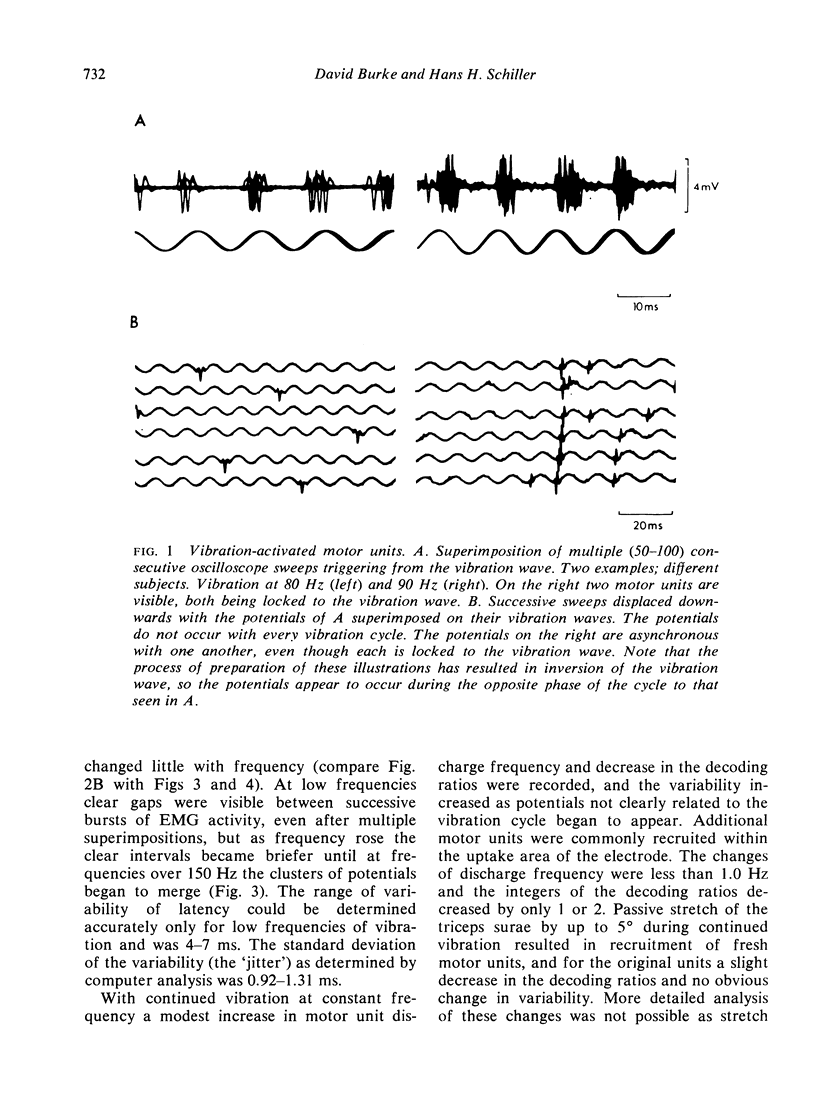
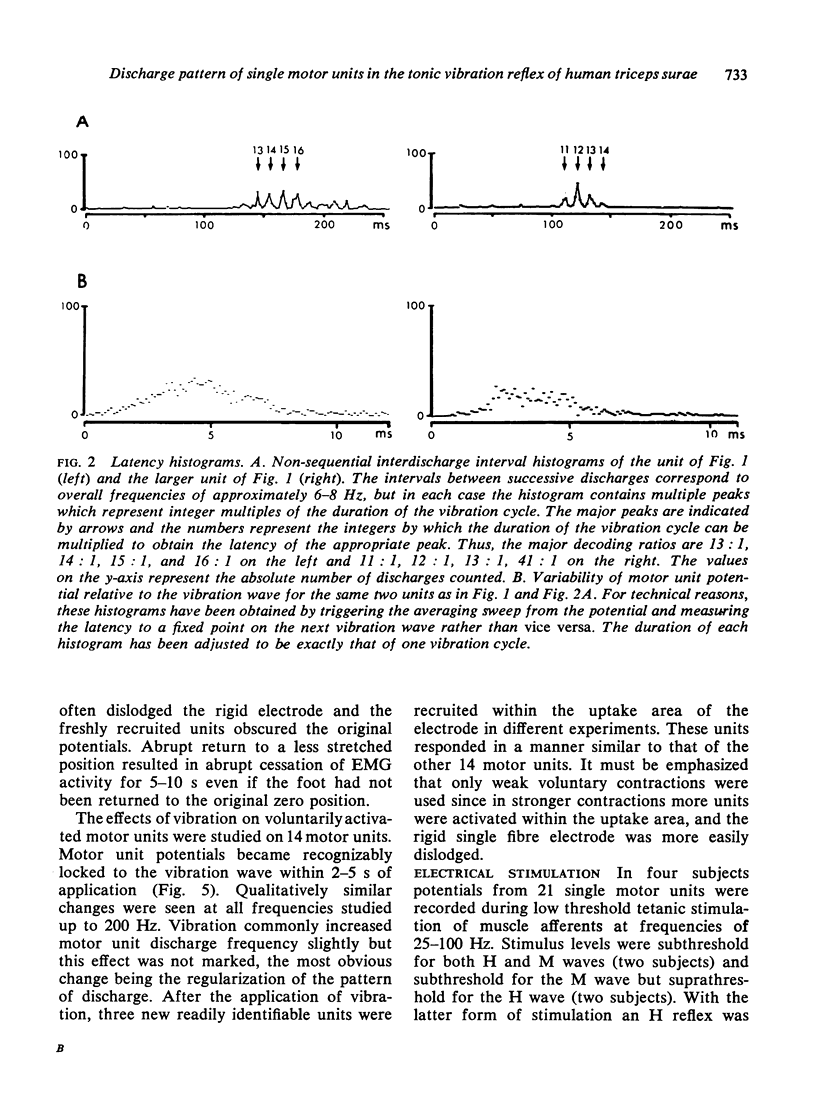
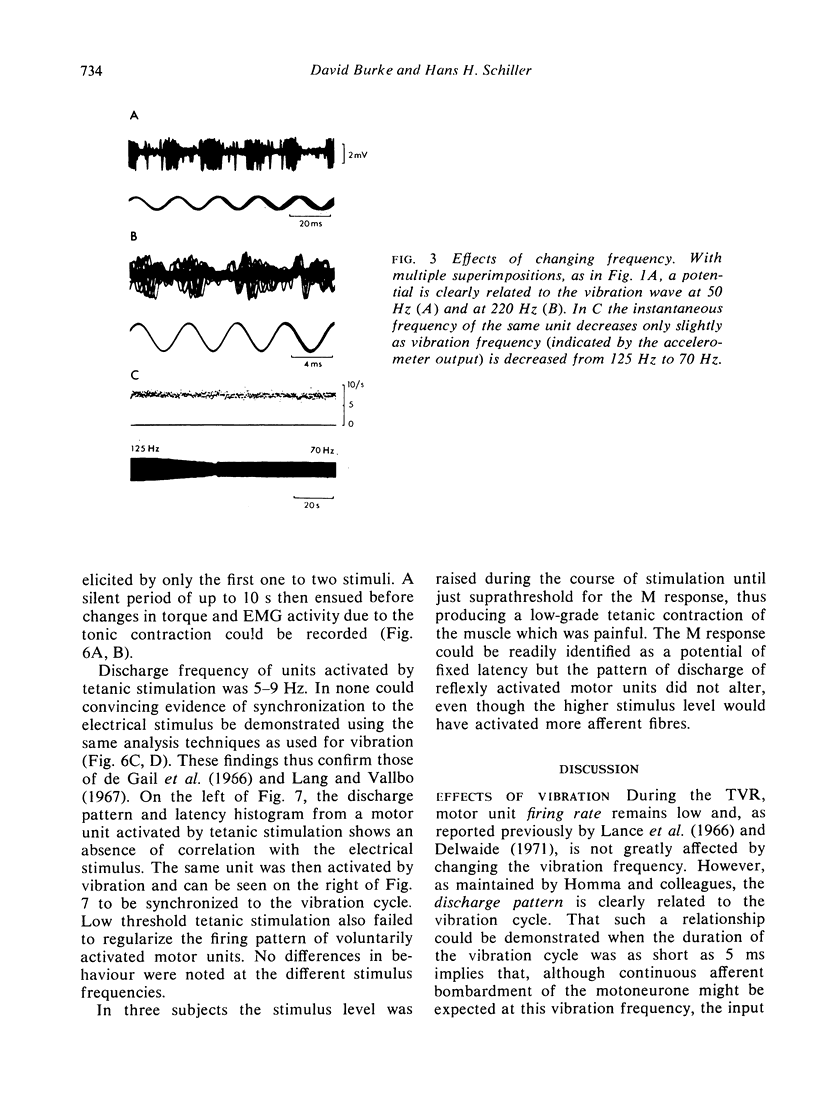
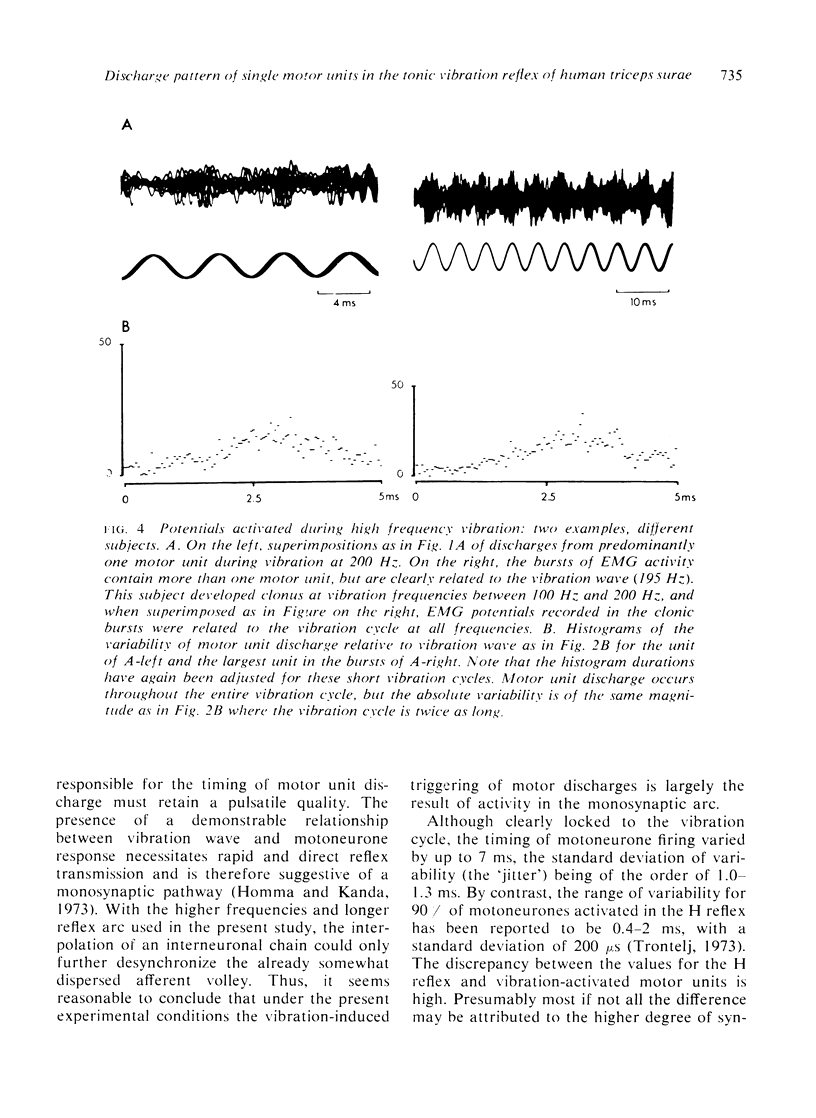



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashby P., Verrier M., Lightfoot E. Segmental reflex pathways in spinal shock and spinal spasticity in man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1974 Dec;37(12):1352–1360. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.37.12.1352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes C. D., Pompeiano O. Presynaptic and postsynaptic effects in the monosyaptic reflex pathway to extensor motoneurons folowing vibration of synergic muscles. Arch Ital Biol. 1970 Apr;108(2):259–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D., Andrews C. J., Lance J. W. Tonic vibration reflex in spasticity, Parkinson's disease, and normal subjects. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1972 Aug;35(4):477–486. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.35.4.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D., Ashby P. Are spinal "presynaptic" inhibitory mechanisms suppressed in spasticity? J Neurol Sci. 1972 Mar;15(3):321–326. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(72)90073-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppin C. M., Jack J. J., MacLennan C. R. A method for the selective electrical activation of tendon organ afferent fibres from the cat soleus muscle. J Physiol. 1970 Sep;210(1):18P–20P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppin C. M., Jack J. J., McIntyre A. K. Properties of group I afferent fibres from semitendinosus muscle in the cat. J Physiol. 1969 Jul;203(1):45P–46P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Gail P., Lance J. W., Neilson P. D. Differential effects on tonic and phasic reflex mechanisms produced by vibration of muscles in man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1966 Feb;29(1):1–11. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.29.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmedt J. E., Godaux E. Vibration-induced discharge patterns of single motor units in the masseter muscle in man. J Physiol. 1975 Dec;253(2):429–442. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EKSTEDT J. HUMAN SINGLE MUSCLE FIBER ACTION POTENTIALS. EXTRACELLULAR RECORDING DURING VOLUNTARY AND CHEMICAL ACTIVATION. WITH SOME COMMENTS ON END-PLATE PHYSIOLOGY AND ON THE FIBER ARRANGEMENT OF THE MOTOR UNIT. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1964:SUPPL 226–226:1+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies J. D., Lance J. W., Neilson P. D., Tassinari C. A. Presynaptic inhibition of the monosynaptic reflex by vibration. J Physiol. 1969 Nov;205(2):329–339. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godaux E., Desmedt J. E., Demaret P. Vibration of human limb muscles: the alleged phase-locking of motor unit spikes. Brain Res. 1975 Dec 12;100(1):175–177. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90255-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godaux E., Desmedt J. E. Evidence for a monosynaptic mechanism in the tonic vibration reflex of the human masseter muscle. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975 Feb;38(2):161–168. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.38.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagbarth K. E., Eklund G. The effects of muscle vibration in spasticity, rigidity, and cerebellar disorders. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1968 Jun;31(3):207–213. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.31.3.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagbarth K. E., Hellsing G., Löfstedt L. TVR and vibration-induced timing of motor impulses in the human jaw elevator muscles. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1976 Aug;39(8):719–728. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.39.8.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagbarth K. E., Wallen G., Löfstedt L. Muscle spindle activity in man during voluntary fast alternating movements. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975 Jul;38(7):625–635. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.38.7.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirayama K., Homma S., Mizote M., Nakajima Y., Watanabe S. Separation of the contributions of voluntary and vibratory activation of motor units in man by cross-correlograms. Jpn J Physiol. 1974 Jun;24(3):293–304. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.24.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma S., Kanda K., Watanabe S. Preferred spike intervals in the vibration reflex. Jpn J Physiol. 1972 Aug;22(4):421–432. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.22.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma S., Mizote M., Watanabe S. Participation of mono- and polysynaptic transmission during tonic activation of the stretch reflex arcs. Jpn J Physiol. 1975;25(2):135–146. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.25.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanda K. Contribution of polysynaptic pathways to the tonic vibration reflex. Jpn J Physiol. 1972 Aug;22(4):367–377. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.22.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang A. H., Vallbo A. B. Motoneuron activation by low intensity tetanic stimulation of muscle afferents in man. Exp Neurol. 1967 Aug;18(4):383–391. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(67)90056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoden U., Magherini P. C., Pompeiano O. Evidence that presynaptic inhibition may decrease the autogenetic excitation caused by vibration of extensor muscles. Arch Ital Biol. 1972 May;110(1):90–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trontelj J. V. A study of the H-reflex by single fibre EMG. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1973 Dec;36(6):951–959. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.36.6.951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


