Abstract
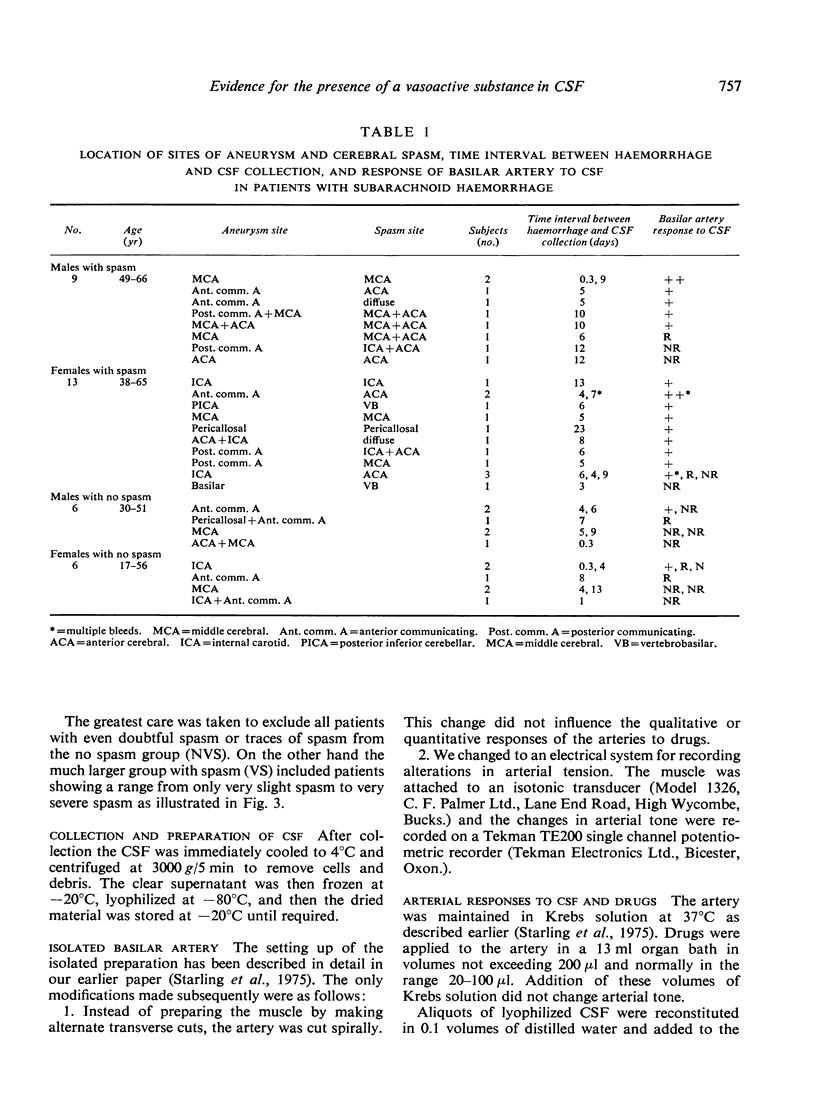
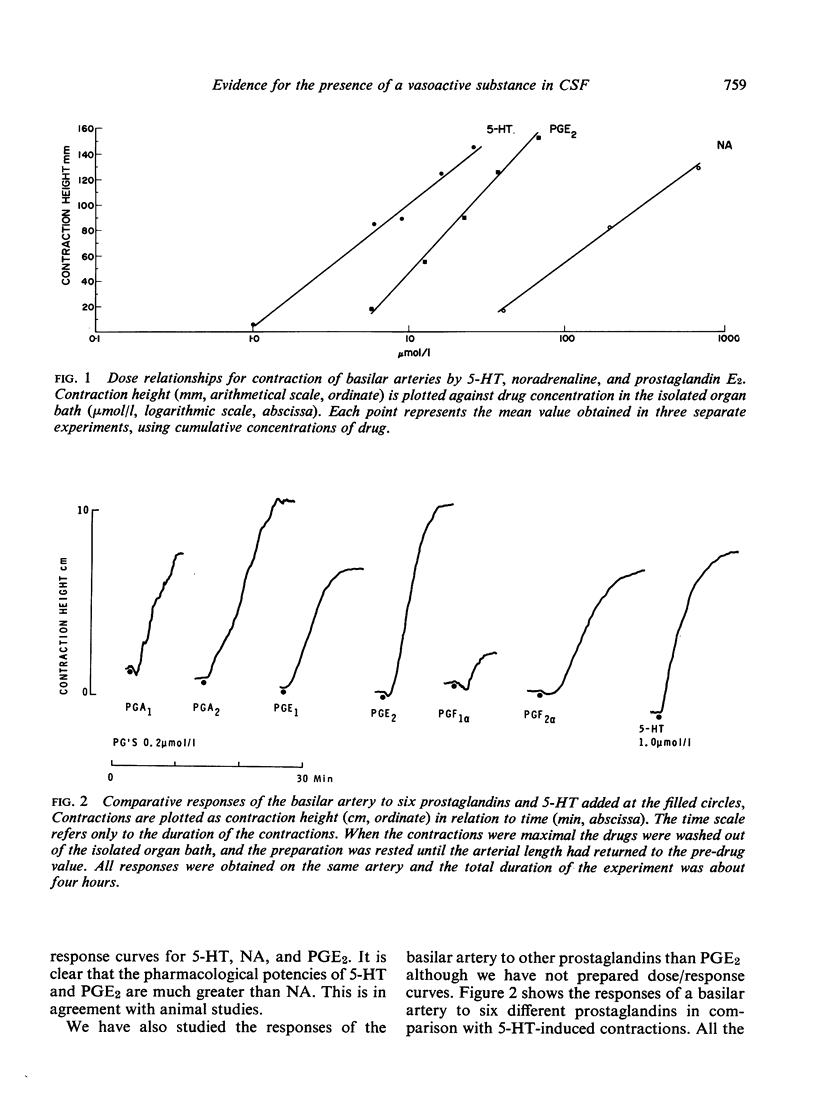
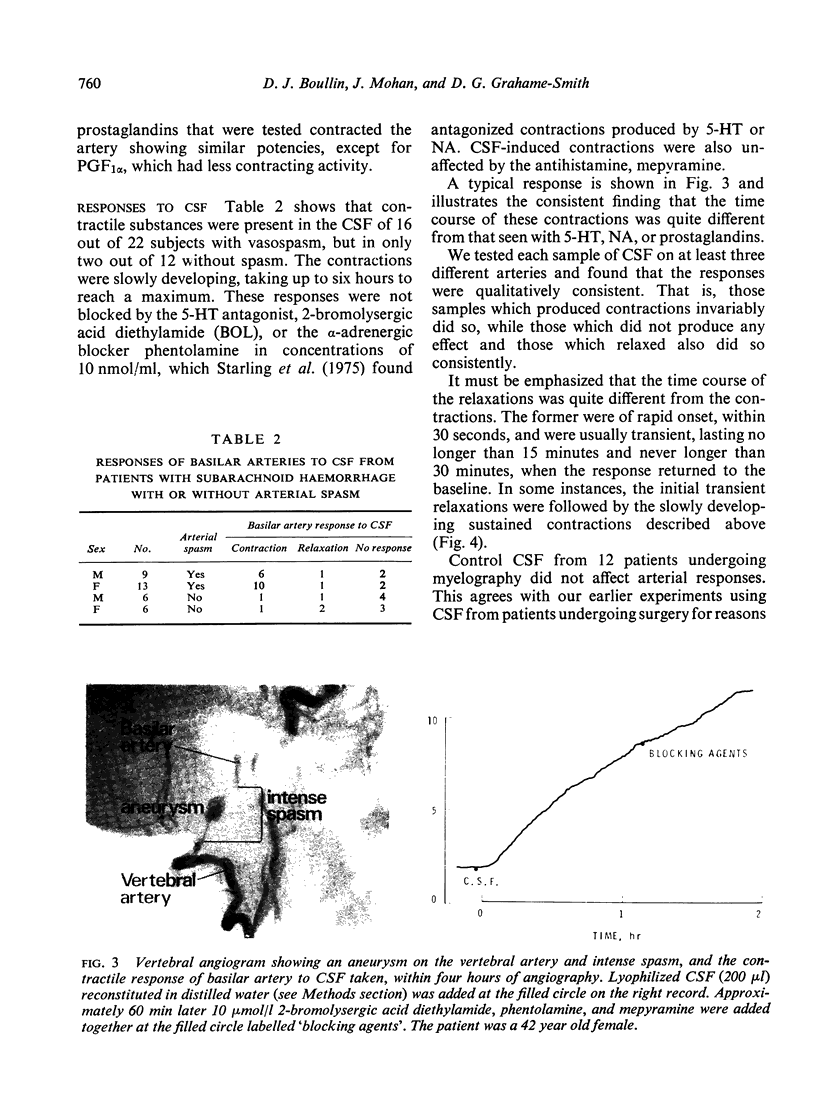
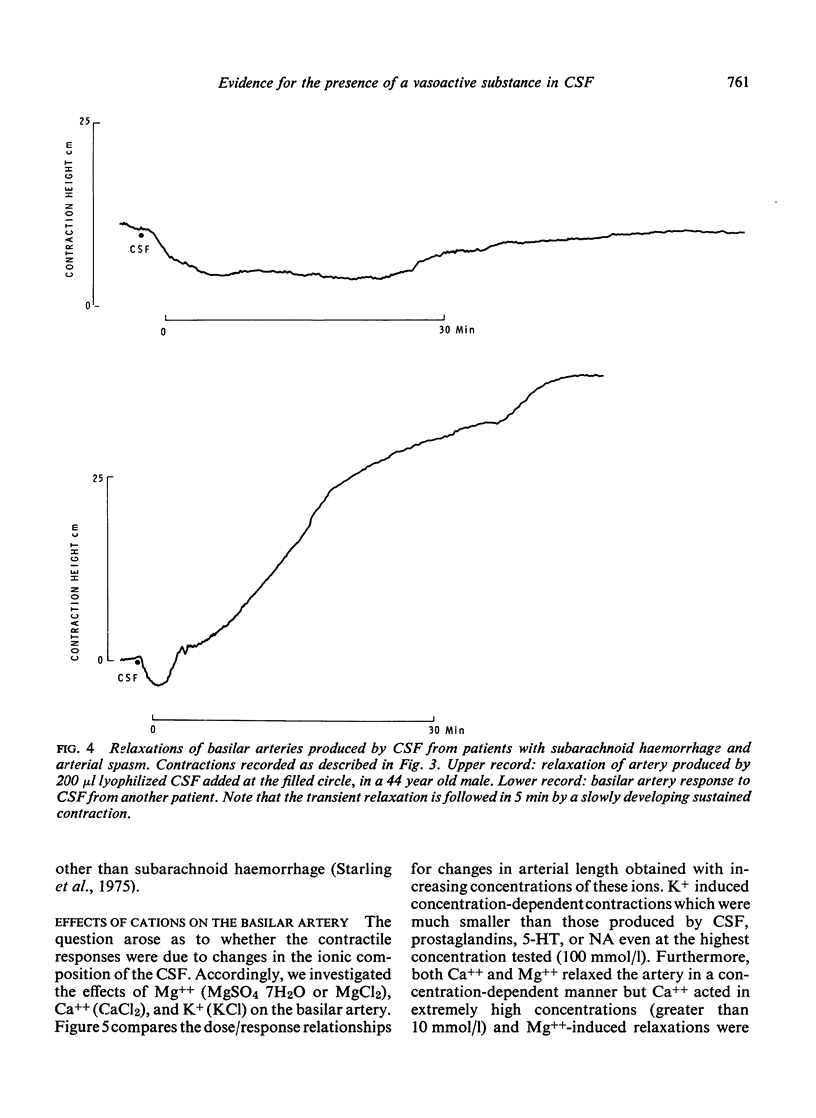
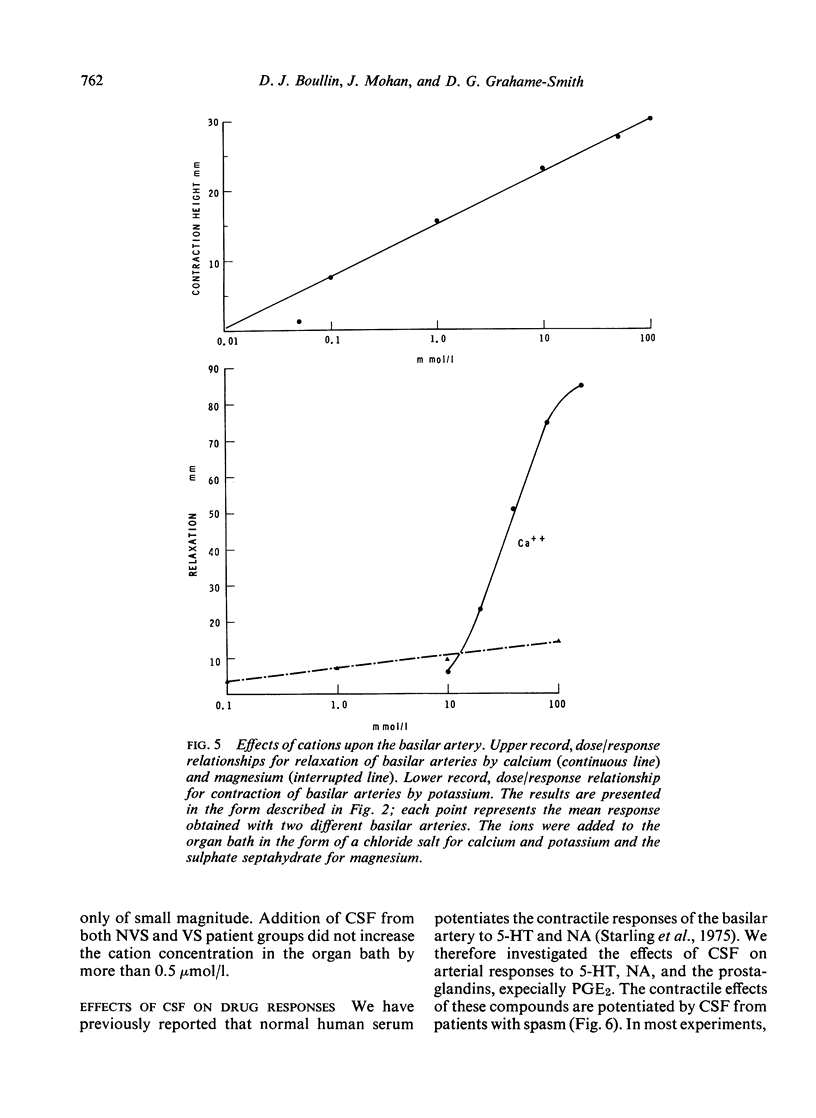
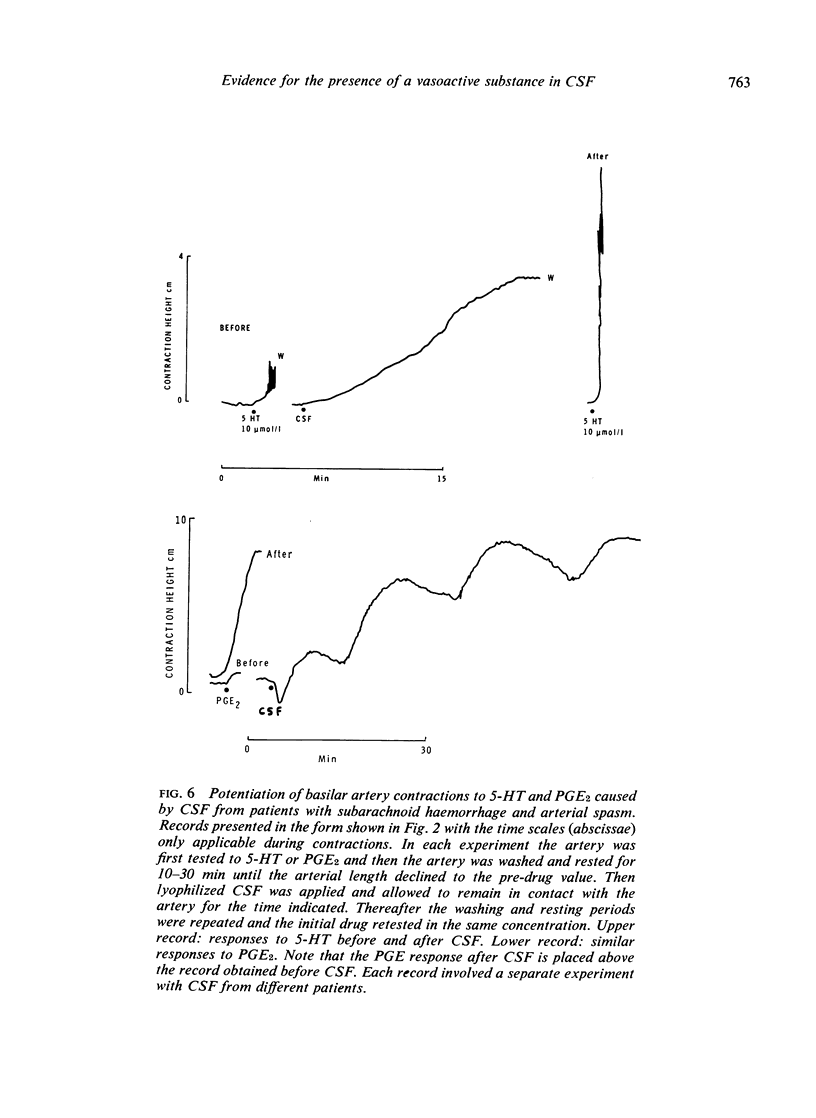
Cerebrospinal fluid from patients with subarachnoid haemorrhage and cerebral arterial spasm contracted the isolated basilar artery and potentiated contractions produced by 5-hydroxytryptamine, noradrenaline, and six prostaglandins. The unidentified substance in cerebrospinal fluid probably plays a role in the aetiology of cerebral arterial spasm.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen G. S., Henderson L. M., Chou S. N., French L. A. Cerebral arterial spasm. 1. In vitro contractile activity of vasoactive agents on canine basilar and middle cerebral arteries. J Neurosurg. 1974 Apr;40(4):433–441. doi: 10.3171/jns.1974.40.4.0433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen G. S., Henderson L. M., Chou S. N., French L. A. Cerebral arterial spasm. 2. In vitro contractile activity of serotonin in human serum and CSF on the canine basilar artery, and its blockage by methylsergide and phenoxybenzamine. J Neurosurg. 1974 Apr;40(4):442–450. doi: 10.3171/jns.1974.40.4.0442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUCKELL M. DEMONSTRATION OF SUBSTANCES CAPABLE OF CONTRACTING SMOOTH MUSCLE IN THE HAEMATOMA FLUID FROM CERTAIN CASES OF RUPTURED CEREBRAL ANEURYSM. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1964 Jun;27:198–199. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.27.3.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan J. A., Duckles S. P., Lee T. J. Histamine potentiation of nerve- and drug-induced responses of a rabbit cerebral artery. Circ Res. 1975 May;36(5):647–653. doi: 10.1161/01.res.36.5.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton I. C., Jr, White R. P., Robertson J. T. The effects of prostaglandins E 1 , A 1 , and F 2a on the cerebral circulation of dogs and monkeys. J Neurosurg. 1972 Jan;36(1):34–42. doi: 10.3171/jns.1972.36.1.0034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echlin F. A. Current concepts in the etiology and treatment of vasospasm. Clin Neurosurg. 1968;15:133–160. doi: 10.1093/neurosurgery/15.cn_suppl_1.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echlin F. Experimental vasospasm, acute and chronic, due to blood in the subarachnoid space. J Neurosurg. 1971 Dec;35(6):646–656. doi: 10.3171/jns.1971.35.6.0646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes S. W. The spontaneous release of prostaglandins into the cerebral ventricles of the dog and the effect of external factors on this release. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Apr;38(4):653–658. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb09874.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARLSBERG P., ELLIOTT H. W., ADAMS J. E. EFFECT OF VARIOUS PHARMACOLOGIC AGENTS ON CEREBRAL ARTERIES. Neurology. 1963 Sep;13:772–778. doi: 10.1212/wnl.13.9.772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapp J., Mahaley M. S., Jr, Odom G. L. Cerebral arterial spasm. 2. Experimental evaluation of mechanical and humoral factors in pathogenesis. J Neurosurg. 1968 Oct;29(4):339–349. doi: 10.3171/jns.1968.29.4.0339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapp J., Mahaley M. S., Jr, Odom G. L. Cerebral arterial spasm. 3. Partial purification and characterization of a spasmogenic substance in feline platelets. J Neurosurg. 1968 Oct;29(4):350–356. doi: 10.3171/jns.1968.29.4.0350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Torre E., Patrono C., Fortuna A., Grossi-Belloni D. Role of prostaglandin F2 in human cerebral vasospasm. J Neurosurg. 1974 Sep;41(3):293–299. doi: 10.3171/jns.1974.41.3.0293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. A., Yashon D., Locke G., Hunt W. E. Autonomous activity in the human basilar artery: relationship to cerebral vascular spasm. Neurology. 1971 Dec;21(12):1249–1254. doi: 10.1212/wnl.21.12.1249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano J., Chang A. C., Fisher R. G. Effects of prostaglandins E 1 , E 2 , A 1 , A 2 , and F 2 on canine carotid arterial blood flow, cerebrospinal fluid pressure, and intraocular pressure. J Neurosurg. 1973 Jan;38(1):32–39. doi: 10.3171/jns.1973.38.1.0032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelofsky S., Jacobson E. D., Fisher R. G. Effects of prostaglandin E 1 on experimental cerebral vasospasm. J Neurosurg. 1972 May;36(5):634–639. doi: 10.3171/jns.1972.36.5.0634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennink M., White R. P., Crockarell J. R., Robertson J. T. Role of prostaglandin F 2 in the genesis of experimental cerebral vasospasm. Angiographic study in dogs. J Neurosurg. 1972 Oct;37(4):398–406. doi: 10.3171/jns.1972.37.4.0398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAYNOR R. B., McMURTRY J. G., POOL J. L. Cerebrovascular effects of topically applied serotonin in the cat. Neurology. 1961 Mar;11:190–195. doi: 10.1212/wnl.11.3.190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starling L. M., Boullin D. J., Grahame-Smith D. G., Adams C. B., Gye R. S. Responses of isolated human basilar arteries to 5-hydroxytryptamine, noradrenaline, serum, platelets, and erythrocytes. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975 Jul;38(7):650–656. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.38.7.650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. P., Hagen A. A., Morgan H., Dawson W. N., Robertson J. T. Experimental study on the genesis of cerebral vasospasm. Stroke. 1975 Jan-Feb;6(1):52–57. doi: 10.1161/01.str.6.1.52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins R. H., Wilkins G. K., Gunnells J. C., Odom G. L. Experimental studies of intracranial arterial spasm using aortic strip assays. J Neurosurg. 1967 Dec;27(6):490–500. doi: 10.3171/jns.1967.27.6.0490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto Y. L., Feindel W., Wolfe L. S., Katoh H., Hodge C. P. Experimental vasoconstriction of cerebral arteries by prostaglandins. J Neurosurg. 1972 Oct;37(4):385–397. doi: 10.3171/jns.1972.37.4.0385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zervas N. T., Kuwayama A., Rosoff C. B., Salzman E. W. Cerebral arterial spasm. Modification by inhibition of platelet function. Arch Neurol. 1973 Jun;28(6):400–404. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490240060010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]