Abstract
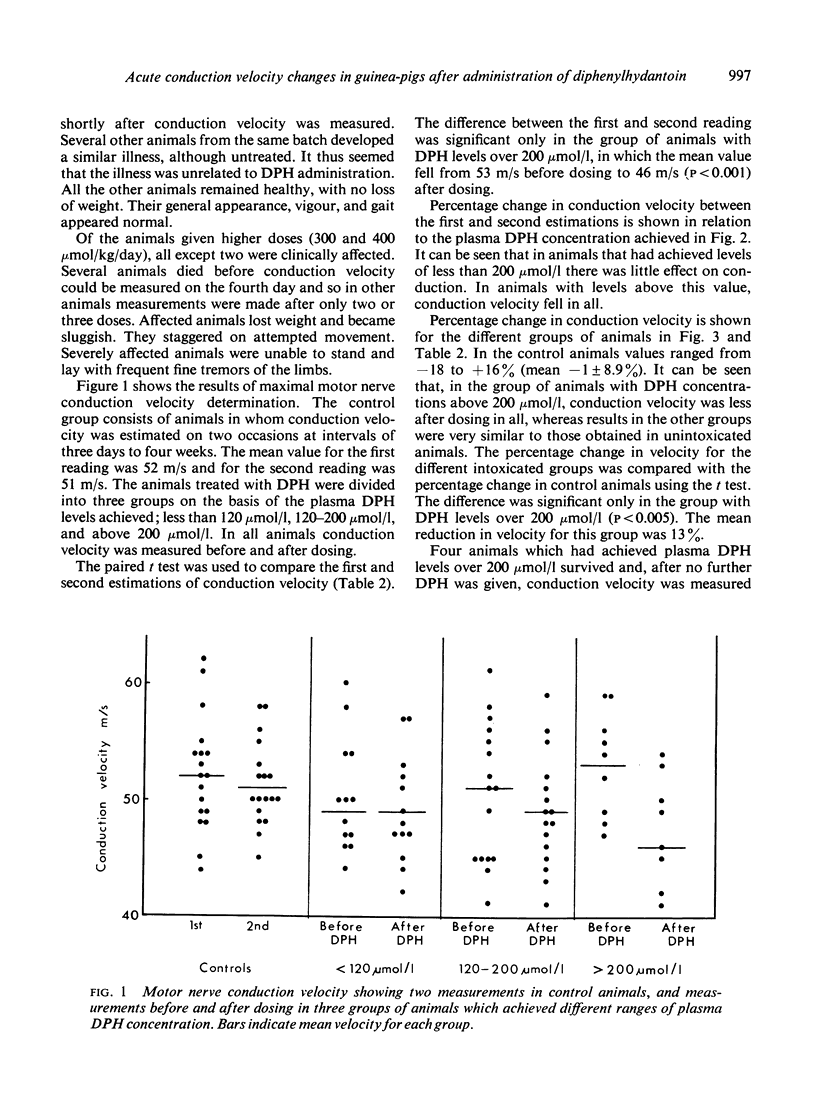
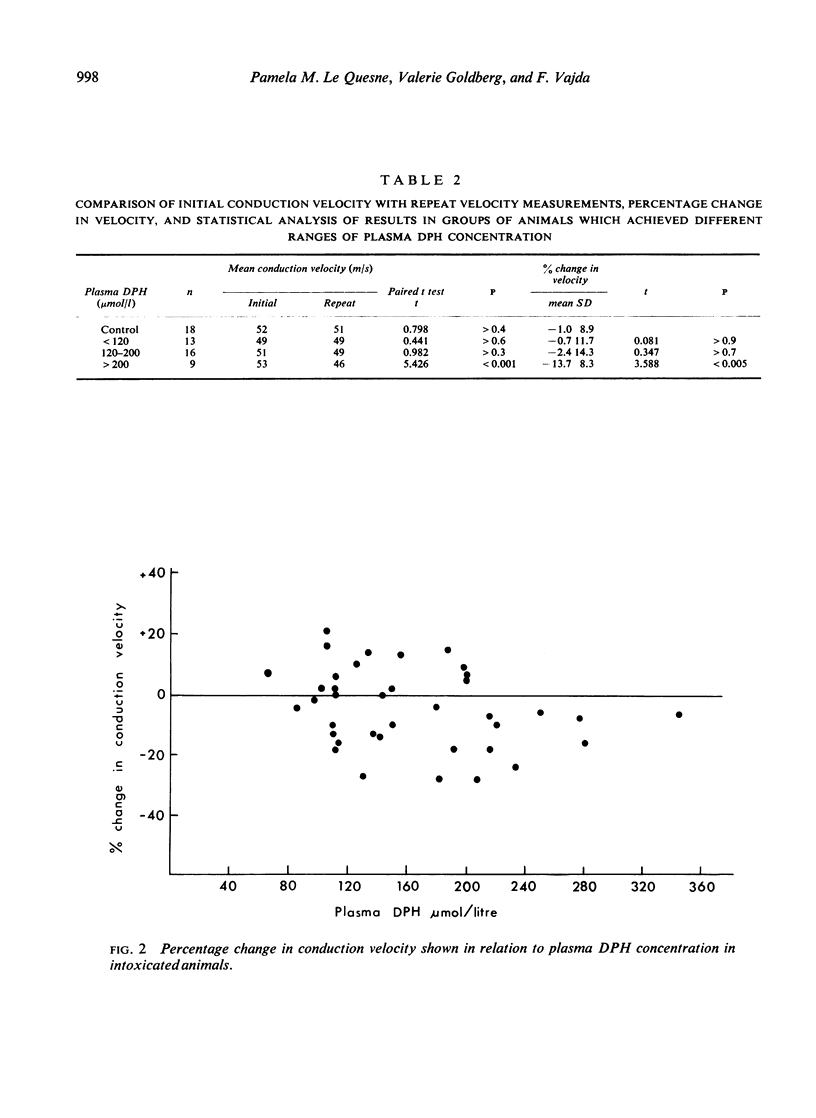
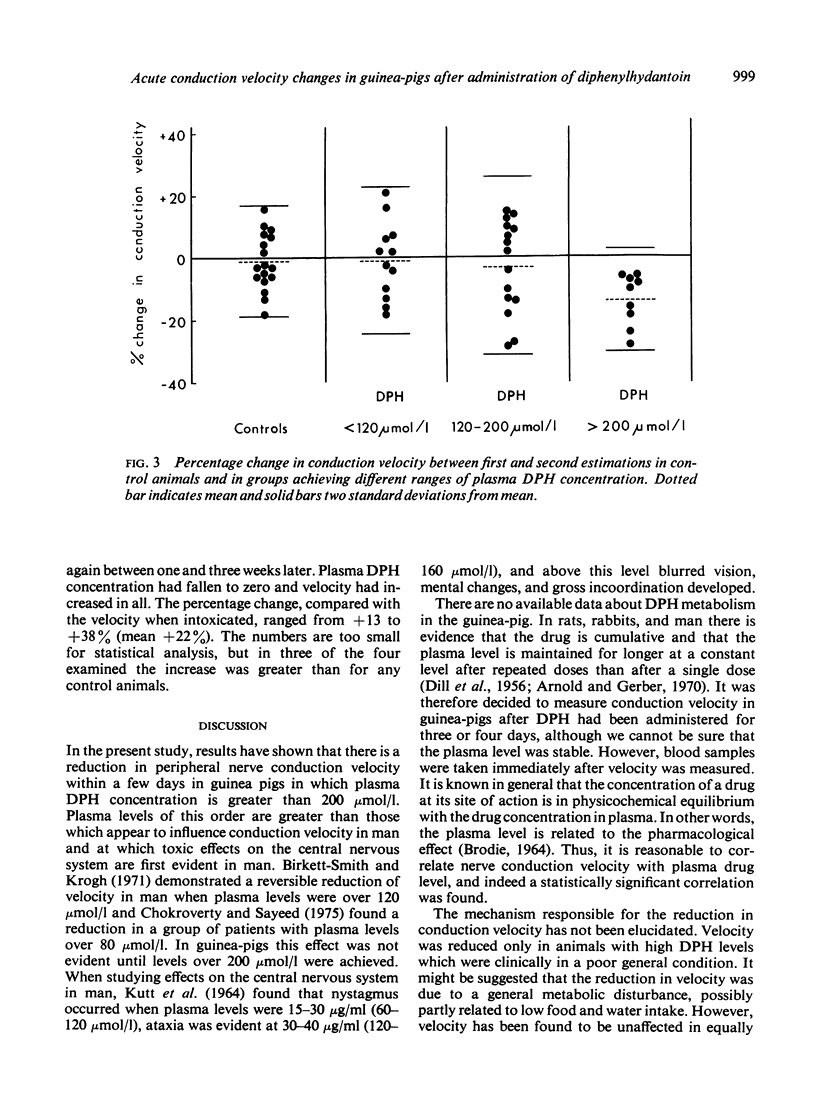
Motor nerve conduction velocity was measured after dosing guinea-pigs with 200-400 μmol/kg diphenylhydantoin (DPH) daily for three to four days. Conduction velocity fell by a mean value of 13% in animals that achieved plasma DPH levels over 200 μmol/l. There was no change in velocity with DPH levels below this value.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold K., Gerber N. The rate of decline of diphenylhydantoin in human plasma. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1970 Jan-Feb;11(1):121–134. doi: 10.1002/cpt1970111121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRODIE B. B. Symposium on clinical drug evaluation and human pharmacology. VI. Difficulties in extrapolating data on metabolism of drugs from animal to man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1962 May-Jun;3:374–380. doi: 10.1002/cpt196233374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birket-Smith E., Krogh E. Motor nerve conduction velocity during diphenylhydantoin intoxication. Acta Neurol Scand. 1971;47(3):265–271. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1971.tb07482.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chokroverty S., Sayeed Z. A. Motor nerve conduction study in patients on diphenylhydantoin therapy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975 Dec;38(12):1235–1239. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.38.12.1235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DILL W. A., GLAZKO A. J., KAZENKO A., WOLF L. M. Studies on 5, 5'-diphenylhydantoin (dilantin) in animals and man. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1956 Nov;118(3):270–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen A. A., Woods J. F., Sherwin A. L. Peripheral nerve function in long-term therapy with diphenylhydantoin. A clinical and electrophysiologic correlation. Neurology. 1974 May;24(5):411–417. doi: 10.1212/wnl.24.5.411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Encinoza O. Nerve conduction velocity in patients on long-term diphenylhydantoin therapy. Epilepsia. 1974 Jun;15(2):147–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1974.tb04938.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullerton P. M. Chronic peripheral neuropathy produced by lead poisoning in guinea-pigs. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1966 Apr;25(2):214–236. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196604000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopf H. C. Uber die Veränderung der Leitfunktion peripherer motorischer Nervenfasern durch Diphenylhydantoin. Dtsch Z Nervenheilkd. 1968;193(1):41–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUTT H., WINTERS W., KOKENGE R., MCDOWELL F. DIPHENYLHYDANTOIN METABOLISM, BLOOD LEVELS, AND TOXICITY. Arch Neurol. 1964 Dec;11:642–648. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1964.00460240074010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovelace R. E., Horwitz S. J. Peripheral neuropathy in long-term diphenylhydantoin therapy. Arch Neurol. 1968 Jan;18(1):69–77. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1968.00470310083007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORRELL F., BRADLEY W., PTASHNE M. Effect of diphenylhydantoin on peripheral nerve. Neurology. 1958 Feb;8(2):140–144. doi: 10.1212/wnl.8.2.140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGee J. Rapid determination of diphenylhydantoin in blood plasma by gas-liquid chromatography. Anal Chem. 1970 Mar;42(3):421–422. doi: 10.1021/ac60285a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toseland P. A., Grove J., Berry D. J. An isothermal GLC determination of the plasma levels of carbamazepine, diphenylhydantoin, phenobarbitone and primidone. Clin Chim Acta. 1972 May;38(2):321–328. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(72)90122-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vajda F., Williams F. M., Davidson S., Falconer M. A., Breckenridge A. Human brain, cerebrospinal fluid, and plasma concentrations of diphenylhydantoin and phenobarbital. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1974 Jun;15(6):597–603. doi: 10.1002/cpt1974156597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xavier de Castro J. H., Acosta M. L., Sica R. E., Guercio N. Sensory and motor nerve conduction velocity in long-term diphenylhydantoin therapy. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 1972 Sep;30(3):215–220. doi: 10.1590/s0004-282x1972000300002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


